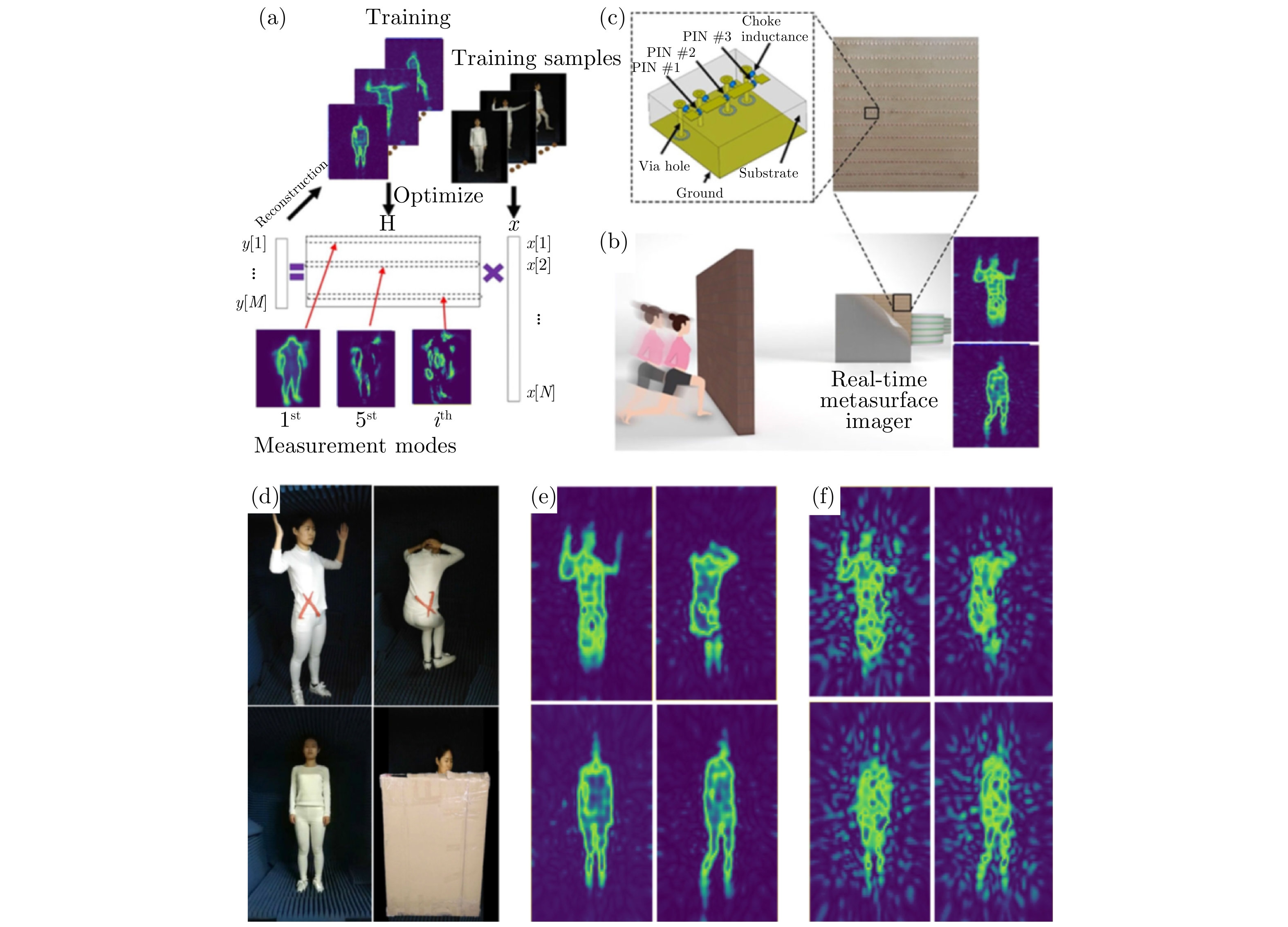
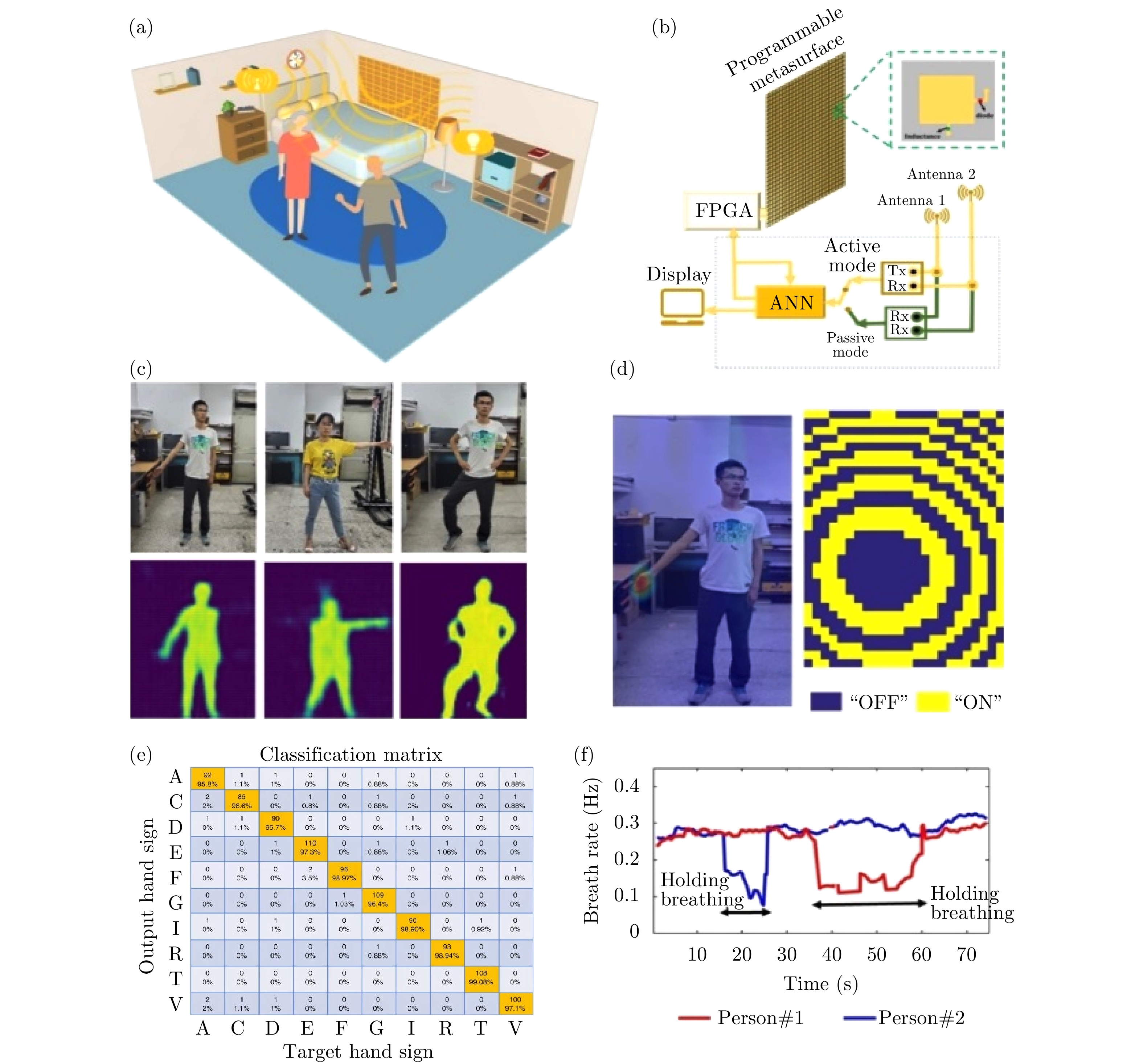
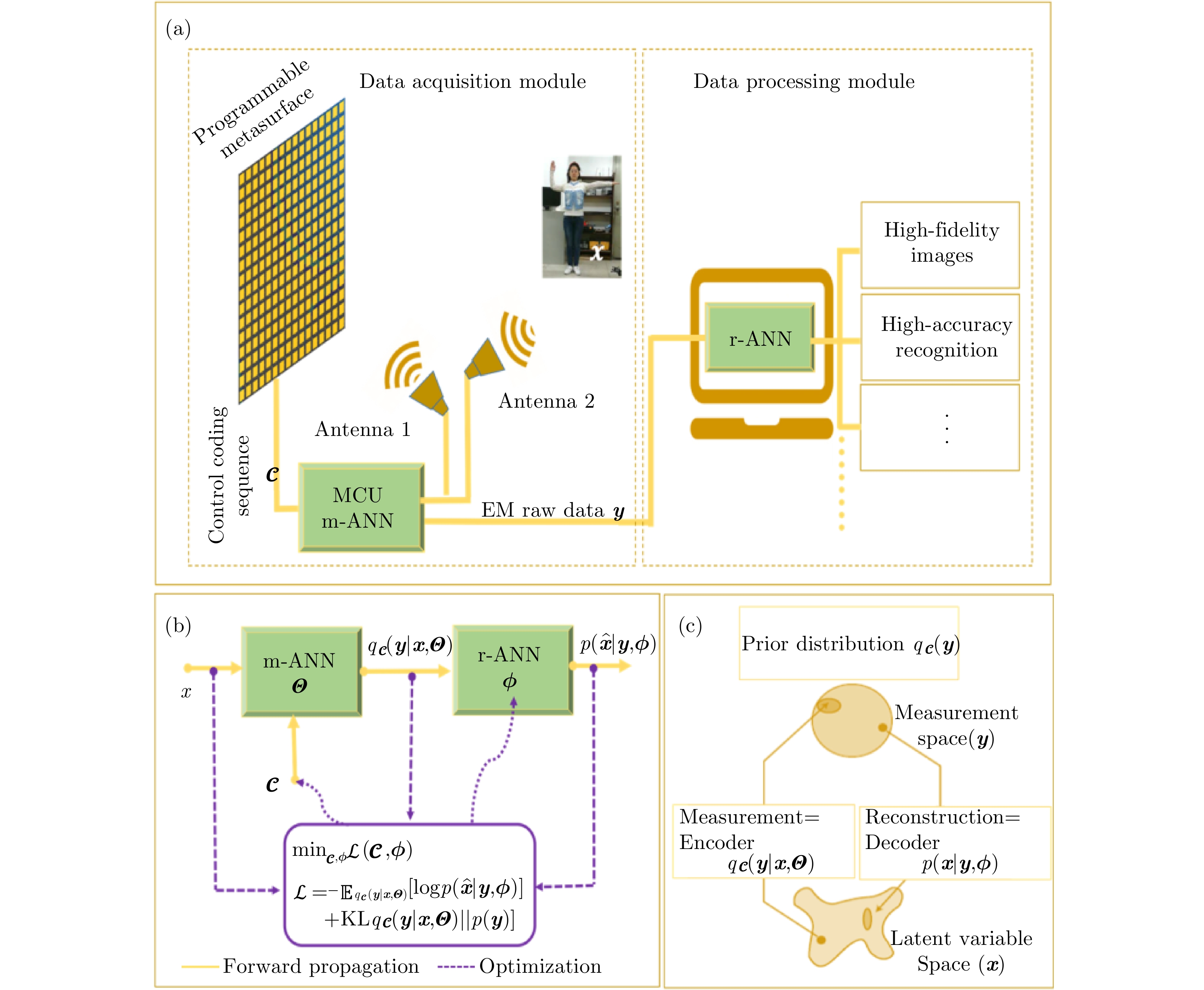
| [1] |
SMITH D R, PADILLA W J, VIER D C, et al. Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(18): 4184–4187. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4184 |
| [2] |
PENDRY J B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 85(18): 3966–3969. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.3966 |
| [3] |
SHELBY R A, SMITH D R, and SCHULTZ S. Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5514): 77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.1058847 |
| [4] |
PENDRY J B, SCHURIG D, and SMITH D R. Controlling electromagnetic fields[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5781): 1780–1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1125907 |
| [5] |
SCHURIG D, MOCK J J, JUSTICE B J, et al. Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5801): 977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.1133628 |
| [6] |
MA Huifeng and CUI Tiejun. Three-dimensional broadband ground-plane cloak made of metamaterials[J]. Nature Communications, 2010, 1(3): 21.
|
| [7] |
JIANG Weixiang, CUI Tiejun, YANG Xinmi, et al. Shrinking an arbitrary object as one desires using metamaterials[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 98(20): 204101. doi: 10.1063/1.3590203 |
| [8] |
MA Huifeng and CUI Tiejun. Three-dimensional broadband and broad-angle transformation-optics lens[J]. Nature Communications, 2010, 1: 124. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1126 |
| [9] |
YU Nanfang, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: Generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333–337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713 |
| [10] |
AIETA F, GENEVET P, YU Nanfang, et al. Out-of-plane reflection and refraction of light by anisotropic optical antenna metasurfaces with phase discontinuities[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(3): 1702–1706. doi: 10.1021/nl300204s |
| [11] |
KHORASANINEJAD M, CHEN Weiting, DEVLIN R C, et al. Metalenses at visible wavelengths: Diffraction-limited focusing and subwavelength resolution imaging[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6290): 1190–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf6644 |
| [12] |
CONG Longqing, PITCHAPPA P, LEE C, et al. Active phase transition via loss engineering in a terahertz MEMS metamaterial[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(26): 1700733. doi: 10.1002/adma.201700733 |
| [13] |
CUI Tiejun, QI Meiqing, WAN Xiang, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(10): e218.
|
| [14] |
CUI Tiejun, LIU Shuo, and ZHANG Lei. Information metamaterials and metasurfaces[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(15): 3644–3668. doi: 10.1039/C7TC00548B |
| [15] |
CUI Tiejun, LIU Shuo, and LI Lianlin. Information entropy of coding metasurface[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2016, 5(11): e16172.
|
| [16] |
CUI Tiejun. Microwave metamaterials–from passive to digital and programmable controls of electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Optics, 2017, 19(8): 084004. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/aa7009 |
| [17] |
LI Lianlin and CUI Tiejun. Information metamaterials-from effective media to real-time information processing systems[J]. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8(5): 703–724. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0006 |
| [18] |
MA Qian and CUI Tiejun. Information metamaterials: Bridging the physical world and digital world[J]. PhotoniX, 2020, 1(1): 1. doi: 10.1186/s43074-020-00006-w |
| [19] |
CUI Tiejun, LI Lianlin, LIU Shuo, et al. Information metamaterial systems[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(8): 101403. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101403 |
| [20] |
LIU Shuo, CUI Tiejun, ZHANG Lei, et al. Convolution operations on coding metasurface to reach flexible and continuous controls of terahertz beams[J]. Advanced Science, 2016, 3(10): 1600156. doi: 10.1002/advs.201600156 |
| [21] |
SHUANG Ya, ZHAO Hanting, JI Wei, et al. Programmable high-order OAM-carrying beams for direct-modulation wireless communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2020, 10(1): 29–37. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2020.2973391 |
| [22] |
LI Lianlin, CUI Tiejun, JI Wei, et al. Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00164-9 |
| [23] |
CUI Tiejun, LIU Shuo, BAI Guodong, et al. Direct transmission of digital message via programmable coding metasurface[J]. Research, 2019, 2019: 2584509.
|
| [24] |
LI Lianlin, RUAN Hengxin, LIU Che, et al. Machine-learning reprogrammable metasurface imager[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1082. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09103-2 |
| [25] |
LI Lianlin, SHUANG Ya, MA Qian, et al. Intelligent metasurface imager and recognizer[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2019, 8: 97.
|
| [26] |
LI Lianlin, WANG Longgang, TEIXEIRA F L, et al. DeepNIS: Deep neural network for nonlinear electromagnetic inverse scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(3): 1819–1825. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2885437 |
| [27] |
ZHAO Hanting, SHUANG Ya, WEI Menglin, et al. Metasurface-assisted massive backscatter wireless communication with commodity Wi-Fi signals[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3926.
|
| [28] |
LI Haoyang, ZHAO Hanting, WEI Menglin, et al. Intelligent electromagnetic sensing with learnable data acquisition and processing[J]. Patterns, 2020, 1(1): 100006. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2020.100006 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: