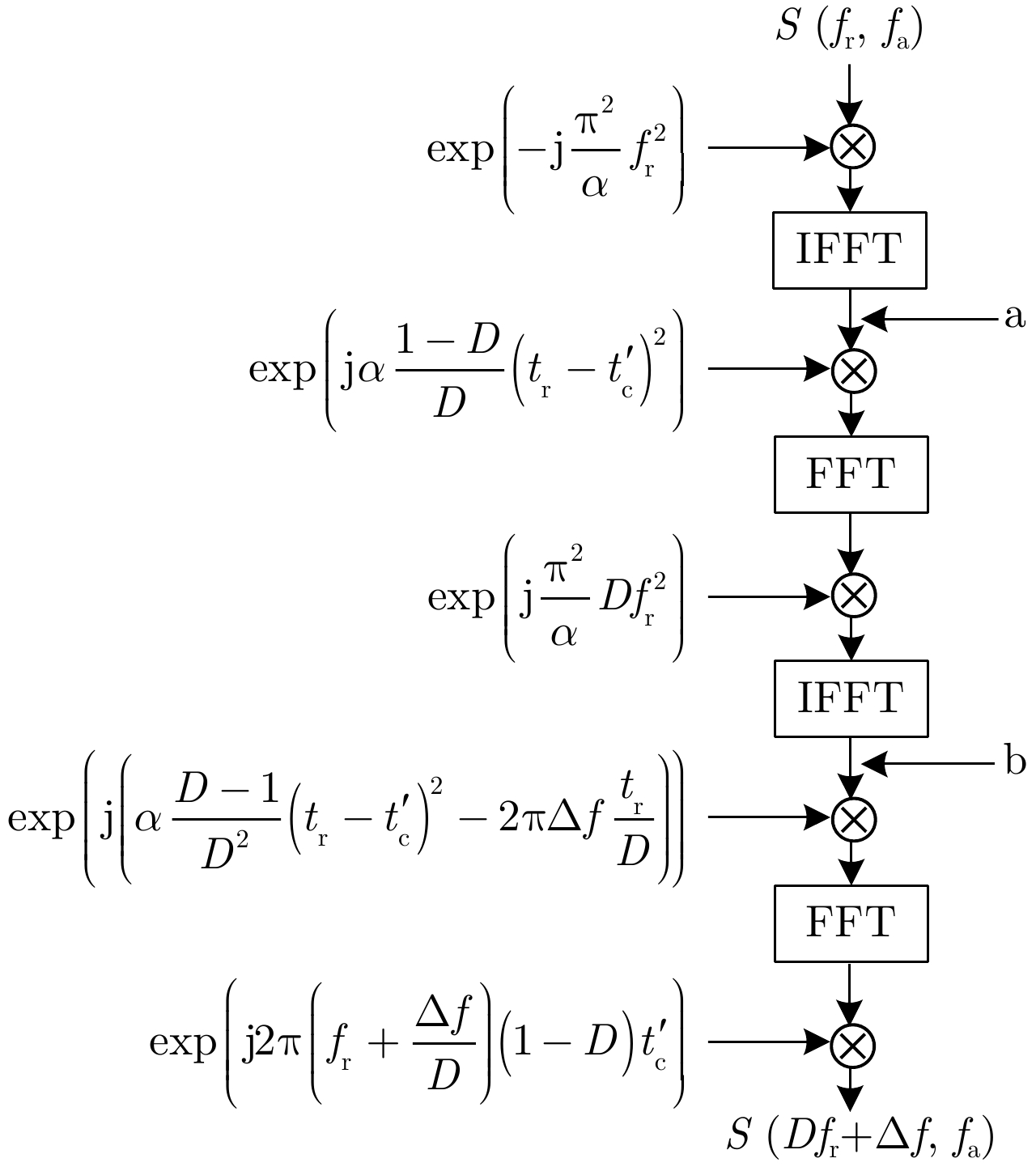
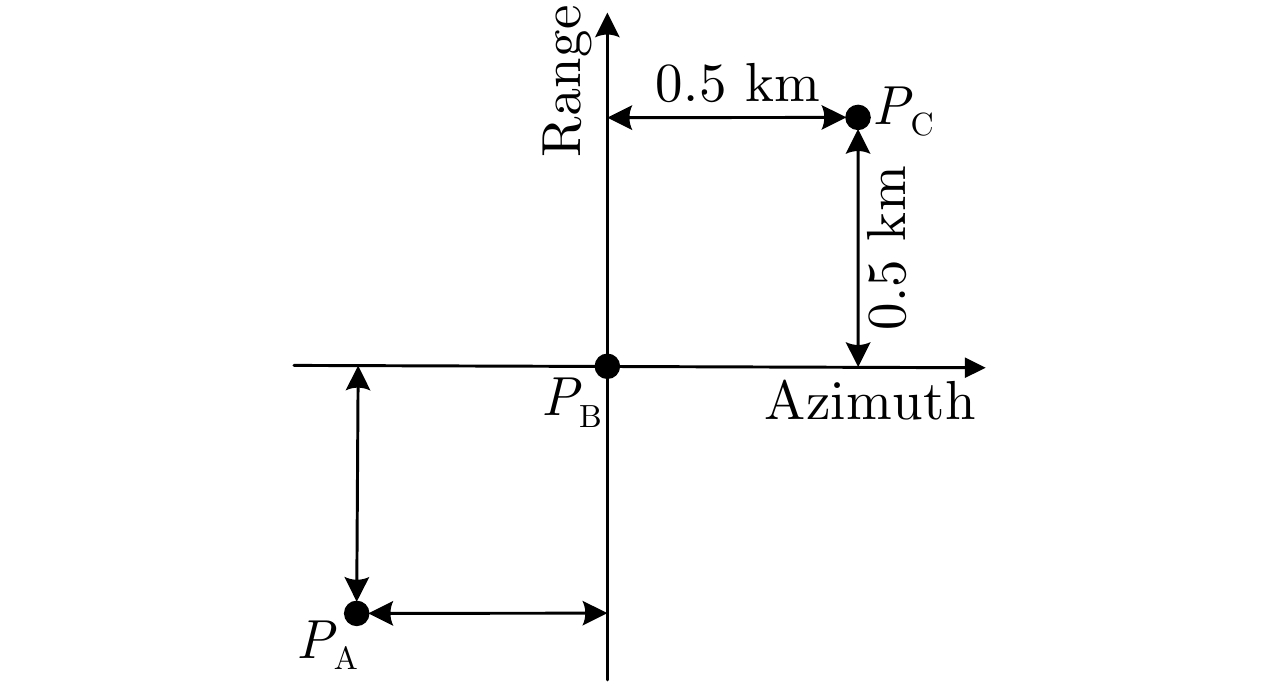
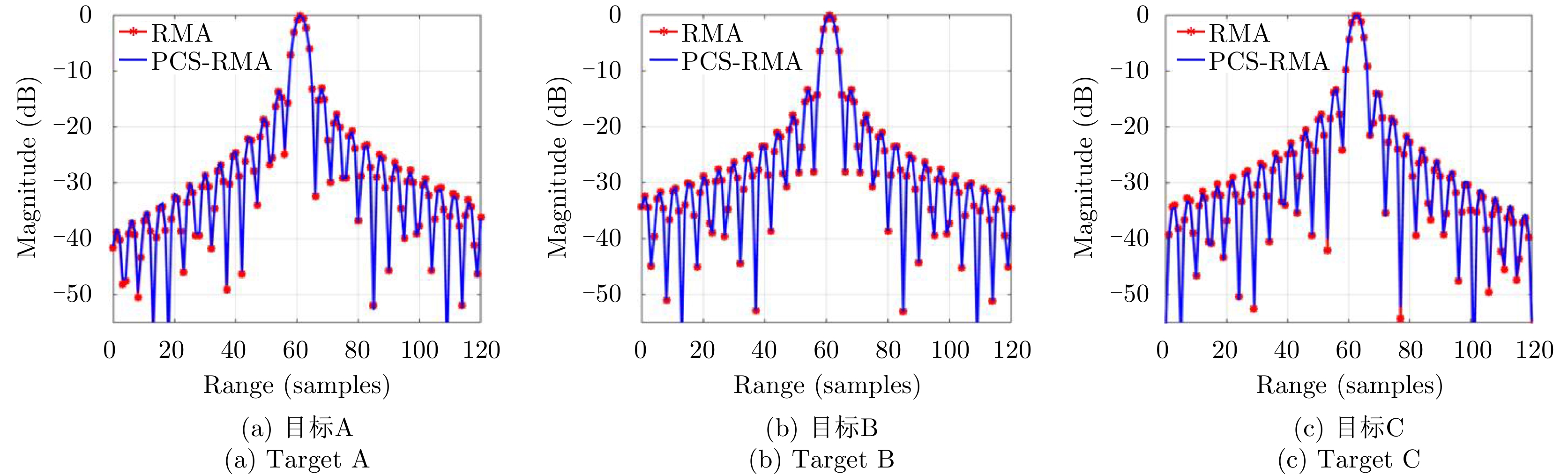
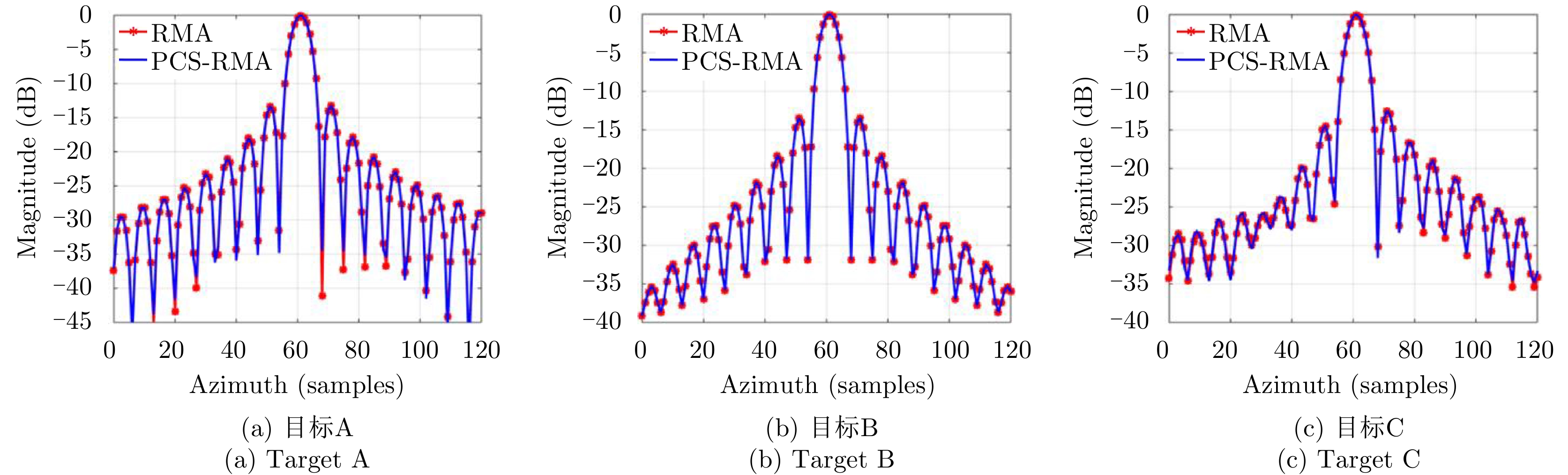
| [1] |
MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 |
| [2] |
詹学丽, 王岩飞, 王超, 等. 一种基于脉冲压缩的机载条带SAR重叠子孔径实时成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 199–208. doi: 10.12000/JR14126ZHAN Xueli, WANG Yanfei, WANG Chao, et al. Research on overlapped subaperture real-time imaging algorithm for pulse compression airborne strip SAR system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 199–208. doi: 10.12000/JR14126 |
| [3] |
唐江文, 邓云凯, 王宇, 等. 高分辨率滑动聚束SAR BP成像及其异构并行实现[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 368–375. doi: 10.12000/JR16053TANG Jiangwen, DENG Yunkai, WANG Yu, et al. High-resolution slide spotlight SAR imaging by BP algorithm and heterogeneous parallel implementation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 368–375. doi: 10.12000/JR16053 |
| [4] |
胡静秋, 刘发林, 周崇彬, 等. 一种新的基于omega-K算法的稀疏场景压缩感知SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 25–33. doi: 10.12000/JR16027HU Jingqiu, LIU Falin, ZHOU Chongbin, et al. CS-SAR imaging method based on inverse omega-K algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 25–33. doi: 10.12000/JR16027 |
| [5] |
王金波, 唐劲松, 张森, 等. 一种宽带大斜视STOLT插值及距离变标补偿方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(7): 1575–1582. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171068WANG Jinbo, TANG Jinsong, ZHANG Sen, et al. Range scaling compensation method based on STOLT interpolation in broadband squint SAS imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(7): 1575–1582. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171068 |
| [6] |
LIN Yun, HONG Wen, TAN Weixian, et al. Extension of range migration algorithm to squint circular SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 651–655. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098843 |
| [7] |
TANG Shiyang, ZHANG Linrang, GUO Ping, et al. An omega-K algorithm for highly squinted missile-borne SAR with constant acceleration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(9): 1569–1573. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2301718 |
| [8] |
SHIN H S and LIM J T. Omega-K algorithm for spaceborne spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 343–347. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2168380 |
| [9] |
ZHU Daiyin, YE Shaohua, and ZHU Zhaoda. Polar format agorithm using chirp scaling for spotlight SAR image formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(4): 1433–1448. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4667720 |
| [10] |
FAN Bo, QIN Yuliang, YOU Peng, et al. An improved PFA with aperture accommodation for widefield spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2322858 |
| [11] |
LUO Xiulian, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. Image formation processing for sliding spotlight SAR with stepped frequency chirps[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1692–1696. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2306206 |
| [12] |
LIU Yongcai, WANG Wei, PAN Xiaoyi, et al. Inverse omega-K algorithm for the electromagnetic deception of synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(7): 3037–3049. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2543961 |
| [13] |
NIE Xin, ZHU Daiyin, MAO Xinhua, et al. The application of the principle of chirp scaling in processing stepped chirps in spotlight SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(4): 860–864. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2027212 |
| [14] |
PIGNOL F, COLONE F, and MARTELLI T. Lagrange-polynomial-interpolation-based keystone transform for a passive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1151–1167. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2775924 |
| [15] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005: 225–362.
|
| [16] |
LANARI R and FORNARO G. A short discussion on the exact compensation of the SAR range-dependent range cell migration effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(6): 1446–1452. doi: 10.1109/36.649799 |
| [17] |
吴玉峰, 叶少华, 冯大政. 基于方位相位编码的脉内聚束SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 437–445. doi: 10.12000/JR17114WU Yufeng, YE Shaohua, and FENG Dazheng. Intra-pulse spotlight SAR imaging method based on azimuth phase coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 437–445. doi: 10.12000/JR17114 |
| [18] |
YANG Mingdong, ZHU Daiyin, and SONG Wei. Comparison of two-step and one-step motion compensation algorithms for airborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(14): 1108–1110. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.1350 |
| [19] |
XING Mengdao, WU Yufeng, ZHANG Y D, et al. Azimuth resampling processing for highly squinted synthetic aperture radar imaging with several modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4339–4352. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281454 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work.jpg)




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: