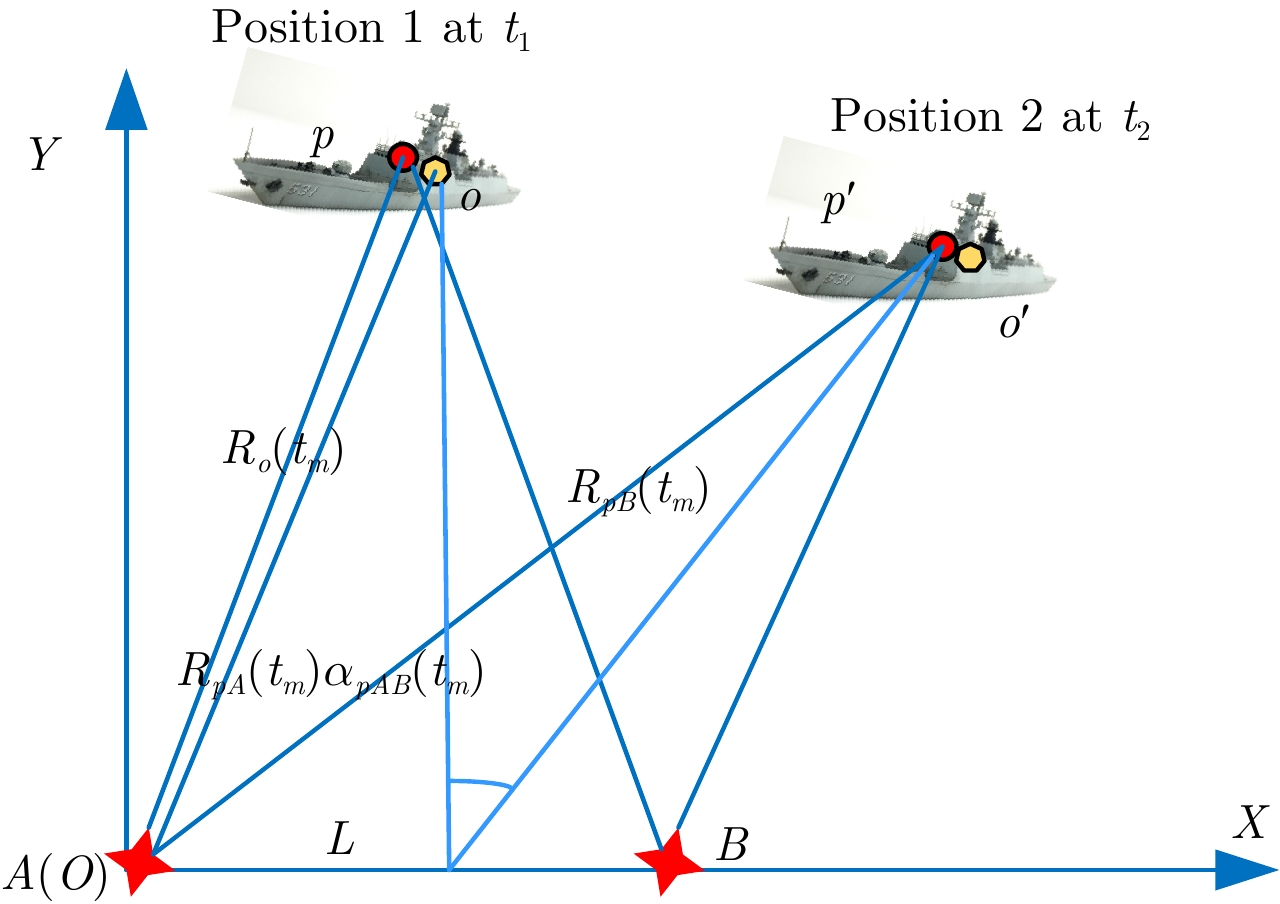
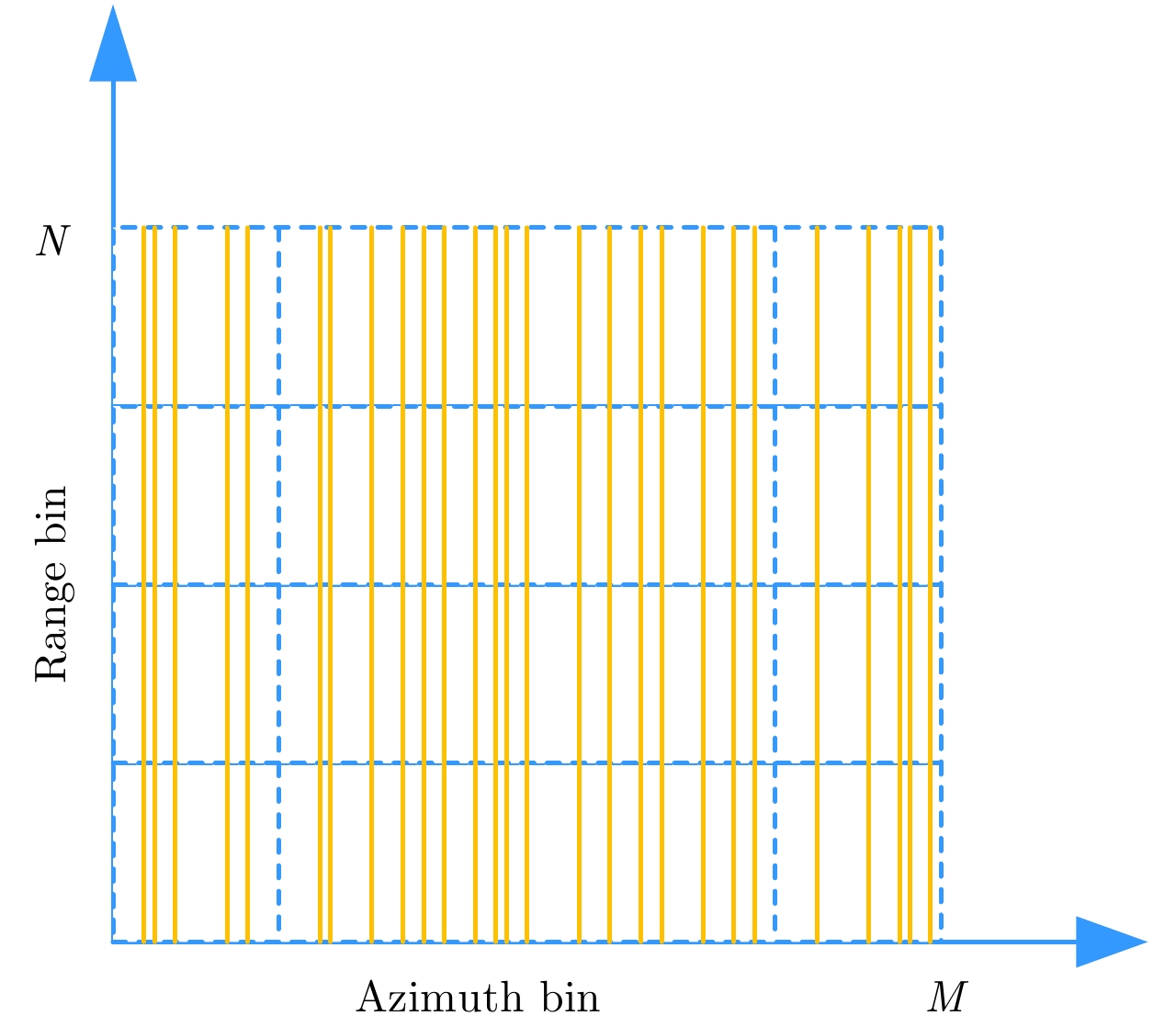
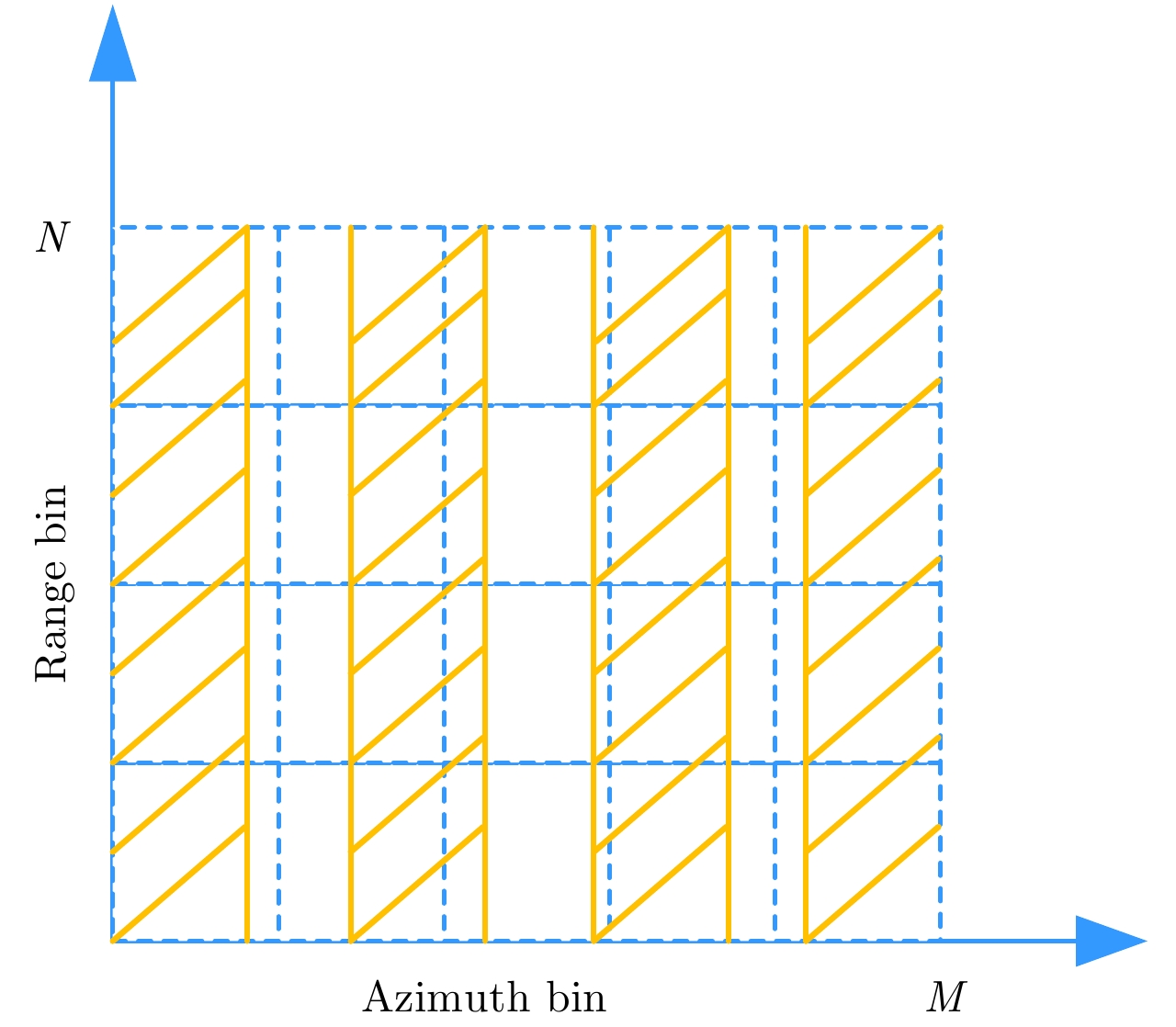
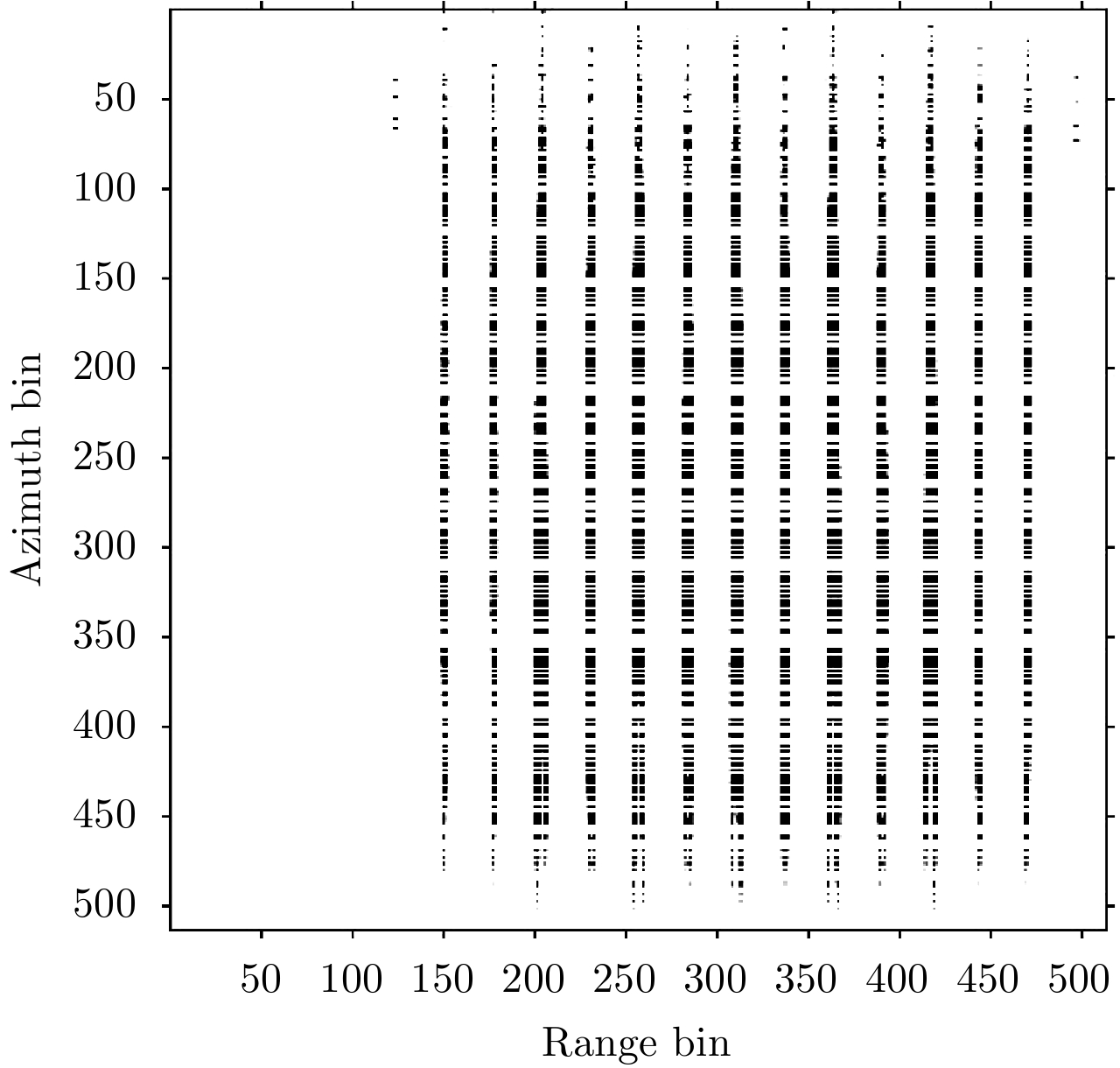
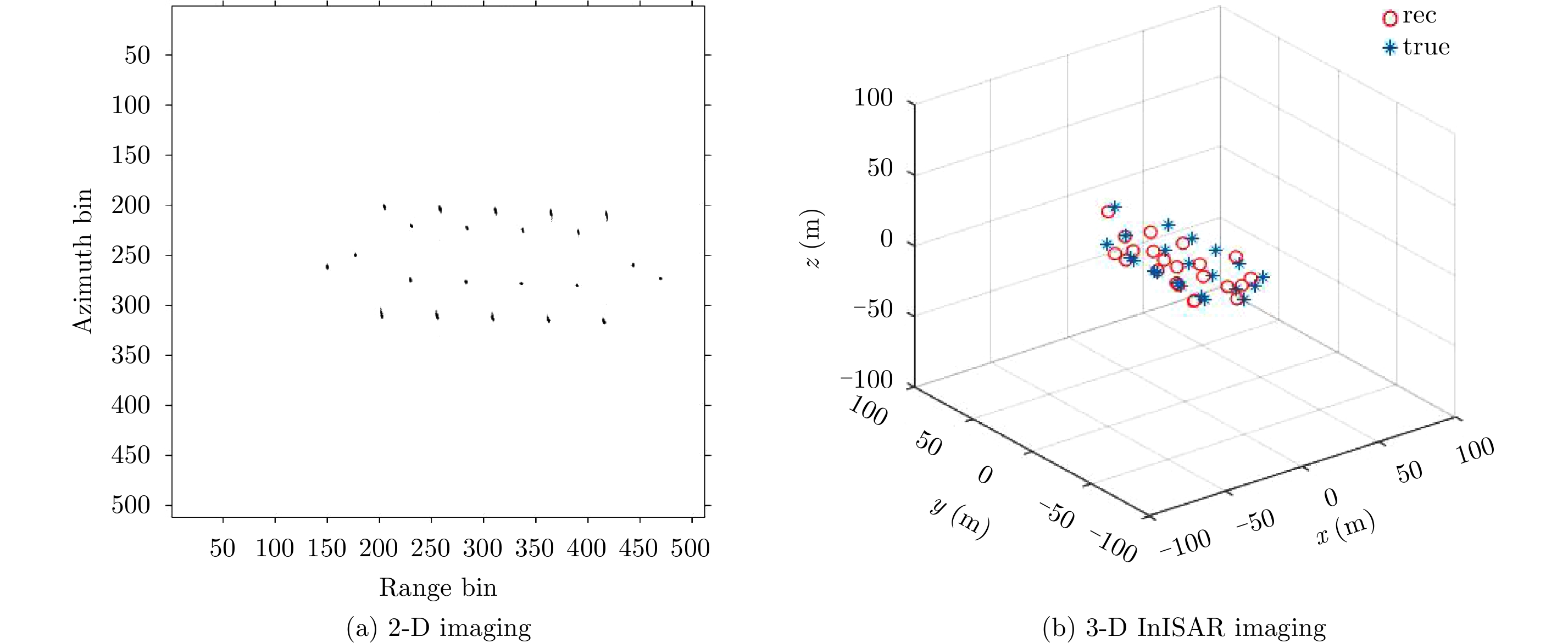
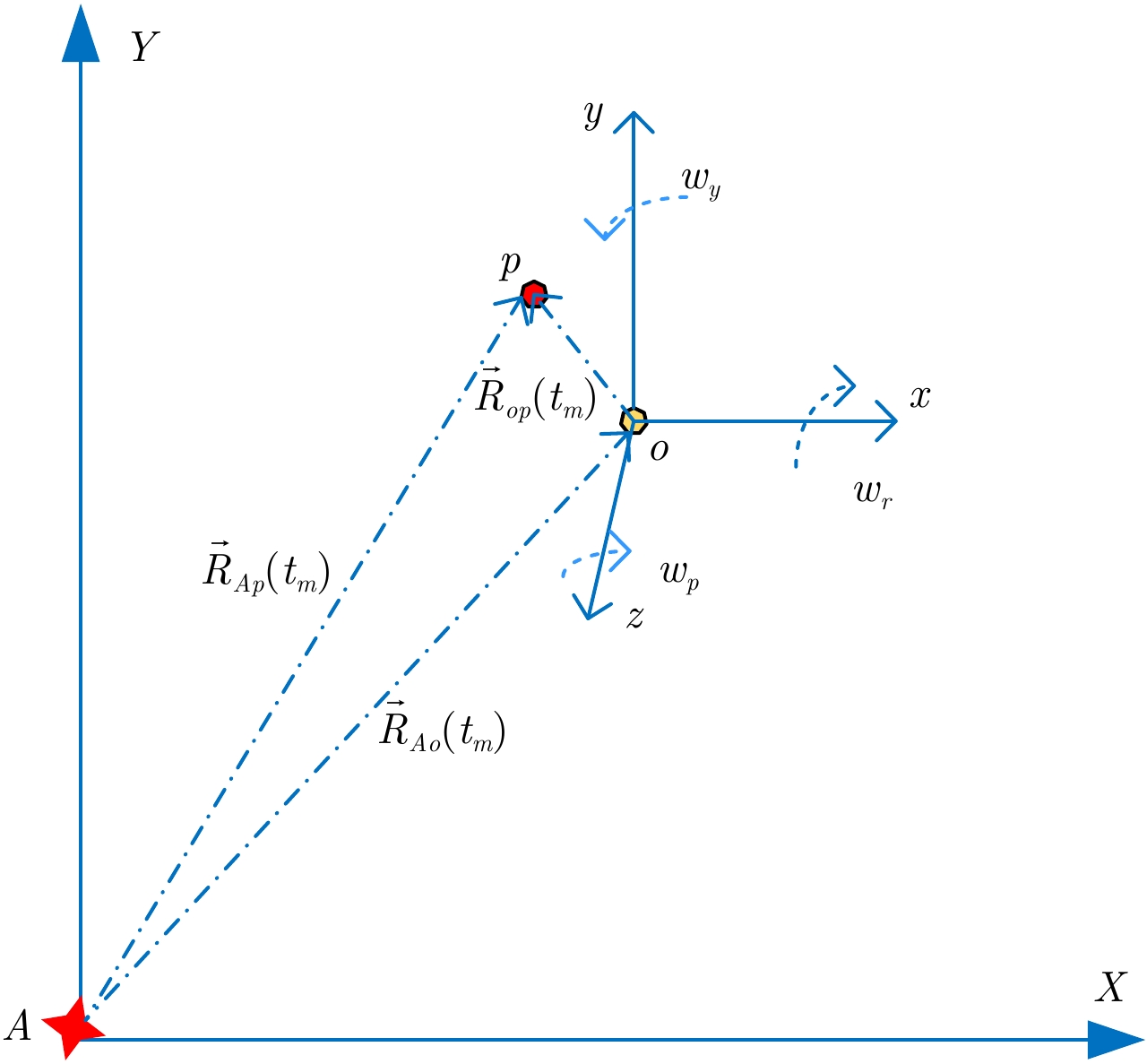
| [1] |
Wang G Y, Xia X G, and Chen V C. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets using three receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(3): 436–447. DOI: 10.1109/83.908519 |
| [2] |
Ma C Z, Yeo T S, Zhang Q, et al. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging based on antenna array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(2): 504–515. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.909946 |
| [3] |
Liu L, Zhou F, Bai X R, et al. Joint cross-range scaling and 3D geometry reconstruction of ISAR targets based on factorization method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1740–1750. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2526905 |
| [4] |
Wang Y and Li X L. Three-dimensional interferometric ISAR imaging for the ship target under the bi-static configuration[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(4): 1505–1520. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2513774 |
| [5] |
Cao X H, Su F L, Sun H D, et al.. Three-dimensional In-ISAR imaging via the emulated Bistatic radar[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Harbin, China, 2007: 2826–2830.
|
| [6] |
Ma C Z, Yeo T S, Tan H S, et al. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging using a two-dimensional sparse antenna array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(3): 378–382. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.916071 |
| [7] |
Ng B, Tran H T, and An P. Total rotational velocity estimation using 3D interferometrie ISAR with squint geometry[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016: 1–6.
|
| [8] |
Tran H T, Giusti E, Martorella M, et al.. Estimation of the total rotational velocity of a non-cooperative target using a 3D InISAR system[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, VA, USA, 2015: 937–941.
|
| [9] |
Martorella M, Stagliano D, Salvetti F, et al. 3D interferometric ISAR imaging of noncooperative targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(4): 3102–3114. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130210 |
| [10] |
Lv Q, Su T, Zheng J B, et al. Three-dimensional interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of maneuvering target based on the joint cross modified Wigner-Ville distribution[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(1): 1–17.
|
| [11] |
Zhang L, Qiao Z J, Xing M D, et al. High-resolution ISAR imaging by exploiting sparse apertures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(2): 997–1008. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2011.2173130 |
| [12] |
Zhong Li-hua, Hu Dong-hui, Ding Chi-biao, et al. ISAR sparse aperture imaging algorithm for large size target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(3): 292–300. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20033 |
| [13] |
Pang L N, Zhang S S, Liu C, et al.. CS-based high-resolution ISAR imaging with adaptive sparse basis[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2014: 362–365.
|
| [14] |
Bacci A, Staglianó D, Giusti E, et al.. 3D interferometric ISAR via compressive sensing[C]. Proceedings of 2014 11th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2014: 233–236.
|
| [15] |
Liu Y B, Li N, Wang R, et al. Achieving high-quality three-dimensional InISAR imageries of maneuvering target via super-resolution ISAR imaging by exploiting sparseness[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(4): 828–832. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2279402 |
| [16] |
Chen Q Q, Xu G, Zhang L, et al. Three-dimensional interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging with limited pulses by exploiting joint sparsity[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(6): 692–701.
|
| [17] |
Xu G, Xing M D, Xia X G, et al. 3D geometry and motion estimations of maneuvering targets for interferometric ISAR with sparse aperture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(5): 2005–2020. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2535362 |
| [18] |
Qiu W, Martorella M, Zhou J X, et al. Three-dimensional inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging based on compressive sensing[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2014, 9(4): 411–420.
|
| [19] |
Zhu D Y, Wang L, Yu Y S, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 204–208. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562 |
| [20] |
Zhu D Y, Li Y, Yu X, et al.. Compressed ISAR autofocusing: Experimental results[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012: 425–430.
|
| [21] |
Wang J, Liu X, and Zhou Z. Minimum-entropy phase adjustment for ISAR[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2004, 151(4): 203–209. DOI: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20040692 |
| [22] |
Wu W Z, Hu P J, Xu S Y, et al. Image registration for InISAR based on joint translational motion compensation[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2017, 11(10): 1597–1603.
|
| [23] |
Zhu F, Zhang Q, Yan J B, et al.. Compressed sensing in ISAR imaging with sparse sub-aperture[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011, 2: 1463–1466.
|
| [24] |
Stanković L and Daković M. On a gradient-based algorithm for sparse signal reconstruction in the signal/measurements domain[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016, 2016: 6212674.
|
| [25] |
Wang Y. Radar imaging of non-uniformly rotating targets via a novel approach for multi-component AM-FM signal parameter estimation[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(3): 6905–6923. DOI: 10.3390/s150306905 |
| [26] |
Fornaro G, Franceschetti G, and Lanari R. Interferometric SAR phase unwrapping using Green’s formulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(3): 720–727. DOI: 10.1109/36.499751 |
| [27] |
Li Fang-fang, Zhan Yi, Hu Dong-hui, et al. A fast method for InSAR phase unwrapping based on quality guide[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 196–202. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20023 |
| [28] |
Li N, Wang L, and Zhu D Y. Optimal ISAR imaging time selection of ship targets using real data[C]. Proceedings of IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 1–4.
|
| [29] |
Wang Y and Jiang Y C. ISAR imaging of a ship target using product high-order matched-phase transform[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(4): 658–661. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2013876 |
| [30] |
Wang Y and Jiang Y C. New approach for ISAR imaging of ship target with 3D rotation[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2010, 21(4): 301–318. DOI: 10.1007/s11045-010-0111-6 |
| [31] |
Li Y N, Fu Y W, Li X, et al.. An ISAR imaging method for multiple moving targets based on fractional Fourier transformation[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, CA, USA, 2009: 1–6.
|
| [32] |
Yamamoto K, Iwamoto M, and Kirimoto T. A new algorithm to calculate the reference image of ship targets for ATR using ISAR[C]. Proceedings of MTS/IEEE Conference and Exhibition OCEANS 2001, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2001, 4: 2601–2607.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

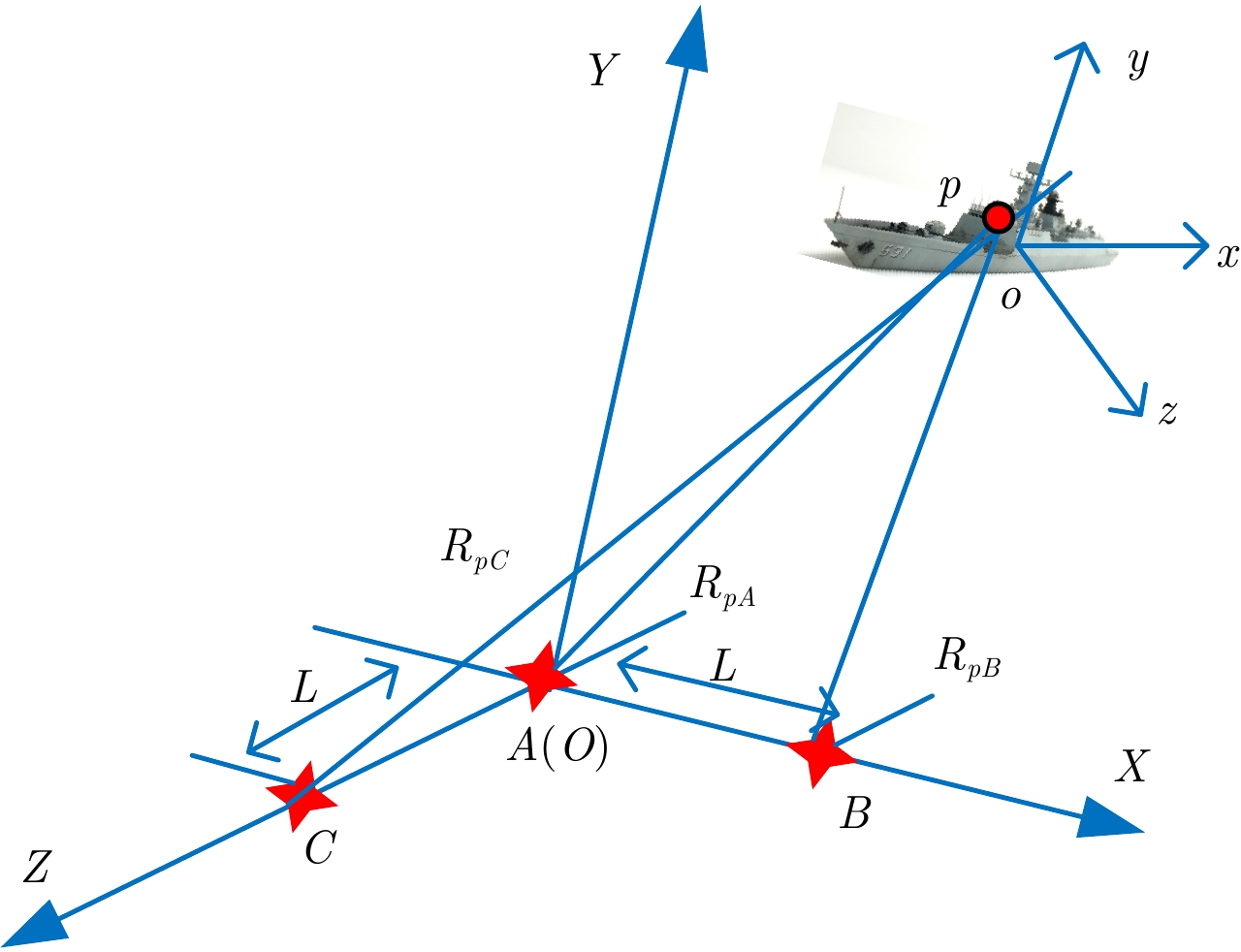



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: