| [1] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1006–1114.
|
| [2] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–14. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556. |
| [3] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. |
| [4] |
TAN Mingxing and LE Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114.
|
| [5] |
LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986. |
| [6] |
DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021: 1−22. https://iclr.cc/virtual/2021/index.html.
|
| [7] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720. |
| [8] |
喻玲娟, 王亚东, 谢晓春, 等. 基于FCNN和ICAE的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066. YU Lingjuan, WANG Yadong, XIE Xiaochun, et al. SAR ATR based on FCNN and ICAE[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066. |
| [9] |
赵鹏菲, 黄丽佳. 一种基于EfficientNet与BiGRU的多角度SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 895–904. doi: 10.12000/JR20133. ZHAO Pengfei and HUANG Lijia. Target recognition method for multi-aspect synthetic aperture radar images based on EfficientNet and BiGRU[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 895–904. doi: 10.12000/JR20133. |
| [10] |
HUANG Xiayuan, YANG Qiao, and QIAO Hong. Lightweight two-stream convolutional neural network for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(4): 667–671. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2983718. |
| [11] |
LIU Jiaming, XING Mengdao, YU Hanwen, et al. EFTL: Complex convolutional networks with electromagnetic feature transfer learning for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5209811. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3083261. |
| [12] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A novel deep learning network with HOG feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3082759. |
| [13] |
QOSJA D, WAGNER S, and BRÜGGENWIRTH S. Benchmarking convolutional neural network backbones for target classification in SAR[C]. 2023 IEEE Radar Conference, San Antonio, USA, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2351548.2023.10149802. |
| [14] |
LIU Zhuang, MAO Hanzi, WU Chaoyuan, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 11966–11976. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01167. |
| [15] |
张翼鹏, 卢东东, 仇晓兰, 等. 基于散射点拓扑和双分支卷积神经网络的SAR图像小样本舰船分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(2): 411–427. doi: 10.12000/JR23172. ZHANG Yipeng, LU Dongdong, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Few-shot ship classification of SAR images via scattering point topology and dual-branch convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 411–427. doi: 10.12000/JR23172. |
| [16] |
LUAN Shangzhen, CHEN Chen, ZHANG Baochang, et al. Gabor convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4357–4366. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2835143. |
| [17] |
XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. Microwave vision and intelligent perception of radar imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 285–306. doi: 10.12000/JR23225. |
| [18] |
GERRY M J, POTTER L C, GUPTA I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750. |
| [19] |
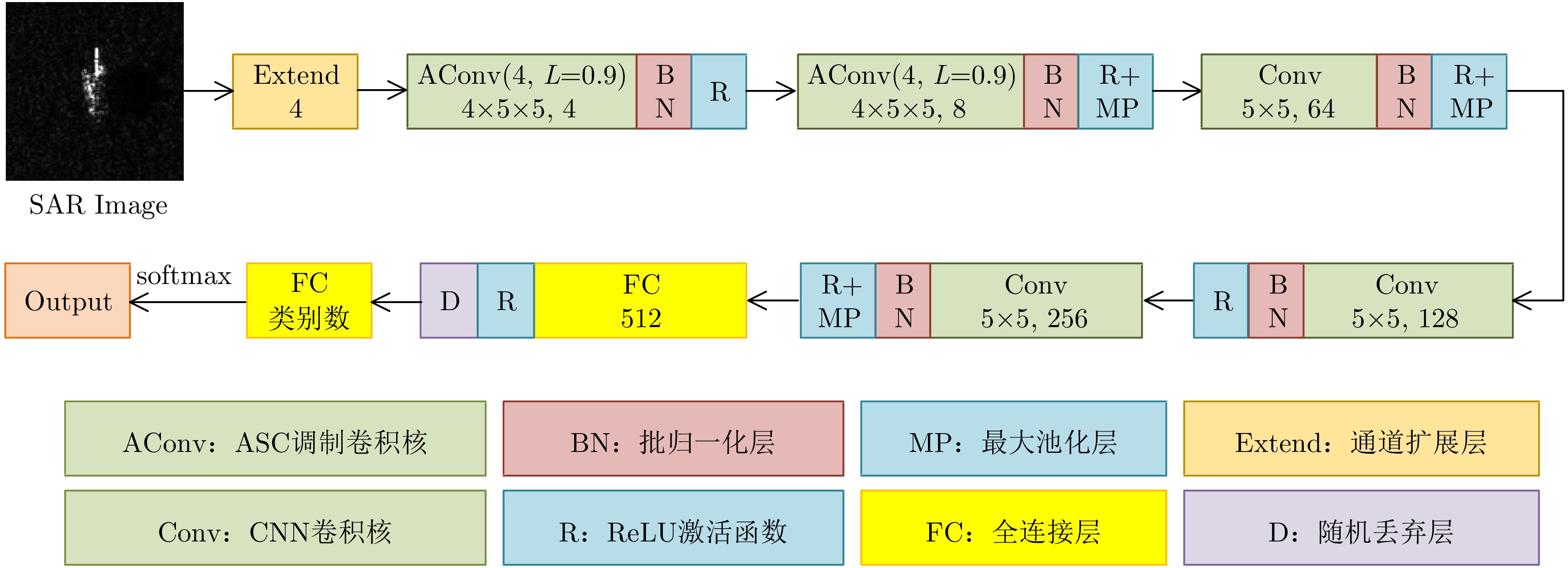
POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098. |
| [20] |
李飞. 雷达图像目标特征提取方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.
LI Fei. Study on target feature extraction based on radar image[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2014.
|
| [21] |
ROSS T D, WORRELL S W, VELTEN V J, et al. Standard SAR ATR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 566–573. doi: 10.1117/12.321859. |
| [22] |
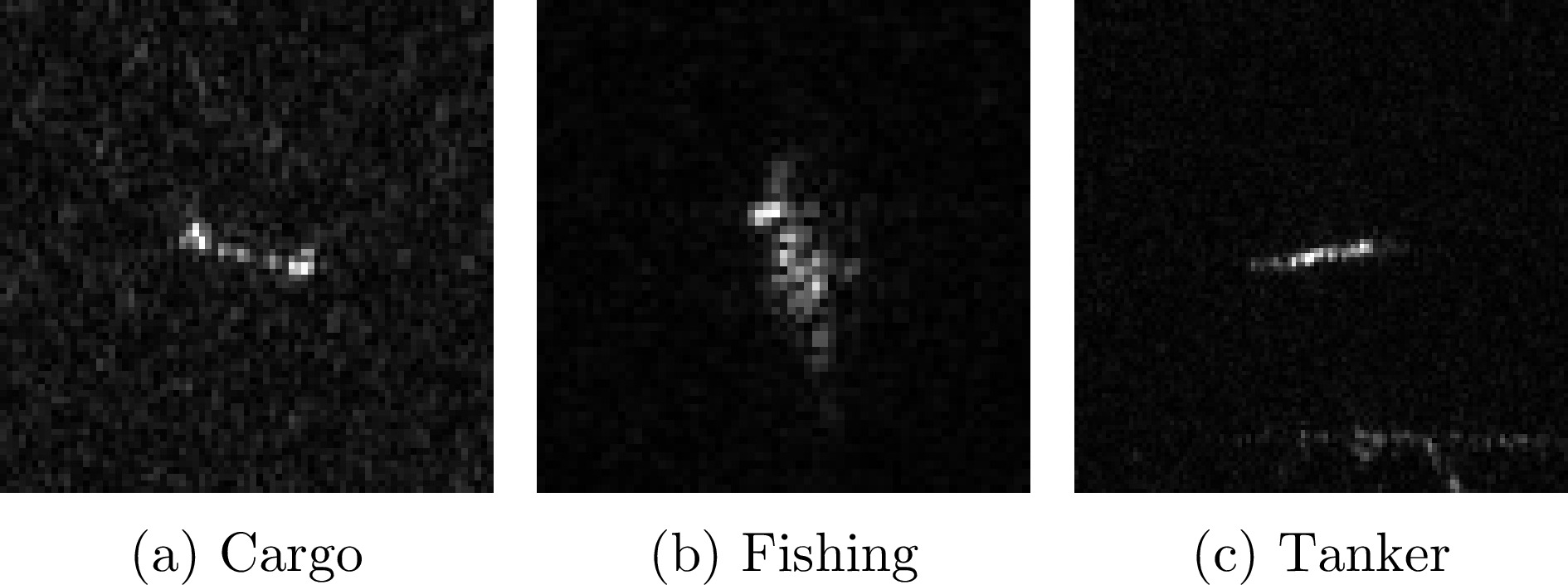
HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672. |
| [23] |
SUN Yongguang, DU Lan, WANG Yan, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on dictionary learning and joint dynamic sparse representation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1777–1781. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2608578. |
| [24] |
DENG Sheng, DU Lan, LI Chen, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on Euclidean distance restricted autoencoder[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(7): 3323–3333. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2670083. |
| [25] |
NI Jiacheng and XU Yuelei. SAR automatic target recognition based on a visual cortical system[C]. 2013 6th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2013: 778–782. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2013.6745270. |
| [26] |
LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: