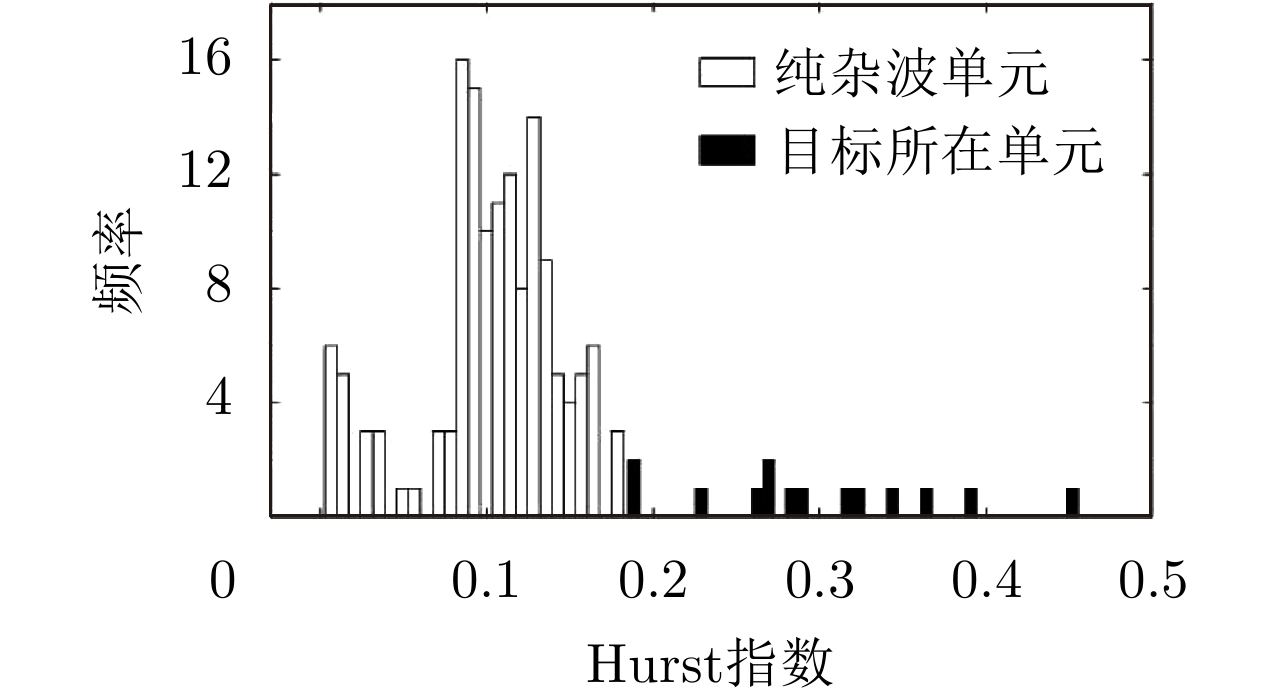
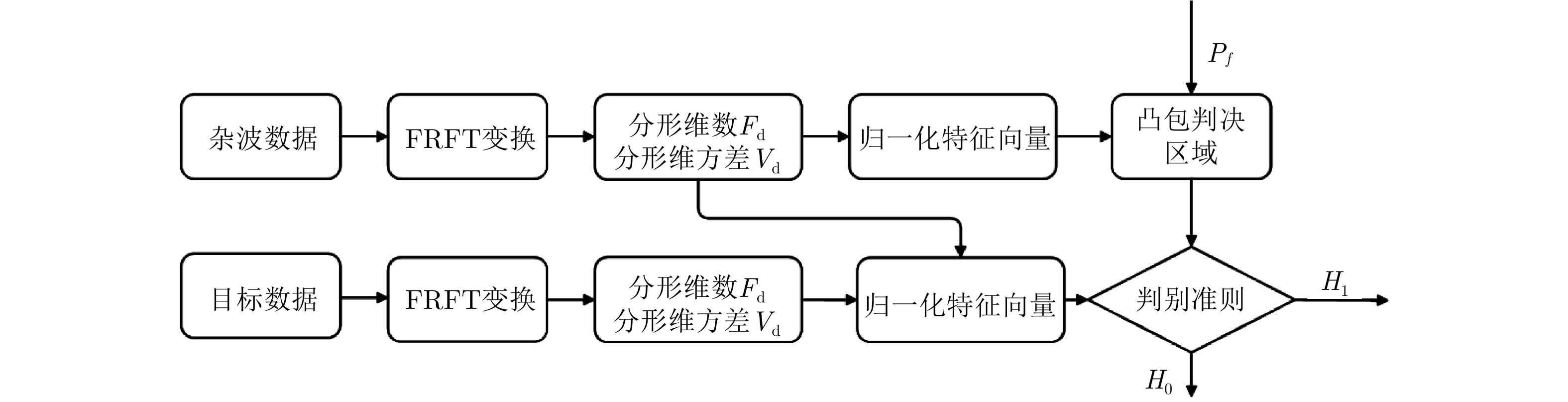
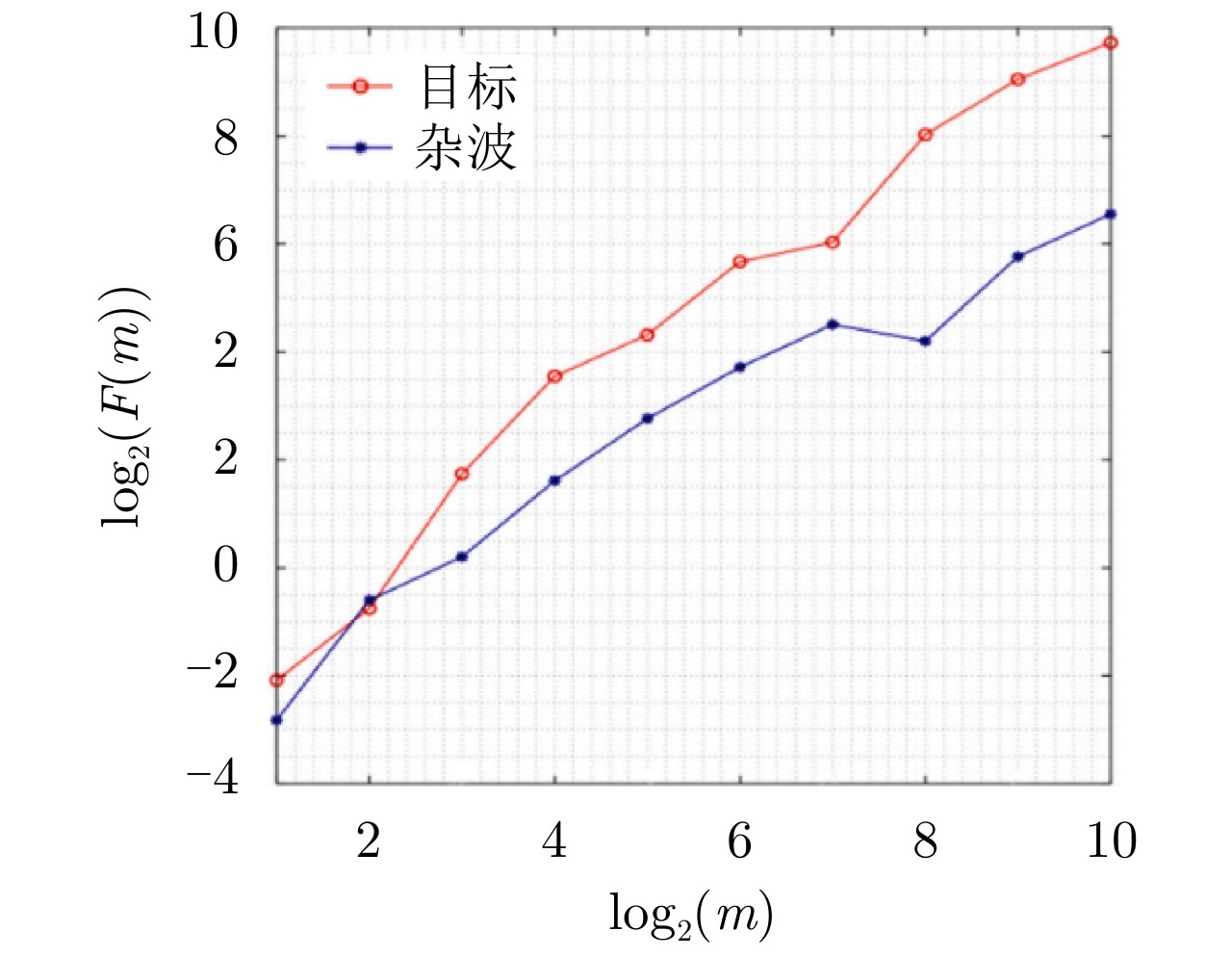
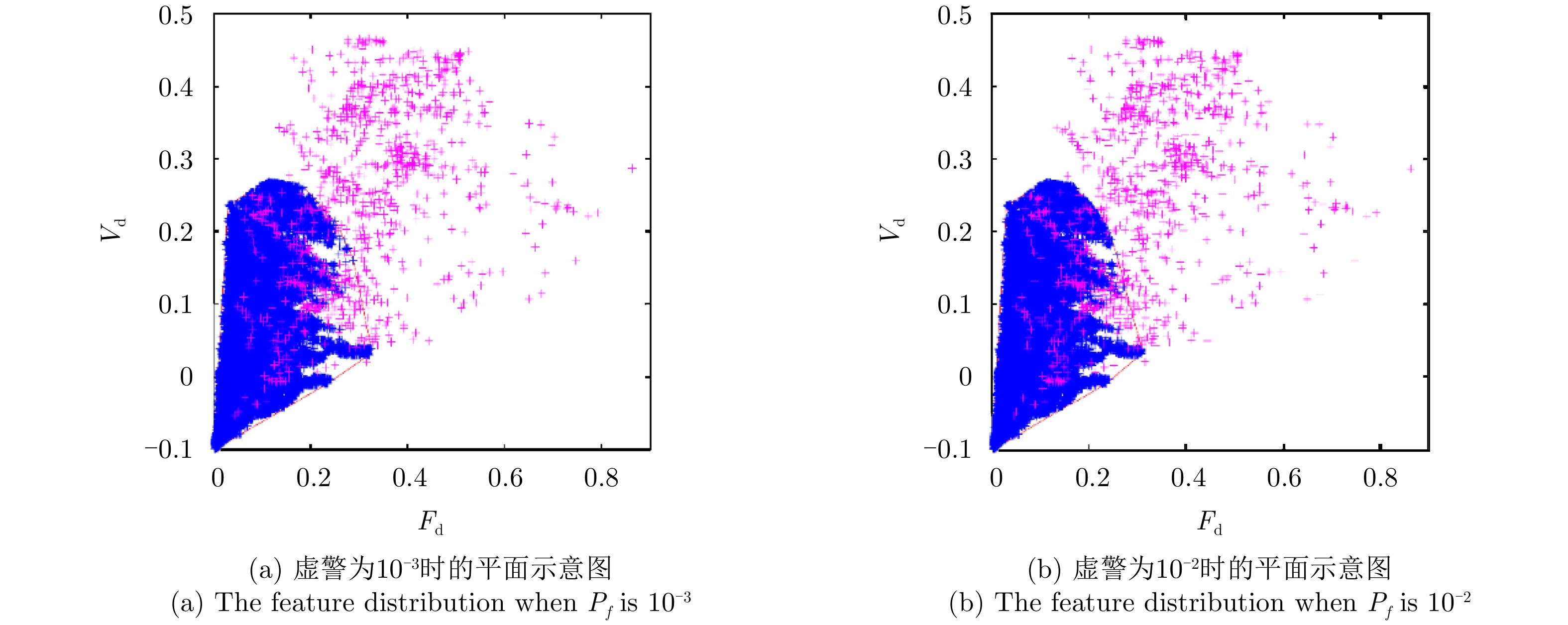
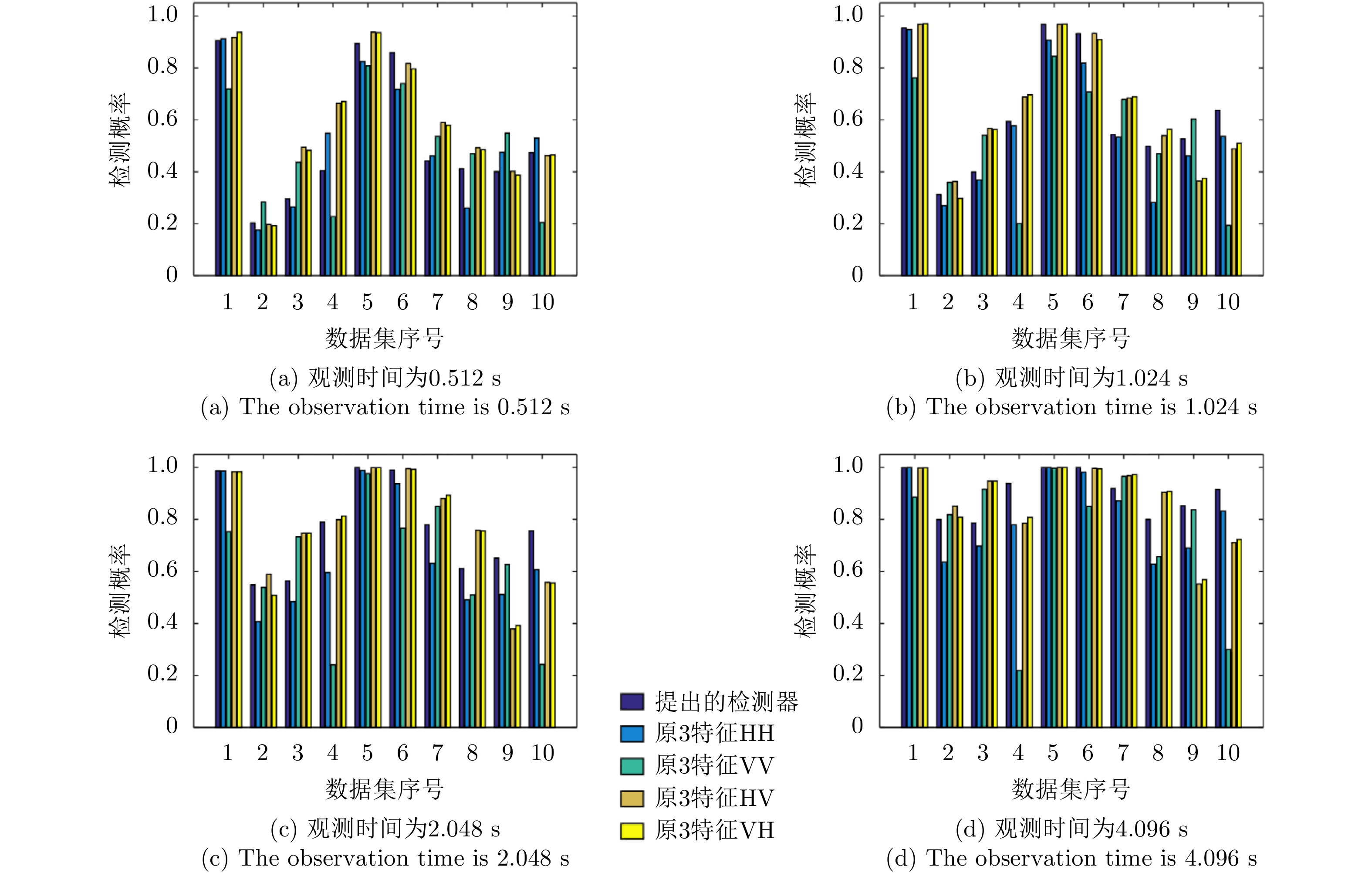
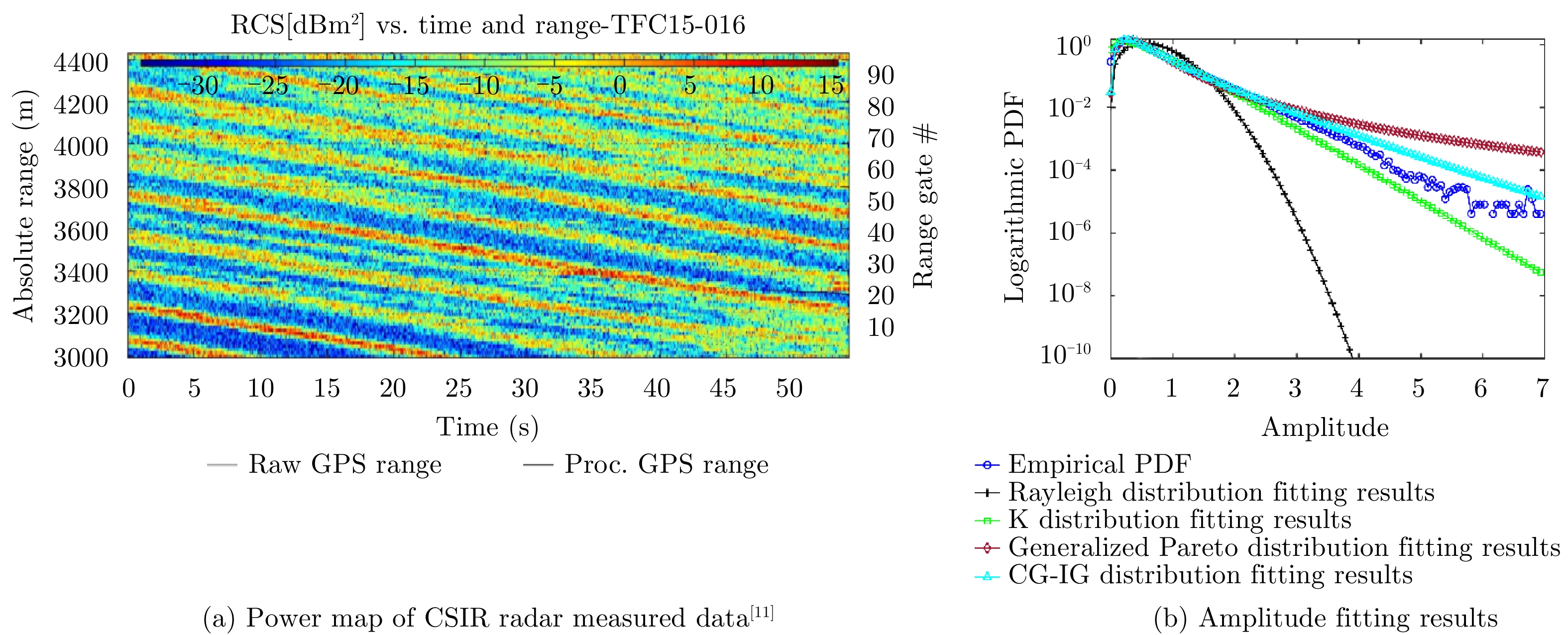
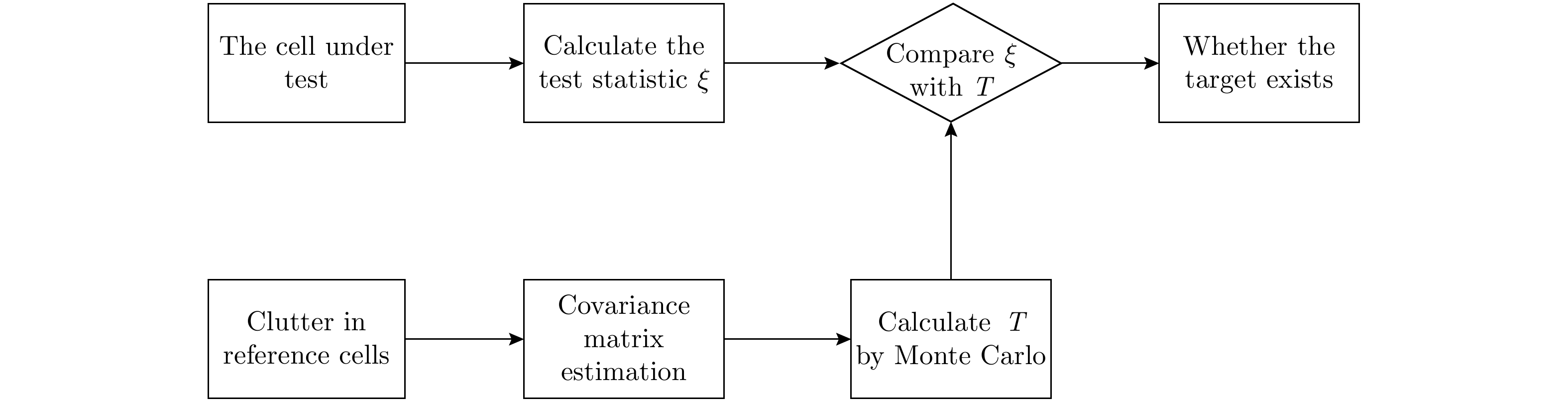
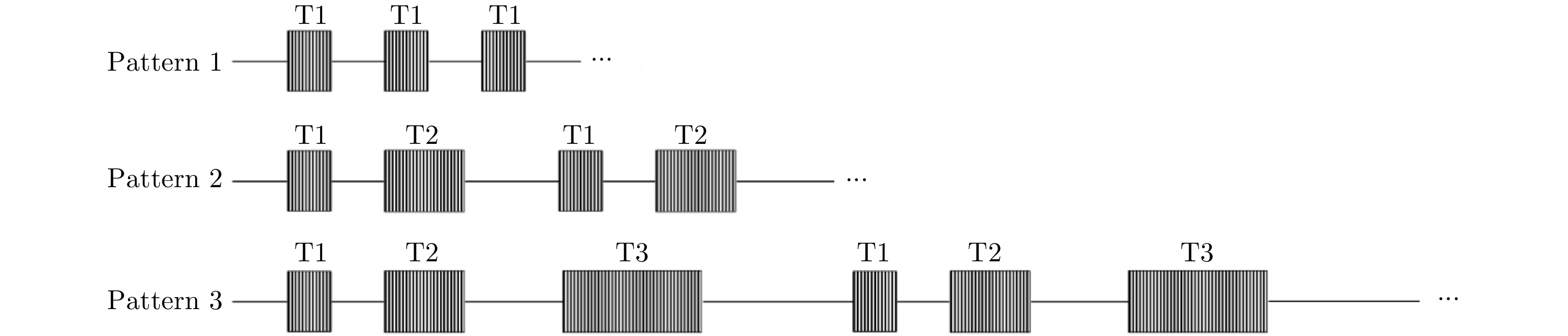
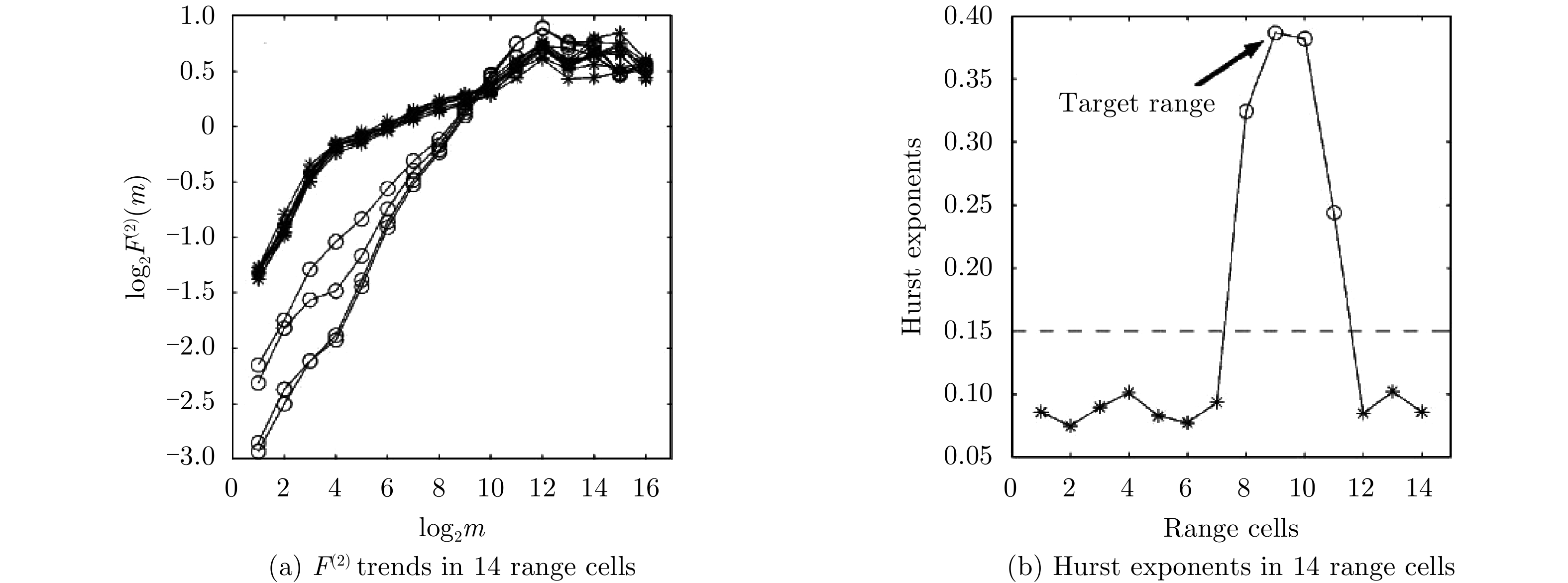
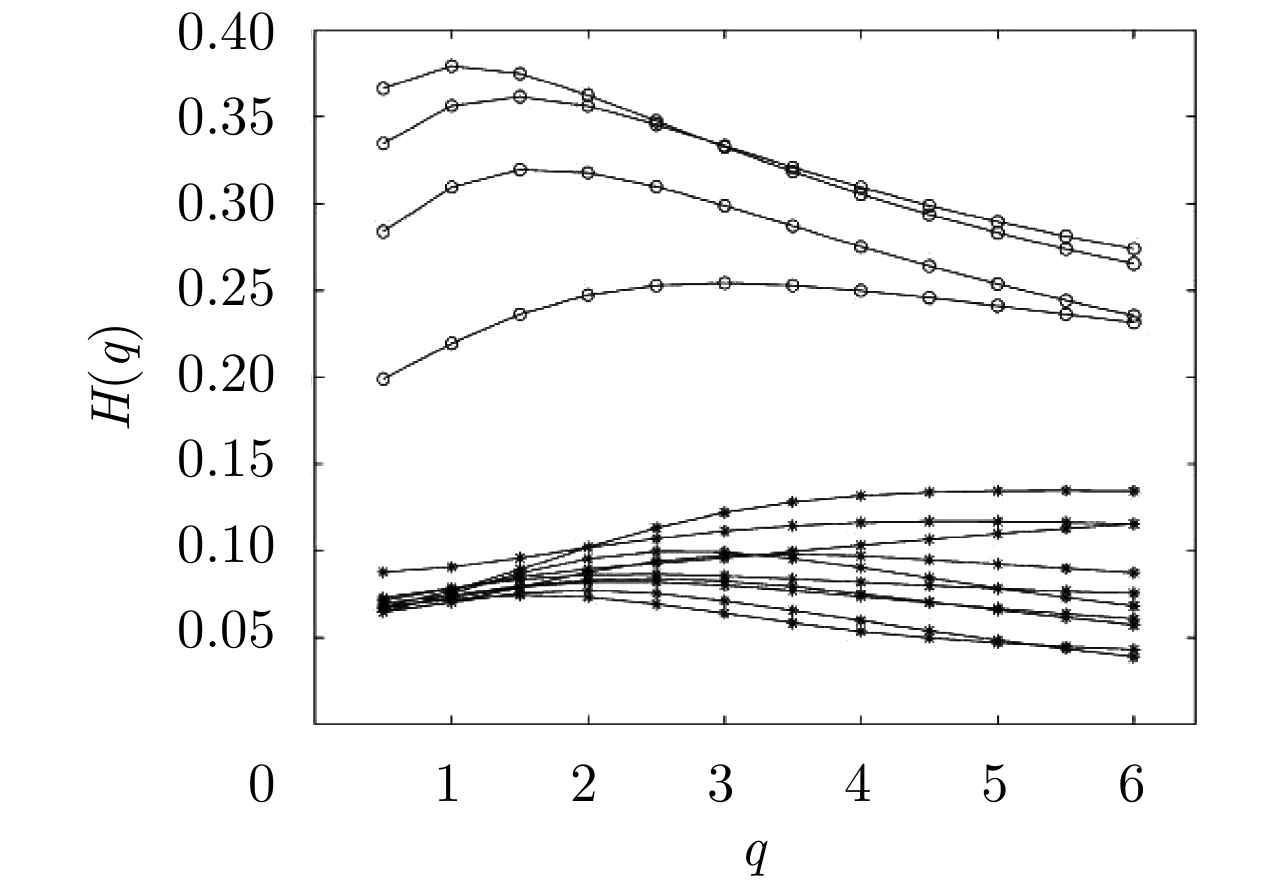
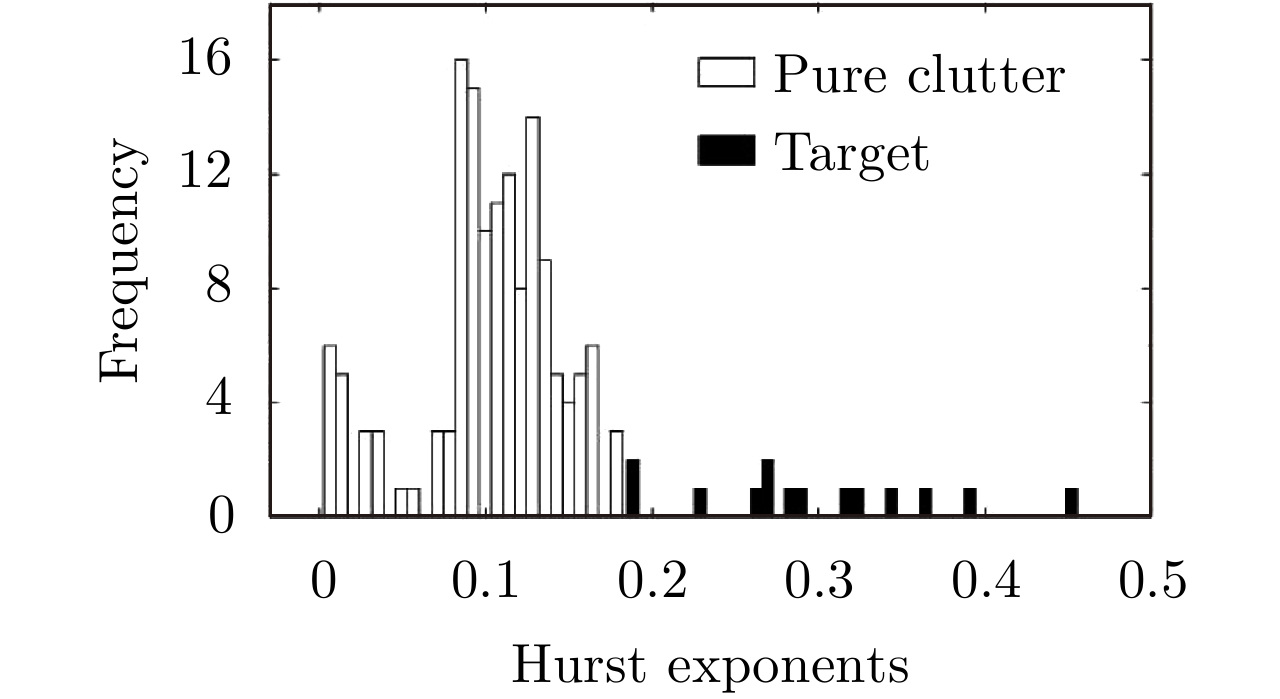
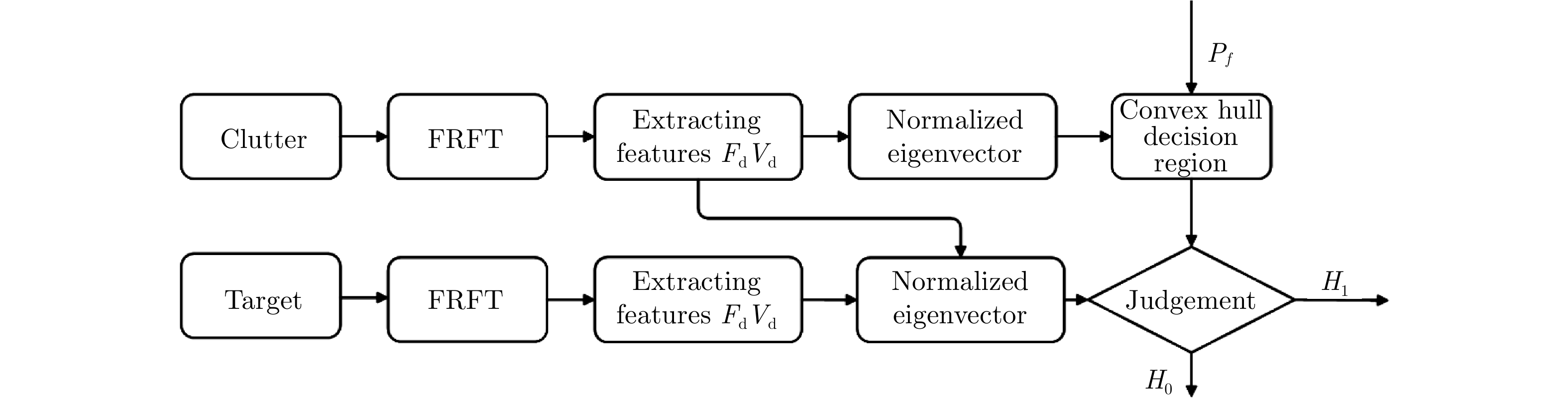
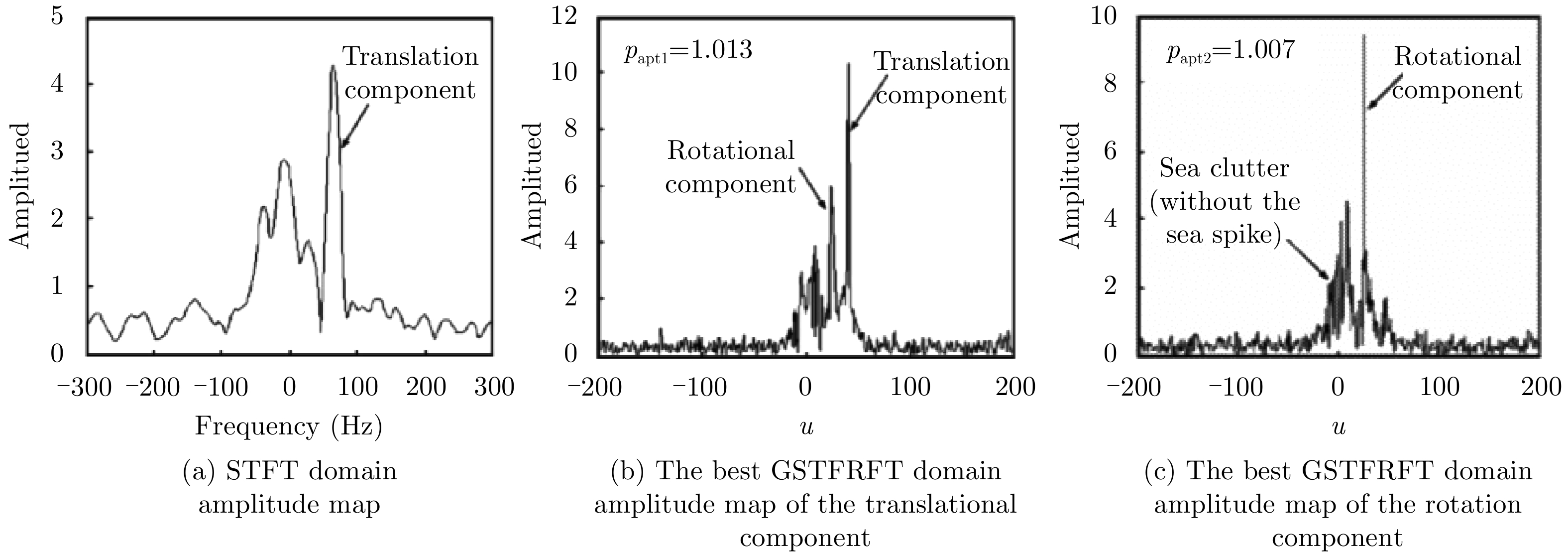
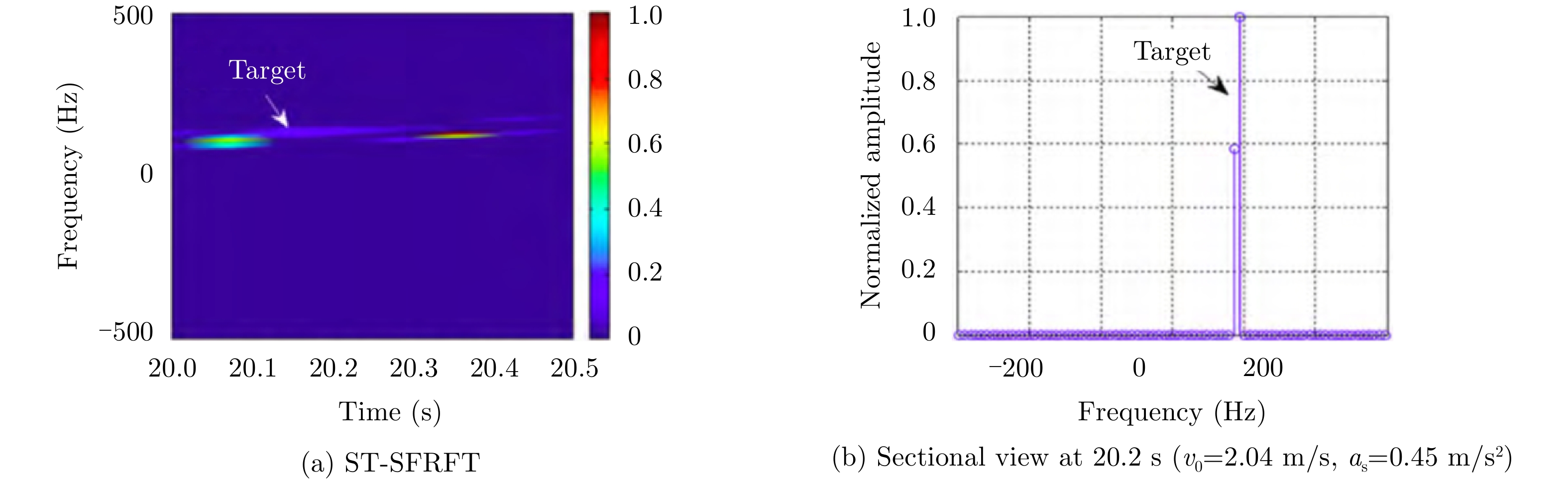
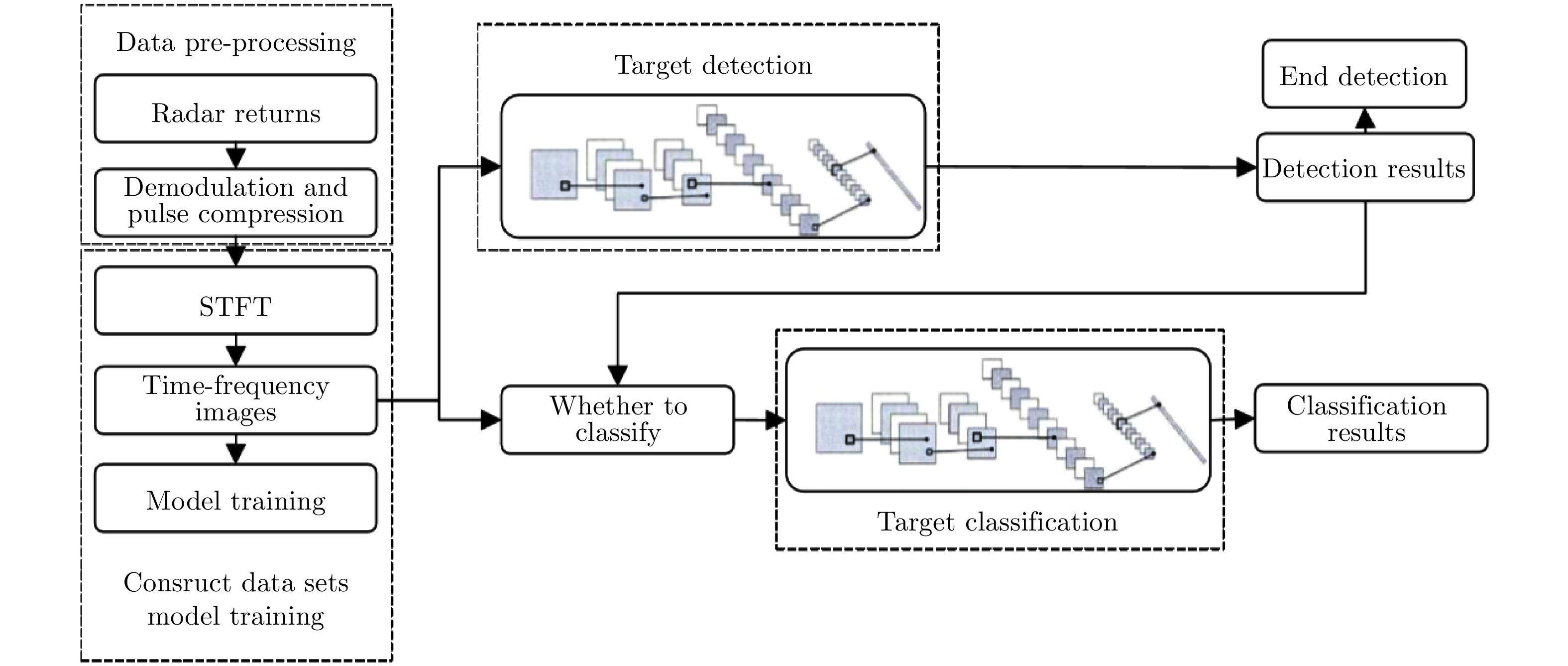
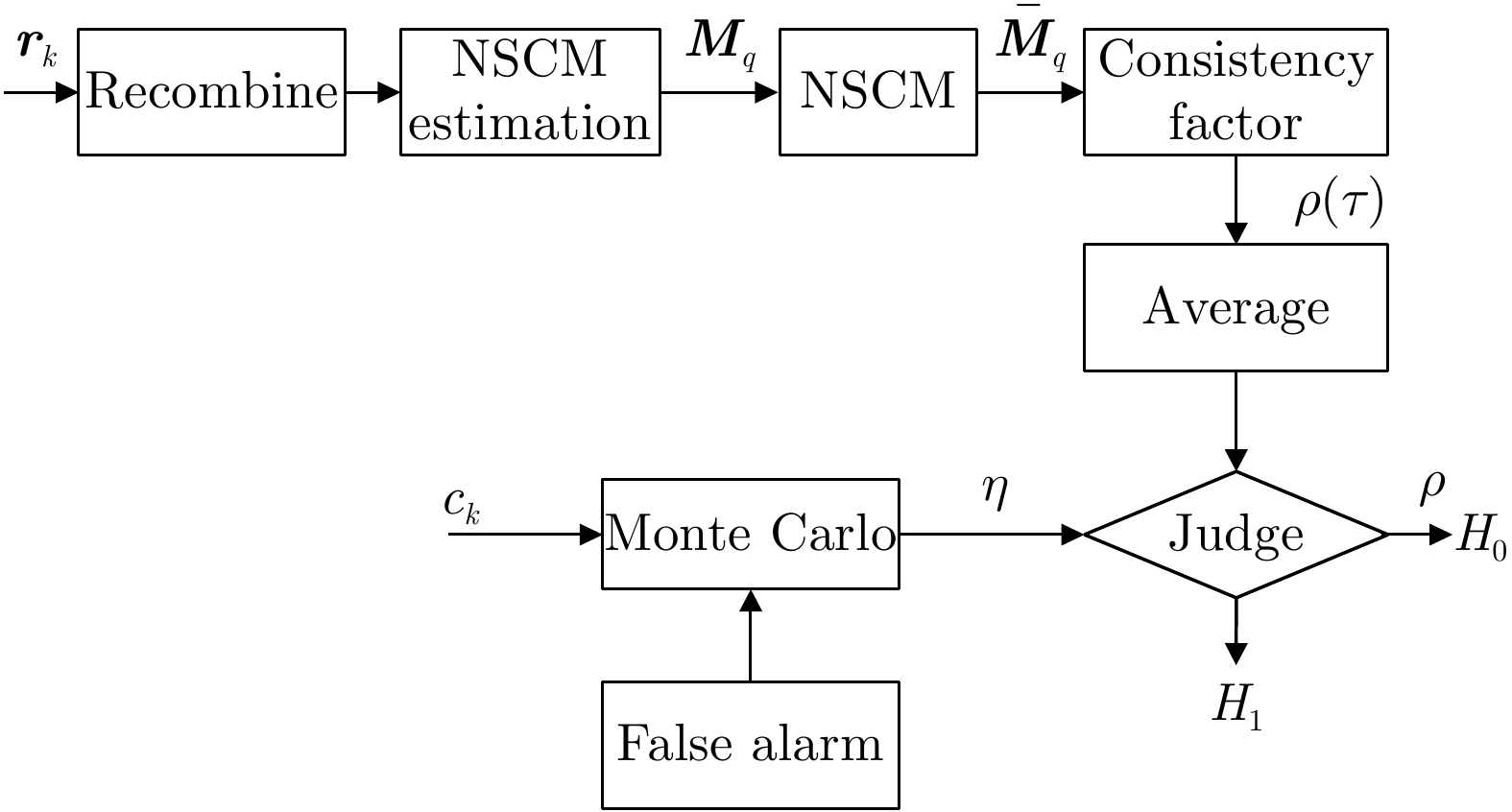
| [1] |
FARINA A, GINI F, GRECO M V, et al. High resolution sea clutter data: Statistical analysis of recorded live data[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1997, 144(3): 121–130. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19971107 |
| [2] |
CONTE E, DE MAIO A, and GALDI C. Statistical analysis of real clutter at different range resolutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(3): 903–918. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1337463 |
| [3] |
WARD K, TOUGH R, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2013. doi: 10.1049/PBRA025E. |
| [4] |
CONTE E and DE MAIO A. Mitigation techniques for Non-Gaussian sea clutter[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2004, 29(2): 284–302. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.826901 |
| [5] |
WALKER D. Doppler modelling of radar sea clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2001, 148(2): 73–80. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20010182 |
| [6] |
RAYNAL A M and DOERRY A W. Doppler characteristics of sea clutter[R]. SAND2010-3828, 2010.
|
| [7] |
TOPORKOV J V and SLETTEN M A. Statistical properties of low-grazing range-resolved sea surface backscatter generated through two-dimensional direct numerical simulations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(5): 1181–1197. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.894442 |
| [8] |
LIU Yong, FRASIER S J, and MCINTOSH R E. Measurement and classification of low-grazing-angle radar sea spikes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1998, 46(1): 27–40. doi: 10.1109/8.655448 |
| [9] |
GRECO M, STINCO P, and GINI F. Identification and analysis of sea radar clutter spikes[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(2): 239–250. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0088 |
| [10] |
MELIEF H W, GREIDANUS H, VAN GENDEREN P, et al. Analysis of sea spikes in radar sea clutter data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(4): 985–993. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.862497 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002 |
| [14] |
WATTS S. Cell-averaging CFAR gain in spatially correlated K-distributed clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(5): 321–327. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960745 |
| [15] |
何友, 关键, 孟祥伟. 雷达目标检测与恒虚警处理[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011.
HE You, GUAN Jian, and MENG Xiangwei. Radar Target Detection and CFAR Processing[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011.
|
| [16] |
ZHOU Wei, XIE Junhao, LI Gaopeng, et al. Robust CFAR detector with weighted amplitude iteration in nonhomogeneous sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1520–1535. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2671798 |
| [17] |
KELLY E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745 |
| [18] |
ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446 |
| [19] |
GINI F and GRECO M. Texture modelling, estimation and validation using measured sea clutter data[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2002, 149(3): 115–124. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20020272 |
| [20] |
CONTE E, LOPS M, and RICCI G. Asymptotically optimum radar detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(2): 617–625. doi: 10.1109/7.381910 |
| [21] |
RICHMOND C D. Analysis of an adaptive detection algorithm for non-homogeneous environments[C]. The 1998 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seattle, USA, 1998: 2005–2008.
|
| [22] |
JAY E, OVARLEZ J P, DECLERCQ D, et al. BORD: Bayesian optimum radar detector[J]. Signal Processing, 2003, 83(6): 1151–1162. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(03)00034-3 |
| [23] |
DONG Yunhan. Optimal coherent radar detection in a K-distributed clutter environment[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 283–292. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0273 |
| [24] |
SANGSTON K J, GINI F, and GRECO M S. Coherent radar target detection in heavy-tailed compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(1): 64–77. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6129621 |
| [25] |
SHANG X and SONG H. Radar detection based on Compound-Gaussian model with inverse gamma texture[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2011, 5(3): 315–321. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2010.0125 |
| [26] |
XU Shuwen, XUE Jian, and SHUI Penglang. Adaptive detection of range-spread targets in compound Gaussian clutter with the square root of inverse Gaussian texture[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 56: 132–139. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.06.009 |
| [27] |
SHUI Penglang, LIU Ming, and XU Shuwen. Shape-parameter-dependent coherent radar target detection in K-distributed clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(1): 451–465. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140109 |
| [28] |
SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 |
| [29] |
LO T, LEUNG H, LITVA J, et al. Fractal characterisation of sea-scattered signals and detection of sea-surface targets[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1993, 140(4): 243–250. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1993.0034 |
| [30] |
HU Jing, TUNG W W, and GAO Jianbo. Detection of low observable targets within sea clutter by structure function based multifractal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2006, 54(1): 136–143. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2005.861541 |
| [31] |
GUAN Jian, LIU N B, HUANG Y, et al. Fractal characteristic in frequency domain for target detection within sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 293–306. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0250 |
| [32] |
CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HE You, et al. Detection of low observable moving target in sea clutter via fractal characteristics in fractional Fourier transform domain[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2013, 7(6): 635–651. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2012.0116 |
| [33] |
HAYKIN S and LI Xiaobo. Detection of signals in chaos[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1995, 83(1): 95–122. doi: 10.1109/5.362751 |
| [34] |
HE Nan and HAYKIN S. Chaotic modelling of sea clutter[J]. Electronics Letters, 1992, 28(22): 2076–2077. doi: 10.1049/el:19921331 |
| [35] |
HAYKIN S and THOMSON D J. Signal detection in a nonstationary environment reformulated as an adaptive pattern classification problem[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2325–2344. doi: 10.1109/5.726792 |
| [36] |
DJUROVIĆ I and STANKOVIĆ L. An algorithm for the Wigner distribution based instantaneous frequency estimation in a high noise environment[J]. Signal Processing, 2004, 84(3): 631–643. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2003.12.006 |
| [37] |
HAYKIN S and BHATTACHARYA T K. Modular learning strategy for signal detection in a nonstationary environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(6): 1619–1637. doi: 10.1109/78.600003 |
| [38] |
PANAGOPOULOS S and SORAGHAN J J. Small-target detection in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(7): 1355–1361. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.827259 |
| [39] |
ZHANG Xiaowei, YANG Dongdong, GUO Jianxin, et al.. Weak moving target detection based on short-time fourier transform in sea clutter[C]. The IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 2019: 415–419. doi: 10.1109/SIPROCESS.2019.8868771. |
| [40] |
CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function-based detection and estimation method for marine target with micromotion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2225–2240. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2358456 |
| [41] |
CHEN Xiaolong, LIU Ningbo, WANG Guoqing, et al. Gaussian short-time fractional Fourier transform based detection algorithm of target with Micro-Motion at sea[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(5): 971–977. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2014.05.021 |
| [42] |
陈小龙, 关键, 于晓涵, 等. 基于短时稀疏时频分布的雷达目标微动特征提取及检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1017–1023. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161040CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, YU Xiaohan, et al. Radar Micro-Doppler signature extraction and detection via short-time sparse time-frequency distribution[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1017–1023. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161040 |
| [43] |
苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077 |
| [44] |
MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Marine target detection based on improved faster R-CNN for navigation radar PPI images[C]. 2019 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCAIS46528.2019.9074588. |
| [45] |
LEUNG H, DUBASH N, and XIE Nan. Detection of small objects in clutter using a GA-RBF neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(1): 98–118. doi: 10.1109/7.993232 |
| [46] |
METCALF J, BLUNT S D, and HIMED B. A machine learning approach to cognitive radar detection[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 1405–1411.
|
| [47] |
CALLAGHAN D, BURGER J, and MISHRA A K. A machine learning approach to radar sea clutter suppression[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 1222–1227.
|
| [48] |
MACHADO J R F and VIDAL J D L C B. Improved shape parameter estimation in K clutter with neural networks and deep learning[J]. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 3(7): 96–103. doi: 10.9781/ijimai.2016.3714 |
| [49] |
DEL-REY-MAESTRE N, MATA-MOYA D, JARABO-AMORES M P, et al. Artificial intelligence techniques for small boats detection in radar clutter. Real data validation[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 67: 296–308. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2017.10.005 |
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089 |
| [52] |
ANTIPOV I. Analysis of sea clutter data[R]. Technical Report, DSTO-TR-0647, 1998.
|
| [53] |
DONG Yunhan and MERRETT D. Statistical measures of S-band sea clutter and targets[R]. Technical Report, DSTO-TR-2221, 2008.
|
| [54] |
DONG Yunhan and MERRETT D. Analysis of L-band multi-channel sea clutter[R]. Technical Report, DSTO-TR-2455, 2010.
|
| [55] |
DALEY J C, RANSONE J T, BURKETT J A, et al. Sea clutter measurements on four frequencies[R]. Naval Research Laboratory Report 6806, 1968. doi: 10.1109/7.993229. |
| [56] |
CARRETERO-MOYA J, GISMERO-MENOYO J, BLANCO-DEL-CAMPO Á, et al. Statistical analysis of a high-resolution sea-clutter database[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2024–2037. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2033193 |
| [57] |
SIEGEL A, OCHADLICK A, DAVIS J, et al. Spatial and temporal correlation of LOGAN-1 high-resolution radar sea clutter data[C]. Proceedings of IGARSS’ 94-1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 1994: 818–821. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1994.399273. |
| [58] |
RINO C L, ECKERT E, SIEGEL A, et al. X-band low-grazing-angle ocean backscatter obtained during LOGAN 1993[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1997, 22(1): 18–26. doi: 10.1109/48.557536 |
| [59] |
HAIR T, LEE T, and BAKER C J. Statistical properties of multifrequency high-range-resolution sea reflections[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1991, 138(2): 75–79. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0012 |
| [60] |
ISHII S, SAYAMA S, and MIZUTANI K. Effect of changes in sea-surface state on statistical characteristics of sea clutter with X-band radar[J]. Wireless Engineering and Technology, 2011, 2(3): 175–183. doi: 10.4236/wet.2011.23025 |
| [61] |
FABBRO V, BIEGEL G, FÖRSTER J, et al. Measurements of sea clutter at low grazing angle in Mediterranean coastal environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6379–6389. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2727057 |
| [62] |
AL-ASHWAL W A, BAKER C J, BALLERI A, et al. Statistical analysis of simultaneous monostatic and bistatic sea clutter at low grazing angles[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(10): 621–622. doi: 10.1049/el.2011.0557 |
| [63] |
AL-ASHWAL W A, WOODBRIDGE K, and GRIFFITHS H D. Analysis of bistatic sea clutter-Part I: Average reflectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1283–1292. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120426 |
| [64] |
AL-ASHWAL W A, WOODBRIDGE K, and GRIFFITHS H D. Analysis of bistatic sea clutter-Part II: Amplitude statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1293–1303. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120434 |
| [65] |
RITCHIE M, STOVE A, WOODBRIDGE K, et al. NetRAD: Monostatic and bistatic sea clutter texture and Doppler spectra characterization at S-Band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5533–5543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2567598 |
| [66] |
FIORANELLI F, RITCHIE M, GRIFFITHS H, et al. Analysis of polarimetric bistatic sea clutter using the NetRAD radar system[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(8): 1356–1366. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0416 |
| [67] |
LIU Ningbo, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. Fractal analysis of real sea clutter in frequency domain[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 929–935. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00856 |
| [68] |
GAO Jianbo and YAO K. Multifractal features of sea clutter[C]. The 2002 IEEE Radar Conference, Long Beach, USA, 2002: 500–505.
|
| [69] |
LIU Ningbo, WANG Guoqing, BAO Zhonghua, et al. Multifractal property of sea clutter FRFT spectrum for target detection[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 29(1): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2013.01.001 |
| [70] |
GU Zhimin, ZHANG Xinggan, and WANG Qiong. Multifractal property and target detection of sea clutter in FRFT domain[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Science, 2017, 53(4): 731–737. doi: 10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2017.04.016 |
| [71] |
田玉芳, 姬光荣, 尹志盈, 等. 基于FRFT域空间分形特征差异的海面弱目标检测[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2013, 43(3): 92–97.
TIAN Yufang, JI Guangrong, YIN Zhiying, et al. Weak targets detection in sea clutter based on modified fractal character differences[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(3): 92–97.
|
| [72] |
LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, WANG Guoqing, et al. Target detection within sea clutter based on multi-scale Hurst exponent in FRFT domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(9): 1847–1853. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.09.029 |
| [73] |
SHI Yanling, ZHANG Xueliang, and LIU Zipeng. Floating small target detection in sea clutter based on jointed features in FRFT domain[C]. The 3rd EAI International Conference on Advanced Hybrid Information Processing, Nanjing, China, 2019: 128–139. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-36405-2_14. |
| [74] |
SHI Yanling, XIE Xiaoyan, and LI Dongchen. Range distributed floating target detection in sea clutter via feature-based detector[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1847–1850. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2614750 |
| [75] |
SHI Sainan and SHUI Penglang. Sea-surface floating small target detection by one-class classifier in time-frequency feature space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6395–6411. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2838260 |
| [76] |
XU Shuwen, ZHENG Jibin, PU Jia, et al. Sea-surface floating small target detection based on polarization features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1505–1509. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2852560 |
| [77] |
LI Yuzhou, XIE Pengcheng, TANG Zeshen, et al. SVM-based sea-surface small target detection: A false-alarm-rate-controllable approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience And Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1225–1229. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2894385 |
| [78] |
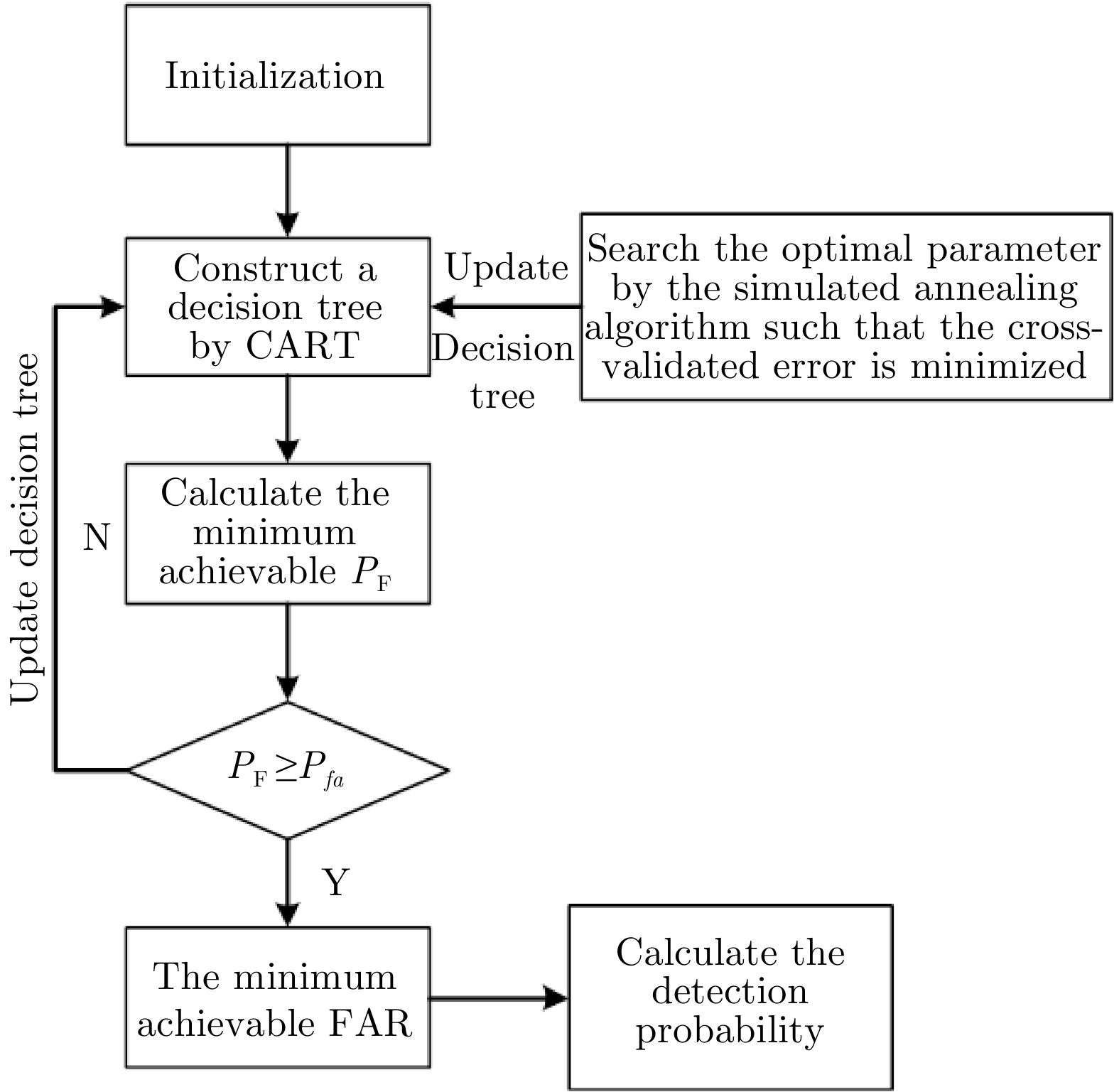
ZHOU Hongkun and JIANG Tao. Decision tree based sea-surface weak target detection with false alarm rate controllable[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(6): 793–797. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2909584 |
| [79] |
MANDELBROT B B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature[M]. San Francisco: Freeman, 1982.
|
| [80] |
MANDELBROT B B and VAN NESS J W. Fractional Brownian motions, fractional noises and applications[J]. SIAM Review, 1968, 10(4): 422–437. doi: 10.1137/1010093 |
| [81] |
JAGGARD D L and SUN Xiaoguang. Scattering from fractally corrugated surfaces[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1990, 7(6): 1131–1139. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.7.001131 |
| [82] |
SAVAIDIS S, FRANGOS P, JAGGARD D L, et al. Scattering from fractally corrugated surfaces: An exact approach[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(23): 2357–2359. doi: 10.1364/OL.20.002357 |
| [83] |
FRANCESCHETTI G, IODICE A, MIGLIACCIO M, et al. Scattering from natural rough surfaces modeled by fractional Brownian motion two-dimensional processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(9): 1405–1415. doi: 10.1109/8.793320 |
| [84] |
BERIZZI F and MESE E D. Fractal theory of sea scattering[C]. International Radar Conference, Beijing, China, 1996: 661–665.
|
| [85] |
BERIZZI F, GRECO M, and VERRAZZANI L. Fractal approach for sea clutter generation[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2000, 147(4): 189–198. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20000465 |
| [86] |
GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, ZHANG Jian, et al. Multifractal correlation characteristic for radar detecting low-observable target in sea clutter[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(2): 523–535. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.07.021 |
| [87] |
LIU Ningbo, GUAN Jian, and SONG Jie. Local Multifractal characteristic of sea clutter in radar scanning mode for target detection[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2009, 7(4): 277–283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2009.04.008 |
| [88] |
GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, ZHANG Jian, et al. Multifractal correlation characteristic of real sea clutter and low-observable targets detection[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2010, 32(1): 54–61. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.00980 |
| [89] |
LEUNG H and LO T. Chaotic radar signal processing over the sea[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1993, 18(3): 287–295. doi: 10.1109/JOE.1993.236367 |
| [90] |
HENNESSEY G, LEUNG H, DROSOPOULOS A, et al. Sea-clutter modeling using a radial-basis-function neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2001, 26(3): 358–372. doi: 10.1109/48.946510 |
| [91] |
LEUNG H, HENNESSEY G, and DROSOPOULOS A. Signal detection using the radial basis function coupled map lattice[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2000, 11(5): 1133–1151. doi: 10.1109/72.870045 |
| [92] |
XIE Nan and LEUNG H. Reconstruction of piecewise chaotic dynamic using a genetic algorithm multiple model approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2004, 51(6): 1210–1222. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2004.826216 |
| [93] |
XIE Nan, LEUNG H, and CHAN H. A multiple-model prediction approach for sea clutter modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(6): 1491–1502. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.811690 |
| [94] |
HAYKIN S, BAKKER R, and CURRIE B W. Uncovering nonlinear dynamics-the case study of sea clutter[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2002, 90(5): 860–881. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2002.1015011 |
| [95] |
UNSWORTH C P, COWPER M R, MCLAUGHLIN S, et al. Re-examining the nature of radar sea clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2002, 149(3): 105–114. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20020301 |
| [96] |
GAO J B, HWANG S K, CHEN H F, et al. Can sea clutter and indoor radio propagation be modeled as strange attractors?[C]. The 7th Experimental Chaos Conference, Melville, Canada, 2003: 25–29.
|
| [97] |
MCDONALD M and DAMINI A. Limitations of nonlinear chaotic dynamics in predicting sea clutter returns[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2004, 151(2): 105–113. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20040261 |
| [98] |
王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040 |
| [99] |
WOOD J C and BARRY D T. Linear signal synthesis using the Radon-Wigner transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(8): 2105–2111. doi: 10.1109/78.301845 |
| [100] |
WOOD J C and BARRY D T. Radon transformation of time-frequency distributions for analysis of multicomponent signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(11): 3166–3177. doi: 10.1109/78.330375 |
| [101] |
WANG Minsheng, CHAN A K, and CHUI C K. Linear frequency-modulated signal detection using Radon-ambiguity transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1998, 46(3): 571–586. doi: 10.1109/78.661326 |
| [102] |
MANN S and HAYKIN S. The chirplet transform: Physical considerations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(11): 2745–2761. doi: 10.1109/78.482123 |
| [103] |
SHUI Penglang, BAO Zheng, and SU Hongtao. Nonparametric detection of FM signals using time-frequency ridge energy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(5): 1749–1760. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.909322 |
| [104] |
WANG Shiqing and JIN Yaqiu. Ship wake detection in SAR images based on radon transformation and morphologic image processing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2001, 5(4): 289–294. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-4619.2001.04.008 |
| [105] |
TANG Ziyue, ZHU Minhui, and WANG Weiyan. A CFAR detection method of ship wakes in SAR images[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2002, 30(9): 1336–1339. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2002.09.022 |
| [106] |
GUAN Jian, LI Bao, LIU Jianeng, et al. Two approaches of detecting weak moving target with constant acceleration in sea clutter[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2009, 31(8): 1898–1902. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01023 |
| [107] |
CARRETERO-MOYA J, GISMERO-MENOYO J, ASENSIO-LOPEZ A, et al. Application of the radon transform to detect small-targets in sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2009, 3(2): 155–166. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20080123 |
| [108] |
LIU Jiancheng, WANG Xuesong, LIU Zhong, et al. Detection performance of linear frequency modulated signals based on Wigner-Hough transform[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(6): 1212–1217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.06.041 |
| [109] |
ZHANG Yu, QIAN S, and THAYAPARAN T. Detection of a manoeuvring air target in strong sea clutter via joint time-frequency representation[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2008, 2(3): 216–222. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr:20070047 |
| [110] |
SHUI Penglang, LIU Hongwei, and BAO Zheng. Range-spread target detection based on cross time-frequency distribution features of two adjacent received signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(10): 3733–3745. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2029715 |
| [111] |
ZUO Lei, LI Ming, ZHANG Xiaowei, et al. Small-target detection in sea clutter based on improved Hough transform[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 923–928. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00373 |
| [112] |
ZUO Lei, LI Ming, ZHANG Xiaowei, et al. An efficient method for detecting slow-moving weak targets in sea clutter based on time-frequency iteration decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3659–3672. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2224665 |
| [113] |
ZUO Lei, LI Ming, ZHANG Xiaowei, et al. CFAR detection of range-spread targets based on the time-frequency decomposition feature of two adjacent returned signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(24): 6307–6319. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2282274 |
| [114] |
CHEN Xiaolong, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al.. Sea clutter suppression and moving target detection method based on clutter map cancellation in FRFT domain[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 438–441. doi: 10.1109/CIE-Radar.2011.6159571. |
| [115] |
GUAN Jian, CHEN Xiaolong, HUANG Y, et al. Adaptive fractional Fourier transform-based detection algorithm for moving target in heavy sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 389–401.
|
| [116] |
CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, BAO Zhonghua, et al. Detection and extraction of target with micromotion in spiky sea clutter via short-time fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1002–1018. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2246574 |
| [117] |
JANGAL F, SAILLANT S, and HELIER M. Wavelet contribution to remote sensing of the sea and target detection for a high-frequency surface wave radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(3): 552–556. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.923211 |
| [118] |
陈小龙, 董云龙, 李秀友, 等. 海面刚体目标微动特征建模及特性分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 630–638. doi: 10.12000/JR15079CHEN Xiaolong, DONG Yunlong, LI Xiuyou, et al. Modeling of micromotion and analysis of properties of rigid marine targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 630–638. doi: 10.12000/JR15079 |
| [119] |
POSNER F L. Spiky sea clutter at high range resolutions and very low grazing angles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(1): 58–73. doi: 10.1109/7.993229 |
| [120] |
WANG Pu, LI Hongbin, DJUROVIC I, et al. Integrated cubic phase function for linear FM signal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 963–977. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545167 |
| [121] |
BI Guoan, LI Xiumei, and SEE C M S. LFM signal detection using LPP-Hough transform[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 91(6): 1432–1443. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.08.001 |
| [122] |
AOI M, LEPAGE K, LIM Y, et al. An approach to time-frequency analysis with ridges of the continuous chirplet transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(3): 699–710. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2365756 |
| [123] |
CHASSANDE-MOTTIN É and PAI A. Best chirplet chain: near-optimal detection of gravitational wave chirps[J]. Physical Review D, 2006, 73(4): 042003.
|
| [124] |
LI Dongchen, SHUI Penglang, and XU Shuwen. Floating small target detection in the sea clutter via block-whitened clutter suppression[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2016, 43(6): 21–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2016.06.004 |
| [125] |
(美)科恩 L, 白居宪译. 时-频分析: 理论与应用[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 1998.
COHEN L, BAI Juxian translation. Time-Frequency Analysis: Theory and Application[M]. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, 1998
|
| [126] |
RICHARD C. Time-frequency-based detection using discrete-time discrete-frequency Wigner distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(9): 2170–2176. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.801927 |
| [127] |
FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 |
| [128] |
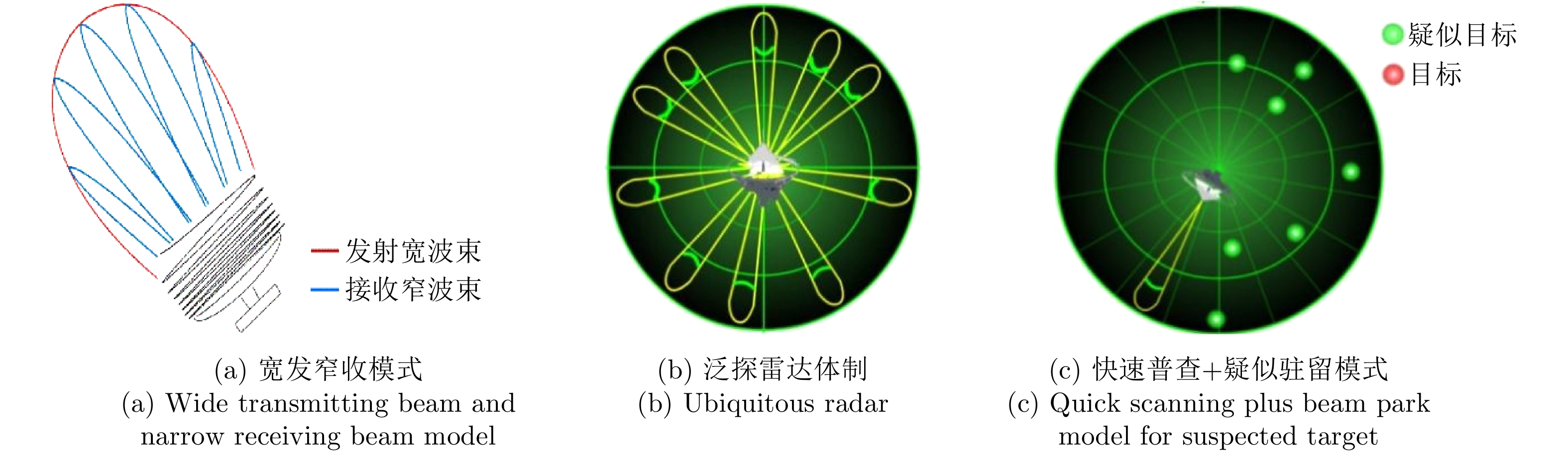
RABIDEAU D J and PARKER P. Ubiquitous MIMO multifunction digital array radar[C]. The 37th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, 2003, Pacific Grove, USA, 2003: 1057–1064. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2003.1292087. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: