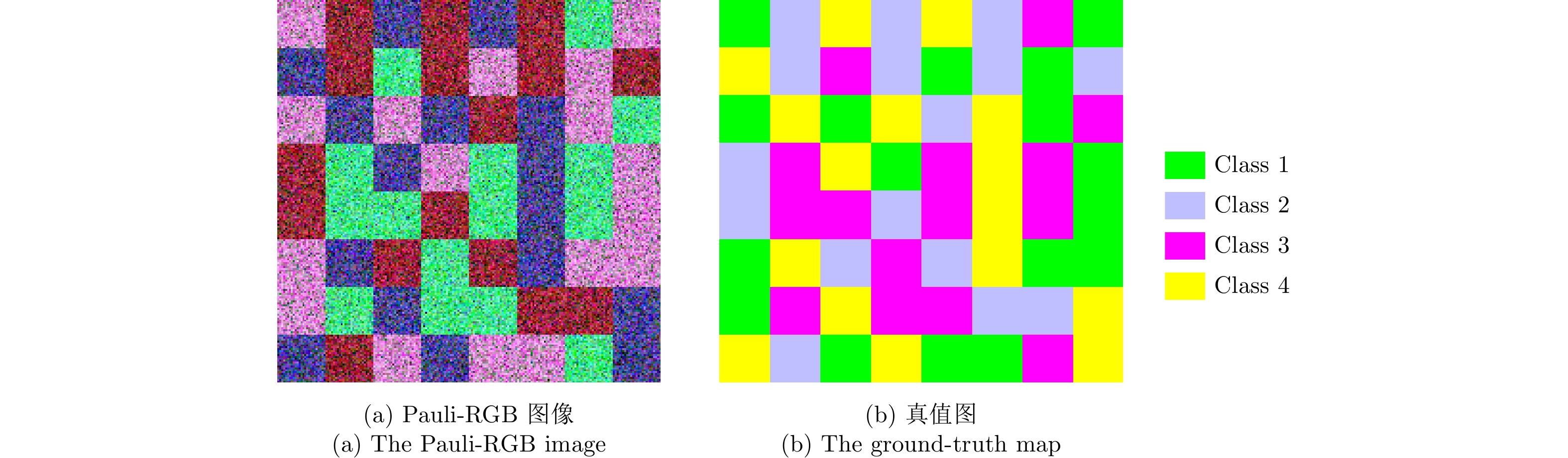
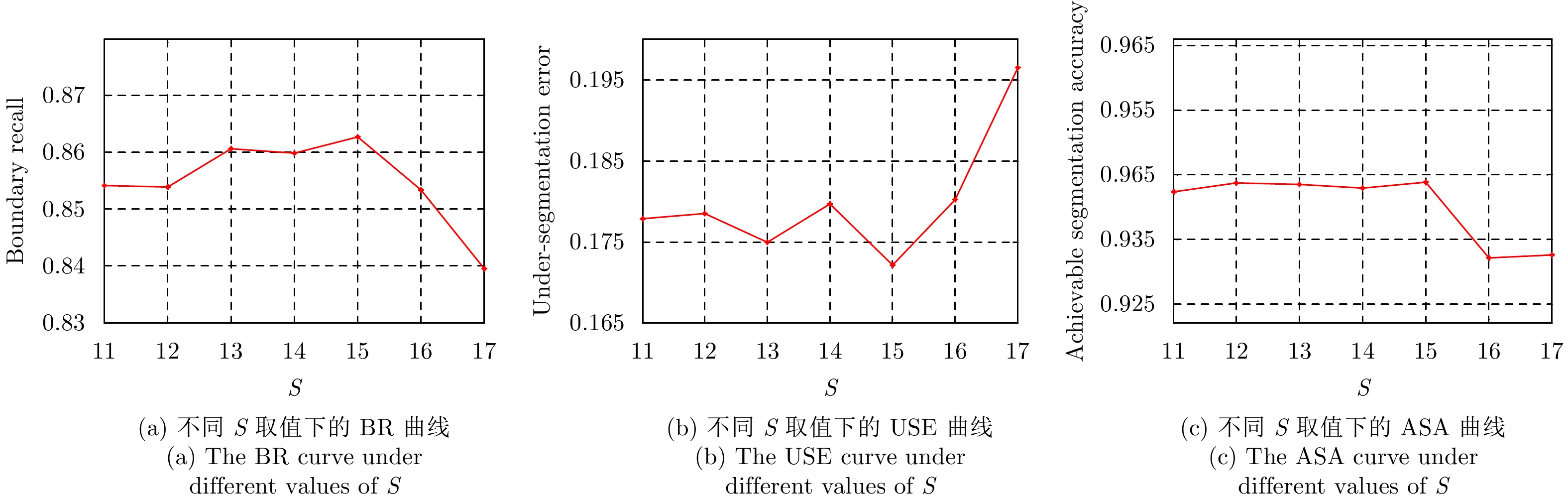
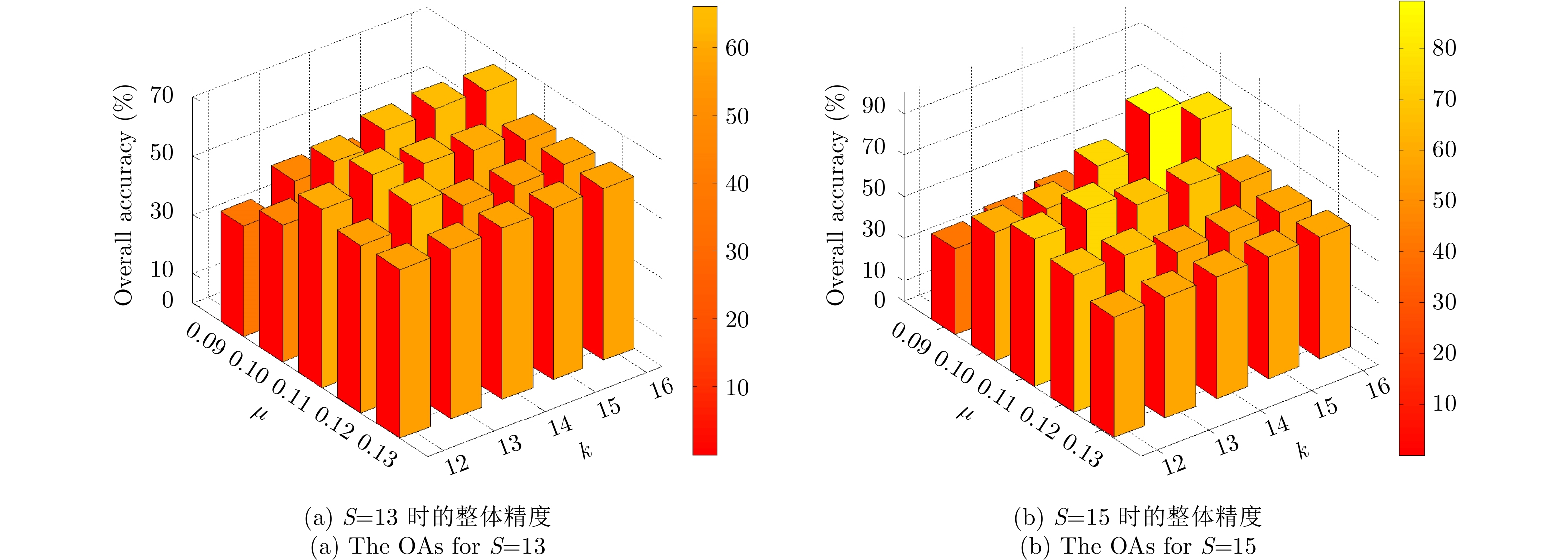
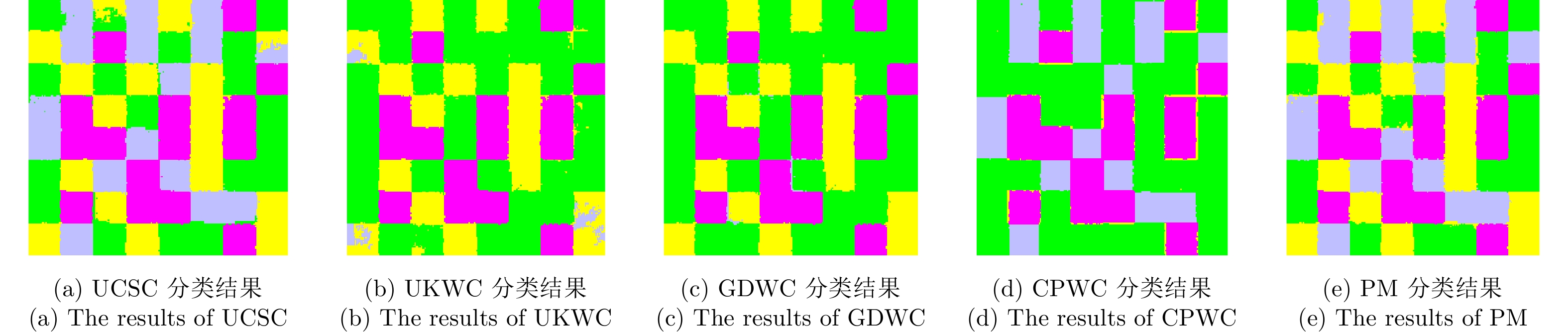
| [1] |
SHI Lei, ZHANG Lefei, ZHAO Lingli, et al. Adaptive Laplacian Eigenmap-based dimension reduction for ocean target discrimination[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(7): 902–906. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2553046 |
| [2] |
杨文, 钟能, 严天恒, 等. 基于黎曼流形的极化SAR图像分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 433–441. doi: 10.12000/JR17031YANG Wen, ZHONG Neng, YAN Tianheng, et al. Classification of polarimetric SAR images based on the Riemannian manifold[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 433–441. doi: 10.12000/JR17031 |
| [3] |
LIU Wensong, YANG Jie, LI Pingxiang, et al. A novel object-based supervised classification method with active learning and random forest for PolSAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(7): 1092. doi: 10.3390/rs10071092 |
| [4] |
SHI Lei, ZHANG Lefei, ZHAO Lingli, et al. The potential of linear discriminative Laplacian Eigenmaps dimensionality reduction in polarimetric SAR classification for agricultural areas[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 86: 124–135. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.09.013 |
| [5] |
WANG Shuang, LIU Kun, PEI Jingjing, et al. Unsupervised classification of fully polarimetric SAR images based on scattering power entropy and copolarized ratio[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(3): 622–626. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2216249 |
| [6] |
LEE J S, GRUNES M R, POTTIER E, et al. Unsupervised terrain classification preserving polarimetric scattering characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(4): 722–731. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.819883 |
| [7] |
RATHA D, BHATTACHARYA A, and FRERY A C. Unsupervised classification of polsar data using a scattering similarity measure derived from a geodesic distance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2778749 |
| [8] |
LEE J S, GRUNES M R, AINSWORTH T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258. doi: 10.1109/36.789621 |
| [9] |
钟能, 杨文, 杨祥立, 等. 基于混合Wishart模型的极化SAR图像非监督分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 533–540. doi: 10.12000/JR16133ZHONG Neng, YANG Wen, YANG Xiangli, et al. Unsupervised classification for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on Wishart mixture models[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 533–540. doi: 10.12000/JR16133 |
| [10] |
WU Yonghui, JI Kefeng, YU Wenxian, et al. Region-based classification of polarimetric SAR images using Wishart MRF[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 668–672. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2002263 |
| [11] |
VON LUXBURG U. A tutorial on spectral clustering[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2007, 17(4): 395–416. doi: 10.1007/s11222-007-9033-z |
| [12] |
YANG Yifang, WANG Yuping, XUE Xingsi, et al. A novel spectral clustering method with superpixels for image segmentation[J]. Optik, 2016, 127(1): 161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.10.053 |
| [13] |
HU Jingliang, WANG Yuanyuan, GHAMISI P, et al. Evaluation of polsar similarity measures with spectral clustering[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 3254–3257.
|
| [14] |
LI Yonggang, ZHANG Shichao, CHENG Debo, et al. Spectral clustering based on hypergraph and self-re-presentation[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(16): 17559–17576. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-4131-6 |
| [15] |
YANG Xingwei, PRASAD L, and JAN LATECKI L. Affinity learning with diffusion on tensor product graph[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 28–38. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.60 |
| [16] |
ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, LUO Tiancheng, et al. A fast superpixel segmentation algorithm for PolSAR images based on edge refinement and revised Wishart distance[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1687. doi: 10.3390/s16101687 |
| [17] |
CAO Fang, HONG Wen, WU Yirong, et al. An unsupervised segmentation with an adaptive number of clusters using the SPAN/H/α/A space and the complex Wishart clustering for fully polarimetric SAR data analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(11): 3454–3467. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907601 |
| [18] |
ZHOU Xiaofeng, WANG Shuang, HUA Wenqiang, et al. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR data based on a novel polarization feature[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 4594–4599.
|
| [19] |
ZHANG Yue, ZOU Huanxin, SHAO Ningyuan, et al. Terrain classification of polarimetric SAR images based on consensus similarity network fusion[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(2): 295–302. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.02.09 |
| [20] |
FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 |
| [21] |
CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127 |
| [22] |
YANG Xingwei, SZYLD D B, and JAN LATECKI L. Diffusion on a tensor product graph for semi-supervised learning and interactive image segmentation[J]. Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, 2011, 169: 147–172. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385981-5.00004-5 |
| [23] |
VAN LOAN C F. The ubiquitous Kronecker product[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2000, 123(1/2): 85–100.
|
| [24] |
QIN Xianxiang, ZOU Huanxin, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Simulation of spatially correlated PolSAR images using inverse transform method[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2015, 9(1): 095082. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.9.095082 |
| [25] |
HOU Biao, WU Qian, WEN Zaidao, et al. Robust semisupervised classification for PolSAR image with noisy labels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6440–6455. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2728186 |
| [26] |
SONG Wanying, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. Unsupervised PolSAR image classification and segmentation using Dirichlet process mixture model and Markov random fields with similarity measure[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3556–3568. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2684301 |
| [27] |
VASILE G, TROUVÉ E, LEE J S, et al. Intensity-driven adaptive-neighborhood technique for polarimetric and interferometric SAR parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(6): 1609–1621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.864142 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: