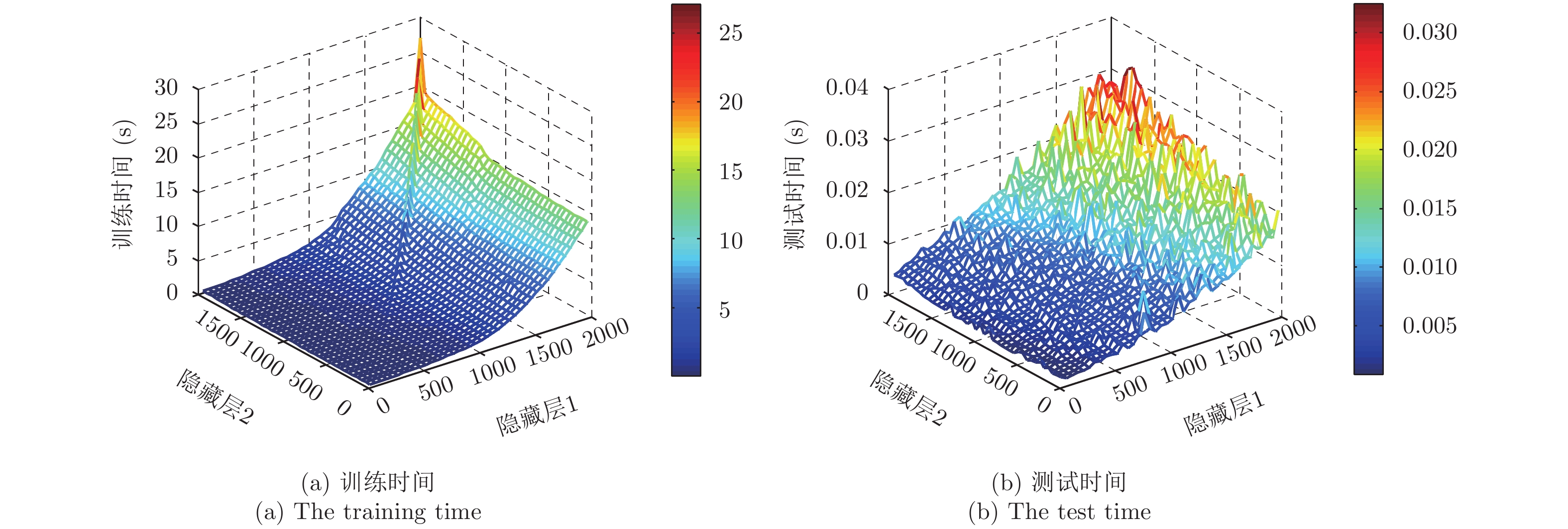
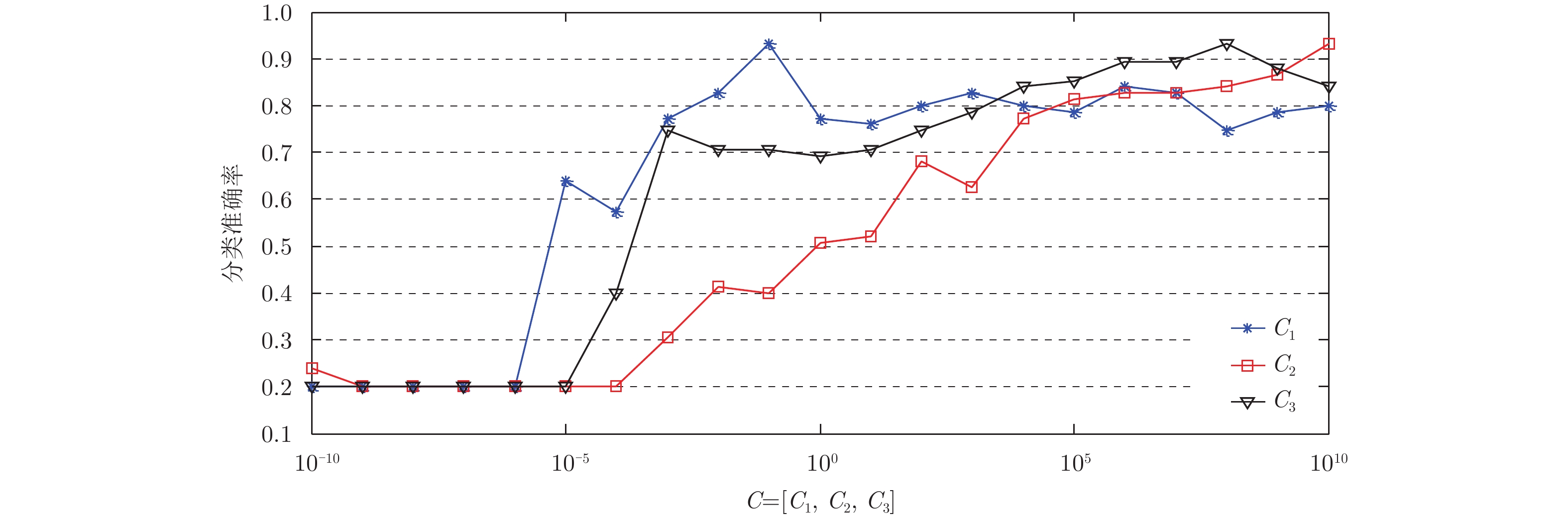
| [1] |
Liu Y X, Zhu D K, Li X, et al. Micromotion characteristic acquisition based on wideband radar phase[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3650–3657. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2274478 |
| [2] |
Bigdeli B and Pahlavani P. Quad-polarized synthetic aperture radar and multispectral data classification using classification and regression tree and support vector machine-based data fusion system[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2017, 11(1): 016007. DOI: 10.1117/1.JRS.11.016007 |
| [3] |
Shi J F, Li L L, Liu F, et al. Unsupervised polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image classification based on sketch map and adaptive Markov random field[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(2): 025008. DOI: 10.1117/1.JRS.10.025008 |
| [4] |
Hinton G E and Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504–507. DOI: 10.1126/science.1127647 |
| [5] |
Lecun Y, Bengio Y, and Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. DOI: 10.1038/nature14539 |
| [6] |
Zhao F X, Liu Y X, Huo K, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on stacked autoencoder and extreme learning machine[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 173. DOI: 10.3390/s18010173 |
| [7] |
Abdel-Hamid O, Mohamed A R, Jiang H, et al. Convolutional neural networks for speech recognition[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(10): 1533–1545. DOI: 10.1109/TASLP.2014.2339736 |
| [8] |
Ding J, Chen B, Liu H W, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2513754 |
| [9] |
Wang X L, Guo R, and Kambhamettu C. Deeply-learned feature for age estimation[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2015: 534–541. DOI: 10.1109/WACV.2015.77. |
| [10] |
Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, and Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1/3): 489–501. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 |
| [11] |
Huang G, Huang G B, Song S J, et al. Trends in extreme learning machines: A review[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 32–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.10.001 |
| [12] |
Liang N Y, Huang G B, Saratchandran P, et al. A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2006, 17(6): 1411–1423. DOI: 10.1109/TNN.2006.880583 |
| [13] |
Zong W W and Huang G B. Face recognition based on extreme learning machine[J]. Neurocomputing, 2011, 74(16): 2541–2551. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2010.12.041 |
| [14] |
Liu N and Wang H. Evolutionary extreme learning machine and its application to image analysis[J]. Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2013, 73(1): 73–81. DOI: 10.1007/s11265-013-0730-x |
| [15] |
Ding S F, Zhang N, Zhang J, et al. Unsupervised extreme learning machine with representational features[J]. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2017, 8(2): 587–595. DOI: 10.1007/s13042-015-0351-8 |
| [16] |
Zhao F X, Liu Y X, Huo K, et al. Radar target classification using an evolutionary extreme learning machine based on improved quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017: 7273061. DOI: 10.1155/2017/7273061 |
| [17] |
Kasun L L C, Zhou H M, Huang G B, et al. Representational learning with ELMs for big data[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2013, 28(6): 31–34.
|
| [18] |
Yu W C, Zhuang F Z, He Q, et al. Learning deep representations via extreme learning machines[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 149: 308–315. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.03.077 |
| [19] |
Zhu W T, Miao J, Qing L Y, et al.. Hierarchical extreme learning machine for unsupervised representation learning[C]. Proceedings of 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Killarney, Ireland, 2015: 1–8. DOI: 10.1109/IJCNN.2015.7280669. |
| [20] |
Tang J X, Deng C W, and Huang G B. Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(4): 809–821. DOI: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2424995 |
| [21] |
Hinton G E, Srivastava N, Krizhevsky A, et al.. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580.2012.07.
|
| [22] |
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929–1958.
|
| [23] |
Iosifidis A, Tefas A, and Pitas I. DropELM: Fast neural network regularization with dropout and dropconnect[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 162: 57–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.04.006 |
| [24] |
Baldi P and Sadowski P. The dropout learning algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 2014, 201: 78–122.
|
| [25] |
Wager S, Wang S D, and Liang P. Dropout training as adaptive regularization[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 2013: 351–359.
|
| [26] |
Yang W X, Jin L W, Tao D C, et al. DropSample: A new training method to enhance deep convolutional neural networks for large-scale unconstrained handwritten Chinese character recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 58: 190–203. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.04.007 |
| [27] |
Baldi P and Sadowski P. Understanding dropout[C]. Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 2013: 2814–2822.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: