- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | WANG Bingnan, ZHAO Juanying, LI Wei, et al. Array synthetic aperture ladar with high spatial resolution technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1110–1118. doi: 10.12000/JR22204 |
Array Synthetic Aperture Ladar with High Spatial Resolution Technology
DOI: 10.12000/JR22204 CSTR: 32380.14.JR22204
More Information-
Abstract
By extending synthetic aperture technology from the microwave band to the laser wavelength, Synthetic Aperture Ladar (SAL) has long-distance imaging and extremely high spatial resolution independent of the target distance. Presently, the small field of view is the key constraint in SAL ground observation because of the laser diffraction limitation. In this paper, an array SAL technology is proposed. With high-power array transmission, array-balanced detection, and pulse-wise dynamic internal calibration, a multichannel coherent laser transceiver is realized. Meanwhile, the field of view has multiplied. The results of turntable experiments show that the imaging resolution is better than 3 cm (distance) × 1 cm (azimuth). This technology provides a scientific and technical approach to SAL with wider swath imaging in ground observation.-
Keywords:
- Array,
- Synthetic Aperture Ladar (SAL),
- High resolution,
- Wide swath
-

-
References
[1] LEWIS T S and HUTCHINS H S. A synthetic aperture at optical frequencies[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1970, 58(4): 587–588. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1970.7698[2] MARCUS S, COLELLA B D, and GREEN T J. Solid-state laser synthetic aperture radar[J]. Applied Optics, 1994, 33(6): 960–964. doi: 10.1364/AO.33.000960[3] GREEN T J, MARCUS S, and COLELLA B D. Synthetic-aperture-radar imaging with a solid-state laser[J]. Applied Optics, 1995, 34(30): 6941–6949. doi: 10.1364/AO.34.006941[4] BASHKANSKY M, LUCKE R L, FUNK E, et al. Two-dimensional synthetic aperture imaging in the optical domain[J]. Optics Letters, 2002, 27(22): 1983–1985. doi: 10.1364/OL.27.001983[5] BECK S M, BUCK J R, BUELL W F, et al. Synthetic-aperture imaging laser radar: Laboratory demonstration and signal processing[J]. Applied Optics, 2005, 44(35): 7621–7629. doi: 10.1364/AO.44.007621[6] KRAUSE B W, BUCK J, RYAN C, et al. Synthetic aperture Ladar flight demonstration[C]. Laser Science to Photonic Applications, Baltimore, USA, 2011: 1–2.[7] 郭亮. 合成孔径成像激光雷达实验与算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2009: 43–62.GUO Liang. Study on experiment and algorithm of synthetic aperture imaging Lidar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2009: 43–62.[8] 刘立人, 周煜, 职亚楠, 等. 大口径合成孔径激光成像雷达演示样机及其实验室验证[J]. 光学学报, 2011, 31(9): 0900112. doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0900112LIU Liren, ZHOU Yu, ZHI Ya’nan, et al. A large-aperture synthetic aperture imaging Ladar demonstrator and its verification in laboratory space[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2011, 31(9): 0900112. doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0900112[9] 吴谨, 杨兆省, 赵志龙, 等. 单程远场衍射合成孔径激光雷达成像实验室演示[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2013, 32(6): 514–518. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00514WU Jin, YANG Zhaosheng, ZHAO Zhilong, et al. Synthetic aperture Ladar imaging with one-way far-field diffraction[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2013, 32(6): 514–518. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2013.00514[10] LI Guangzuo, WANG Ning, WANG Ran, et al. Imaging method for airborne SAL data[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(5): 351–353. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.4205[11] 张珂殊, 潘洁, 王然, 等. 大幅宽激光合成孔径雷达成像技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 1–10. doi: 10.12000/JR16152ZHANG Keshu, PAN Jie, WANG Ran, et al. Study of wide swath synthetic aperture Ladar imaging techology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 1–10. doi: 10.12000/JR16152[12] 张波, 周煜, 孙建锋, 等. 多通道宽幅度合成孔径激光成像雷达收发装置优化研究[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(5): 0528002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0528002ZHANG Bo, ZHOU Yu, SUN Jianfeng, et al. Optimization research on multi-channel wide-swath synthetic aperture imaging Ladar transceiver system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(5): 0528002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0528002[13] 李道京, 周凯, 崔岸婧, 等. 多通道逆合成孔径激光雷达成像探测技术和实验研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(18): 1811017. doi: 10.3788/LOP202158.1811017LI Daojing, ZHOU Kai, CUI Anjing, et al. Multi-channel inverse synthetic aperture Ladar imaging detection technology and experimental research[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(18): 1811017. doi: 10.3788/LOP202158.1811017[14] META A, HOOGEBOOM P, and LIGTHART L. Range non-linearities correction in FMCW SAR[C]. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006: 403–406. -
Proportional views

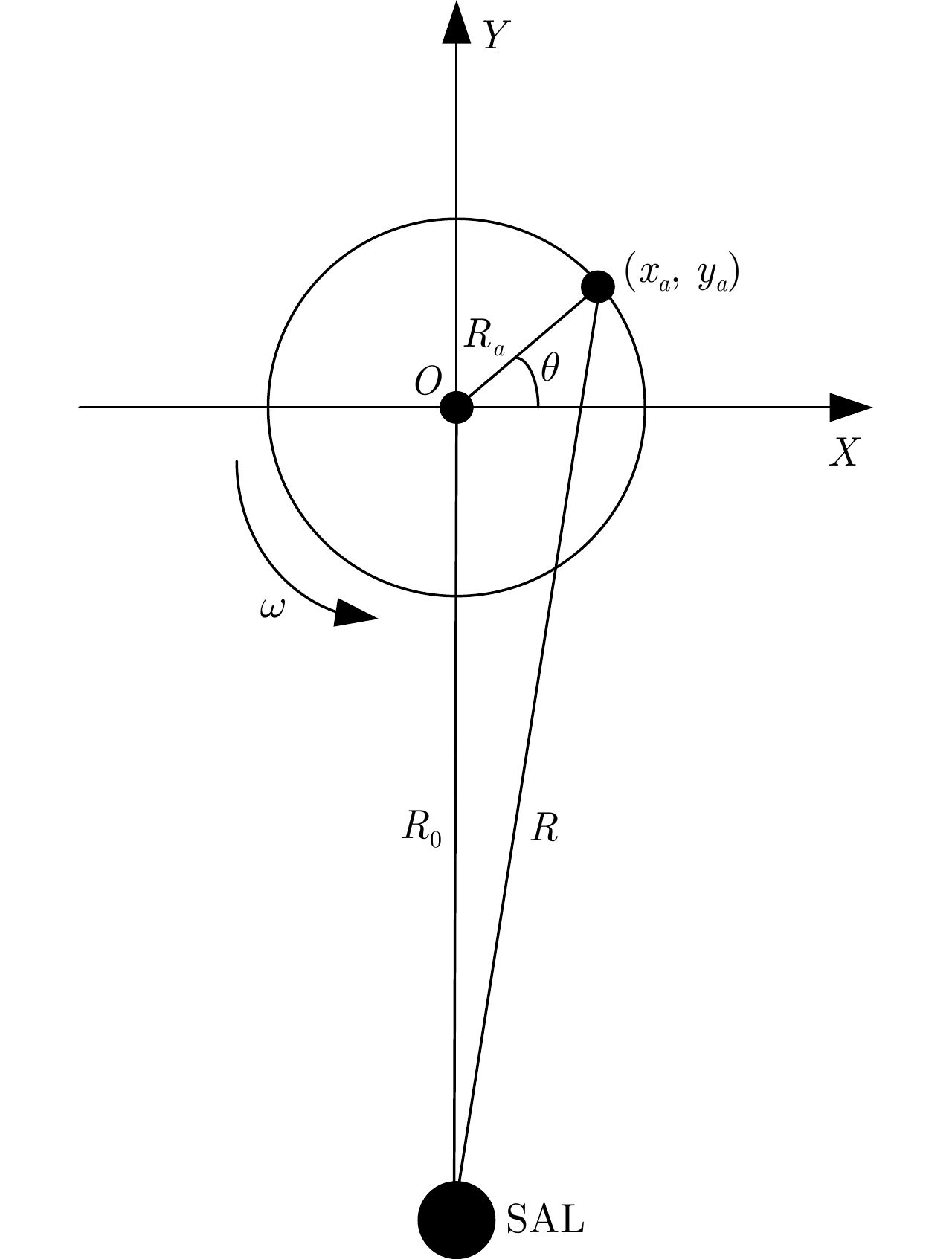
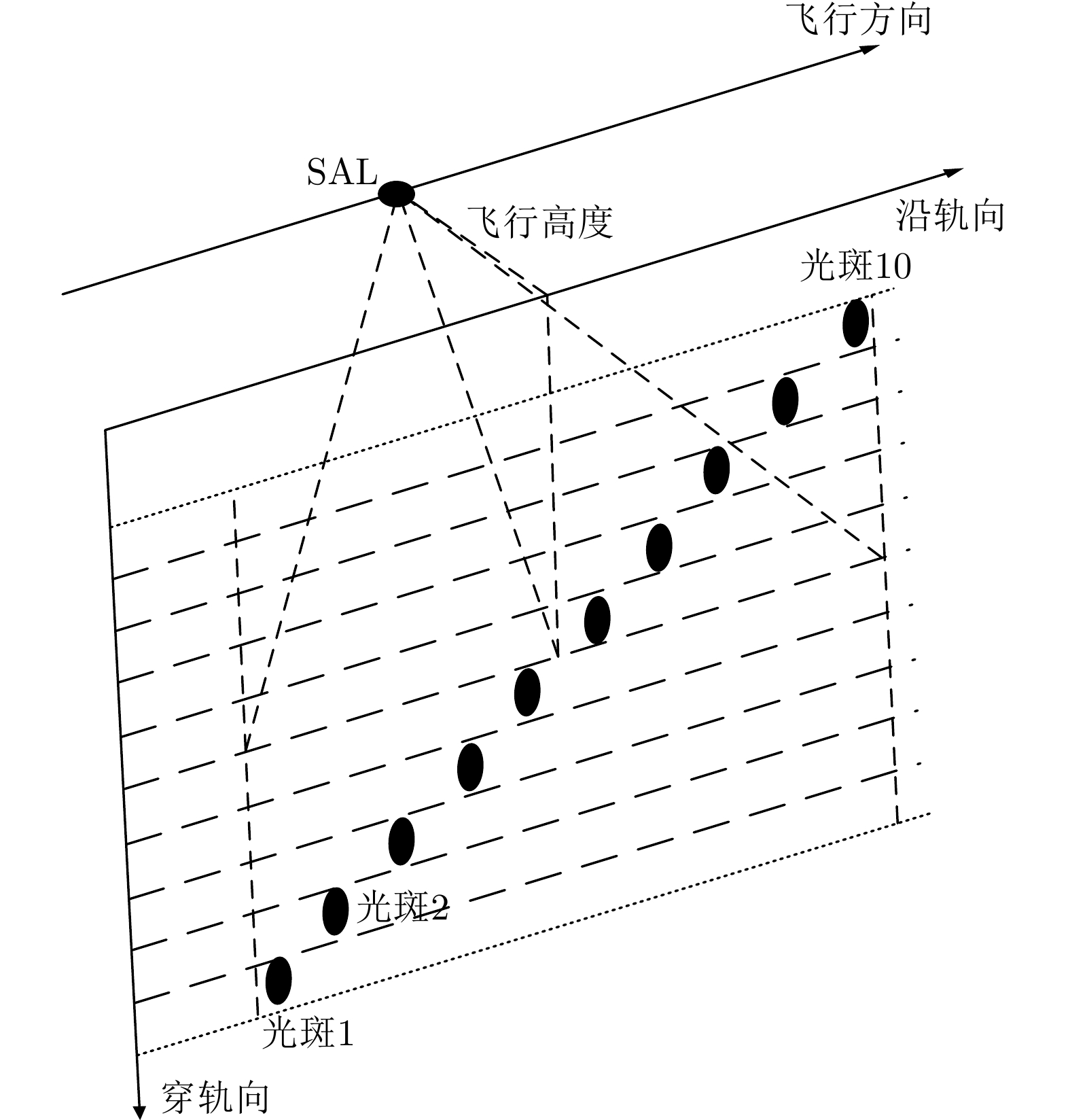
- Figure 1. Geometric diagram of array SAL
- Figure 2. The ISAL imaging model of single spot
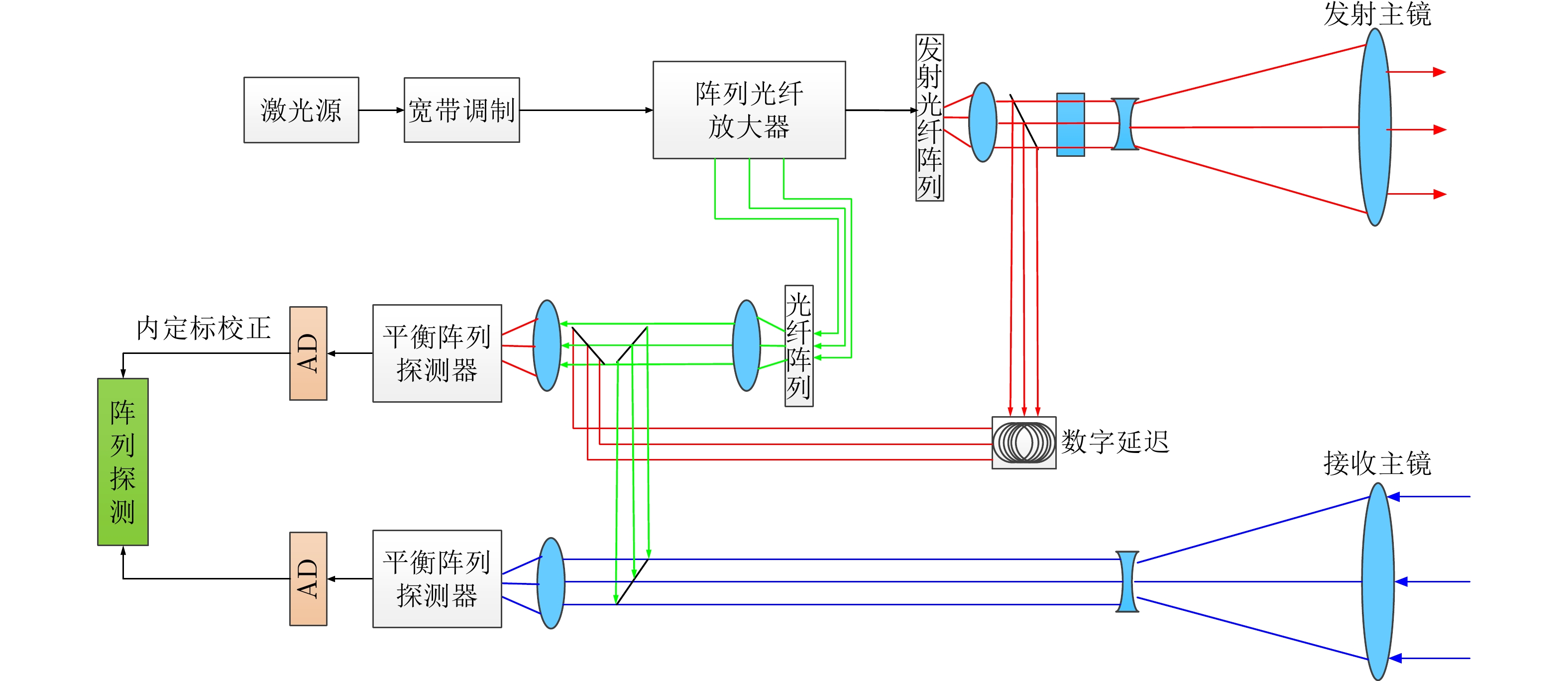
- Figure 3. Schematic diagram of array optical system
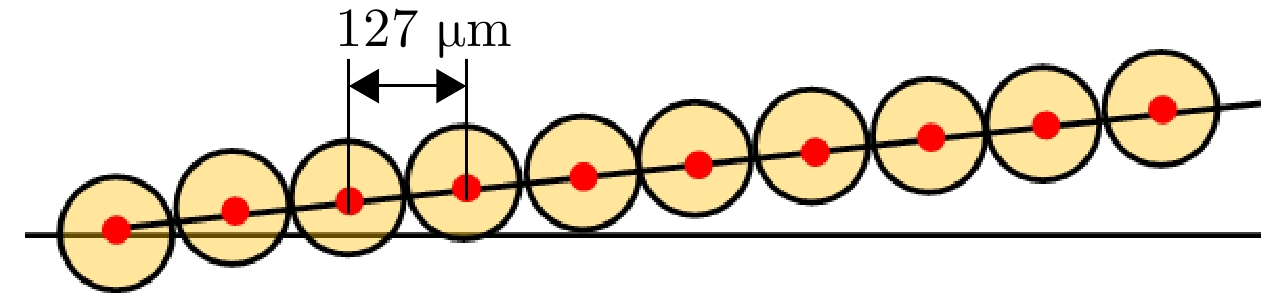
- Figure 4. Configuration of optical fiber array
- Figure 5. Schematic diagram of far field array elliptical laser beam distribution
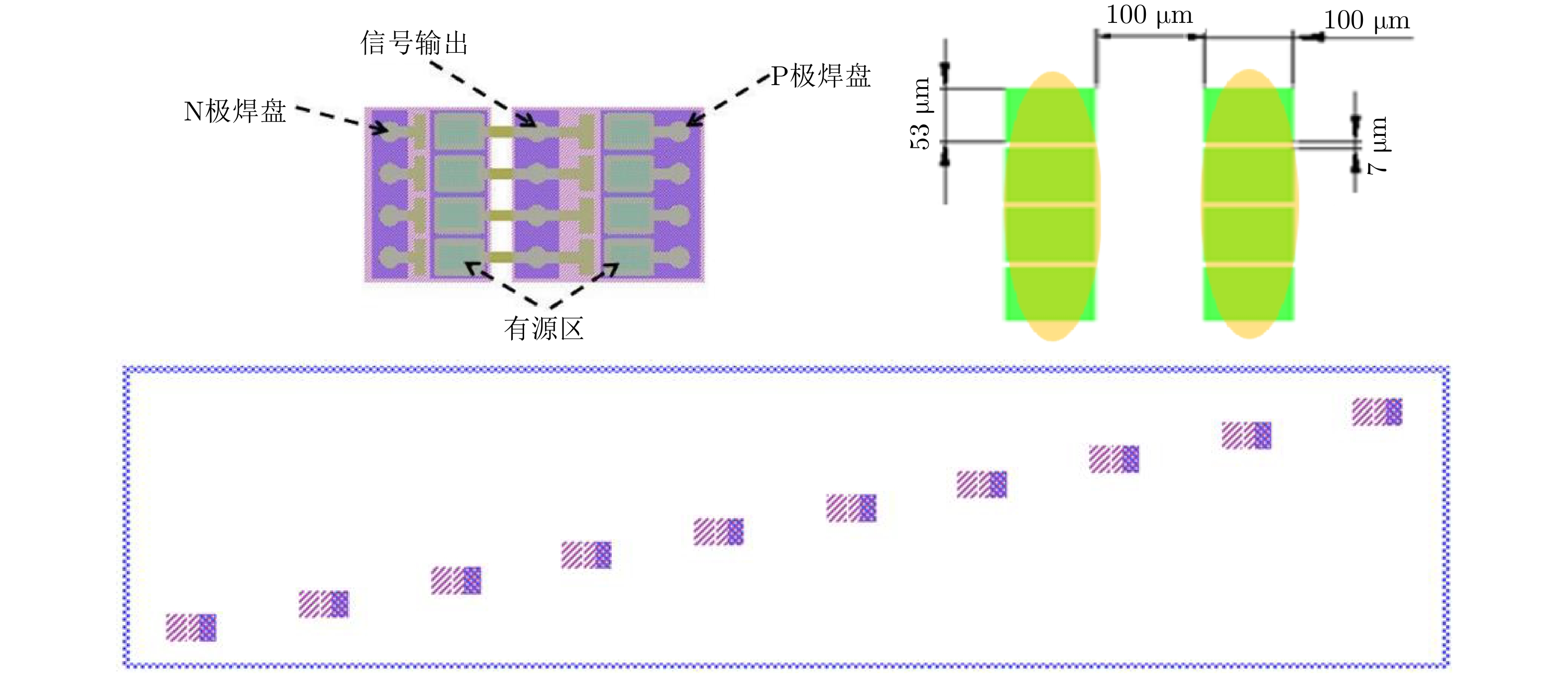
- Figure 6. Ten channels array balanced detection unit (each unit contains four detectors, which receive a laser beam from the far field)
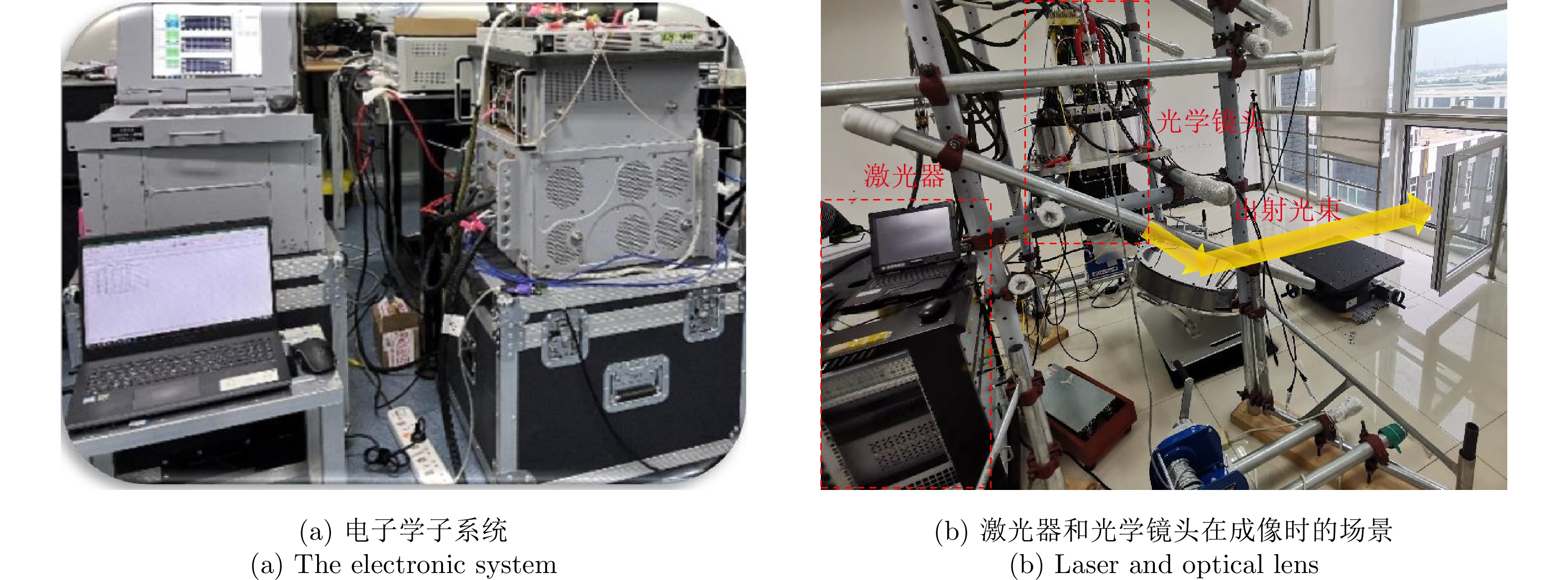
- Figure 7. ISAL prototype in lab
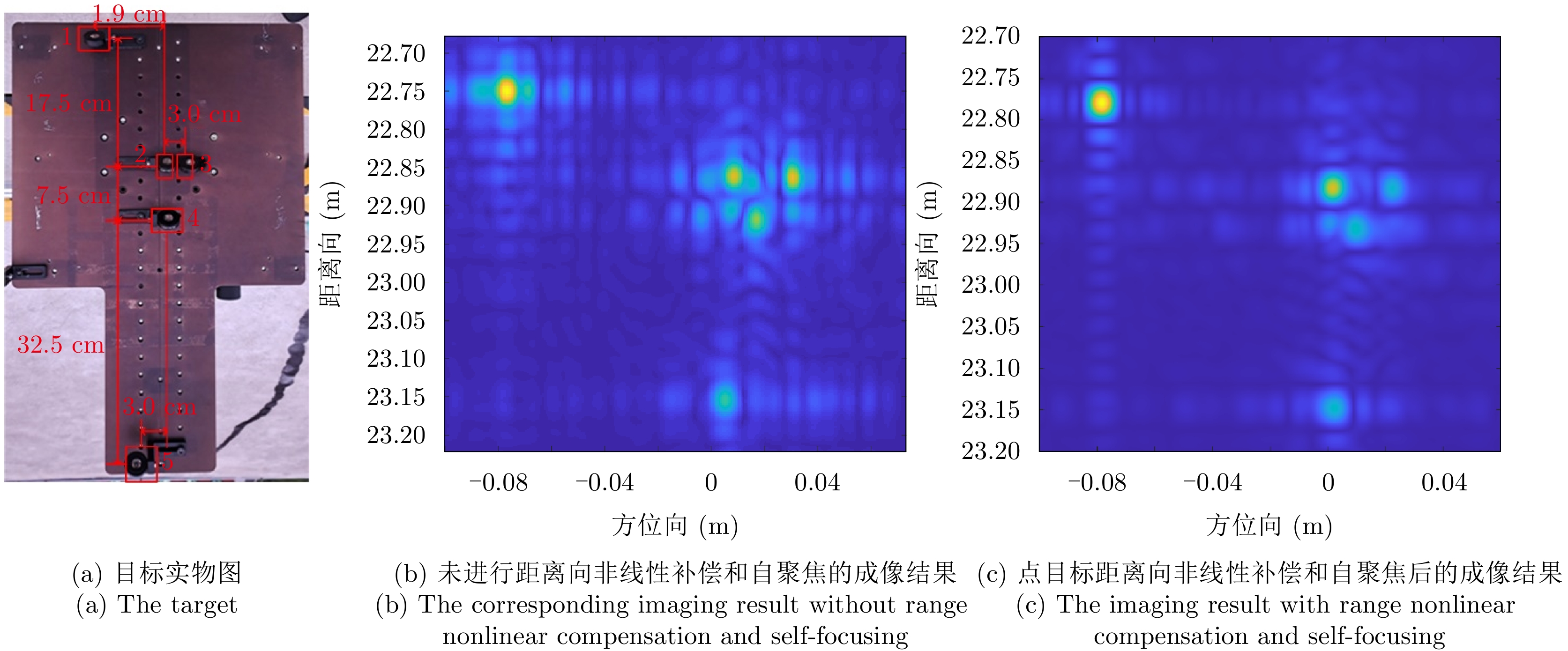
- Figure 8. The imaging scene of point target
- Figure 9. Schematic diagram of ISAL and turntable device
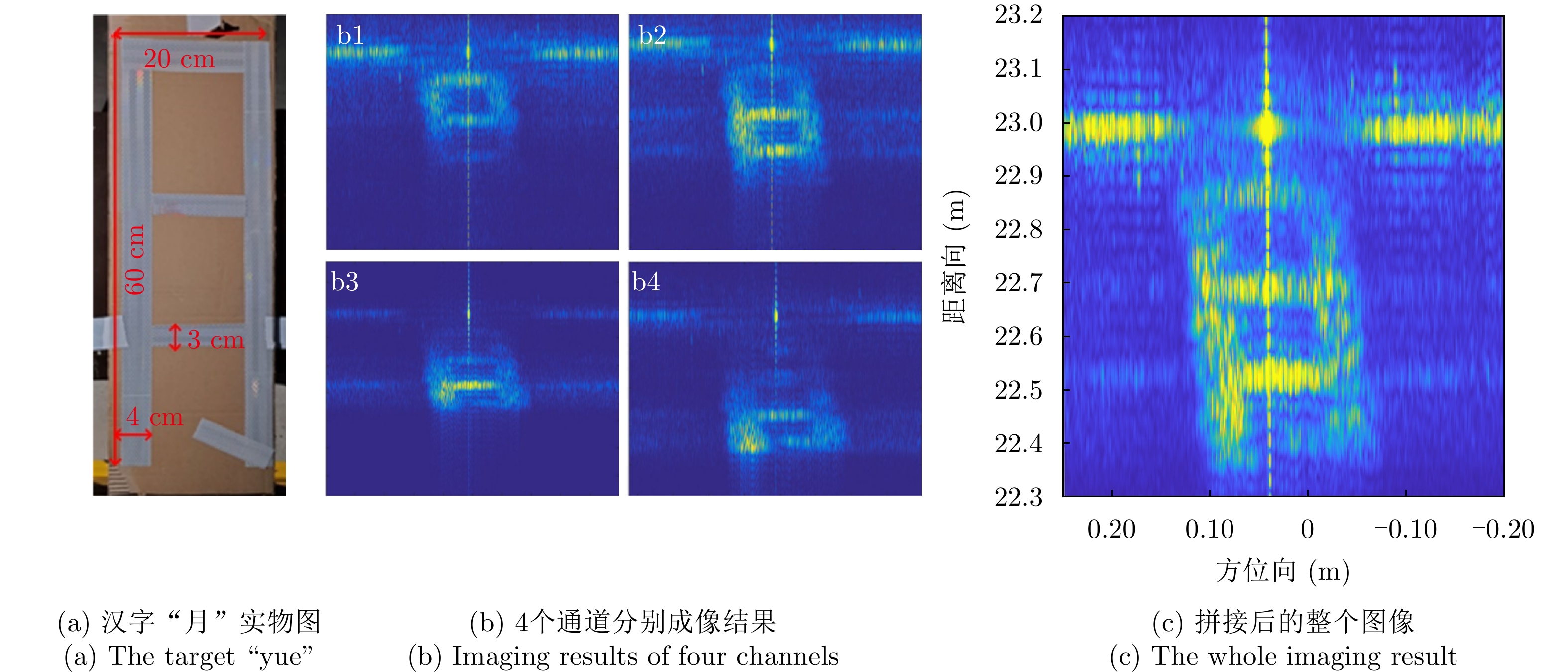
- Figure 10. The imaging scene of “yue”
- Figure 11. The imaging scene of “E”
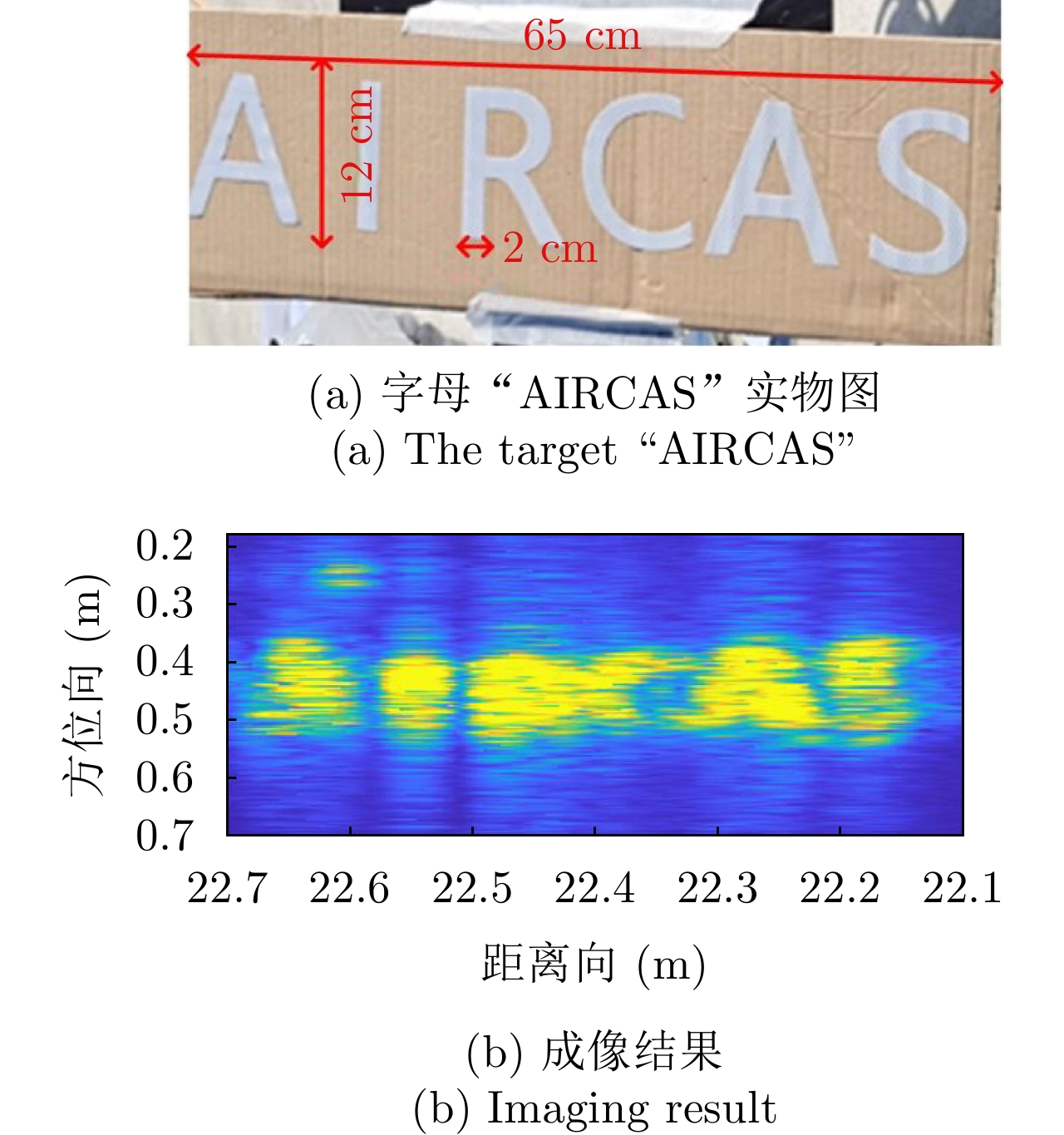
- Figure 12. The imaging scene of “AIRCAS”
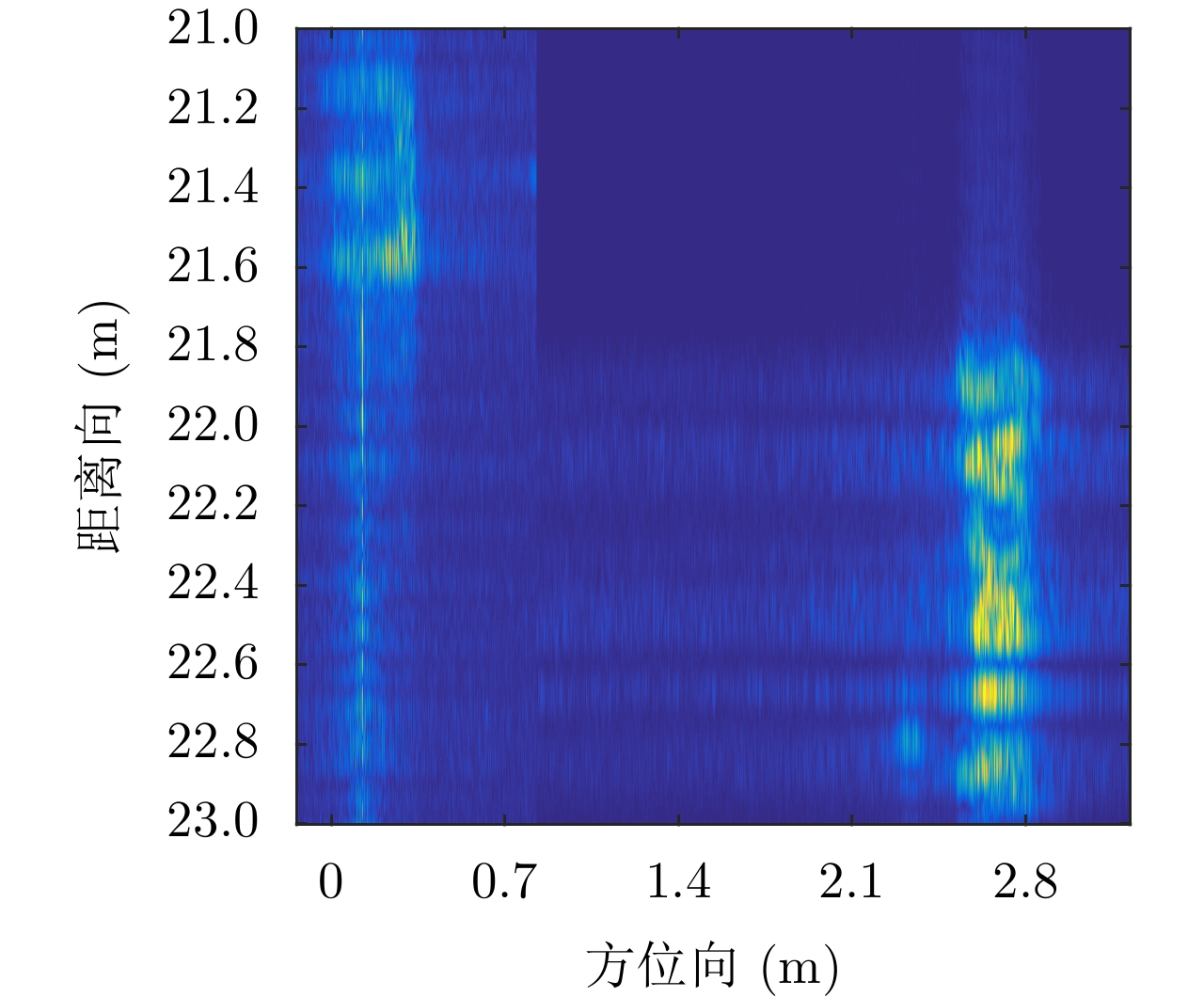
- Figure 13. The imaging result of target “E” and “AIRCAS”


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: