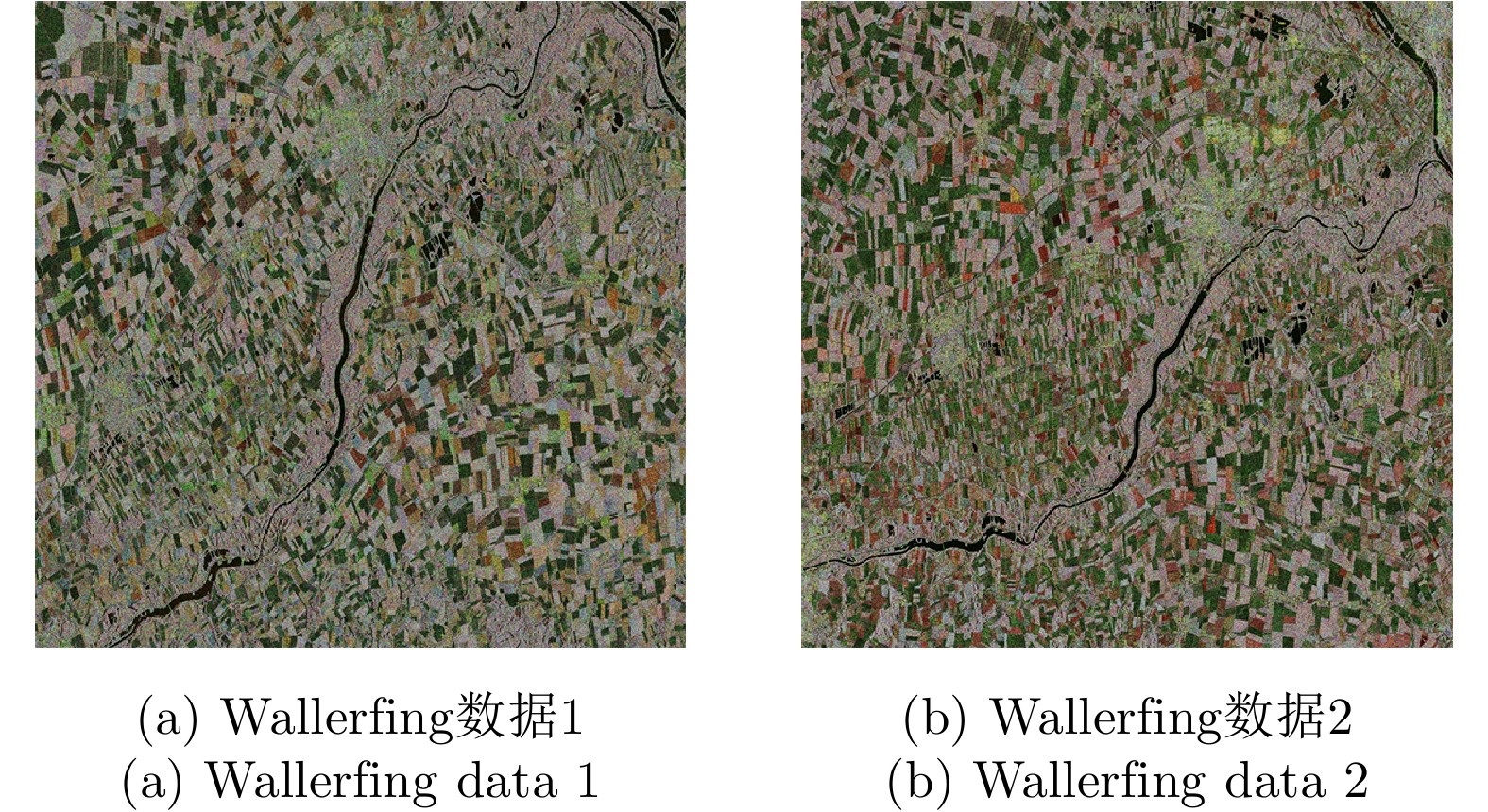
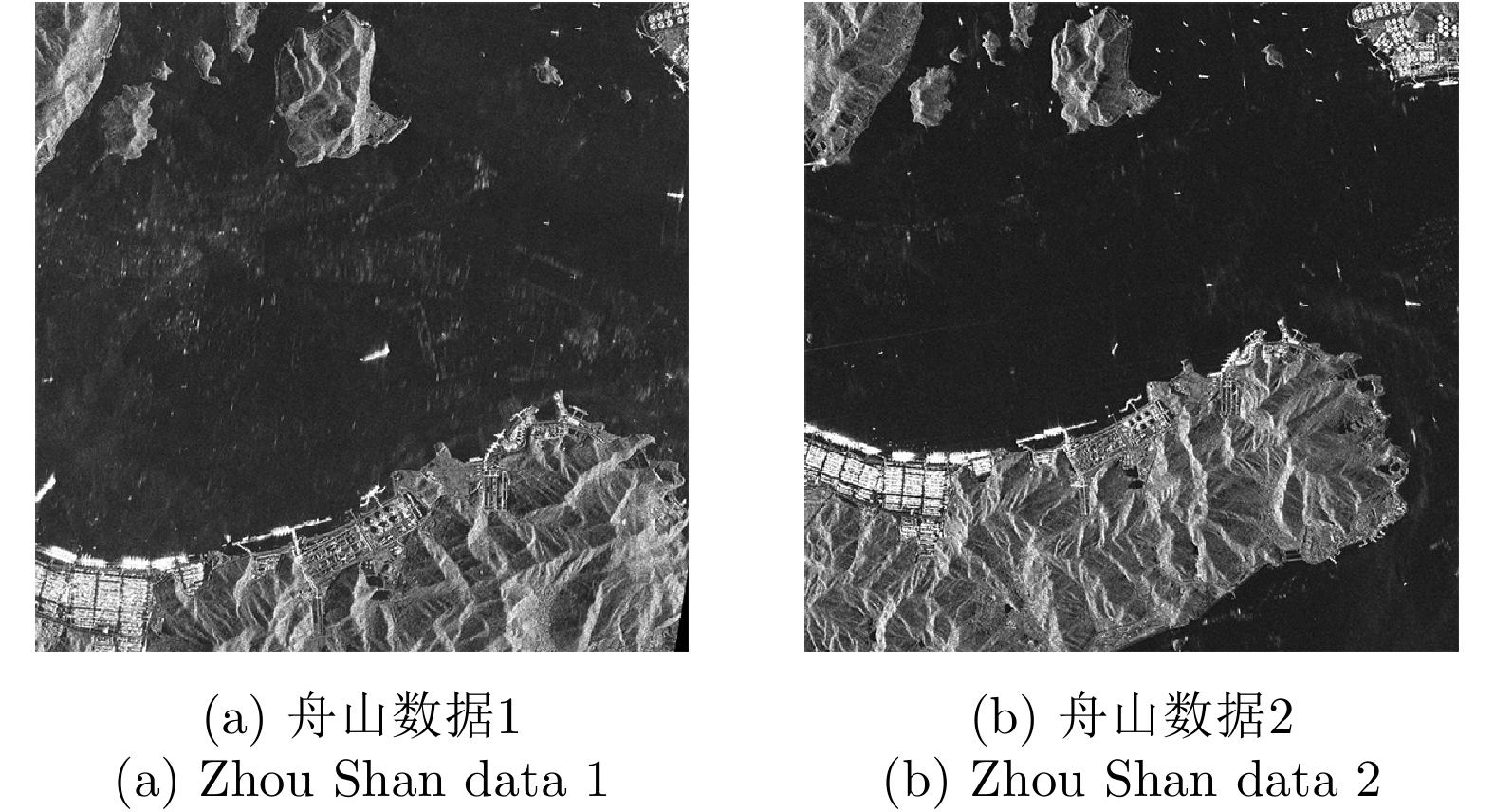
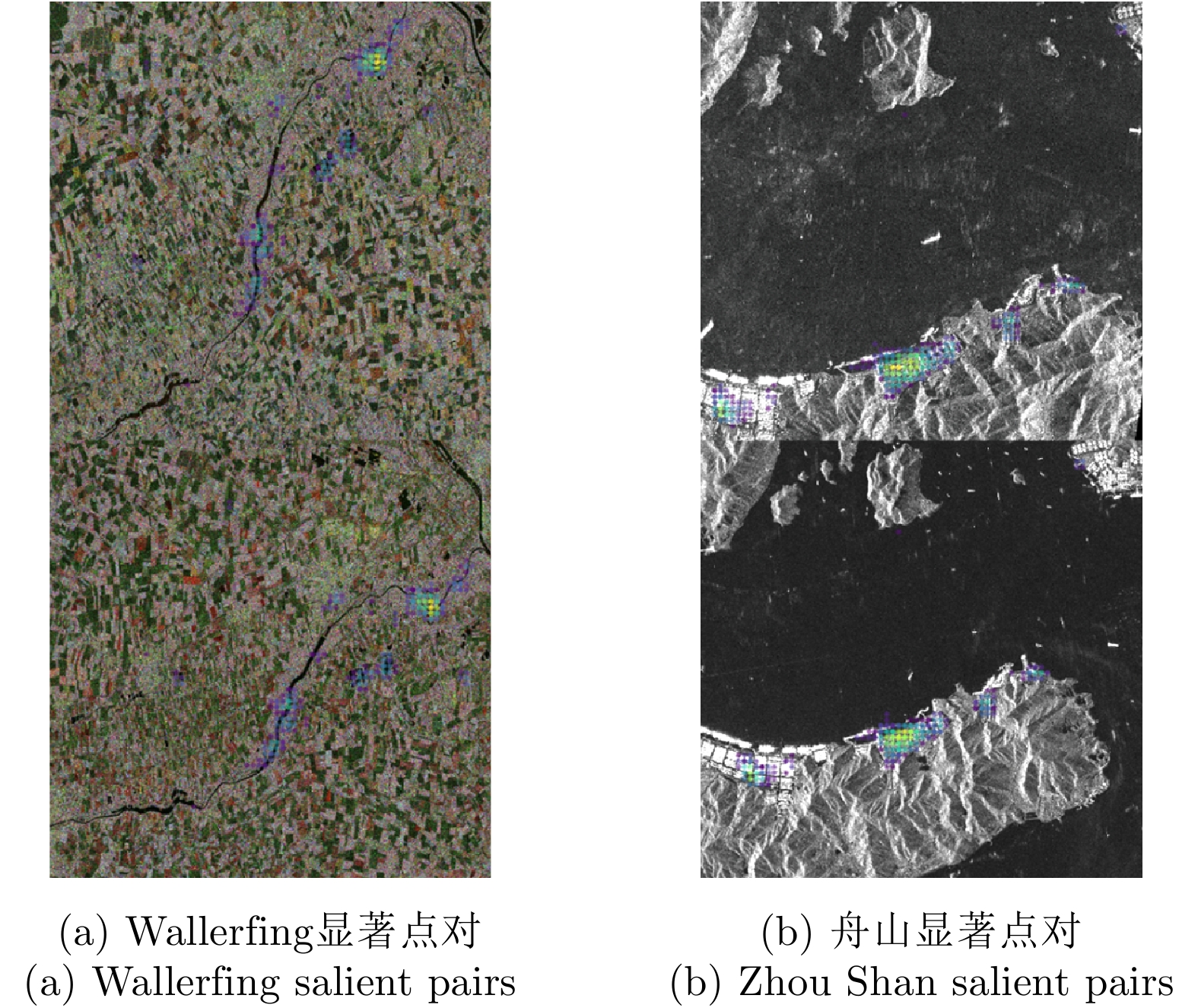
| [1] |
WANG Shuang, QUAN Dou, LIANG Xuefeng, et al. A deep learning framework for remote sensing image registration[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2018, 145: 148–164. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.12.012 |
| [2] |
YANG Zhuoqian, DAN Tingting, and YANG Yang. Multi-temporal remote sensing image registration using deep convolutional features[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 38544–38555. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853100 |
| [3] |
SARVAIYA J N, PATNAIK S, and BOMBAYWALA S. Image registration by template matching using normalized cross-correlation[C]. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, Trivandrum, India, 2009: 819–822. doi: 10.1109/ACT.2009.207. |
| [4] |
GAN Rui, WU Jue, CHUNG A C S, et al. Multiresolution image registration based on Kullback-Leibler distance[C]. The 7th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Saint-Malo, France, 2004: 599–606. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-30135-6_73. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Tao, WANG Zhengyong, ZHANG Ying, et al. Image registration techniques based on harmony search algorithm[J]. Video Engineering, 2014, 38(7): 9–12. doi: 10.16280/j.videoe.2014.07.032 |
| [6] |
AVERBUCH A and KELLER Y. FFT based image registration[C]. 2002 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, USA, 2002: IV-3608–IV-3611. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2002.5745436. |
| [7] |
HARRIS C and STEPHENS M. A combined corner and edge detector[C]. The 4th Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 1988. doi: 10.5244/C.2.23. |
| [8] |
LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 |
| [9] |
WANG Yufan, YU Qiuze, and YU Wenxian. An improved normalized cross correlation algorithm for SAR image registration[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 2086–2089. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6350961. |
| [10] |
DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552 |
| [11] |
MA Wenping, WEN Zelian, WU Yue, et al. Remote sensing image registration with modified SIFT and enhanced feature matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600858 |
| [12] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105.
|
| [13] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 |
| [14] |
JIN Kan, CHEN Yilun, XU Bin, et al. A patch-to-pixel convolutional neural network for small ship detection with PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6623–6638. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2978268 |
| [15] |
DETONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, and RABINOVICH A. Deep image homography estimation[J]. arXiv: 1606.03798, 2016.
|
| [16] |
ROCCO I, ARANDJELOVIC R, and SIVIC J. Convolutional neural network architecture for geometric matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(11): 2553–2567. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865351 |
| [17] |
BALAKRISHNAN G, ZHAO A, SABUNCU M R, et al. VoxelMorph: A learning framework for deformable medical image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(8): 1788–1800. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2897538 |
| [18] |
ROCCO I, CIMPOI M, ARANDJELOVIĆ R, et al. Neighbourhood consensus networks[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 1651–1662.
|
| [19] |
ROCCO I, ARANDJELOVIĆ R, and SIVIC J. Efficient neighbourhood consensus networks via submanifold sparse convolutions[J]. arXiv: 2004.10566, 2020.
|
| [20] |
HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4700–4708.
|
| [21] |
CHOY C, GWAK J Y, and SAVARESE S. 4D Spatio-temporal Convnets: Minkowski convolutional neural networks[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3075–3084.
|
| [22] |
YANG Yi and RAMANAN D. Articulated human detection with flexible mixtures of parts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(12): 2878–2890. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.261 |
| [23] |
魏天华. 基于多核DSP的加速SAR-SIFT算法并行计算设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.
WEI Tianhua. Parallel calculation of speed-up SAR-SIFT algorithm based on multi-score DSP[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: