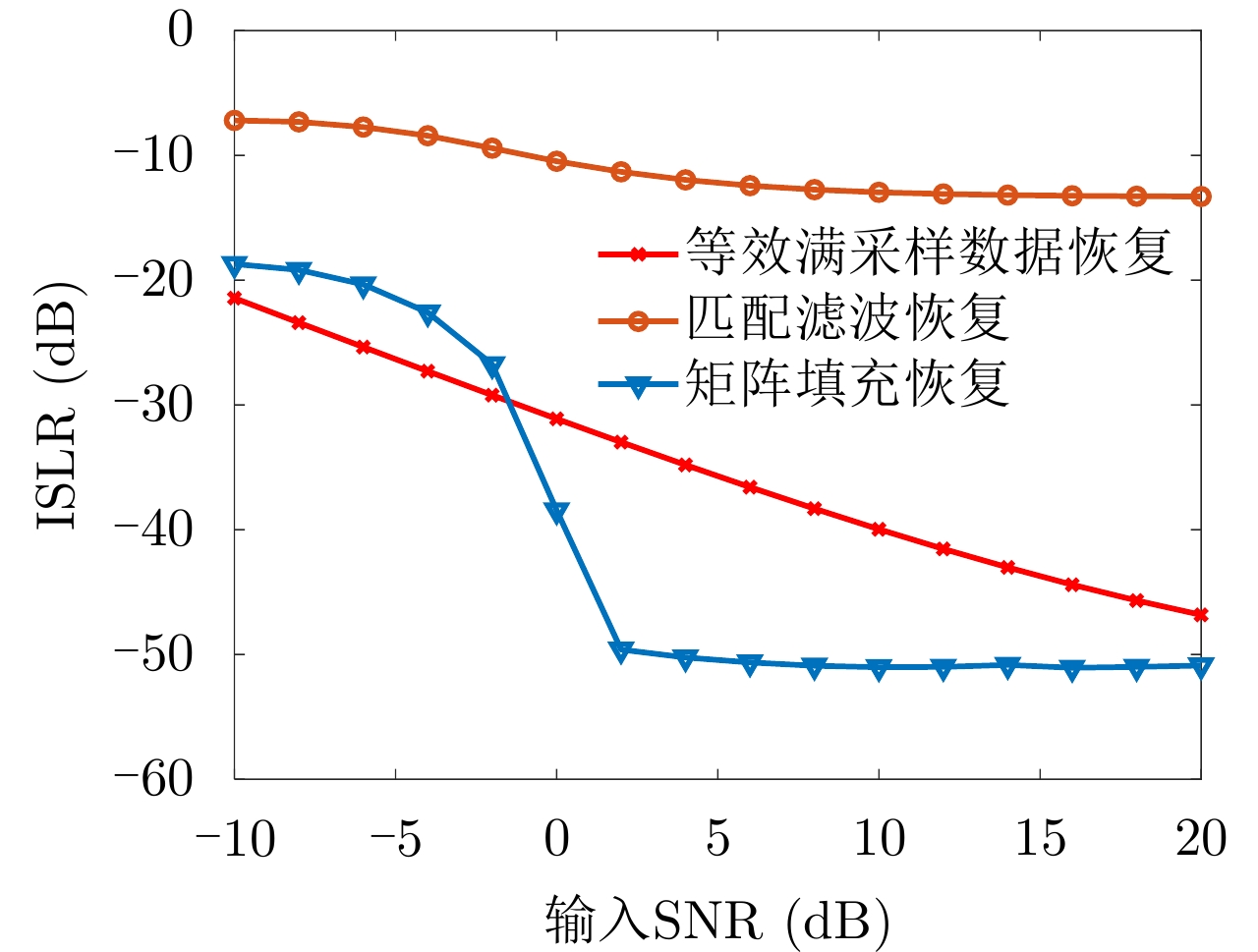
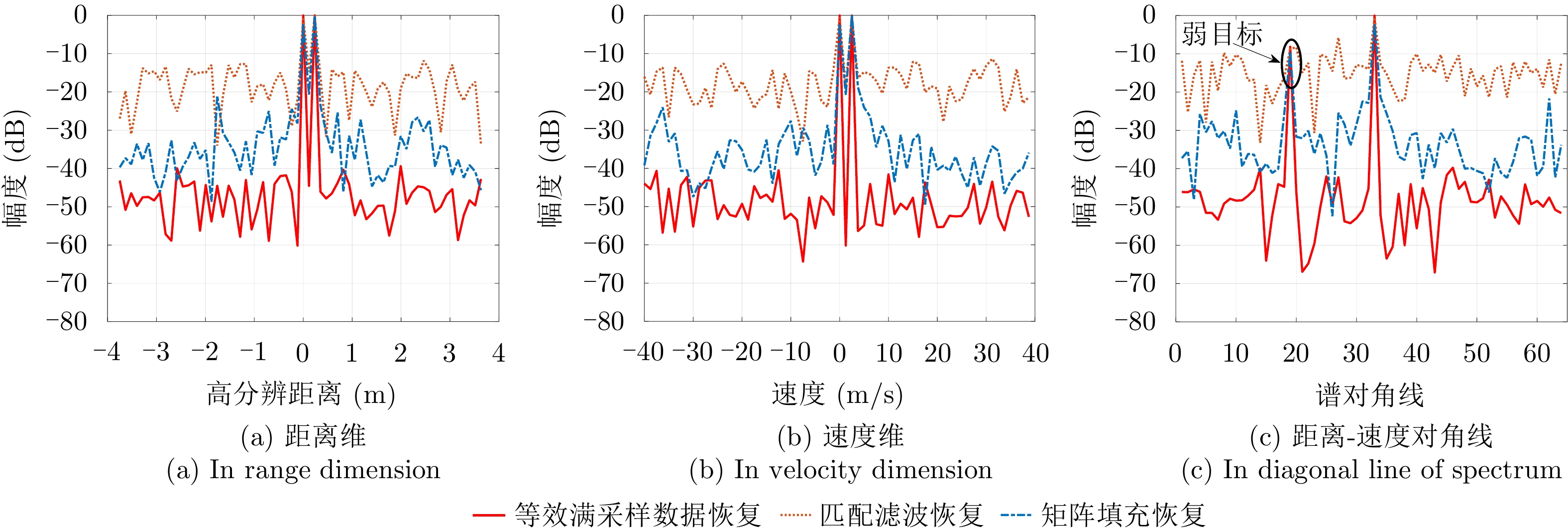
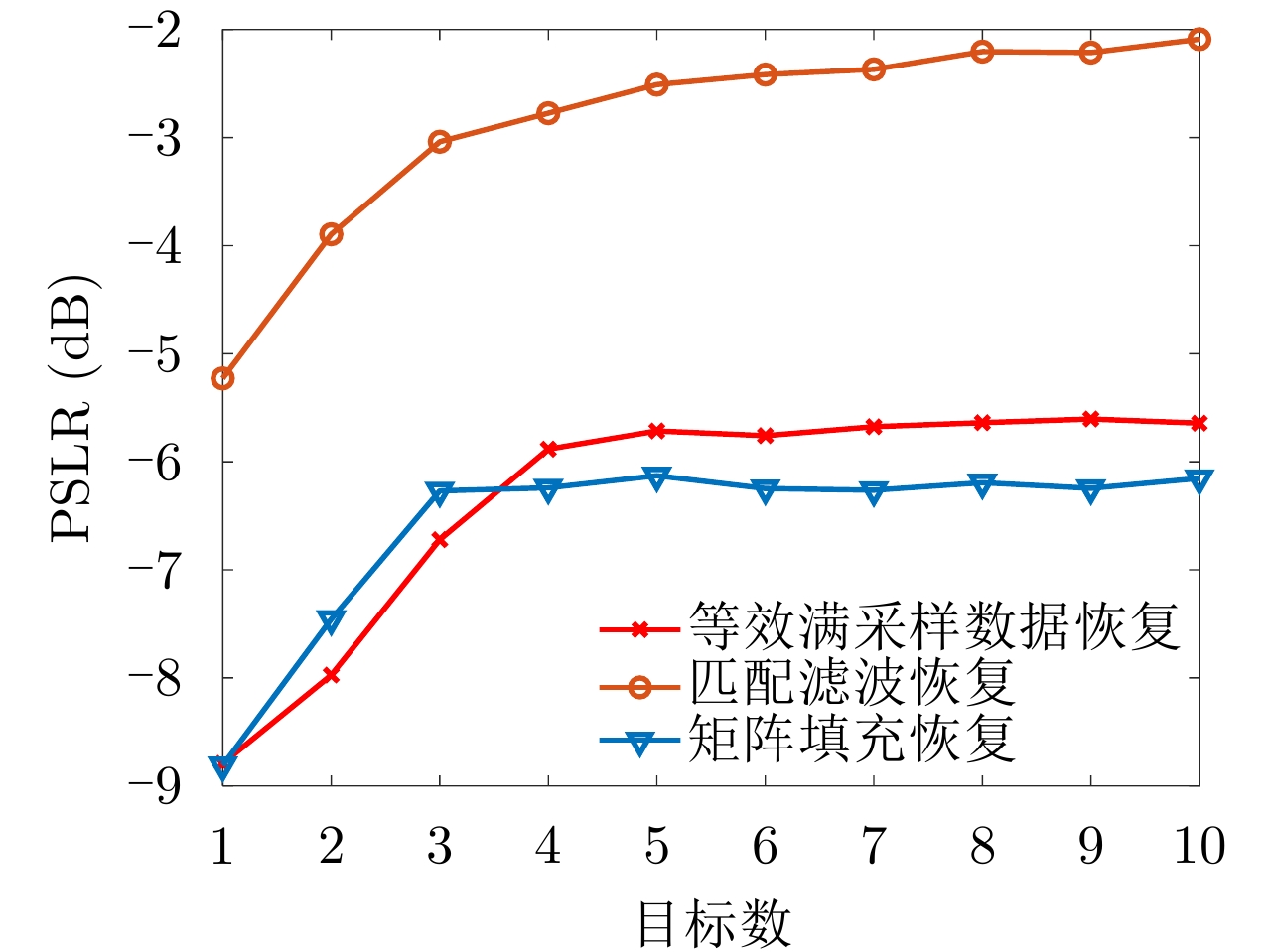
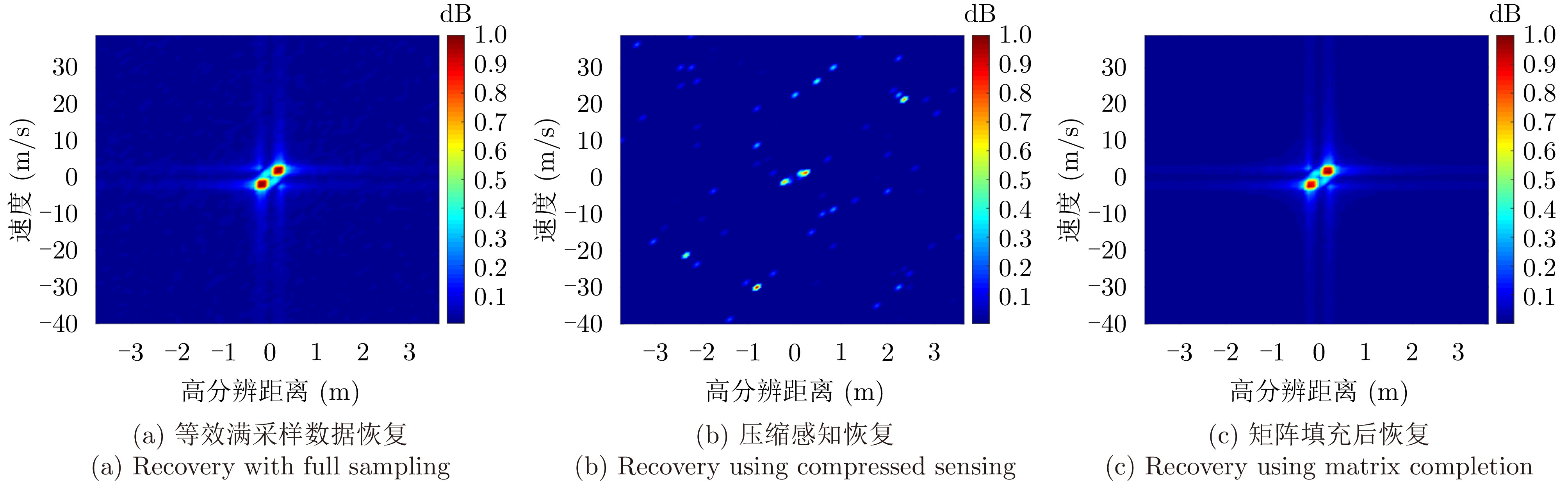
| [1] |
PANDA S S S, PANIGRAHI T, PARNE S R, et al. Recent advances and future directions of microwave photonic radars: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(19): 21144–21158. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3099533. |
| [2] |
向寅, 张凯, 胡程. 基于NUFFT的调频步进频高分辨成像与目标识别算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 639–647. doi: 10.12000/JR15083. XIANG Yin, ZHANG Kai, and HU Cheng. A NUFFT based step-frequency Chirp signal high resolution imaging algorithm and target recognition algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 639–647. doi: 10.12000/JR15083. |
| [3] |
AL-HOURANI A, EVANS R J, MORAN B, et al. Efficient range-Doppler processing for random stepped frequency radar in automotive applications[C]. IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2017.8108414. |
| [4] |
SAPONARA S, GRECO M S, and GINI F. Radar-on-chip/in-package in autonomous driving vehicles and intelligent transport systems: Opportunities and challenges[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36(5): 71–84. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2909074. |
| [5] |
JIANG Yuan, WANG Yanhua, LI Yang, et al. Eigenvalue-based ground target detection in high-resolution range profiles[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(11): 1747–1756. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2020.0002. |
| [6] |
AXELSSON S R J. Analysis of random step frequency radar and comparison with experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(4): 890–904. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.888865. |
| [7] |
HUANG Tianyao, LIU Yimin, LI Gang, et al. Randomized stepped frequency ISAR imaging[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2012: 553–557. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2012.6212202. |
| [8] |
WEHNER D R. High Resolution Radar[M]. Norwood, MA, Artech House, 1987.
|
| [9] |
LIU Yimin, MENG Huadong, LI Gang, et al. Range-velocity estimation of multiple targets in randomised stepped-frequency radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2008, 44(17): 1032–1034. doi: 10.1049/el:20081608. |
| [10] |
ACKROYD M H and GHANI F. Optimum mismatched filters for sidelobe suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES-9(2): 214–218. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1973.309769. |
| [11] |
DAVIS R M, FANTE R L, and PERRY R P. Phase-coded waveforms for radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(1): 401–408. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.357142. |
| [12] |
KAJENSKI P J. Mismatch filter design via convex optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(4): 1587–1591. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140556. |
| [13] |
LIU Shuai, CAO Yunhe, YEO T S, et al. Range sidelobe suppression for randomized stepped-frequency chirp radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3874–3885. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3082670. |
| [14] |
LIAO Zhikun, HU Jiemin, LU Dawei, et al. Motion analysis and compensation method for random stepped frequency radar using the pseudorandom code[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 57643–57654. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2873784. |
| [15] |
LIAO Zhikun, LU Dawei, HU Jiemin, et al. Waveform design for random stepped frequency radar to estimate object velocity[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(14): 894–896. doi: 10.1049/el.2018.1033. |
| [16] |
QUAN Yinghui, LI Yachao, HU Wen, et al. FM sequence optimisation of chaotic-based random stepped frequency signal in through-the-wall radar[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(7): 830–837. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2015.0565. |
| [17] |
HUANG Tianyao, LIU Yimin, XU Xingyu, et al. Analysis of frequency agile radar via compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(23): 6228–6240. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2876301. |
| [18] |
YOON Y S, HONG Yunseog, and KIM S. Simple strategies to build random compressive sensing matrices in step-frequency radars[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(9): 1357–1361. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2841189. |
| [19] |
HUANG Tianyao, LIU Yimin, MENG Huadong, et al. Cognitive random stepped frequency radar with sparse recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 858–870. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.120443. |
| [20] |
QUAN Yinghui, LI Yachao, WU Yaojun, et al. Moving target detection for frequency agility radar by sparse reconstruction[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(9): 094703. doi: 10.1063/1.4962700. |
| [21] |
CHI Yuejie, SCHARF L L, PEZESHKI A, et al. Sensitivity to basis mismatch in compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(5): 2182–2195. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2112650. |
| [22] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHI Jun, et al. CSR-Net: A novel complex-valued network for fast and precise 3-D microwave sparse reconstruction[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4476–4492. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3014696. |
| [23] |
CANDES E J and TAO T. The power of convex relaxation: Near-optimal matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(5): 2053–2080. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2044061. |
| [24] |
马宇欣, 海宇, 李中余, 等. 稀疏轨迹毫米波雷达三维高分辨成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(5): 1000–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR23001. MA Yuxin, HAI Yu, LI Zhongyu, et al. 3D high-resolution imaging algorithm with sparse trajectory for millimeter-wave radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 1000–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR23001. |
| [25] |
SUN Shunqiao and ZHANG Y D. 4D automotive radar sensing for autonomous vehicles: A sparsity-oriented approach[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 879–891. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3079626. |
| [26] |
SUN Shunqiao, BAJWA W U, and PETROPULU A P. MIMO-MC radar: A MIMO radar approach based on matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 1839–1852. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140452. |
| [27] |
HU Xiaowei, TONG Ningning, WANG Jianye, et al. Matrix completion-based MIMO radar imaging with sparse planar array[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 131: 49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.07.034. |
| [28] |
ZHANG Yilong, LI Yuehua, CHEN Jianfei, et al. Sparse millimeter-wave InSAR imaging approach based on MC[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 714–718. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2810234. |
| [29] |
HU Xueyao, LI Yang, LU Man, et al. A multi-carrier-frequency random-transmission Chirp sequence for TDM MIMO automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3672–3685. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900357. |
| [30] |
LIANG Can, LI Yang, HU Xueyao, et al. Coherent-on-Receive synthesis using dominant scatterer in millimeter-wave distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(6): 1505. doi: 10.3390/rs15061505. |
| [31] |
STRANG G. Introduction to Linear Algebra[M]. 6th ed. Wellesley, USA: Wellesley-Cambridge Press, 2022.
|
| [32] |
HORN R A and JOHNSON C R. Matrix Analysis[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1985. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511810817. |
| [33] |
YE Hailiang, LI Hong, CAO Feilong, et al. A hybrid truncated norm regularization method for matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(10): 5171–5186. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2918733. |
| [34] |
HU Yao, ZHANG Debing, YE Jieping, et al. Fast and accurate matrix completion via truncated nuclear norm regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(9): 2117–2130. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.271. |
| [35] |
CAI Jianfeng, CANDÈS E J, and SHEN Zuowei. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2010, 20(4): 1956–1982. doi: 10.1137/080738970. |
| [36] |
邓理康, 张双辉, 张弛, 等. 一种基于多维交替方向乘子法的多输入多输出逆合成孔径雷达成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 416–431. doi: 10.12000/JR20132. DENG Likang, ZHANG Shuanghui, ZHANG Chi, et al. A multiple-input multiple-output inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method based on multidimensional alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 416–431. doi: 10.12000/JR20132. |
| [37] |
范文, 蔚保国, 陈镜, 等. 基于波形优化和天线位置选择的MIMO雷达波束扫描算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 530–542. doi: 10.12000/JR22135. FAN Wen, YU Baoguo, CHEN Jing, et al. Joint waveform optimization and antenna position selection for MIMO radar beam scanning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 530–542. doi: 10.12000/JR22135. |
| [38] |
OH T H, MATSUSHITA Y, TAI Y W, et al. Fast randomized singular value thresholding for low-rank optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(2): 376–391. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2677440. |
| [39] |
CHEN Yuxin and CHI Yuejie. Robust spectral compressed sensing via structured matrix completion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(10): 6576–6601. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2343623. |
| [40] |
GRANT M, BOYD S, and YE Yinyu. MATLAB software for disciplined convex programming[EB/OL]. https://web.stanford.edu/~boyd/papers/disc_cvx_prog.html, 2006.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: