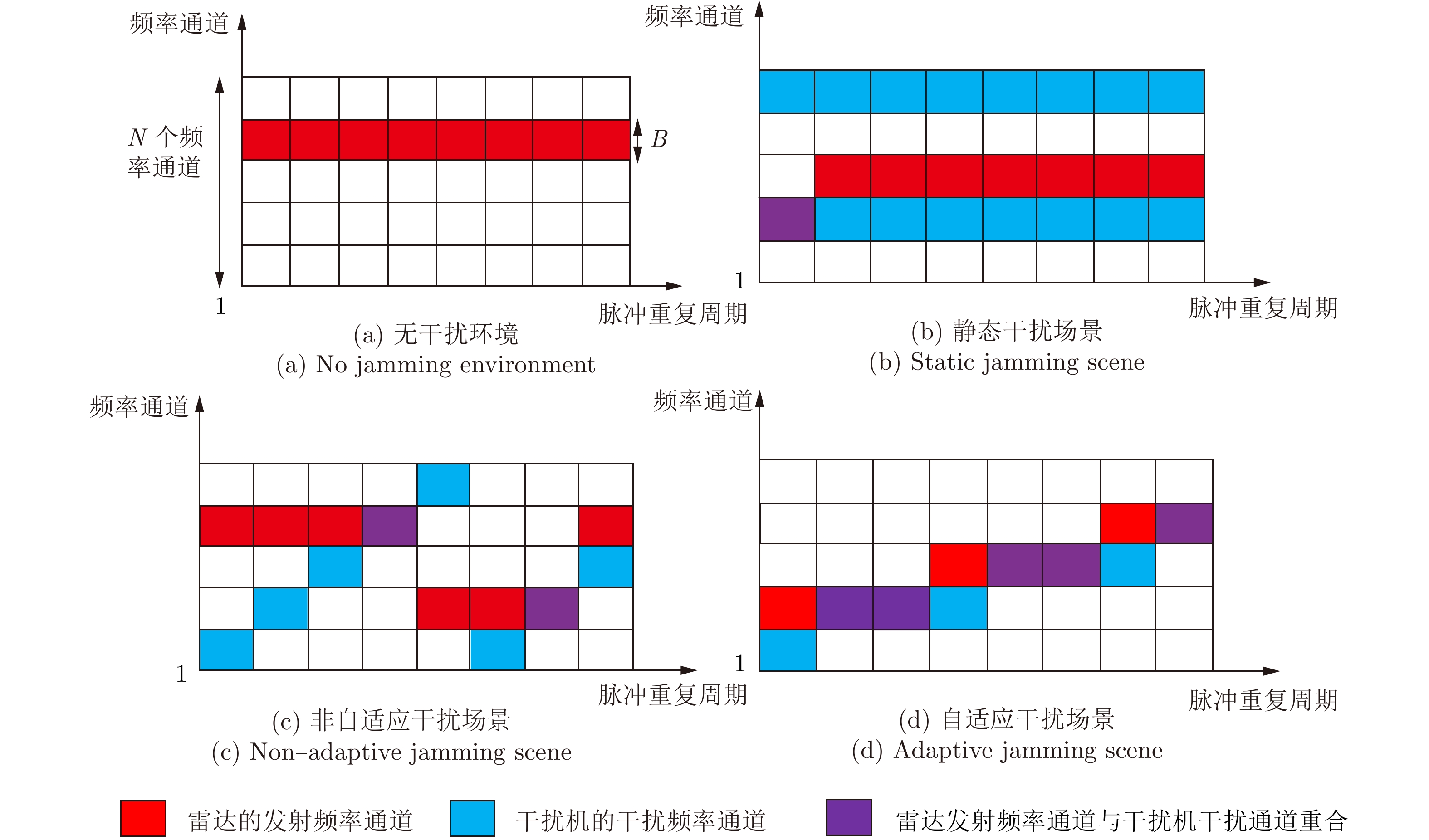
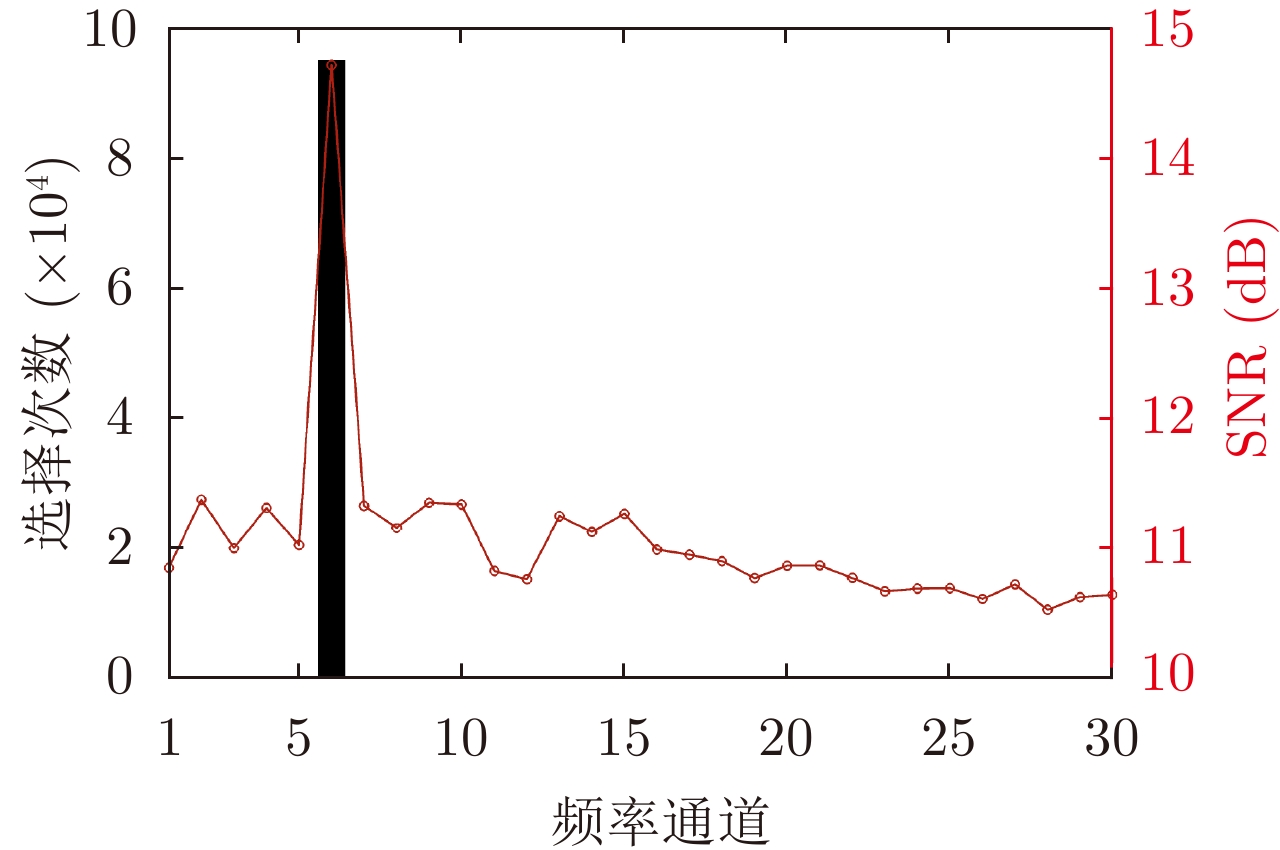
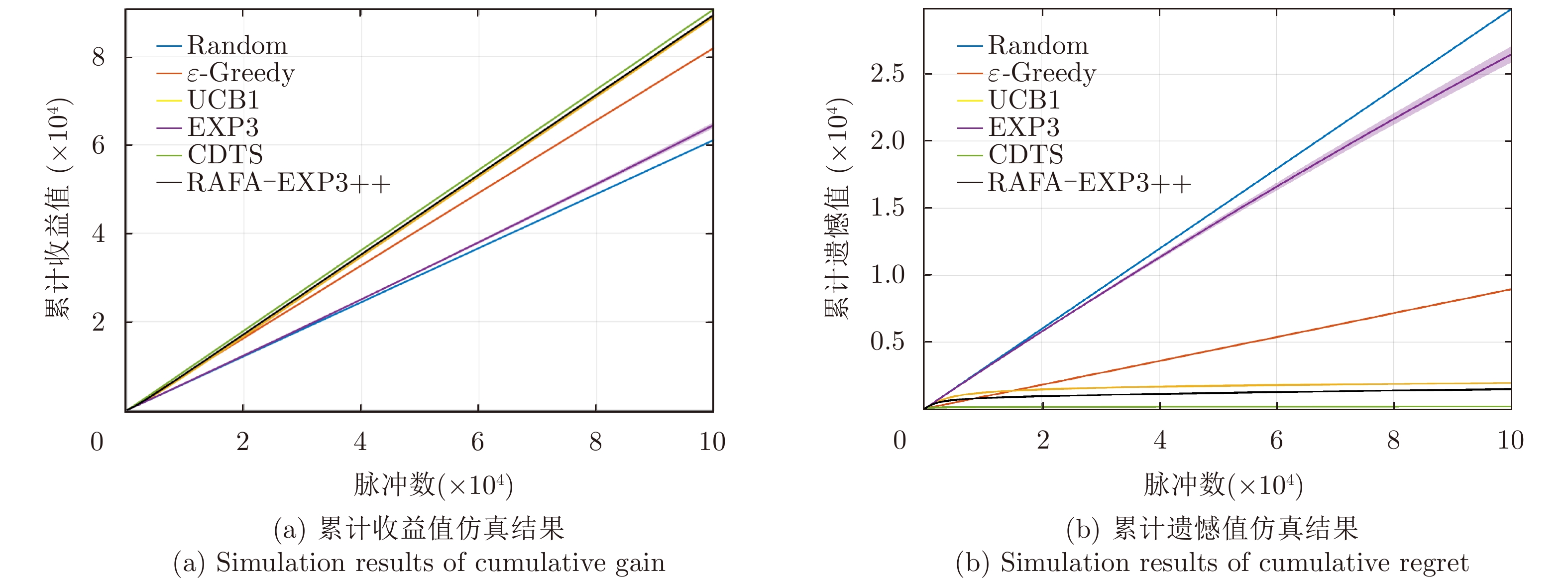
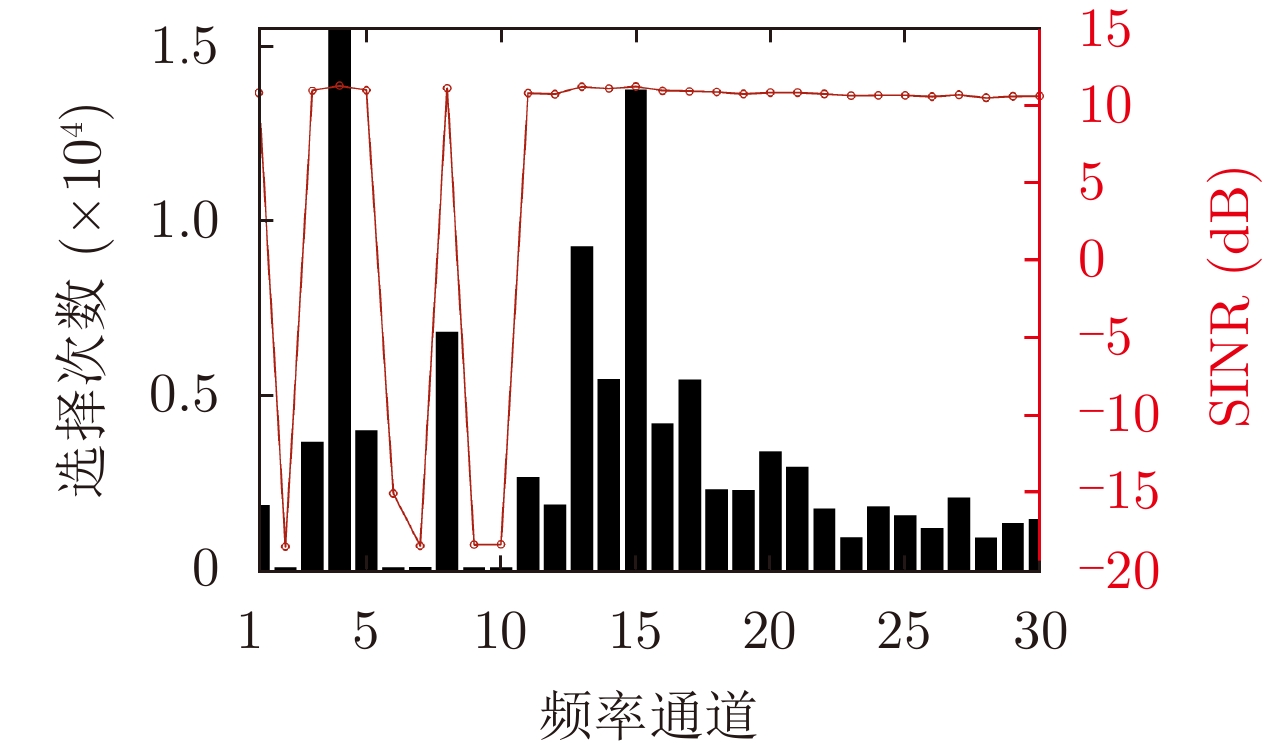
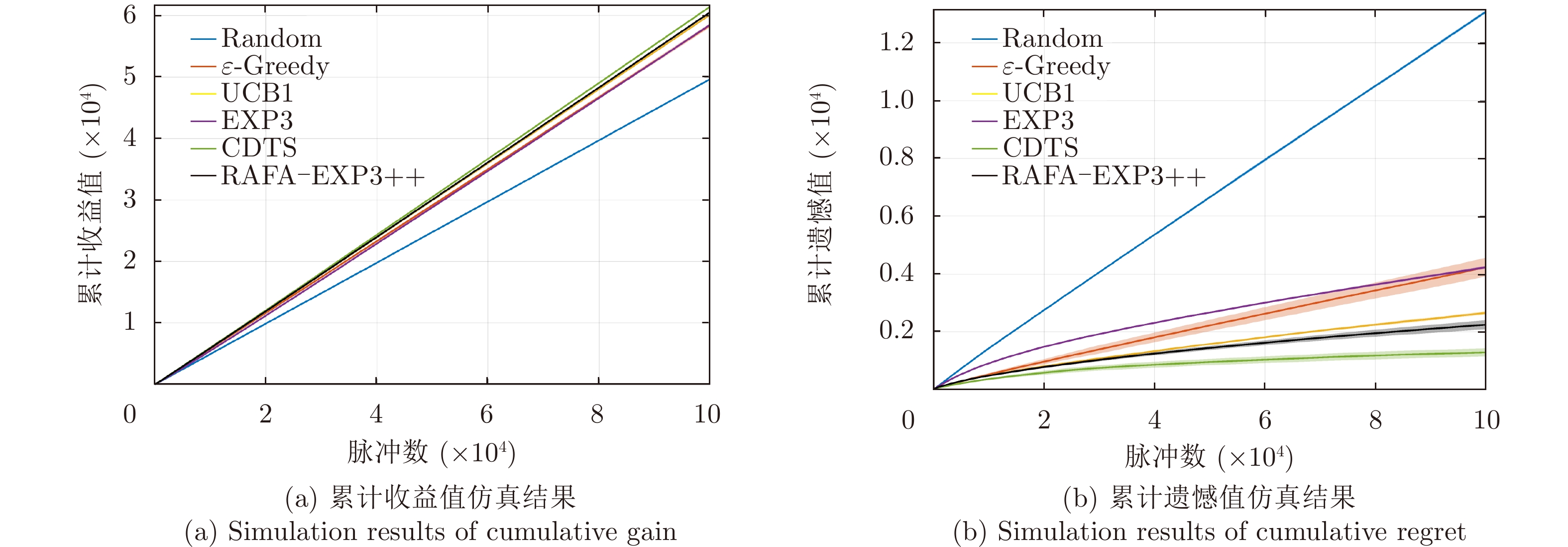
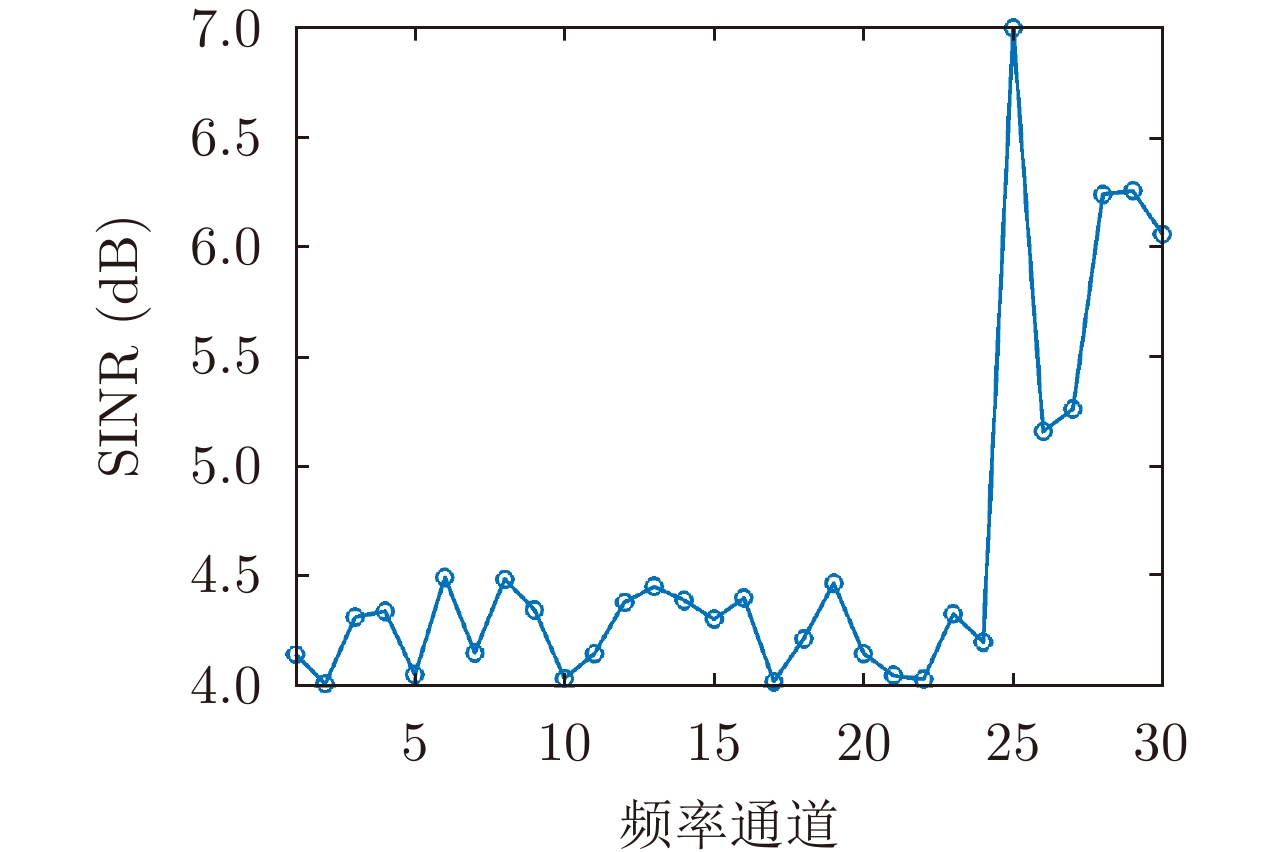
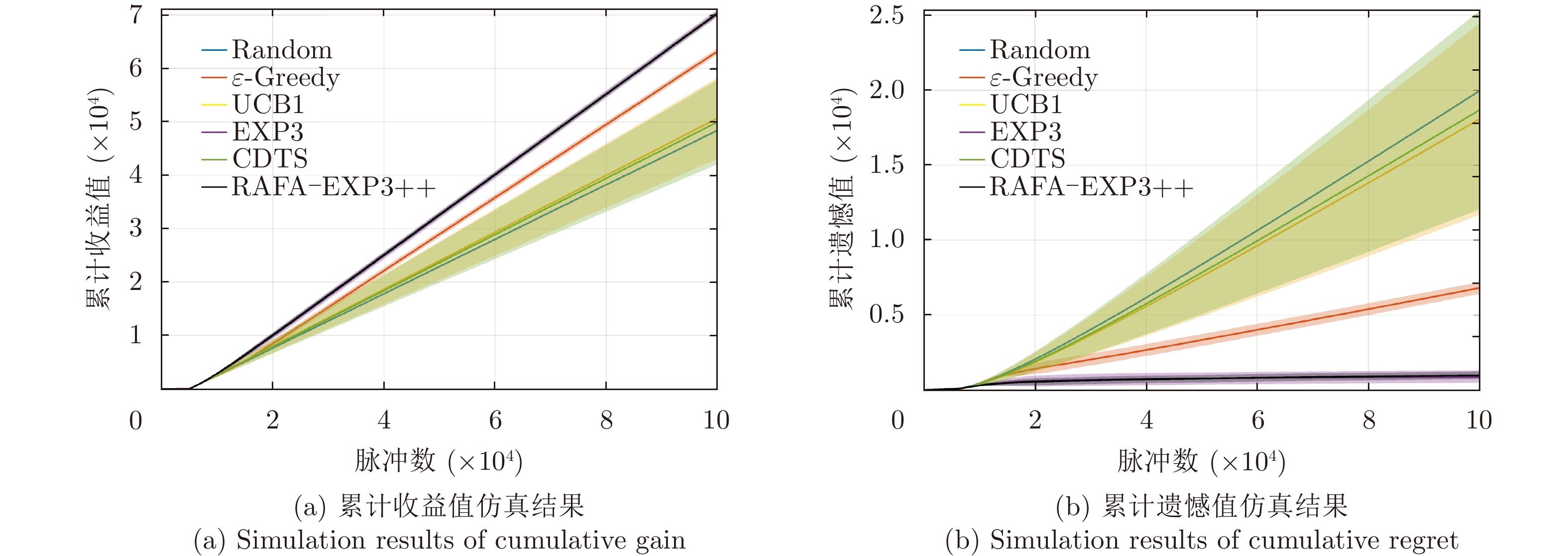
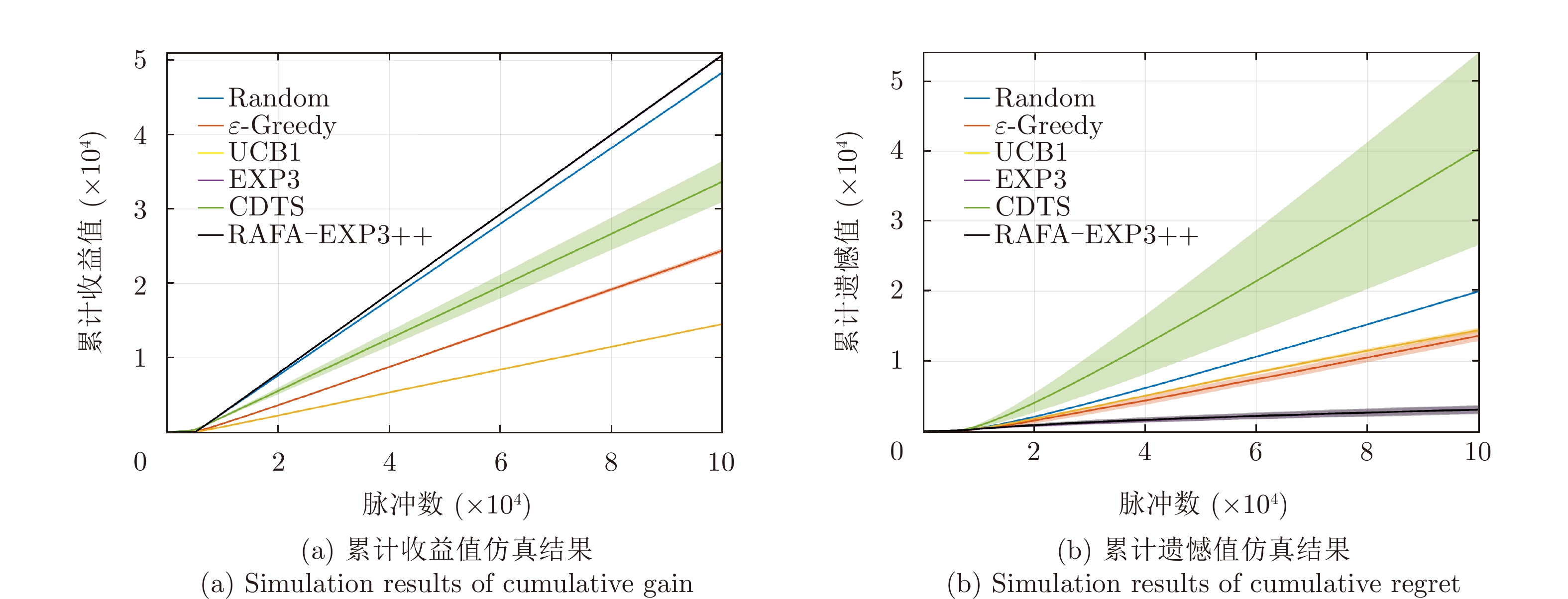
| [1] |
LI Nengjing and ZHANG Yiting. A survey of radar ECM and ECCM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(3): 1110–1120. doi: 10.1109/7.395232 |
| [2] |
HUANG Tianyao, LIU Yimin, MENG Huadong, et al. Cognitive random stepped frequency radar with sparse recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 858–870. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.120443 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
LI Chao and ZHANG Juquan. Research on the combat technology of radar EW with self-adapted frequency agile ability[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2004, 19(1): 30–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2004.01.008 |
| [5] |
QUAN Yinghui, FANG Wen, SHA Minghui, et al. Present situation and prospects of frequency agility radar waveform countermeasures[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.11 |
| [6] |
SMITH G E, CAMMENGA Z, MITCHELL A, et al. Experiments with cognitive radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(12): 34–46. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150215 |
| [7] |
MARTONE A F, RANNEY K I, SHERBONDY K, et al. Spectrum allocation for noncooperative radar coexistence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 90–105. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2735659 |
| [8] |
KIRK B H, NARAYANAN R M, GALLAGHER K A, et al. Avoidance of time-varying radio frequency interference with software-defined cognitive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(3): 1090–1107. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2886614 |
| [9] |
SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018: 32–36.
|
| [10] |
SELVI E, BUEHRER R M, MARTONE A, et al. Reinforcement learning for adaptable bandwidth tracking radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(5): 3904–3921. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2987443 |
| [11] |
PUTERMAN M L. Chapter 8 Markov decision processes[J]. Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science, 1990, 2: 331–434. doi: 10.1016/S0927-0507(05)80172-0 |
| [12] |
THORNTON C E, KOZY M A, BUEHRER R M, et al. Deep reinforcement learning control for radar detection and tracking in congested spectral environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(4): 1335–1349. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3019605 |
| [13] |
MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 |
| [14] |
AILIYA, YI Wei, and VARSHNEY P K. Adaptation of frequency hopping interval for radar anti-jamming based on reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(12): 12434–12449. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3197425 |
| [15] |
LI Kang, JIU Bo, WANG Penghui, et al. Radar active antagonism through deep reinforcement learning: A way to address the challenge of Mainlobe jamming[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 186: 108130. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108130 |
| [16] |
SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347, 2017.
|
| [17] |
LEE S Y, CHOI S, and CHUNG S Y. Sample-efficient deep reinforcement learning via episodic backward update[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 2112–2121.
|
| [18] |
WHITE III C C and WHITE D J. Markov decision processes[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1989, 39(1): 1–16.
|
| [19] |
BUBECK S and CESA-BIANCHI N. Regret analysis of stochastic and nonstochastic multi-armed bandit problems[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2012, 5(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000024 |
| [20] |
HOI S C H, SAHOO D, LU Jing, et al. Online learning: A comprehensive survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 459: 249–289. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.112 |
| [21] |
ZHOU Pan and JIANG Tao. Toward optimal adaptive wireless communications in unknown environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(5): 3655–3667. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2524638 |
| [22] |
WANG Qian, XU Ping, REN Kui, et al. Towards optimal adaptive UFH-based anti-jamming wireless communication[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2012, 30(1): 16–30. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2012.120103 |
| [23] |
KHALEDI M and ABOUZEID A A. Dynamic spectrum sharing auction with time-evolving channel qualities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(11): 5900–5912. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2443796 |
| [24] |
ZHAO Qing, KRISHNAMACHARI B, and LIU Keqin. On myopic sensing for multi-channel opportunistic access: Structure, optimality, and performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2008, 7(12): 5431–5440. doi: 10.1109/T-WC.2008.071349 |
| [25] |
PULKKINEN P, AITTOMÄKI T, and KOIVUNEN V. Reinforcement learning based transmitter-receiver selection for distributed MIMO radars[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, USA, 2020: 1040–1045.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
AUER P, CESA-BIANCHI N, and FISCHER P. Finite-time analysis of the multiarmed bandit problem[J]. Machine Learning, 2002, 47(2): 235–256. doi: 10.1023/A:1013689704352 |
| [28] |
THORNTON C E, BUEHRER R M, and MARTONE A F. Constrained contextual bandit learning for adaptive radar waveform selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 58(2): 1133–1148. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3109110 |
| [29] |
THOMPSON W R. On the likelihood that one unknown probability exceeds another in view of the evidence of two samples[J]. Biometrika, 1933, 25(3/4): 285–294. doi: 10.2307/2332286 |
| [30] |
AUER P, CESA-BIANCHI N, FREUND Y, et al. The nonstochastic multiarmed bandit problem[J]. SIAM Journal on Computing, 2002, 32(1): 48–77. doi: 10.1137/S0097539701398375 |
| [31] |
FANG Yuyuan, ZHANG Lei, WEI Shaopeng, et al. Online frequency-agile strategy for radar detection based on constrained combinatorial nonstationary bandit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 1693–1706. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3203689 |
| [32] |
王跃东, 顾以静, 梁彦, 等. 伴随压制干扰与组网雷达功率分配的深度博弈研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023WANG Yuedong, GU Yijing, LIANG Yan, et al. Deep game of escorting suppressive jamming and networked radar power allocation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023 |
| [33] |
陈伯孝. 现代雷达系统分析与设计[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2012: 79–81.
CHEN Boxiao. Mordern Radar System Analysis and Design[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2012: 79–81.
|
| [34] |
赵国庆. 雷达对抗原理[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2012: 183–186.
ZHAO Guoqing. Principle of Radar Countermeasure[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2012: 183–186.
|
| [35] |
AUDIBERT J Y, MUNOS R, and SZEPESVÁRI C. Exploration–exploitation tradeoff using variance estimates in multi-armed bandits[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2009, 410(19): 1876–1902. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2009.01.016 |
| [36] |
ARORA R, DEKEL O, and TEWARI A. Online bandit learning against an adaptive adversary: From regret to policy regret[C]. The 29th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Edinburgh, Scotland, 2012: 1747–1754.
|
| [37] |
BUBECK S and SLIVKINS A. The best of both worlds: Stochastic and adversarial bandits[C]. The 25th Annual Conference on Learning Theory, Edinburgh, UK, 2012: 23.
|
| [38] |
SELDIN Y and SLIVKINS A. One practical algorithm for both stochastic and adversarial bandits[C]. The 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 2014: 1287–1295.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: