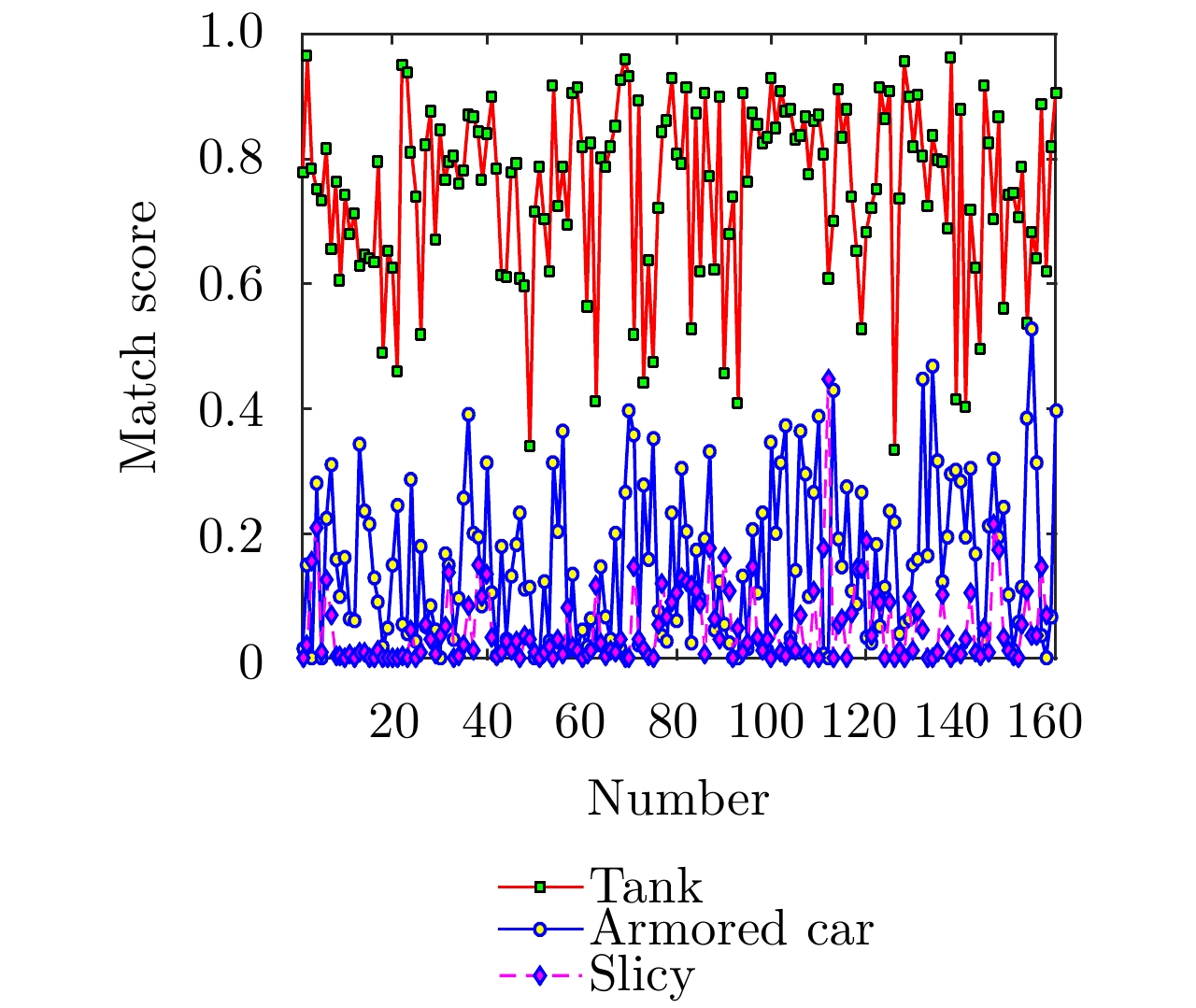
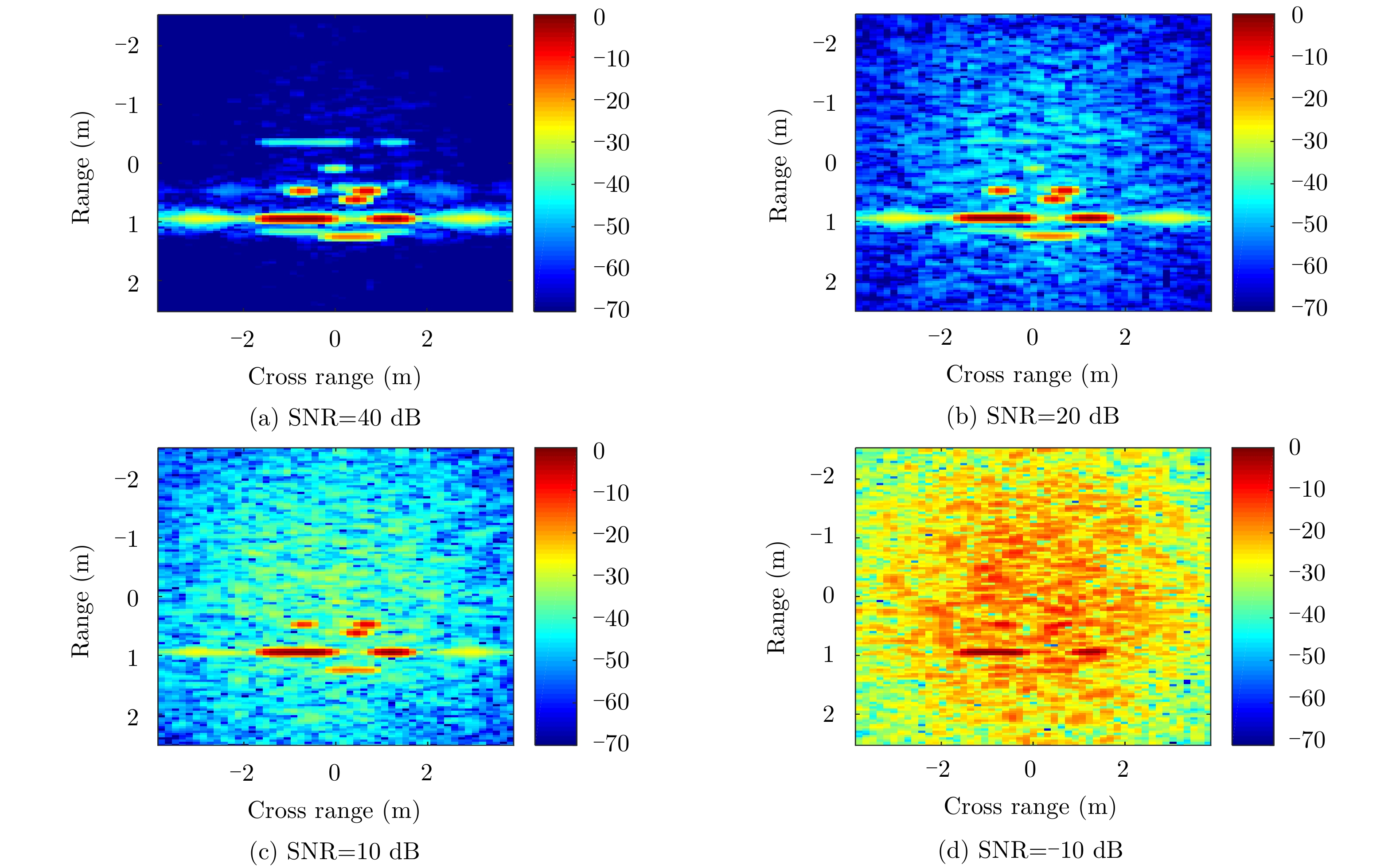
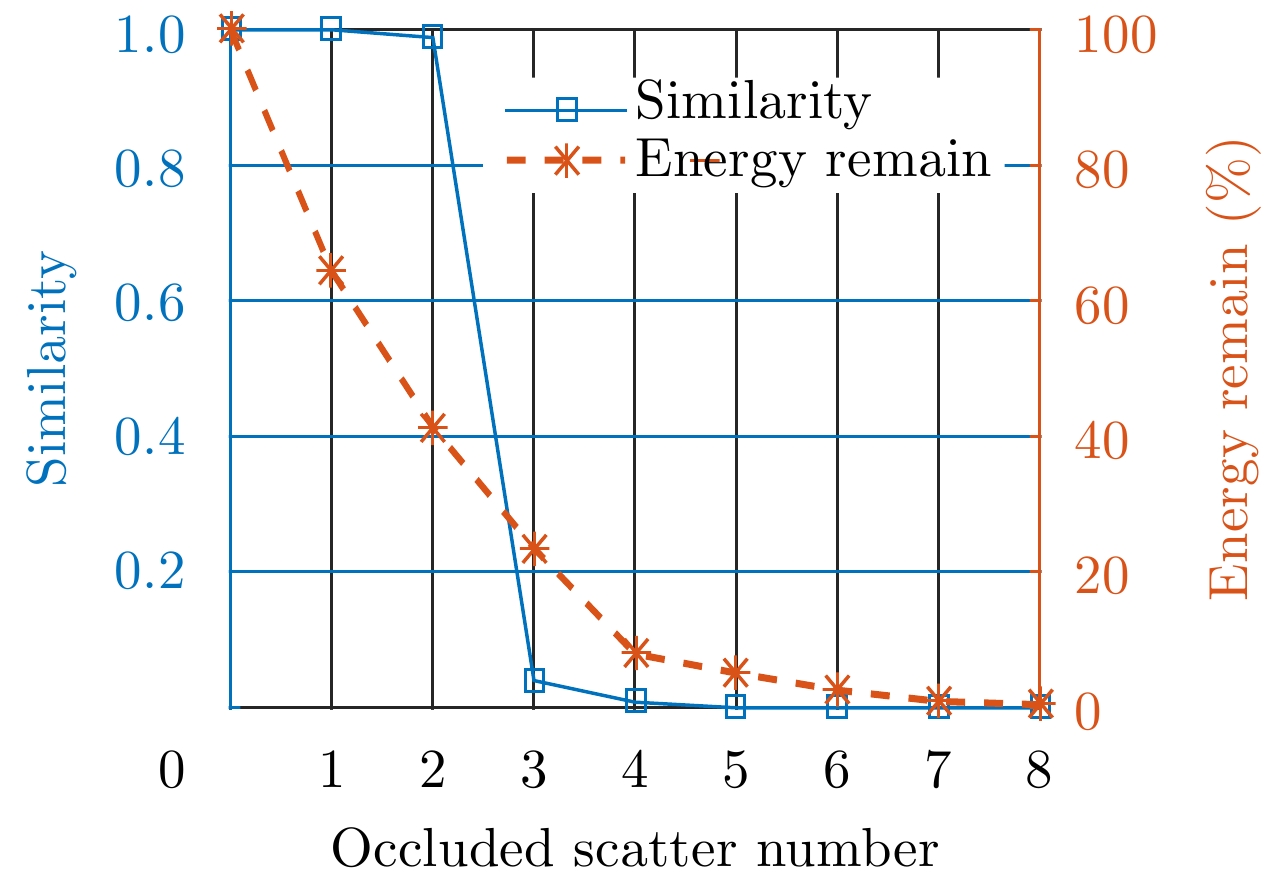
| [1] |
EL-DARYMLI K, GILL E W, MCGUIRE P, et al. Automatic target recognition in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art review[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 6014–6058. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2611492 |
| [2] |
NOVAK L M, OWIRKA G J, BROWER W S, et al. The automatic target-recognition system in SAIP[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1997, 10(2): 187–202.
|
| [3] |
PARK J I, PARK S H, and KIM K T. New discrimination features for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 476–480. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2210385 |
| [4] |
NICOLI L P and ANAGNOSTOPOULOS G C. Shape-based recognition of targets in synthetic aperture radar images using elliptical Fourier descriptors[C]. SPIE 6967, Automatic Target Recognition XVIII, Orlando, USA, 2008.
|
| [5] |
MISHRA A K. Validation of PCA and LDA for SAR ATR[C]. The TENCON 2008 - 2008 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Hyderabad, India, 2008: 1–6.
|
| [6] |
HUAN Ruohong and YANG Ruliang. Synthetic aperture radar images target recognition based on wavelet domain NMF feature extraction[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2009, 31(3): 588–591. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01808 |
| [7] |
DONG Ganggang and KUANG Gangyao. Classification on the monogenic scale space: Application to target recognition in SAR image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(8): 2527–2539. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2421440 |
| [8] |
POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 |
| [9] |
MOSES P L, POTTER L C, and GUPTA I J. Feature extraction using attributed scattering center models for model-based automatic target recognition (ATR)[R]. AFRL-SN-WP-TR-2006-1004, 2005.
|
| [10] |
LIU Xian, HUANG Yulin, PEI Jifang, et al. Sample discriminant analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(12): 2120–2124. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2321164 |
| [11] |
HUANG Yulin, PEI Jifang, YANG Jianyu, et al. Neighborhood geometric center scaling embedding for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(1): 180–192. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.110769 |
| [12] |
DING Jun, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368.
|
| [13] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 |
| [14] |
ROSS T D, BRADLEY J J, HUDSON L J, et al. SAR ATR: So what’s the problem? An MSTAR perspective[C]. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 606–610.
|
| [15] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 228–242.
|
| [16] |
JONES III G and BHANU B. Recognition of articulated and occluded objects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1999, 21(7): 603–613. doi: 10.1109/34.777371 |
| [17] |
DIEMUNSCH J R and WISSINGER J. Moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) model-based automatic target recognition: Search technology for a robust ATR[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 481–492.
|
| [18] |
HUANG Peikang, YIN Hongcheng, and XU Xiaojian. Radar Target Characteristics[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006.
|
| [19] |
CHIANG H C, MOSES R L, and POTTER L C. Model-based Bayesian feature matching with application to synthetic aperture radar target recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2001, 34(8): 1539–1553. doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(00)00089-3 |
| [20] |
ZHOU Jianxiong, SHI Zhiguang, XIAO Cheng, et al. Automatic target recognition of SAR images based on global scattering center model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3713–3729. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2162526 |
| [21] |
JACKSON J A. Three-dimensional feature models for synthetic aperture radar and experiments in feature extraction[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Ohio State University, 2009.
|
| [22] |
文贡坚, 朱国强, 殷红成, 等. 基于三维电磁散射参数化模型的SAR目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034WEN Gongjian, ZHU Guoqiang, YIN Hongcheng, et al. SAR ATR based on 3D parametric electromagnetic scattering model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034 |
| [23] |
GIUSTI E, MARTORELLA M, and CAPRIA A. Polarimetrically-persistent-scatterer-based automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(11): 4588–4599. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164804 |
| [24] |
TANG Tao and SU Yi. Object recognition based on feature matching of scattering centers in SAR imagery[C]. The 5th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Chongqing, China, 2012: 1073–1076.
|
| [25] |
MARTORELLA M, GIUSTI E, DEMI L, et al. Target recognition by means of polarimetric ISAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 225–239. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705672 |
| [26] |
SAVILLE M A, SAINI D K, and SMITH J. Commercial vehicle classification from spectrum parted linked image test-attributed synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(3): 569–576.
|
| [27] |
RICHARDS J A. Target model generation from multiple synthetic aperture radar image[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], 1996, MIT.
|
| [28] |
HE Yang, HE Siyuan, ZHANG Yunhua, et al. A forward approach to establish parametric scattering center models for known complex radar targets applied to SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(12): 6192–6205. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2360700 |
| [29] |
ZHOU Jianxiong, SHI Zhiguang, and FU Qiang. Three-dimensional scattering center extraction based on wide aperture data at a single elevation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1638–1655. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2346509 |
| [30] |
VOICU L I, PATTON R, and MYLER H R. Multicriterion vehicle pose estimation for SAR ATR[C]. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 3721.
|
| [31] |
CUI Xunxue, ZHANG Jichun, and ZHOU Pucheng. Hypothesis testing for target detection model in sensor networks[C]. The 7th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Yantai, China, 2010.
|
| [32] |
BOSE R. Lean CLEAN: Deconvolution algorithm for radar imaging of contiguous targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(3): 2190–2199. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5937291 |
| [33] |
SHAFER G. A Mathematical Theory of Evidence[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1976.
|
| [34] |
FELZENSZWALB P F, GIRSHICK R B, MCALLESTER D, et al. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1627–1645. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: