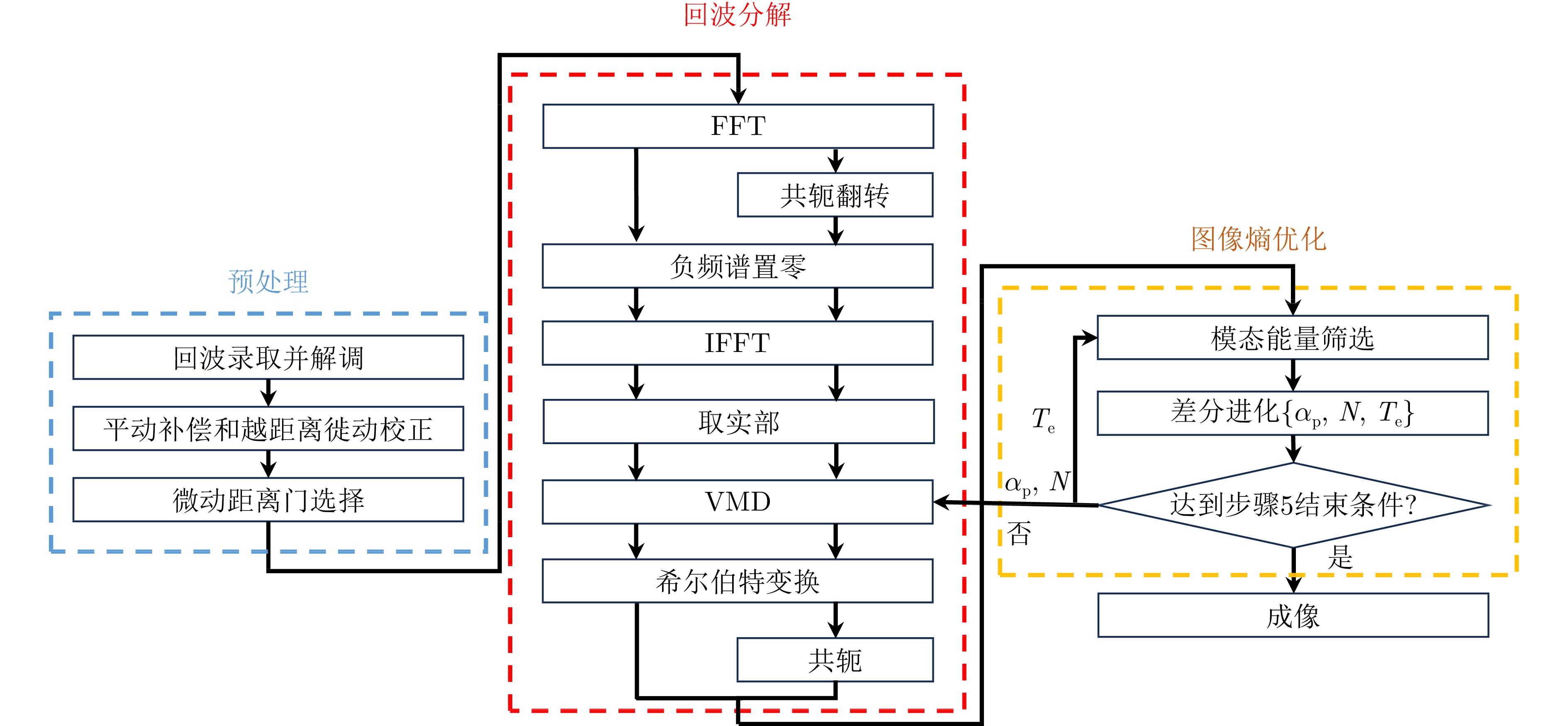
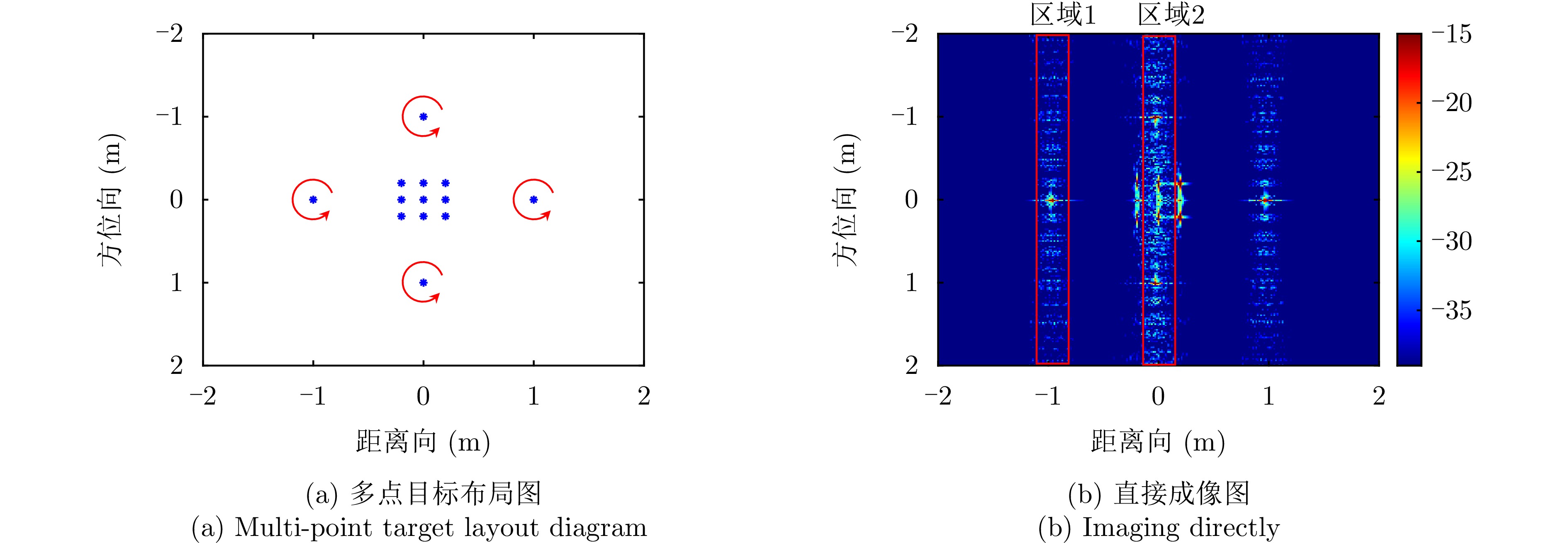
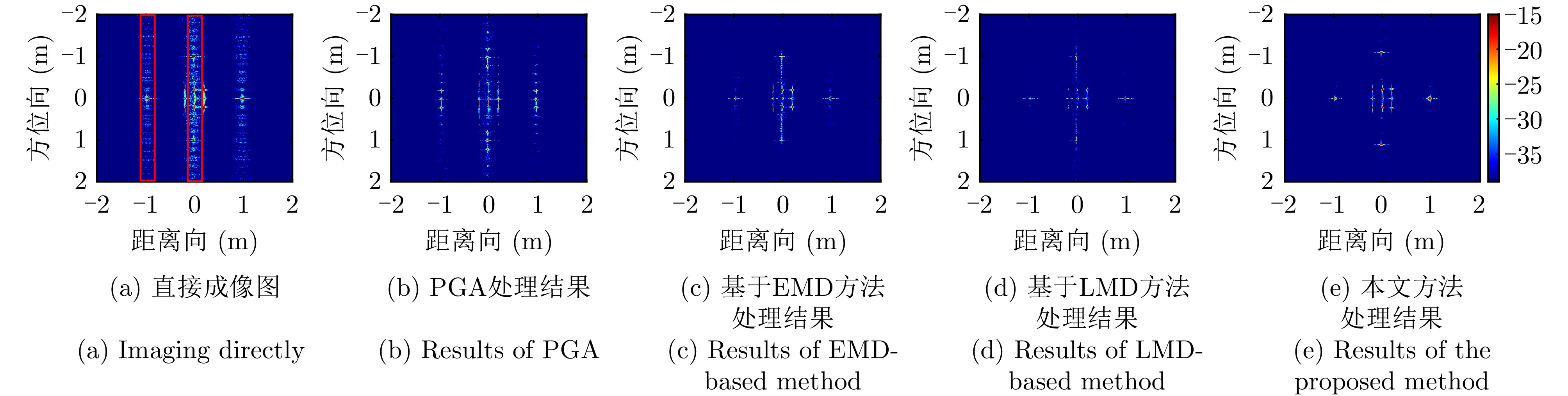
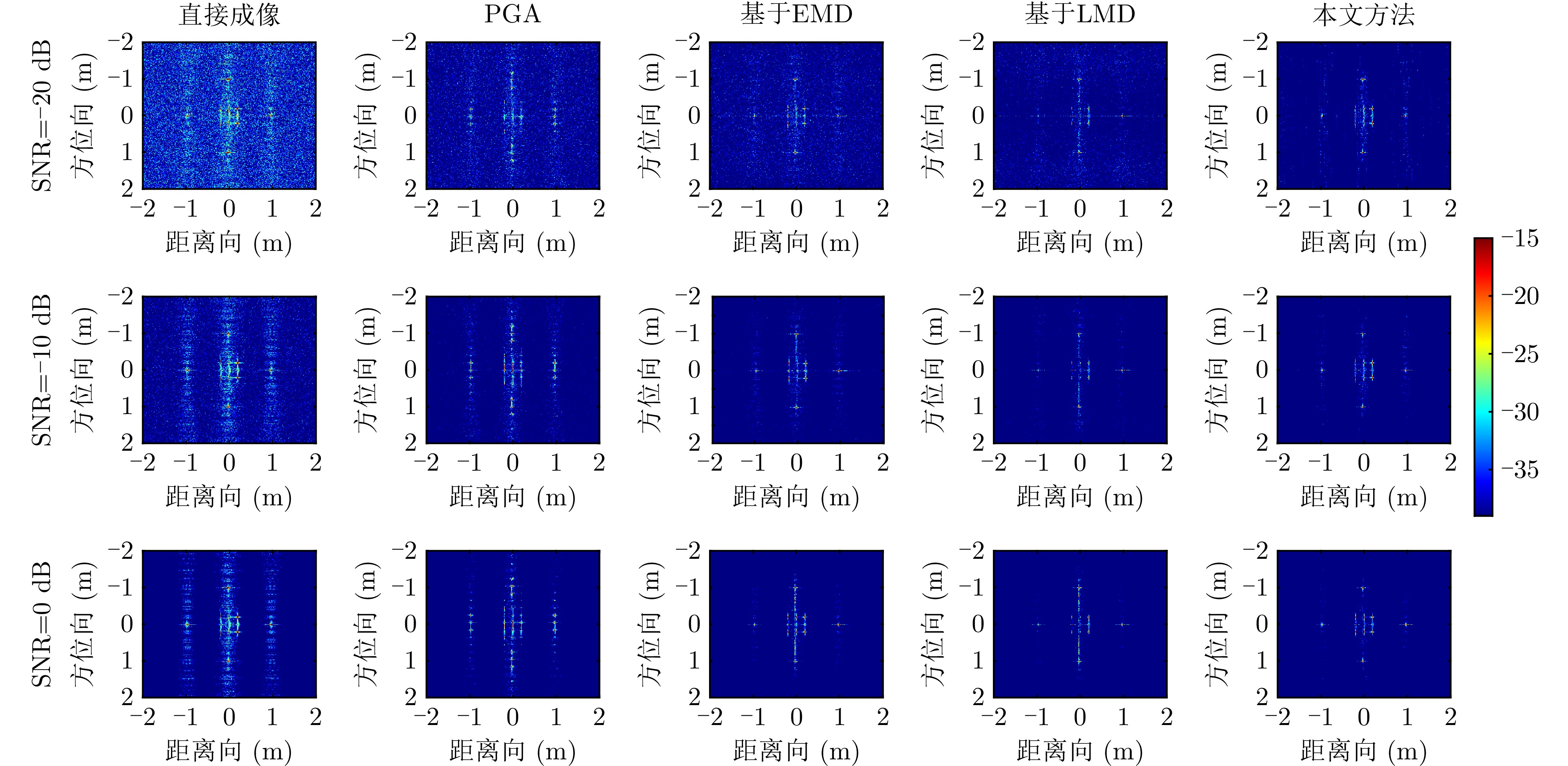
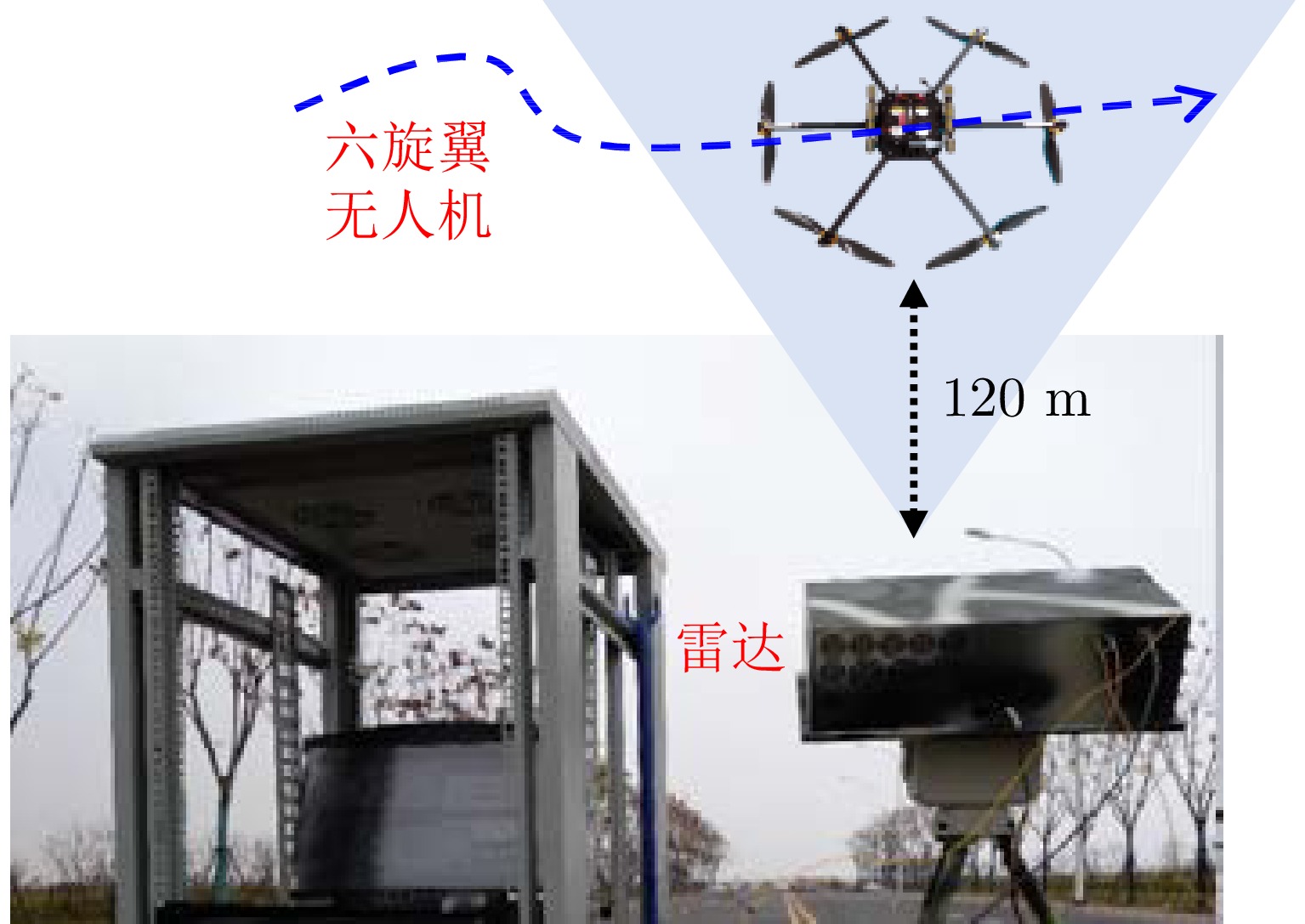
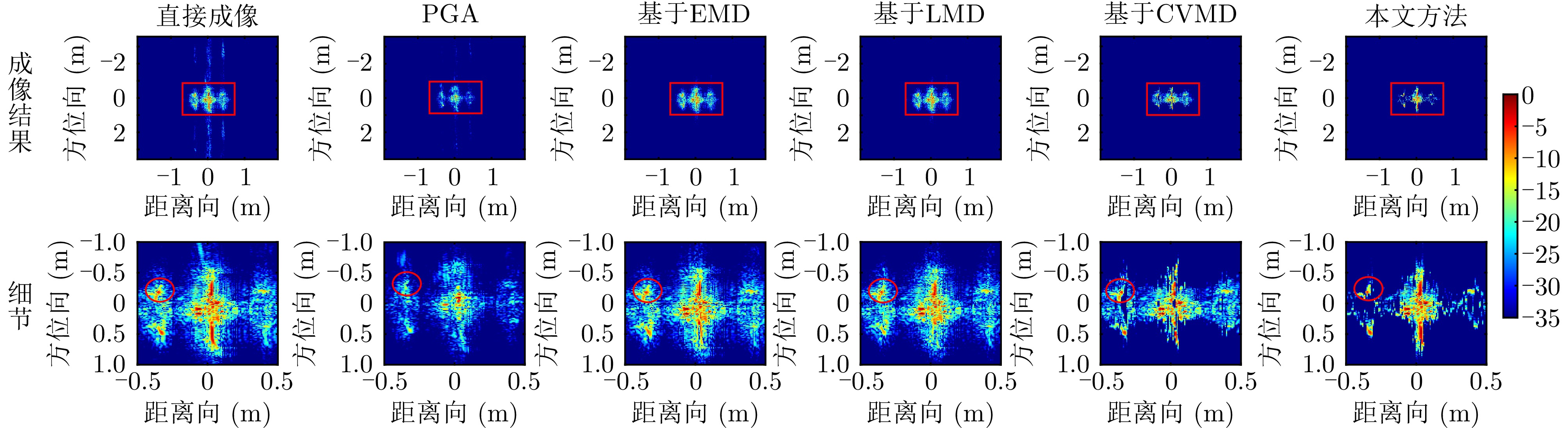
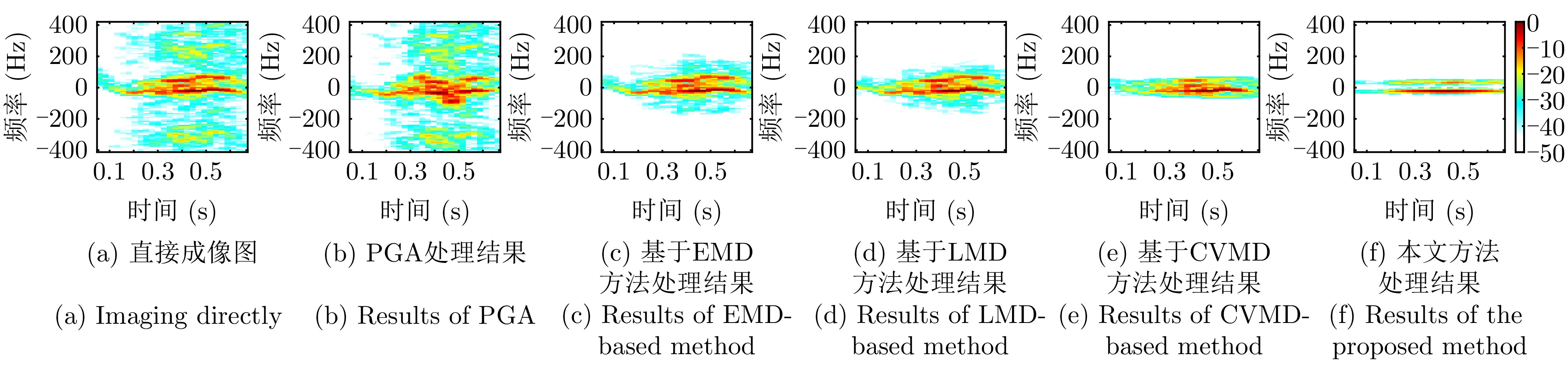
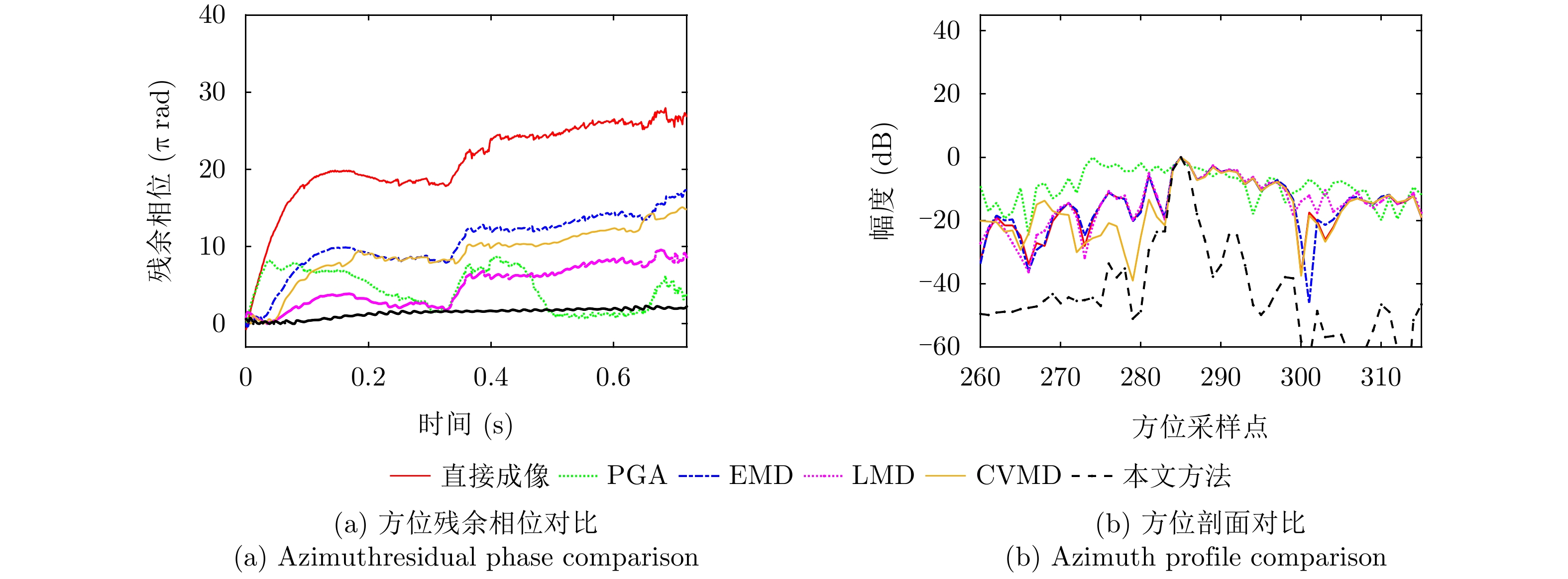
| [1] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 239–241.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 239–241.
|
| [2] |
李源. 逆合成孔径雷达理论与对抗[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: 48–55.
LI Yuan. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Theory and Confrontation[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: 48–55.
|
| [3] |
YANG Jianyu. Development laws and macro trends analysis of radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 19–27. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20010. |
| [4] |
张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049. ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049. |
| [5] |
LIU Zheng and SUN Huixia. Micro-Doppler analysis and application of radar targets[C]. IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Changsha, China, 2008: 1343–1347. doi: 10.1109/ICINFA.2008.4608210. |
| [6] |
ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, and HE Jin. Overview of research on micro-Doppler effect of radar targets[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2011, 12(2): 22–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2011.02.005. |
| [7] |
CHEN V C. Analysis of radar micro-Doppler with time-frequency transform[C]. The 10th IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing, Pocono Manor, USA, 2000: 463–466. doi: 10.1109/SSAP.2000.870167. |
| [8] |
WANG Anle, ZHENG Daikun, DU Shirui, et al. Microwave photonic radar system with ultra-flexible frequency-domain tunability[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(9): 13887–13898. doi: 10.1364/OE.423952. |
| [9] |
LUO Xiong, WANG Anle, WO Jianghai, et al. Microwave photonic video imaging radar with widely tunable bandwidth for monitoring diverse airspace targets[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 451: 296–300. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.06.073. |
| [10] |
CHEN V C, TAHMOUSH D, and MICELI W J. Radar Micro-Doppler Signatures: Processing and Applications[M]. Stevenage: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2014: 187–225. doi: 10.1049/pbra034e. |
| [11] |
CHEN V C, LI Fayin, HO S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402. |
| [12] |
TUSZYNSKI M, WOJTKIEWICZ A, and KLEMBOWSKI W. Bimodal clutter MTI filter for staggered PRF radars[C]. IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 176–180. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.1990.201158. |
| [13] |
万显荣, 谢德强, 易建新, 等. 基于STFT谱图滑窗相消的微动杂波去除方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 794–804. doi: 10.12000/JR22157. WAN Xianrong, XIE Deqiang, YI Jianxin, et al. Micro-Doppler clutter removal method based on the cancelation of sliding STFT spectrogram[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 794–804. doi: 10.12000/JR22157. |
| [14] |
WANG Yong, ZHOU Xingyu, LU Xiaofei, et al. An approach of motion compensation and ISAR imaging for micro-motion targets[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(1): 68–80. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000008. |
| [15] |
何其芳, 张群, 罗迎, 等. 正弦调频Fourier-Bessel变换及其在微动目标特征提取中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 593–601. doi: 10.12000/JR17069. HE Qifang, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. A sinusoidal frequency modulation Fourier-Bessel transform and its application to micro-Doppler feature extraction[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 593–601. doi: 10.12000/JR17069. |
| [16] |
符吉祥, 邢孟道, 徐丹, 等. 一种基于微波光子超高分辨雷达机翼振动参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 232–242. doi: 10.12000/JR19001. FU Jixiang, XING Mengdao, XU Dan, et al. Vibration-parameters estimation method for airplane wings based on microwave-photonics ultrahigh-resolution radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 232–242. doi: 10.12000/JR19001. |
| [17] |
STANKOVIC L, DJUROVIC I, and THAYAPARAN T. Separation of target rigid body and micro-Doppler effects in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(4): 1496–1506. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.314590. |
| [18] |
LI Kaiming, LIANG Xianjiao, ZHANG Qun, et al. Micro-Doppler signature extraction and ISAR imaging for target with micromotion dynamics[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 411–415. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2081660. |
| [19] |
CHOI I, KANG K, KIM K, et al. Use of ICA to separate micro-Doppler signatures in ISAR images of aircraft that has fast-rotating parts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 234–246. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3098110. |
| [20] |
BAI Xueru, XING Mengdao, ZHOU Feng, et al. Imaging of micromotion targets with rotating parts based on empirical-mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(11): 3514–3523. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002322. |
| [21] |
FLANDRIN P, RILLING G, and GONCALVES P. Empirical mode decomposition as a filter bank[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(2): 112–114. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2003.821662. |
| [22] |
GAO Yunchao, GE Guangtao, SHENG Zhengyan, et al. Analysis and solution to the mode mixing phenomenon in EMD[C]. International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Sanya, China, 2008: 223–227. doi: 10.1109/CISP.2008.193. |
| [23] |
YUAN Bin, CHEN Zengping, and XU Shiyou. Micro-Doppler analysis and separation based on complex local mean decomposition for aircraft with fast-rotating parts in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1285–1298. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2249588. |
| [24] |
DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675. |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
SHAO Shuai. Study on high resolution ISAR imaging and fine motion compensation techniques[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2020.003431. |
| [27] |
YANG Degui, LI Jin, LIANG Buge, et al. A multi-rotor drone micro-motion parameter estimation method based on CVMD and SVD[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(14): 3326. doi: 10.3390/rs14143326. |
| [28] |
DAS S and SUGANTHAN P N. Differential evolution: A survey of the state-of-the-art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 15(1): 4–31. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2010.2059031. |
| [29] |
EICHEL P H and JAKOWATZ C V. Phase-gradient algorithm as an optimal estimator of the phase derivative[J]. Optics Letters, 1989, 14(20): 1101–1103. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.001101. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: