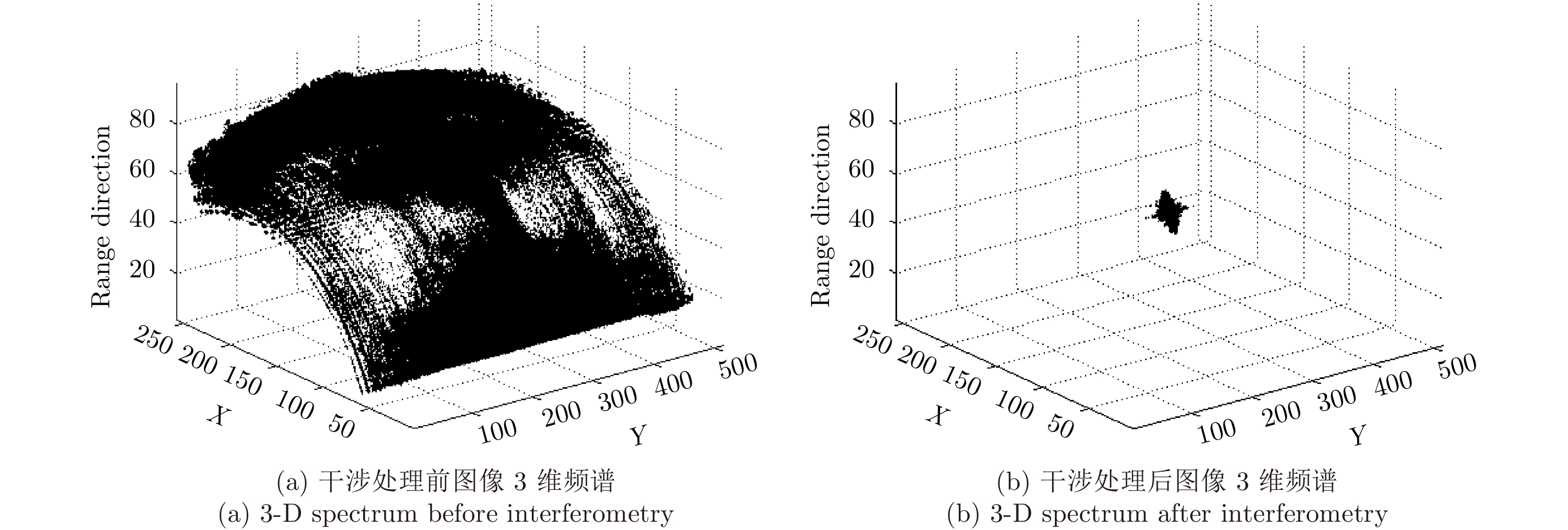
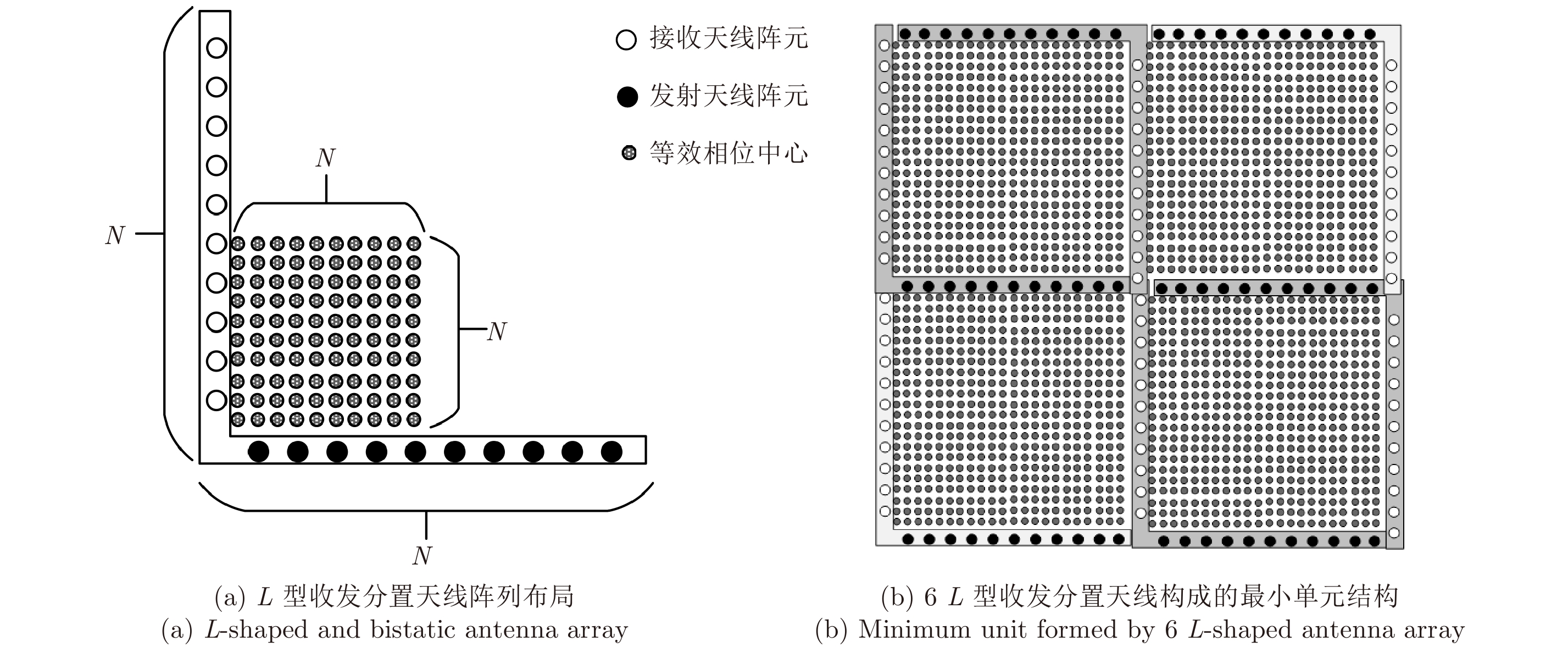
| [1] |
McMillan R W, Currie N C, Ferris D D, et al.. Concealed weapon detection using microwave and millimeter wave sensors[C]. Proceedings of 1998 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology Proceedings, Beijing, 1998: 1–4. DOI: 10.1109/ICMMT.1998.768213. |
| [2] |
Wen Xin, Huang Pei-kang, Nian Feng, et al. Active millimeter-wave near-field cylindrical scanning three-dimensional imaging system[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(6): 1044–1049. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.06.05 |
| [3] |
Farhat N H and Guard W R. Millimeter wave holographic imaging of concealed weapons[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1971, 59(9): 1383–1384. DOI: 10.1109/PROC.1971.8441 |
| [4] |
Gomez-Maqueda I, Almorox-Gonzalez P, Callejero-Andres C, et al. A millimeter-wave imager using an illuminating source[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2013, 14(4): 132–138. DOI: 10.1109/MMM.2013.2248652 |
| [5] |
Ahmed S S, Genghammer A, Schiessl A, et al. Fully electronic E-band personnel imager of 2 m 2 aperture based on a multistatic architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(1): 651–657. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2228221 |
| [6] |
Ahmed S S, Genghammer A, Schiessl A, et al.. Fully electronic active E-band personnel imager with 2 m 2 aperture[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012: 1–3. DOI: 10.1109/MWSYM.2012.6259549. |
| [7] |
Li L C, Li D J, and Pan Z H. Compressed sensing application in interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(10): 102305. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9017-6 |
| [8] |
Tian H, Li D J, and Li L C. Simulation of signal reconstruction based sparse flight downward-looking 3D imaging SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, 2015: 3762–3765. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326642. |
| [9] |
Holubnychyi A. Generalized binary barker sequences and their application to radar technology[C]. Proceedings of 2013 Signal Processing Symposium (SPS), Serock, 2013: 1–9. DOI: 10.1109/SPS.2013.6623610. |
| [10] |
Detlefsen J, Dallinger A, and Schelkshorn S. Approaches to millimeter-wave imaging of humans[C]. Proceedings of the First European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2004: 279–282.
|
| [11] |
Rosen P A, Hensley S, Joughin I R, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2000, 88(3): 333–382. DOI: 10.1109/5.838084 |
| [12] |
Tian H and Li D J. Sparse flight array SAR downward-looking 3-D imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1395–1399. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2560238 |
| [13] |
Zhang Qing-juan, Li Dao-jing, and Li Lie-chen. Research on continuous scene side-looking 3D imaging based on sparse array[J]. Journal of Electronics& Information Technology, 2013, 35(5): 1097–1102. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01136 |
| [14] |
田鹤, 李道京, 潘洁, 等. 基于修正均匀冗余阵列正反编码的稀疏阵列SAR下视三维成像处理[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209Tian He, Li Dao-jing, Pan Jie, et al. Downward-looking 3D imaging processing of sparse array SAR based on modified uniformly redundant arrays positive and negative coding[J]. Journal of Electronics& Information Technology, 2017, 39(9): 2203–2211. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT161209 |
| [15] |
Li Lie-chen and Li Dao-jing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics& Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645 |
| [16] |
Candès E and Romberg J. Sparsity and incoherence in compressive sampling[J]. Inverse Problems, 2007, 23(3): 969–985. DOI: 10.1088/0266-5611/23/3/008 |
| [17] |
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 |
| [18] |
Baraniuk R and Steeghs P. Compressive radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, Mass, USA, 2007: 128–133. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2007.374203. |
| [19] |
Patel V M, Easley G R, Healy jr D M, et al. Compressed synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 244–254. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2039181 |
| [20] |
Tian H and Li D J. Sparse sampling-based microwave 3D imaging using interferometry and frequency-domain principal component analysis[J]. IET Radar, Sonar& Navigation, 2017, 11(12): 1886–1891. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0087 |
| [21] |
Schiessl A, Ahmed S S, Genghammer A, et al.. A technology demonstrator for a 0.5 m x 0.5 m fully electronic digital beamforming mm-Wave imaging system[C]. Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Rome, 2011: 2606–2609.
|
| [22] |
Tian H, Li D J, and Hu X. Microwave three-dimensional imaging under sparse sampling based on MURA code[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, 2016: 7411–7414. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730933. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

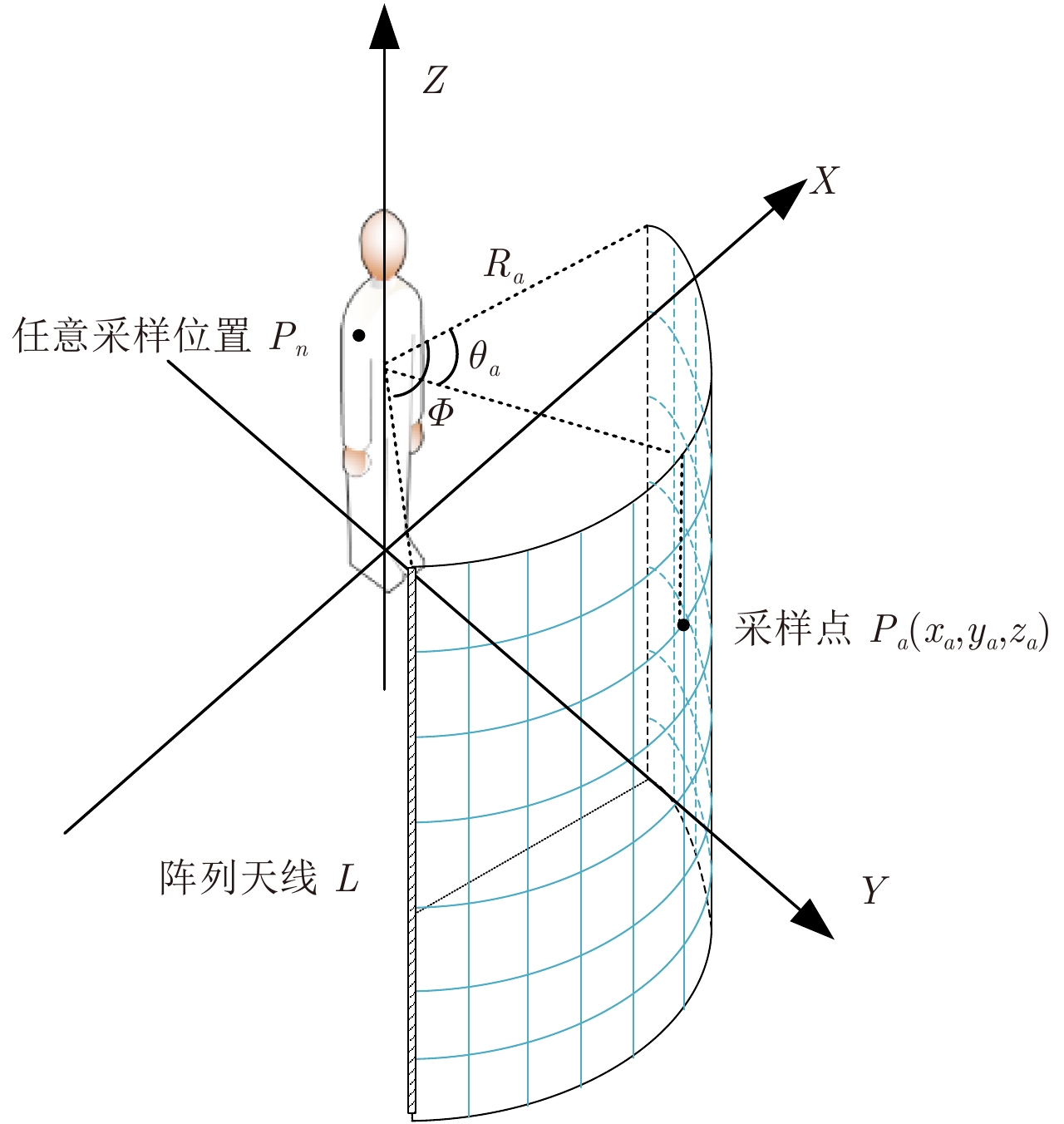



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: