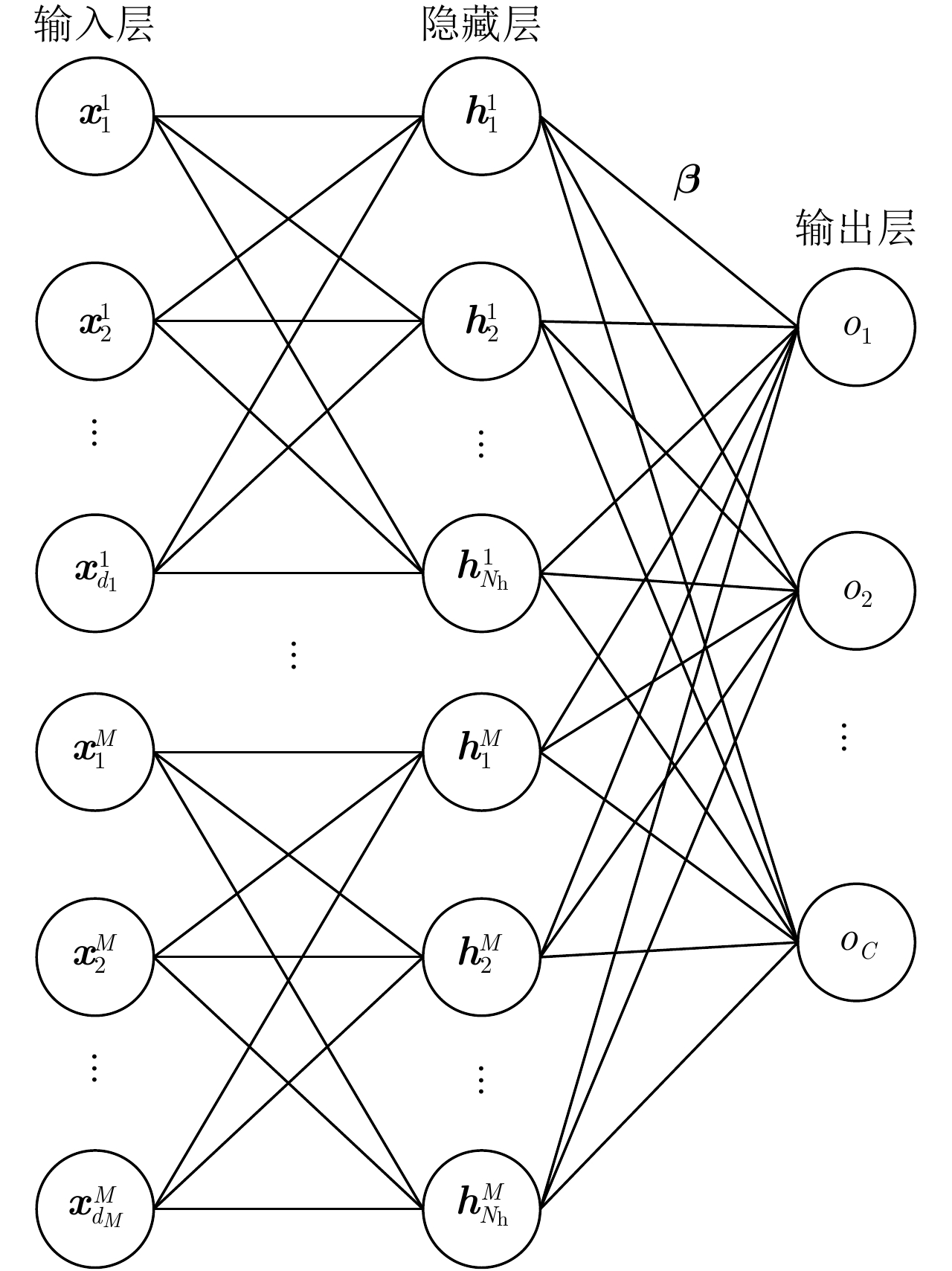
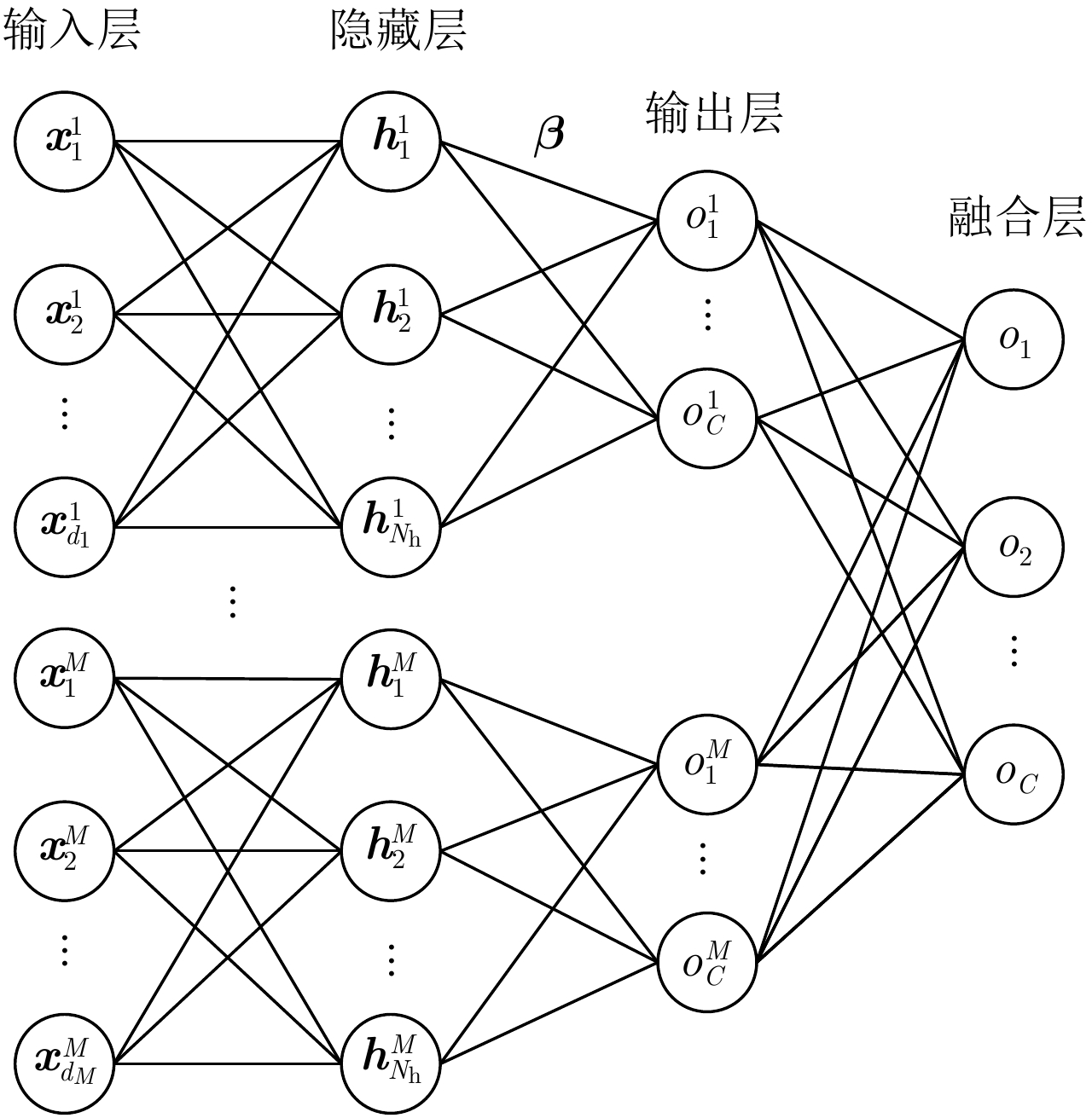
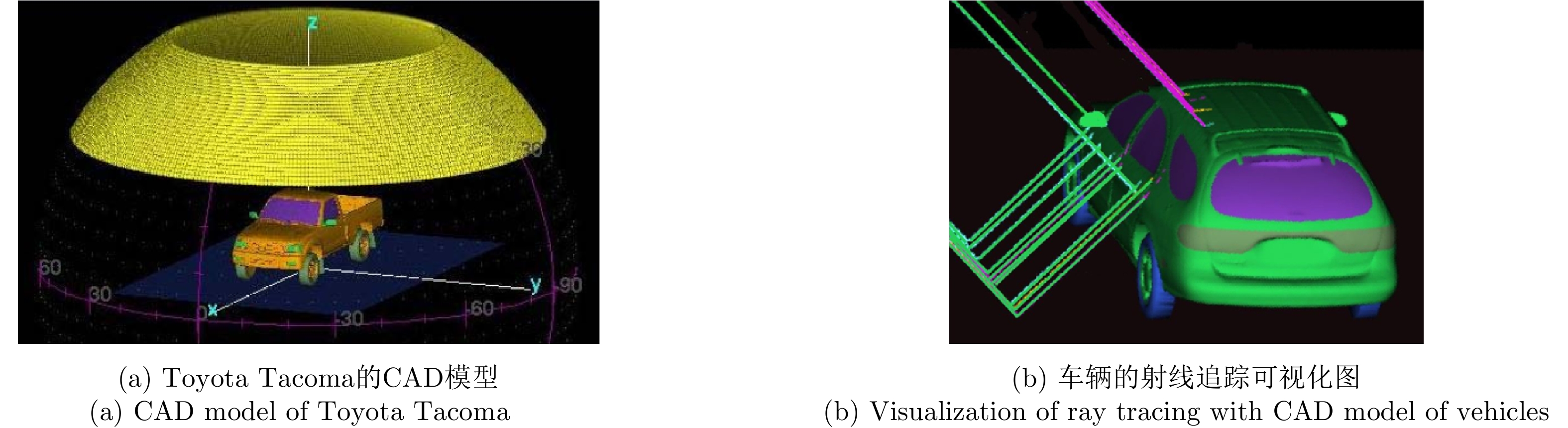
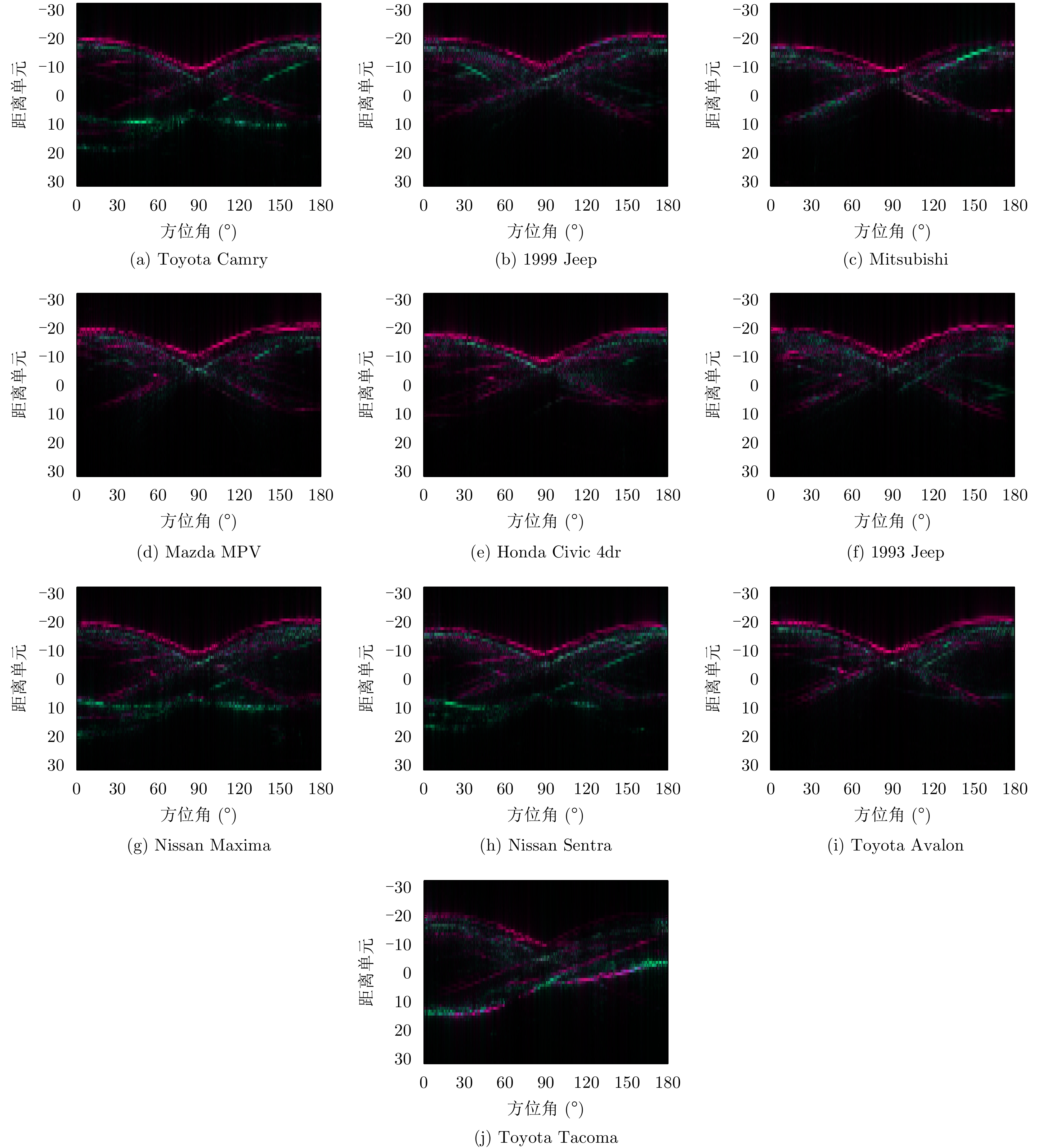
| [1] |
DU Lan, LIU Hongwei, WANG Penghui, et al. Noise robust radar HRRP target recognition based on multitask factor analysis with small training data size[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3546–3559. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2191965 |
| [2] |
WANG Jingjing, LIU Zheng, XIE Rong, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on dynamic learning with limited training data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4): 750. doi: 10.3390/RS13040750 |
| [3] |
NOVAK L M, HALVERSEN S D, OWIRKA G, et al. Effects of polarization and resolution on SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1997, 33(1): 102–116. doi: 10.1109/7.570713 |
| [4] |
GIUSTI E, MARTORELLA M, and CAPRIA A. Polarimetrically-persistent-scatterer-based automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(11): 4588–4599. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164804 |
| [5] |
ZHANG Yuxi, WANG Xiaodan, YAO Xu, et al. Target recognition of fully polarimetric HRRP based on H/A/ α decomposition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(12): 2501–2506. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.12.10 |
| [6] |
ZHANG Yuxi, WANG Xiaodan, YAO Xu, et al. Approach of radar target recognition based on multiple polarization features fusion[J]. Computer Science, 2012, 39(9): 208–210, 234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2012.09.047 |
| [7] |
WANG Fuyou, LUO Ding, and LIU Hongwei. Radar target classification based on some invariant properties of the polarization[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2013, 11(2): 165–172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2013.02.011 |
| [8] |
吴佳妮, 陈永光, 代大海, 等. 基于快速密度搜索聚类算法的极化HRRP分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(10): 2461–2467. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151457WU Jiani, CHEN Yongguang, DAI Dahai, et al. Target recognition for polarimetric HRRP based on fast density search clustering method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(10): 2461–2467. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151457 |
| [9] |
LIU Shengqi, ZHAN Ronghui, WANG Wei, et al. Full-polarization HRRP recognition based on joint sparse representation[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015: 333–338. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf.2015.7411903. |
| [10] |
刘盛启, 占荣辉, 翟庆林, 等. 基于联合稀疏性的多视全极化HRRP目标识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(7): 1724–1730. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151019LIU Shengqi, ZHAN Ronghui, ZHAI Qinglin, et al. Multi-view polarization HRRP target recognition based on joint sparsity[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(7): 1724–1730. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151019 |
| [11] |
ZHAI Qinglin, LIU Shengqi, HU Jiemin, et al. Full-polarization radar target recognition of multitask compressive sensing[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2017, 39(3): 144–150. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.201703022 |
| [12] |
DUAN Jia, XING Mengdao, ZHANG Lei, et al. Novel polarimetric target signal reconstruction method jointed with attributed scattering centers[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2014, 41(6): 18–24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2014.06.004 |
| [13] |
DUAN Jia, ZHANG Lei, XING Mengdao, et al. Polarimetric target decomposition based on attributed scattering center model for synthetic aperture radar targets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(12): 2095–2099. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2320053 |
| [14] |
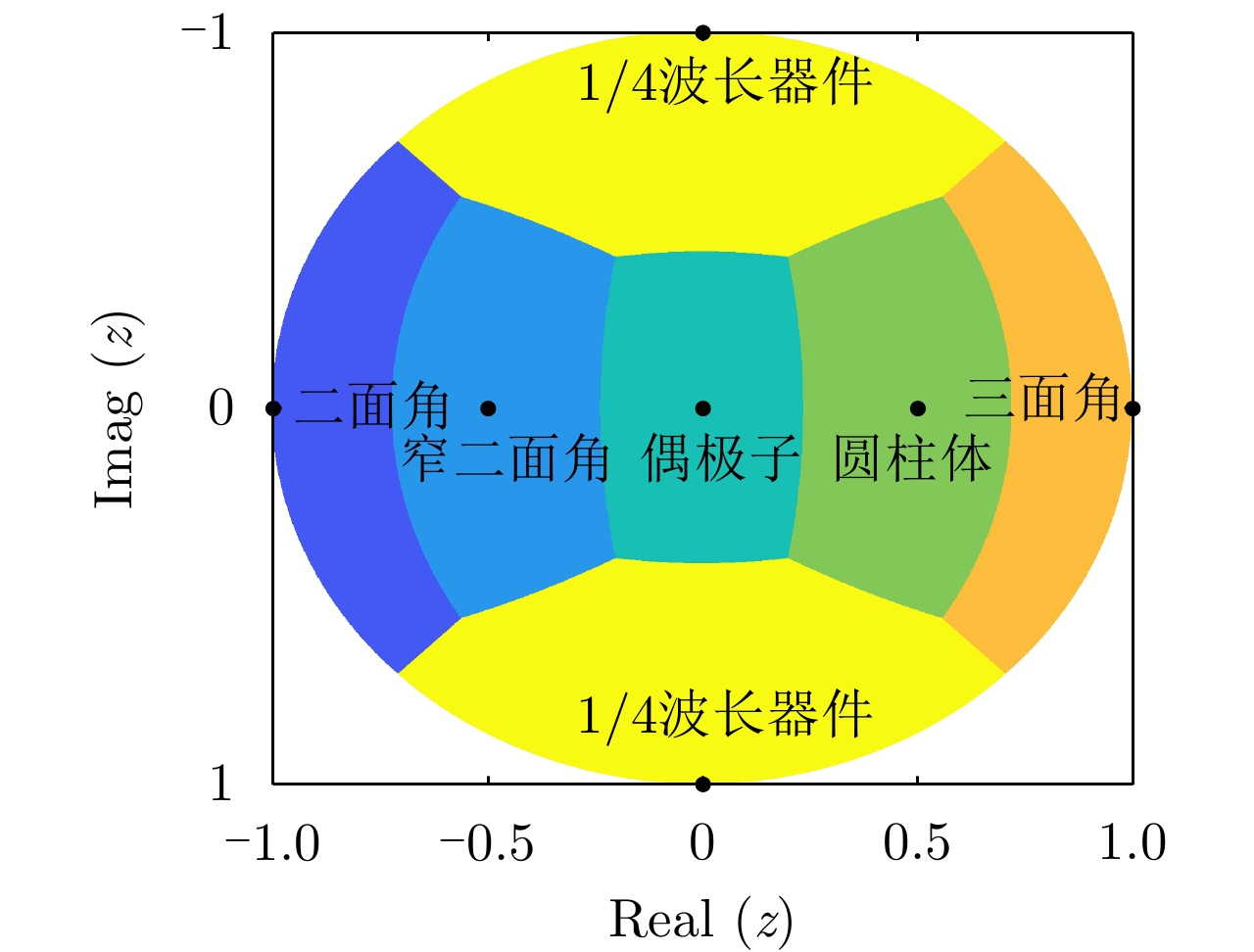
CAMERON W L, YOUSSEF N N, and LEUNG L K. Simulated polarimetric signatures of primitive geometrical shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(3): 793–803. doi: 10.1109/36.499784 |
| [15] |
DENG Wanyu, ONG Y S, and ZHENG Qinghua. A fast reduced kernel extreme learning machine[J]. Neural Networks, 2016, 76: 29–38. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2015.10.006 |
| [16] |
ARTHUR D and VASSILVITSKII S. K-means++: The advantages of careful seeding[C]. The Eighteenth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, USA, 2007: 1027–1035.
|
| [17] |
DUNGAN K E, AUSTIN C, NEHRBASS J, et al. Civilian vehicle radar data domes[C]. SPIE 7699, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVII, Orlando, USA, 2010: 76990P. doi: 10.1117/12.850151. |
| [18] |
KROGAGER E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J]. Electronics Letters, 1990, 26(18): 1525–1527. doi: 10.1049/el:19900979 |
| [19] |
ROBNIK-ŠIKONJA M and KONONENKO I. Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF[J]. Machine Learning, 2003, 53(1): 23–69. doi: 10.1023/A:1025667309714 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: