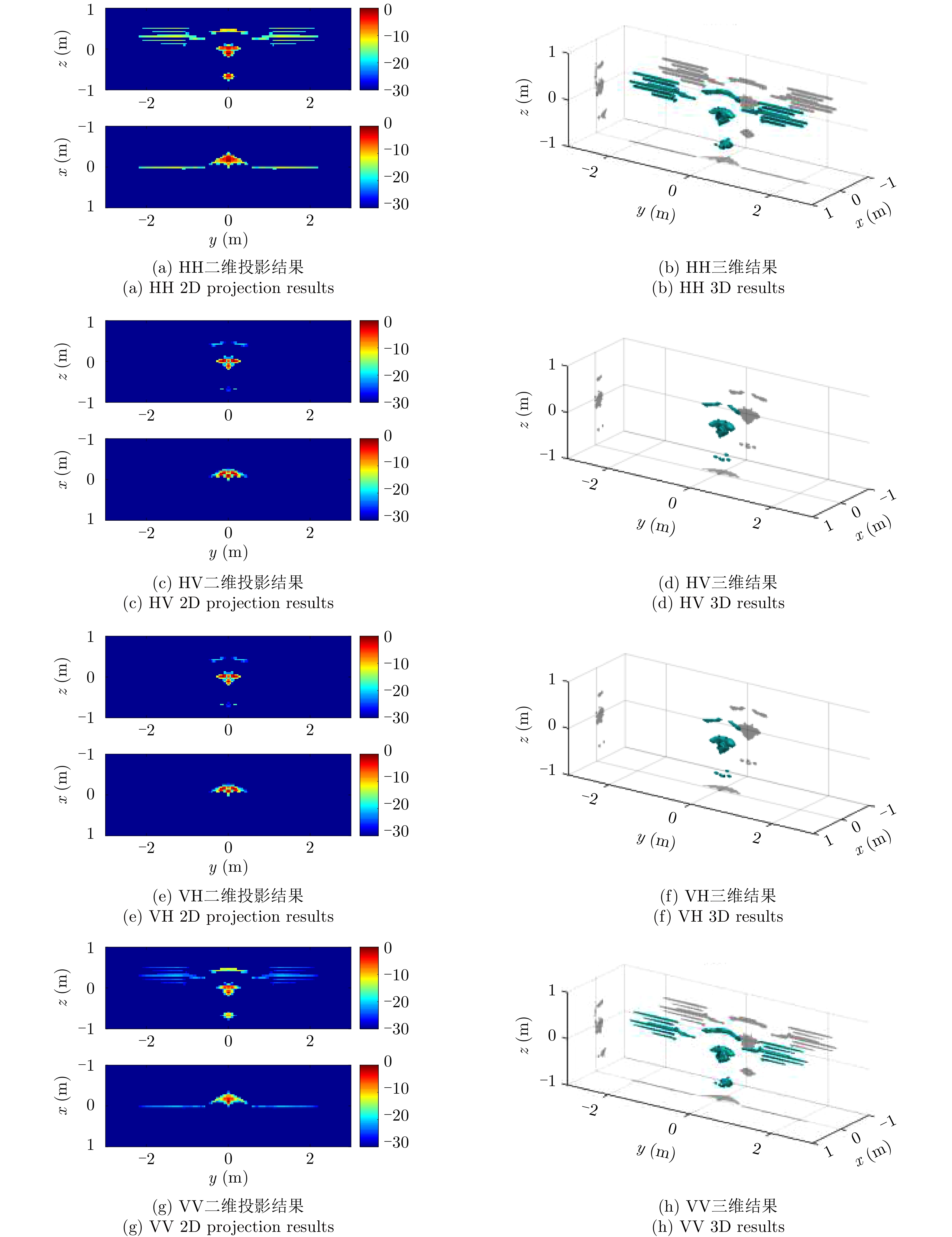
| [1] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging[M] Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005.
|
| [2] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithm and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005.
|
| [3] |
LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2009.
|
| [4] |
庄钊文, 肖顺平, 王雪松. 雷达极化信息处理及其应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1999.
ZHUANG Zhaowen, XIAO Shunping, and WANG Xuesong. Radar Polarization Information Processing and Application[M] Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1999.
|
| [5] |
FREY O and MEIER E. Analyzing tomographic SAR data of a forest with respect to frequency, polarization, and focusing technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3648–3659. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2125972 |
| [6] |
GUILLASO S, FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, et al. Building characterization using L-band polarimetric interferometric SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2005, 2(3): 347–351. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2005.851543 |
| [7] |
PONCE O, PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, et al. First airborne demonstration of holographic SAR tomography with fully polarimetric multicircular acquisitions at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6170–6196. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2582959 |
| [8] |
丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 吴一戎. 全息合成孔径雷达的概念、体制和方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, and WU Yirong. Concept, system, and method of holographic synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063 |
| [9] |
FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. A phase calibration method based on phase gradient autofocus for airborne holographic SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(12): 1864–1868. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2911932 |
| [10] |
SUN Dou, XING Shiqi, LI Yongzhen, et al. Sub-aperture partitioning method for three-dimensional wide-angle synthetic aperture radar imaging with non-uniform sampling[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(6): 629. doi: 10.3390/electronics8060629 |
| [11] |
XING Shiqi, LI Yongzhen, DAI Dahai, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of man-made objects using polarimetric tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3694–3705. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2220145 |
| [12] |
AUSTIN C D, ERTIN E, and MOSES R L. Sparse signal methods for 3-D radar imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2011, 5(3): 408–423. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2090128 |
| [13] |
SUN Dou, PANG Bo, XING Shiqi, et al. Direct 3-D sparse imaging using non-uniform samples without data interpolation[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(2): 321. doi: 10.3390/electronics9020321 |
| [14] |
ERTIN E, MOSES R L, and POTTER L C. Interferometric methods for three-dimensional target reconstruction with multipass circular SAR[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(3): 464–473.
|
| [15] |
HU Xiaowei, TONG Ningning, GUO Yiduo, et al. MIMO radar 3-D imaging based on multi-dimensional sparse recovery and signal support prior information[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(8): 3152–3162. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2810705 |
| [16] |
NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, HORN R, et al. First 3-D reconstructions of targets hidden beneath foliage by means of polarimetric SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 60–64. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2160329 |
| [17] |
NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, and HORN R. Imaging of targets beneath foliage with SAR tomography[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–4.
|
| [18] |
SAUER S, FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, et al. Three-dimensional imaging and scattering mechanism estimation over urban scenes using dual-baseline polarimetric InSAR observations at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(11): 4616–4629. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2147321 |
| [19] |
NGUYEN N H, BERRY P, and TRAN H T. Compressive sensing for tomographic imaging of a target with a narrowband bistatic radar[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(24): 5515. doi: 10.3390/s19245515 |
| [20] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 |
| [21] |
CETIN M and KARL W C. Feature-enhanced synthetic aperture radar image formation based on nonquadratic regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(4): 623–631. doi: 10.1109/83.913596 |
| [22] |
CAMERON W L and LEUNG L K. Feature motivated polarization scattering matrix decomposition[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 549–557.
|
| [23] |
QUE Xiaofeng, NIE Zaiping, and HU Jun. Analysis of EM scattering by composite conducting and dielectric object using combined field integral equation with MLFMA[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(11): 2062–2066. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.11.006 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: