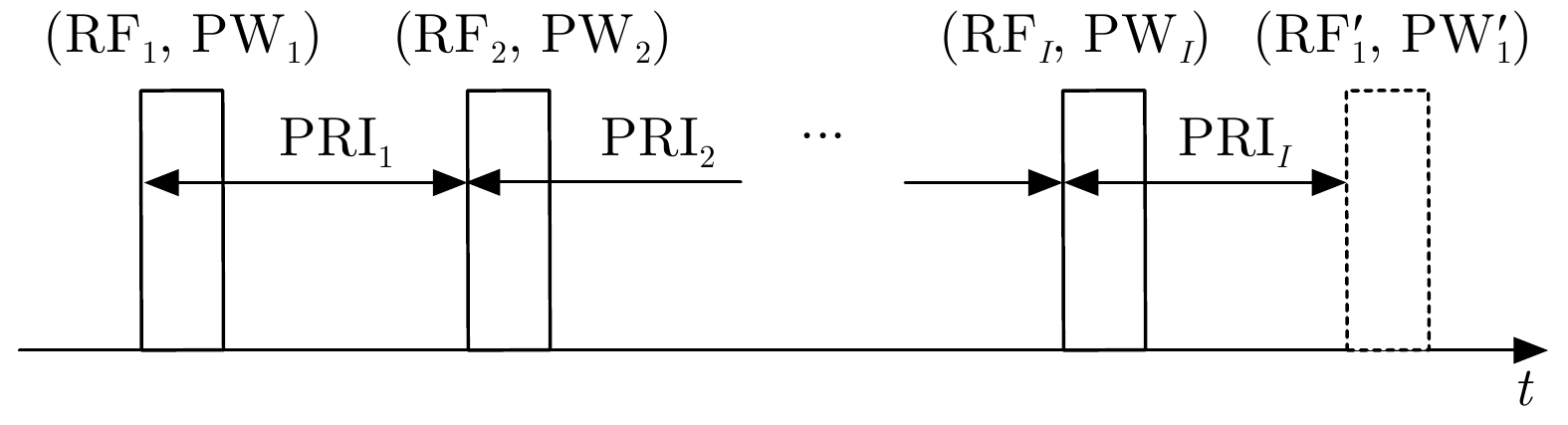
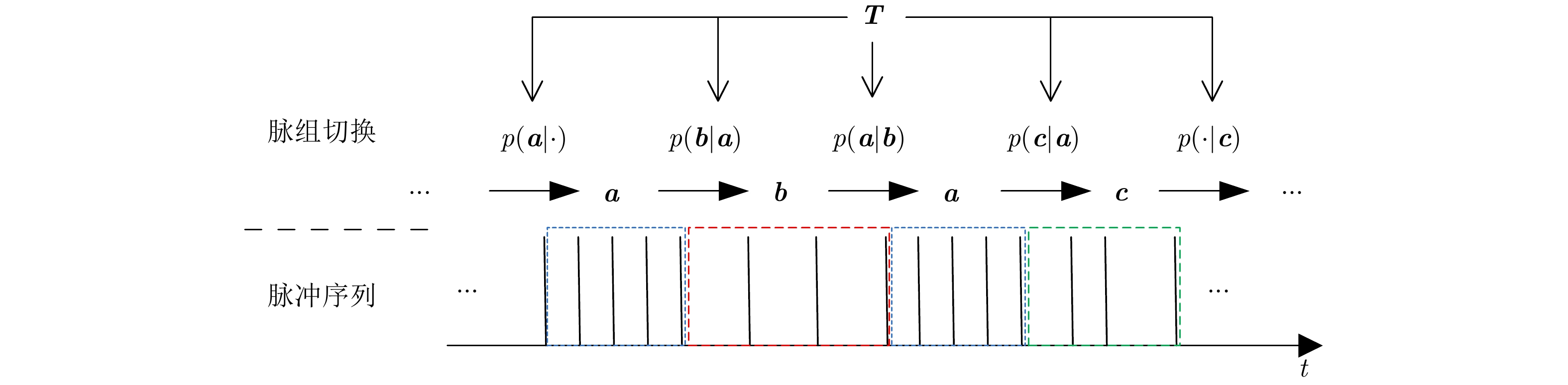
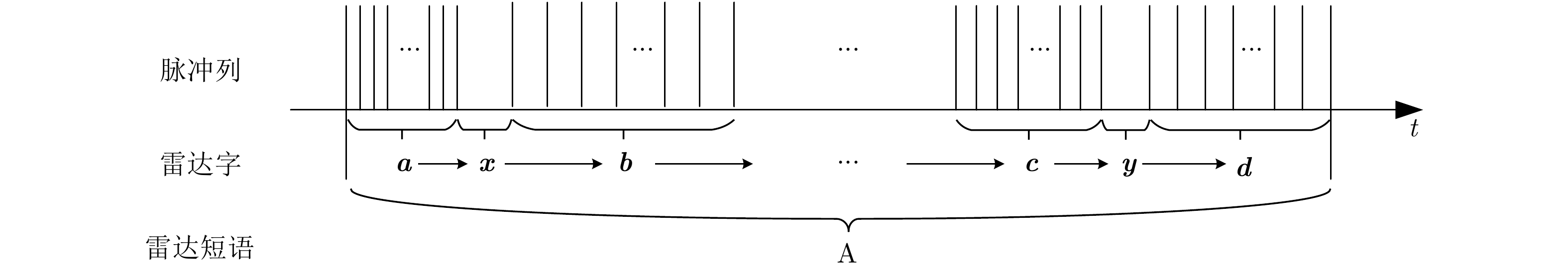
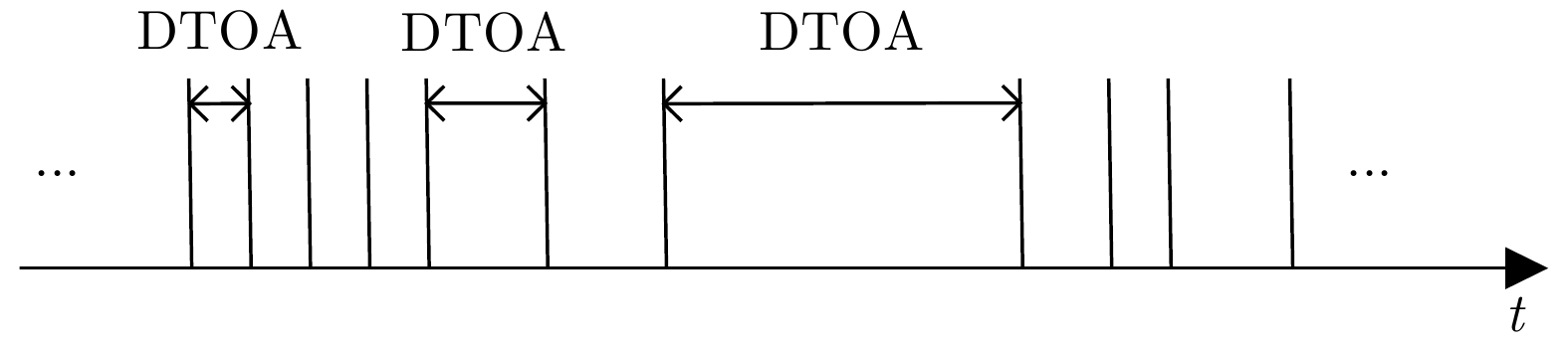
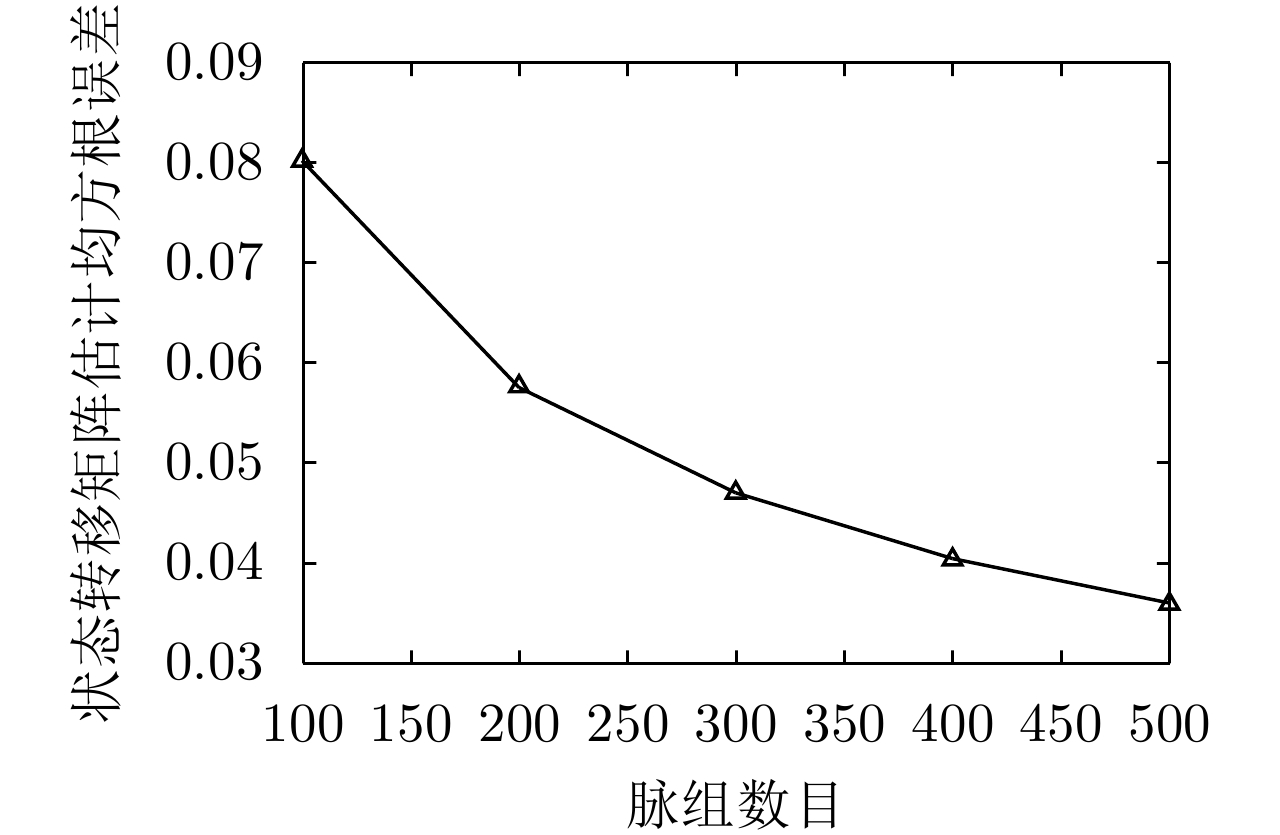
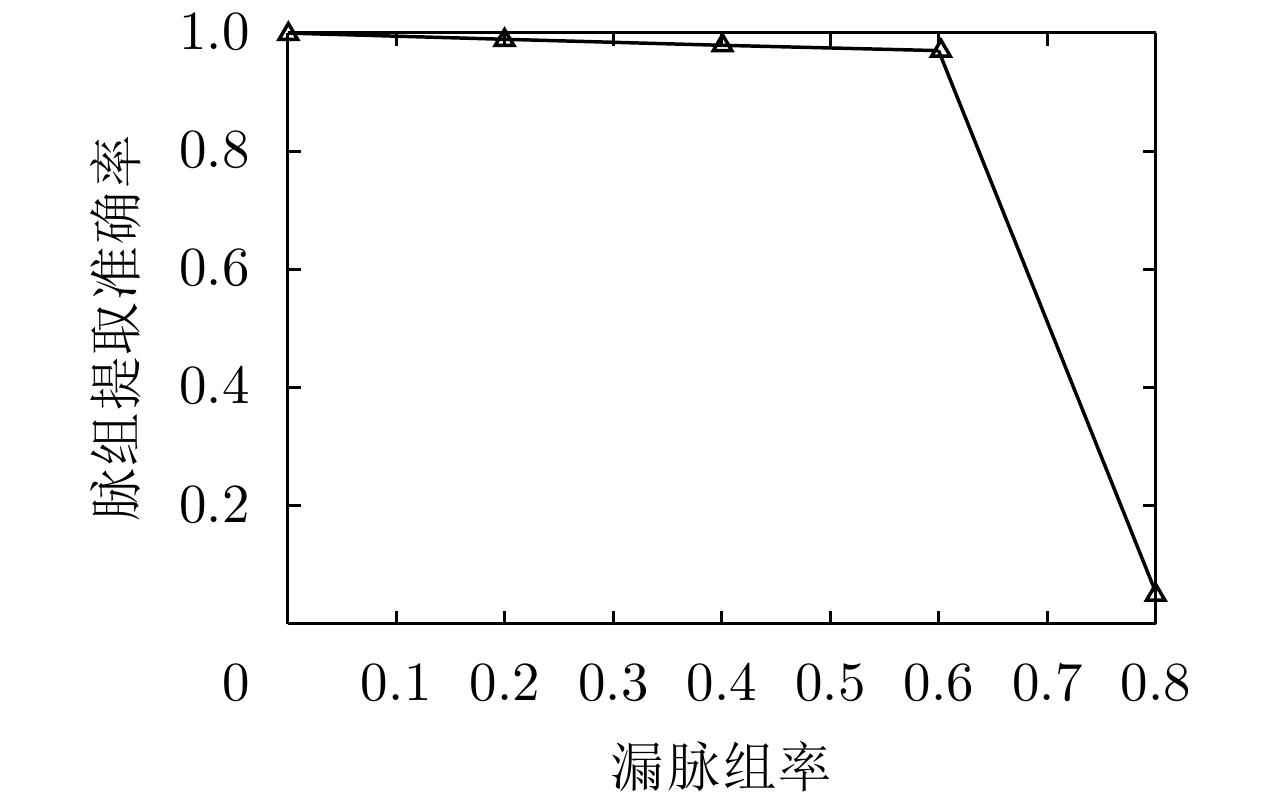
| [1] |
RICHARDS M A, SCHEER J A, and HOLM W A. Principles of Modern Radar: Basic Principles[M]. Raleigh: SciTech Publishing, 2010: 33–36.
|
| [2] |
张光义, 赵玉洁. 相控阵雷达技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2006: 1–6.
ZHANG Guangyi and ZHAO Yujie. Phased Array Radar Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006: 1–6.
|
| [3] |
MELVIN W L and SCHEER J A. Principles of Modern Radar: Radar Applications[M]. Edison: SciTech Publishing, 2014: 8–14.
|
| [4] |
WILEY R G. ELINT: The Interception and Analysis of Radar Signals[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 2006: 1–5.
|
| [5] |
VISNEVSKI N, KRISHNAMURTHY V, WANG A, et al. Syntactic modeling and signal processing of multifunction radars: A stochastic context-free grammar approach[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(5): 1000–1025. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2007.893252 |
| [6] |
VISNEVSKI N A. Syntactic modeling of multi-function radars[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], McMaster University, 2005.
|
| [7] |
LIU Zhangmeng. Recognition of multifunction radars via hierarchically mining and exploiting pulse group patterns[J] . IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4659–4672. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2999163. |
| [8] |
方佳璐. 雷达信号工作模式识别研究[D]. [硕士论文], 浙江大学, 2017.
FANG Jialu. Research of radar signal patter recognition[D]. [Master dissertation], Zhejiang University, 2017.
|
| [9] |
LI Yunjie, ZHU Mengtao, MA Yihao, et al. Work modes recognition and boundary identification of MFR pulse sequences with a hierarchical Seq2seq LSTM[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(9): 1343–1353. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2020.0060 |
| [10] |
欧健. 多功能雷达行为辨识与预测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2017.
OU Jian. Research on behavior recognition and prediction techniques against multi-function radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2017.
|
| [11] |
OU Jian, CHEN Yongguang, ZHAO Feng, et al. Research on extension of hierarchical structure for multi-function radar signals[C]. 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium-Spring, St. Petersburg, Russia, 2017.
|
| [12] |
林令民. 雷达语义结构分析算法设计与应用[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2017.
LIN Lingmin. Design and application of radar semantic structure analysis algorithm[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017.
|
| [13] |
GRÜNWALD P D. The Minimum Description Length Principle[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2007: 29–35.
|
| [14] |
SAYOOD K, 贾洪峰, 译. 数据压缩导论[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2014: 5–8, 259–279.
SAYOOD K, JIA Hongfeng, translation. Introduction on Data Compression[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Posts & Telecom Press, 2014: 5–8, 259–279.
|
| [15] |
傅祖芸. 信息论—基础理论与应用[M]. 4版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015: 1–8.
FU Zuyun. Information Theory—Principles and Application[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2015: 1–8.
|
| [16] |
ROSVALL M and BERGSTROM C T. Maps of random walks on complex networks reveal community structure[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2008, 105(4): 1118–1123.
|
| [17] |
ROSVALL M and BERGSTROM C T. Multilevel compression of random walks on networks reveals hierarchical organization in large integrated systems[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(4): e18209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018209 |
| [18] |
TAN P N, STEINBACH M, KUMAR V, 范明, 范宏建, 译. 数据挖掘导论[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2011: 27–38.
TAN P N, STEINBACH M, KUMAR V, FAN Ming and FAN Hongjian, translation. Introduction to Data Mining[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Posts & Telecom Press, 2011: 27–38.
|
| [19] |
LIU Zhangmeng, KANG Shiqian, and CHAI Xianming. Automatic pulse repetition pattern reconstruction of conventional radars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15(5): 500–509. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12053 |
| [20] |
JAEGER H. Observable operator models for discrete stochastic time series[J]. Neural Computation, 2000, 12(6): 1371–1398. doi: 10.1162/089976600300015411 |
| [21] |
JAEGER H, HAYKIN S, PRINCIPE J, SEJNOWSKI T, et al.. Learning Observable Operator Models Via the ES Algorithm[M]. New Directions in Statistical Signal Processing: From Systems to Brains. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2005.
|
| [22] |
BENGIO Y. Markovian models for sequential data[J]. Neural Computing Surveys, 1999, 2: 129–162.
|
| [23] |
RABINER L R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1989, 77(2): 257–286. doi: 10.1109/5.18626 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

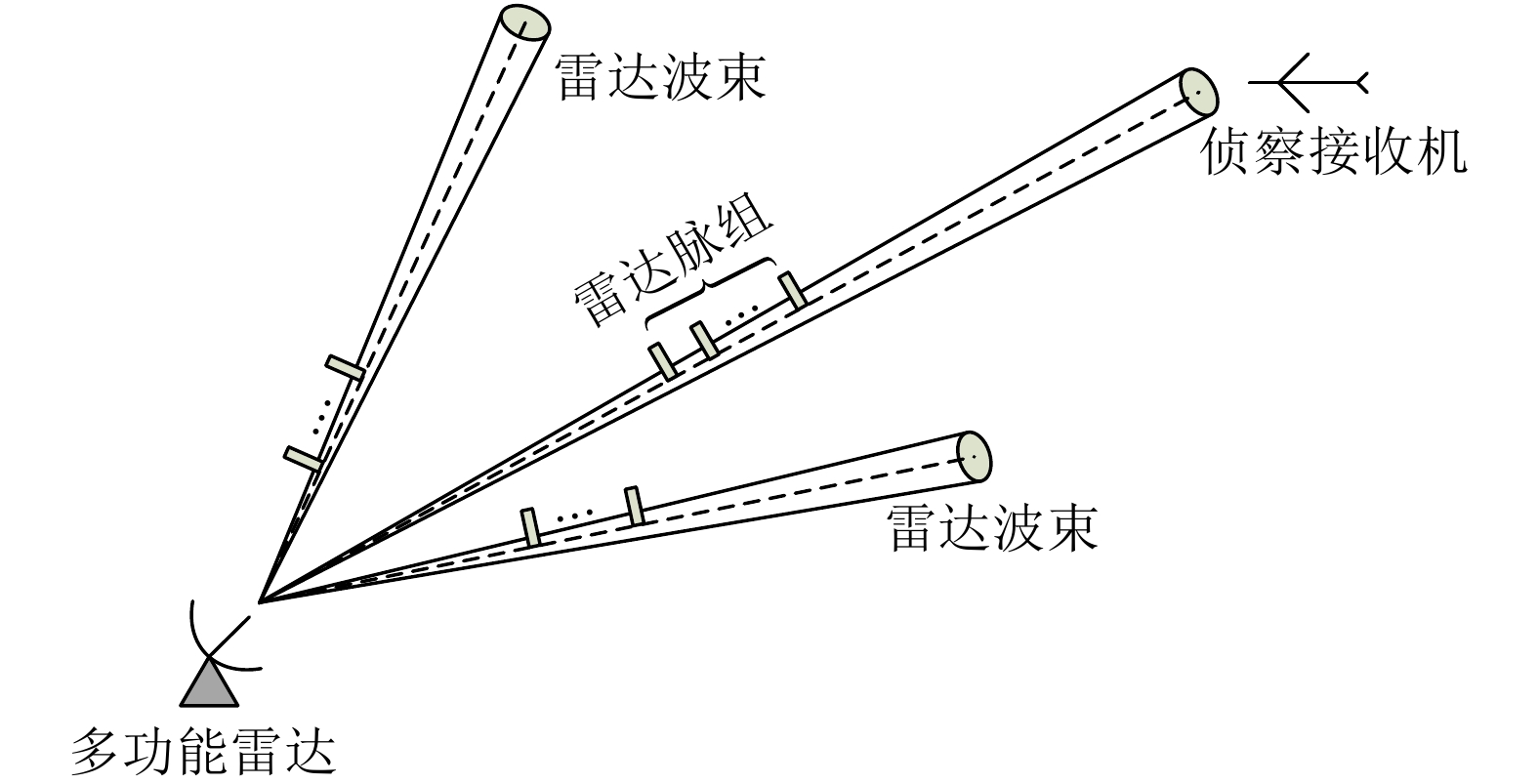



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: