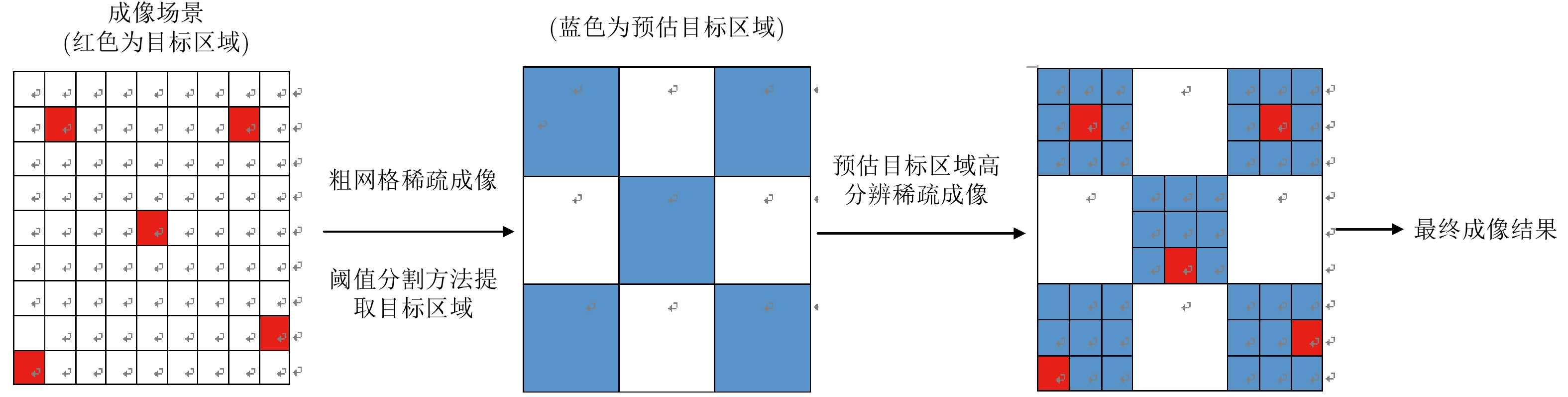
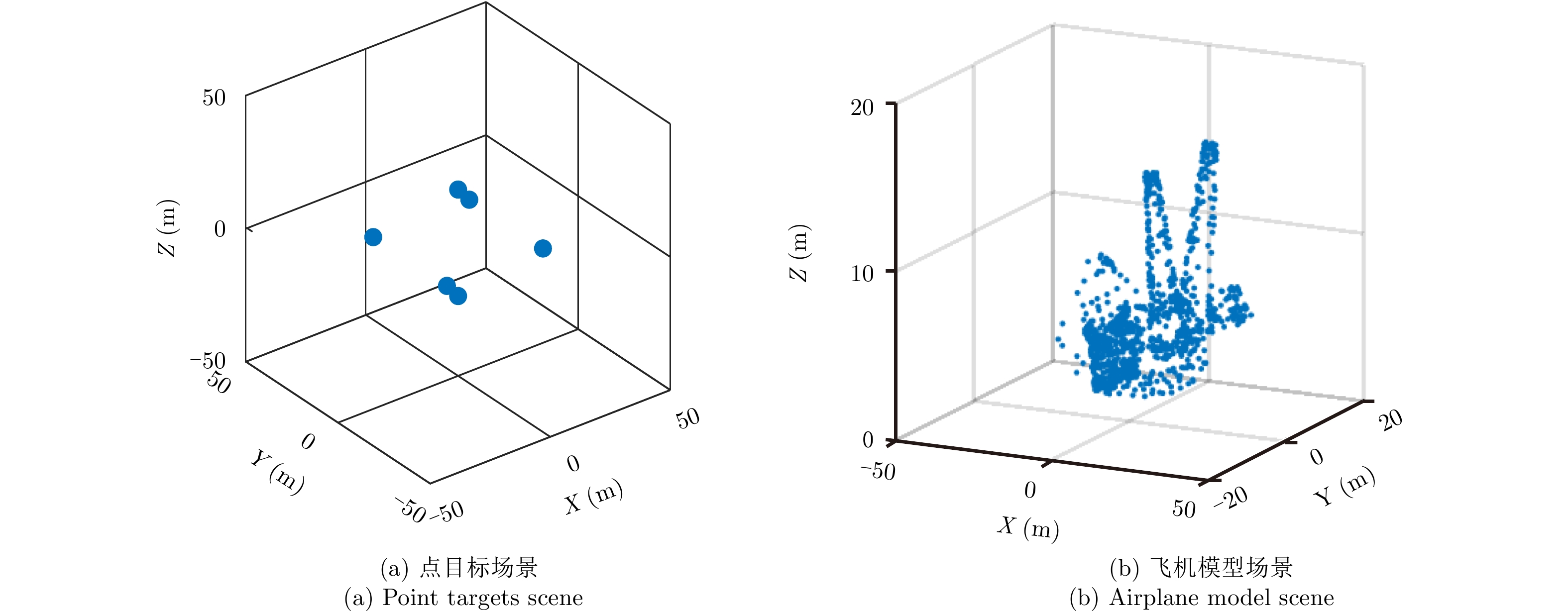
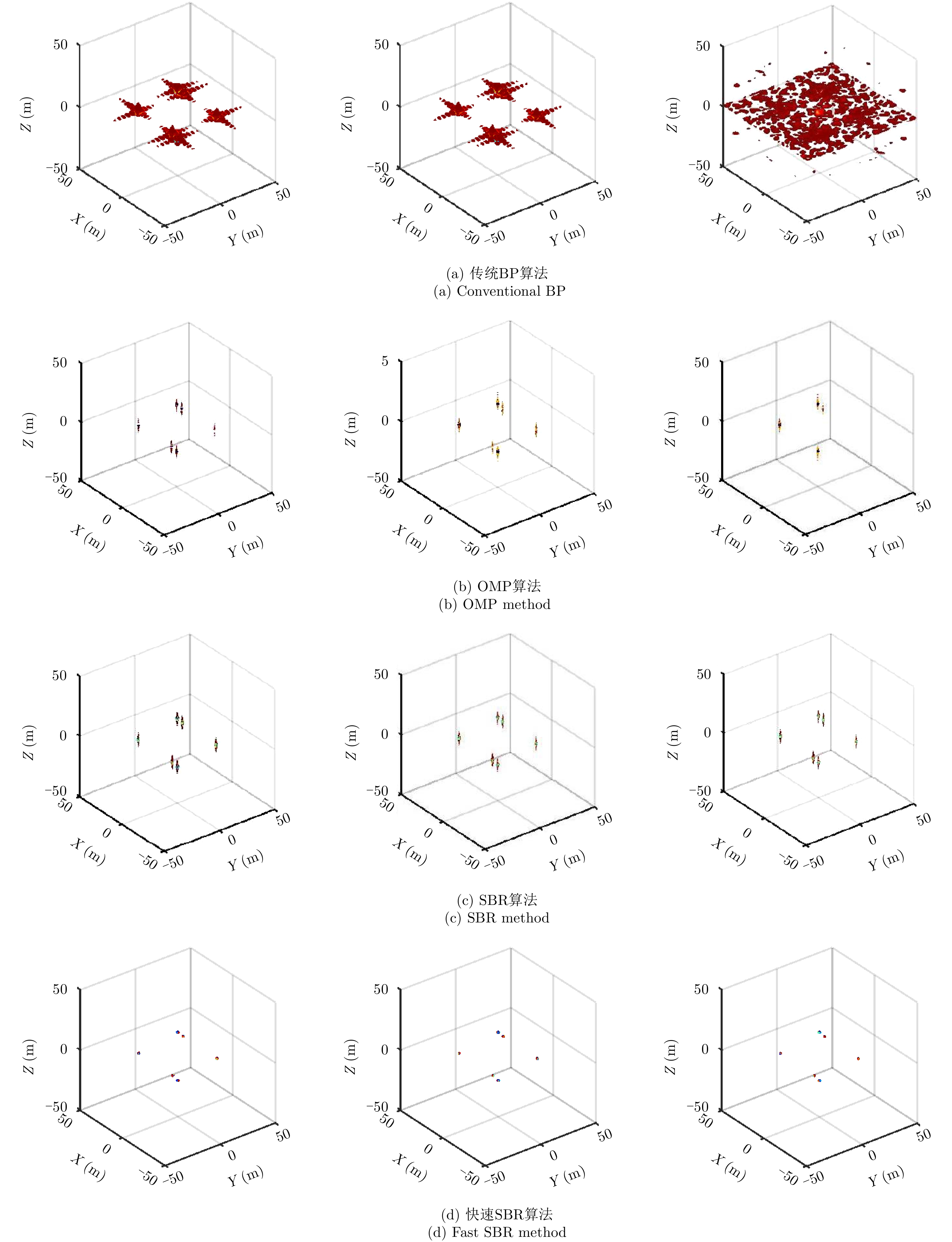
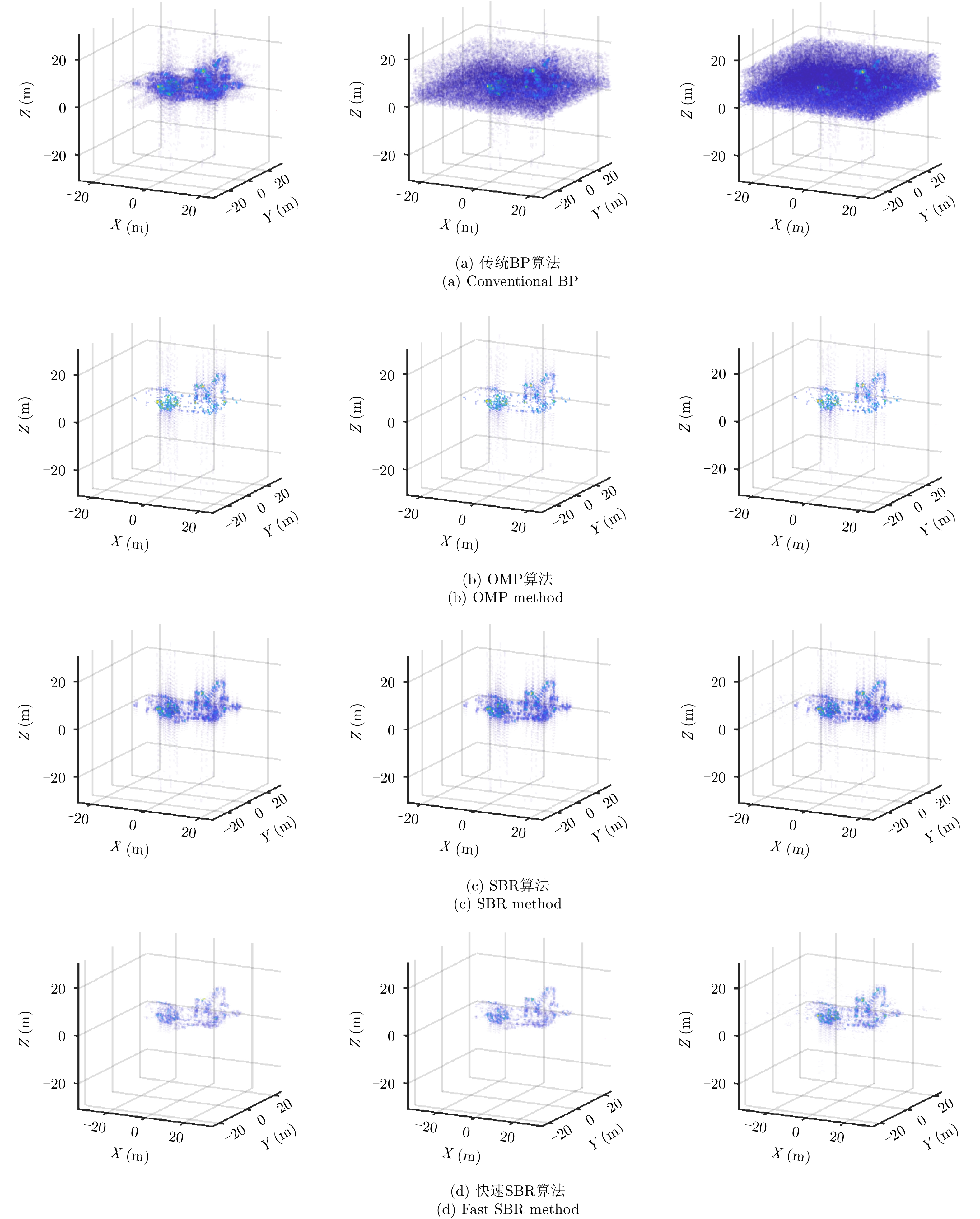
| [1] |
Liao K F, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Plane-wave synthesis and RCS extraction via 3-D linear array SAR[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 994–997. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2389264 |
| [2] |
Han K Y, Wang Y P, Tan W X, et al. Efficient Pseudopolar format algorithm for down-looking linear-array SAR 3-D imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 572–576. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2351792 |
| [3] |
Zhuge X and Yarovoy A G. A sparse aperture MIMO-SAR-based UWB imaging system for concealed weapon detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 509–518. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2053038 |
| [4] |
Wei S J, Zhang X L, Shi J, et al. Sparse array microwave 3-D imaging: Compressed sensing recovery and experimental study[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2013, 135: 161–181. DOI: 10.2528/PIER12082305 |
| [5] |
彭文杰. 基于压缩感知的阵列SAR三维成像方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2013.
Peng Wen-jie. Array SAR3D imaging method based on compressed sensing[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2013.
|
| [6] |
Donoho D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. DOI: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 |
| [7] |
Candès E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing[J]. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9/10): 589–592. DOI: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014 |
| [8] |
Wei S J, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Linear array SAR Imaging via compressed sensing[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2011, 117: 299–319. DOI: 10.2528/PIER11033105 |
| [9] |
Wei S J, Zhang X L, and Shi J. Compressed sensing linear array SAR 3-D imaging via sparse locations prediction[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, Canada, 2014: 1887–1890. DOI: 10.1109/IGARSS.2014.6946825. |
| [10] |
Zhang S Q, Zhu Y T, Dong G G, et al. Truncated SVD-based compressive sensing for downward-looking three-dimensional SAR imaging with uniform/nonuniform linear array[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1853–1857. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2431254 |
| [11] |
Tan X, Fang Y, Feng X Y, et al.. Sparse linear array three-dimensional imaging approach based on compressed sensing[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Beijing, China, 2016: 296–299. DOI: 10.1109/SIPROCESS.2016.7888271. |
| [12] |
Bao Q, Peng X M, Wang Z R, et al. DLSLA 3-D SAR imaging based on reweighted gridless sparse recovery method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 841–845. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2550057 |
| [13] |
Zhang S Q, Dong G G, and Kuang G Y. Superresolution downward-looking linear array three-dimensional SAR imaging based on two-dimensional compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2184–2196. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2549548 |
| [14] |
Peng X M, Tan W X, Hong W, et al. Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR image reconstruction by combination of polar formatting and L1 regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 213–226. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2453202 |
| [15] |
Su W G, Wang H Q, Deng B, et al.. Sparse Bayesian SAR imaging of moving target via the EXCOV method[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing, Gold Coast, Australia, 2014: 448–451. DOI: 10.1109/SSP.2014.6884672. |
| [16] |
Zou Y Q, Gao X Z, and Li X. Block sparse Bayesian learning based strip map SAR imaging method[C]. Proceedings of the 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Davos, Switzerland, 2016: 1–4. DOI: 10.1109/EuCAP.2016.7481637. |
| [17] |
Kang Le, Zhang Qun, Li Tao-yong, et al. Imaging method of downward-looking three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar based on Bayesian learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. DOI: 10.3788/aos201737.0611003 |
| [18] |
韦顺军, 田博坤, 张晓玲, 等. 基于半正定规划的压缩感知线阵三维SAR自聚焦成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 664–675. DOI: 10.12000/JR17103Wei Shun-jun, Tian Bo-kun, Zhang Xiao-ling, et al. Compressed sensing linear array sar autofocusing imaging via semi-definite programming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 664–675. DOI: 10.12000/JR17103 |
| [19] |
Yang J G, Thompson J, Huang X T, et al. Random-frequency SAR imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(2): 983–994. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2204891 |
| [20] |
Xu J, Pi Y, and Cao Z. Bayesian compressive sensing in synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IET Radar, Sonar& Navigation, 2012, 6(1): 2–8. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2010.0375 |
| [21] |
Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B( Methodological) , 1996, 58(1): 267–288. DOI: 10.1111/rssb.1996.58.issue-1 |
| [22] |
Chartrand R and Yin W T. Iteratively reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, USA, 2008: 3869–3872. DOI: 10.1109/ICASSP.2008.4518498. |
| [23] |
Ulander L M H, Hellsten H, and Stenstrom G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: