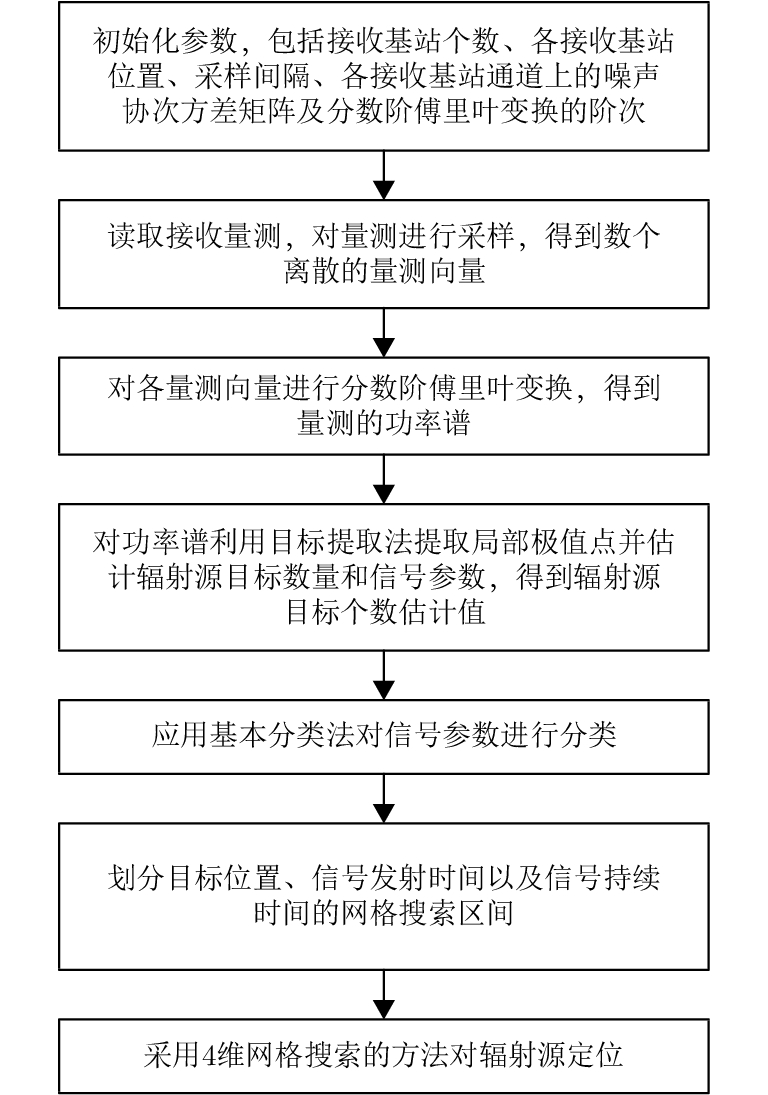
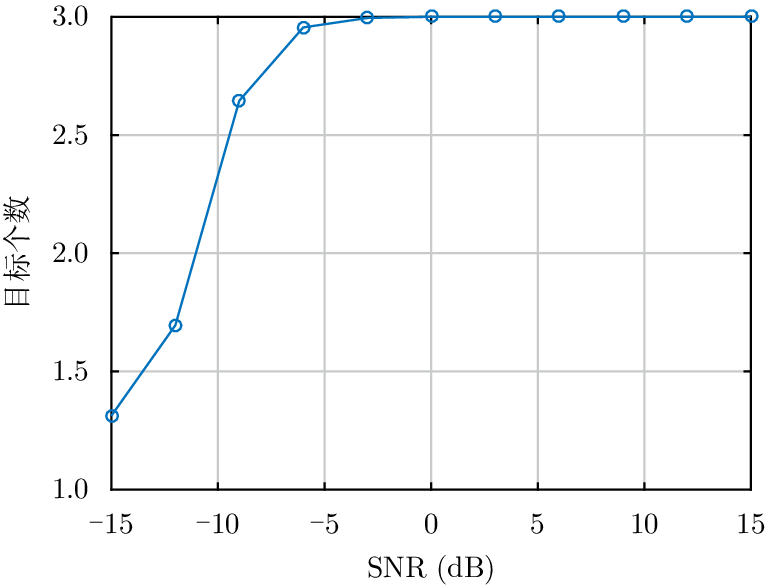
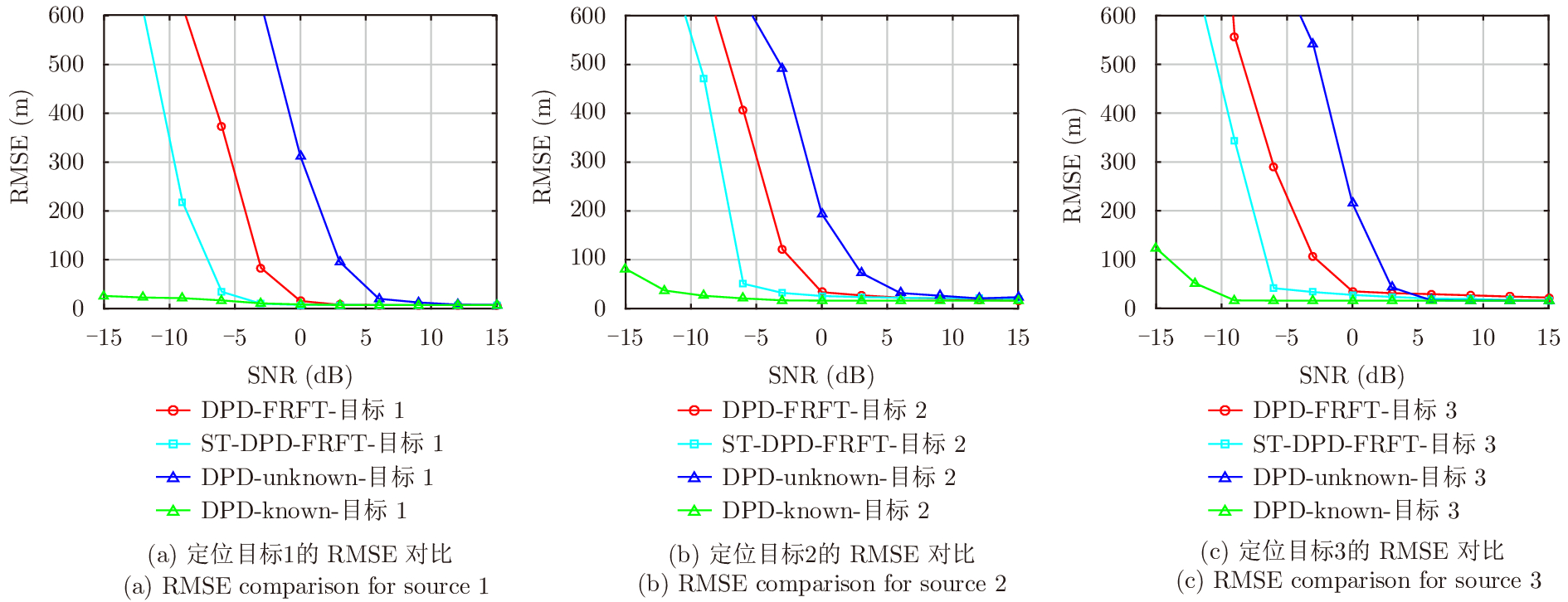
| [1] |
Amar A and Weiss A J. Localization of narrowband radio emitters based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(11): 5500–5508. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2008.929655 |
| [2] |
贾兴江. 运动多站无源定位关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011: 3–42
Jia Xing-jiang. Research on passive location technologies of multiple moving observers[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011: 3–42
|
| [3] |
Tirer T and Weiss A J. High resolution localization of narrowband radio emitters based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 141: 288–298. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.06.019 |
| [4] |
赵勇胜, 赵拥军, 赵闯. 联合角度和时差的单站无源相干定位加权最小二乘算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 302–311. DOI: 10.12000/JR15133Zhao Yong-sheng, Zhao Yong-jun, and Zhao Chuang. Weighted least squares algorithm for single-observer passive coherent location using DOA and TDOA measurements[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 302–311. DOI: 10.12000/JR15133 |
| [5] |
Weiss A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513–516. DOI: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501 |
| [6] |
Yi W, Chen Z H, Hoseinnezhad R, et al. Joint estimation of location and signal parameters for an LFM emitter[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 134: 100–112. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.11.014 |
| [7] |
Oispuu M and Nickel U. Direct detection and position determination of multiple sources with intermittent emission[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 90(12): 3056–3064. DOI: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.05.010 |
| [8] |
Ozaktas H M, Arikan O, Kutay M A, et al. Digital computation of the fractional Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(9): 2141–2150. DOI: 10.1109/78.536672 |
| [9] |
Saxena R and Singh K. Fractional Fourier transform: A novel tool for signal processing[J]. Journal of the Indian Institute of Science, 2005, 85(1): 11–26.
|
| [10] |
Namias V. The fractional order Fourier transform and its application to quantum mechanics[J]. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics, 1980, 25(3): 241–265. DOI: 10.1093/imamat/25.3.241 |
| [11] |
Tian Rui-qi, Bao Qing-long, Wang Ding-he, et al. An algorithm for target parameter estimation based on fractional Fourier and Keystone transforms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(5): 511–517. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14058 |
| [12] |
Almeida L B. The fractional Fourier transform and time-frequency representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(11): 3084–3091. DOI: 10.1109/78.330368 |
| [13] |
吴超楠. 基于分数阶傅里叶变换的高精度线性调频信号参数估计方法[D]. [硕士论文], 华南理工大学, 2014: 15–63
Wu Chaonan. High-precision parameter estimation for LFM signal based on fractional Fourier transform[D]. [Master dissertation], South China University of Technology, 2014: 15–63
|
| [14] |
Schonhoff T A and Giordano A A. Detection and Estimation Theory and its Applications[M]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2006
|
| [15] |
艾越. 分置MIMO雷达多目标信号级定位算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015: 19–23
Ai Yue. Research of MIMO radar with widely separated antennas signal level multi-target localization[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015: 19–23
|
| [16] |
Schultz R R and Stevenson R L. A Bayesian approach to image expansion for improved definition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1994, 3(3): 233–242. DOI: 10.1109/83.287017 |
| [17] |
Sneath P H A and Sokal R R. Numerical taxonomy: The principles and practice of numerical classification[J]. Taxon, 1963, 12(5): 190–199.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

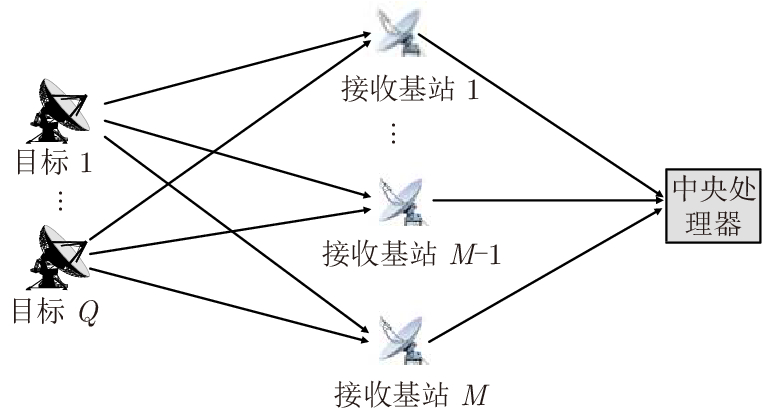



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: