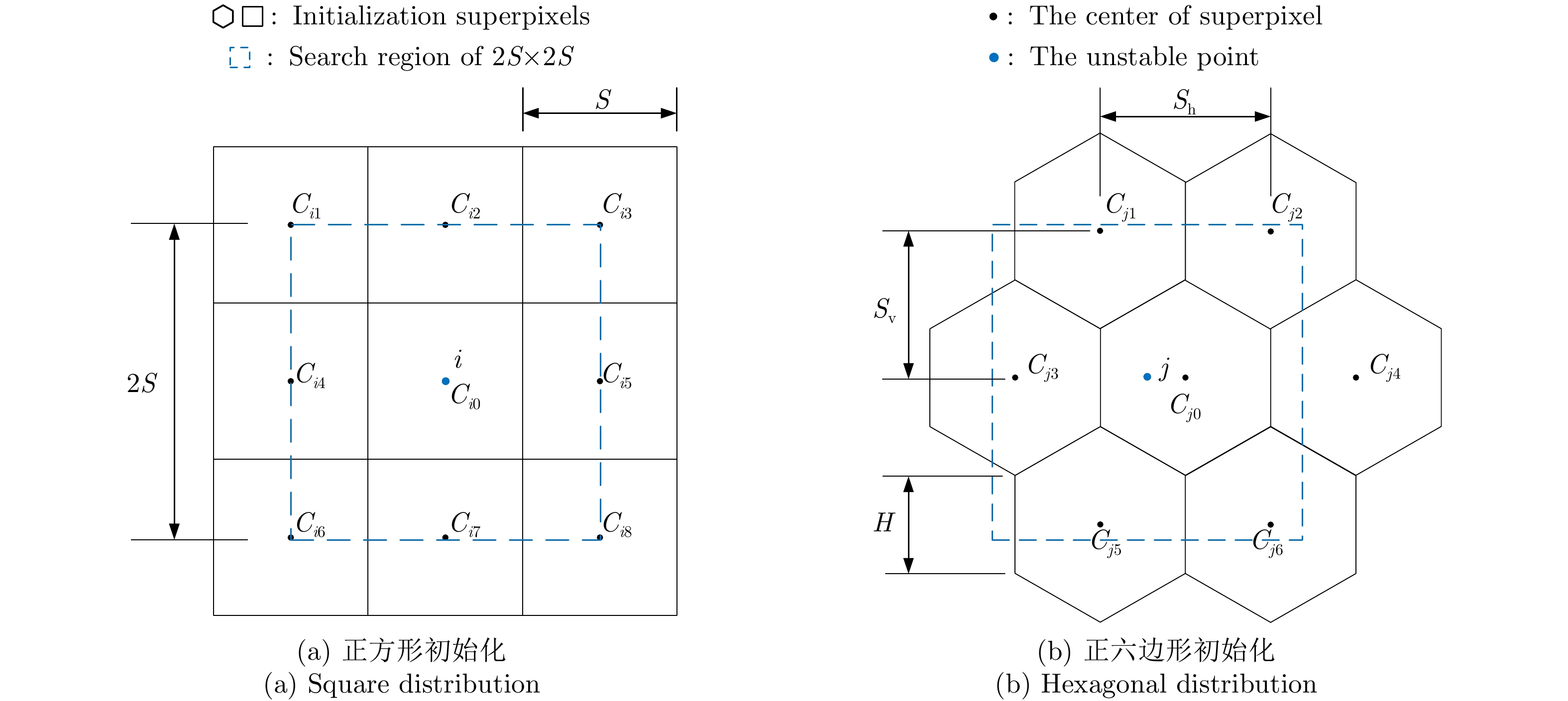
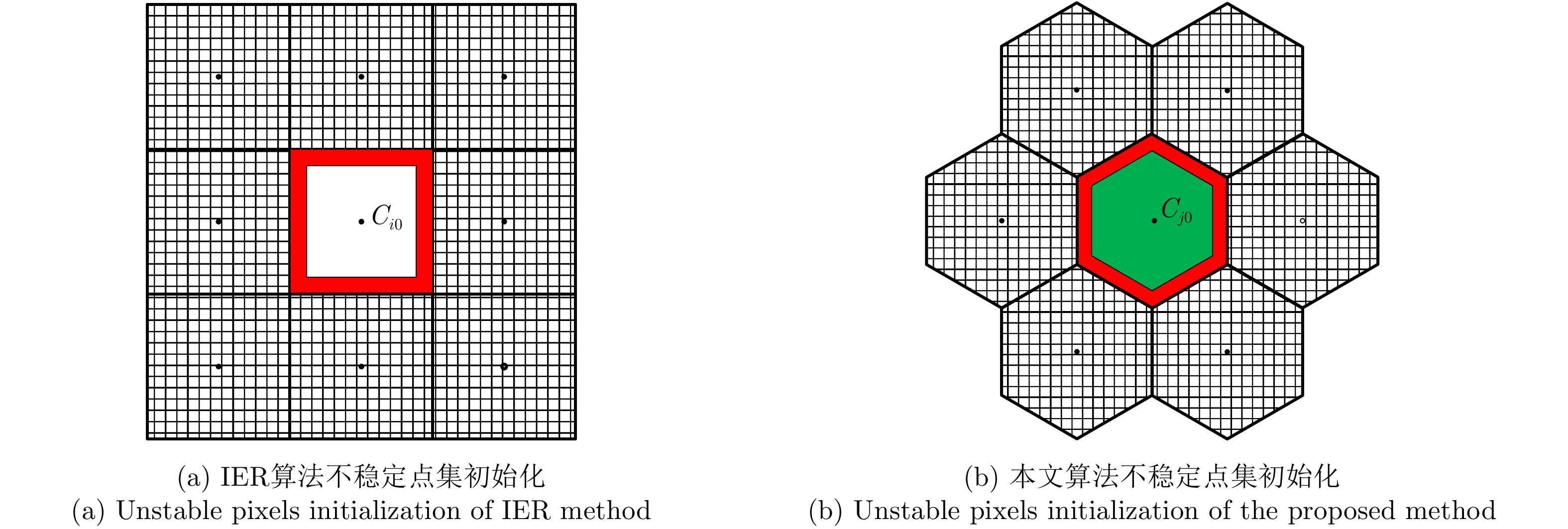
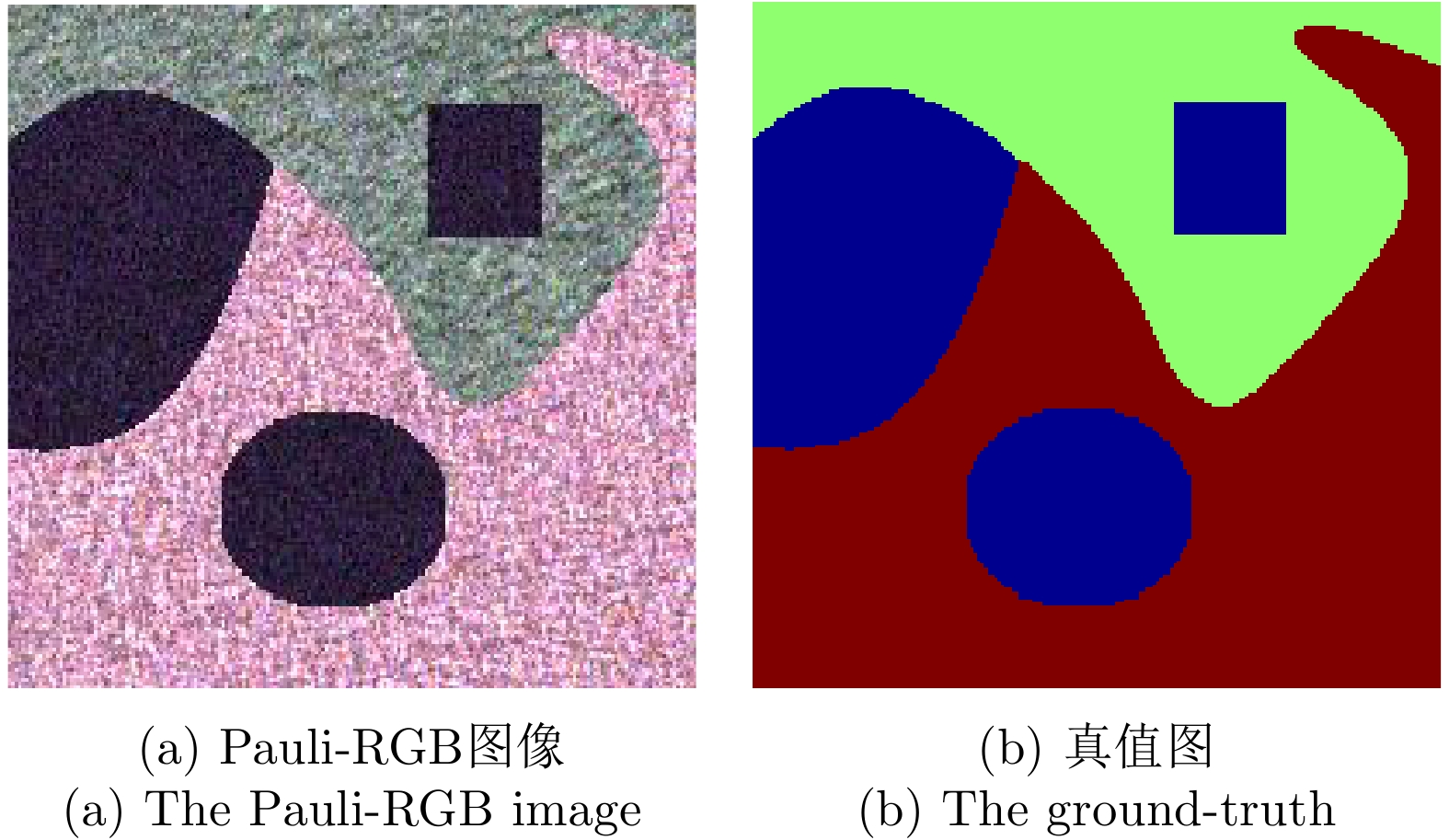
| [1] |
邹焕新, 罗天成, 张月, 等. 基于组合条件随机场的极化SAR图像监督地物分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 541–553. doi: 10.12000/JR16109ZOU Huanxin, LUO Tiancheng, ZHANG Yue, et al. Combined conditional random fields model for supervised PolSAR images classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 541–553. doi: 10.12000/JR16109 |
| [2] |
邹焕新, 李美霖, 马倩, 等. 一种基于张量积扩散的非监督极化SAR图像地物分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057ZOU Huanxin, LI Meilin, MA Qian, et al. An unsupervised PolSAR image classification algorithm based on tensor product graph diffusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057 |
| [3] |
STUTZ D, HERMANS A, and LEIBE B. Superpixels: An evaluation of the state-of-the-art[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2018, 166: 1–27. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2017.03.007 |
| [4] |
LI Meilin, ZOU Huanxin, MA Qian, et al. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR image based on tensor product graph diffusion[C]. The Fourth International Workshop on Pattern Recognition, Nanjing, China, 2019: 11198.
|
| [5] |
TIRANDAZ Z, AKBARIZADEH G, and KAABI H. PolSAR image segmentation based on feature extraction and data compression using weighted neighborhood filter bank and hidden Markov random field-expectation maximization[J]. Measurement, 2020, 153: 107432. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107432 |
| [6] |
SONG Wanying, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. Superpixel-based hybrid discriminative random field for fast PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 24547–24558. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899116 |
| [7] |
LIN Huiping, BAO Junliang, YIN Junjun, et al. Superpixel segmentation with boundary constraints for polarimetric SAR images[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 6195–6198.
|
| [8] |
LANG Fengkai, YANG Jie, LI Deren, et al. Mean-shift-based speckle filtering of polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4440–4454. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282036 |
| [9] |
LANG Fengkai, YANG Jie, YAN Shiyong, et al. Superpixel segmentation of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images based on generalized mean shift[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1592. doi: 10.3390/rs10101592 |
| [10] |
LIU Mingyu, TUZEL O, RAMALINGAM S, et al. Entropy rate superpixel segmentation[C]. CVPR 2011, Providence, USA, 2011: 2097–2104.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Yuhang, HARTLEY R, MASHFORD J, et al. Superpixels via pseudo-Boolean optimization[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1387–1394.
|
| [12] |
LEVINSHTEIN A, STERE A, KUTULAKOS K N, et al. TurboPixels: Fast superpixels using geometric flows[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(12): 2290–2297. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.96 |
| [13] |
NOCK R and NIELSEN F. Statistical region merging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(11): 1452–1458. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.110 |
| [14] |
ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 |
| [15] |
LI Zhengqin and CHEN Jiansheng. Superpixel segmentation using linear spectral clustering[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1356–1363.
|
| [16] |
ZHU Song, CAO Danhua, JIANG Shixiong, et al. Fast superpixel segmentation by iterative edge refinement[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(3): 230–232. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.3379 |
| [17] |
FENG Jilan, CAO Zongjie, and PI Yiming. Polarimetric contextual classification of PolSAR images using sparse representation and superpixels[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(8): 7158–7181. doi: 10.3390/rs6087158 |
| [18] |
XIANG Deliang, NI W, ZHANG H, et al. Superpixel segmentation for PolSAR images with local iterative clustering and heterogeneous statistical model[C]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Wuhan, China, 2017: 499–506.
|
| [19] |
HOU Biao, YANG Chen, REN Bo, et al. Decomposition-feature-iterative-clustering-based superpixel segmentation for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(8): 1239–1243. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2833492 |
| [20] |
张月, 邹焕新, 邵宁远, 等. 一种用于极化SAR图像的快速超像素分割算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 564–573. doi: 10.12000/JR17018ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, SHAO Ningyuan, et al. Fast superpixel segmentation algorithm for PolSAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 564–573. doi: 10.12000/JR17018 |
| [21] |
RATHA D, DE S, CELIK T, et al. Change detection in polarimetric SAR images using a geodesic distance between scattering mechanisms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1066–1070. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2696158 |
| [22] |
RATHA D, BHATTACHARYA A, and FRERY A C. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR data using a scattering similarity measure derived from a geodesic distance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2778749 |
| [23] |
NAKAHARA M. Geometry, Topology and Physics[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press, 2003.
|
| [24] |
王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 |
| [25] |
YOU Biao, YANG Jian, YIN Junjun, et al. Decomposition of the Kennaugh matrix based on a new norm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(5): 1000–1004. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2284336 |
| [26] |
QIN Fachao, GUO Jiming, and LANG Fengkai. Superpixel segmentation for polarimetric SAR imagery using local iterative clustering[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 13–17. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2322960 |
| [27] |
VASILE G, TROUVÉ E, LEE J S, et al. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1609–1621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.864142 |
| [28] |
QIN Xianxiang, ZOU Huanxin, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Simulation of spatially correlated PolSAR images using inverse transform method[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2015, 9(1): 095082. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.9.095082 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

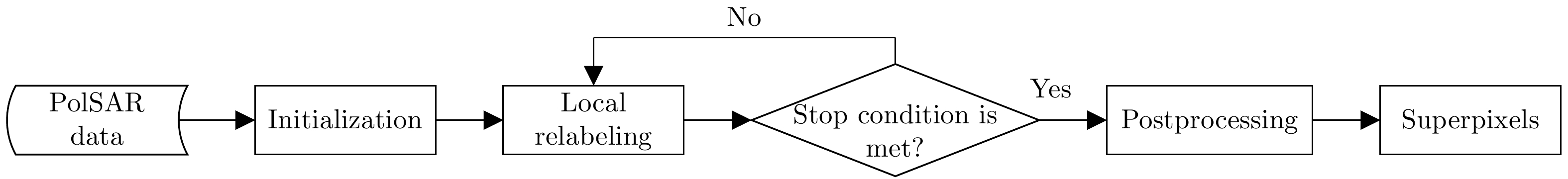



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: