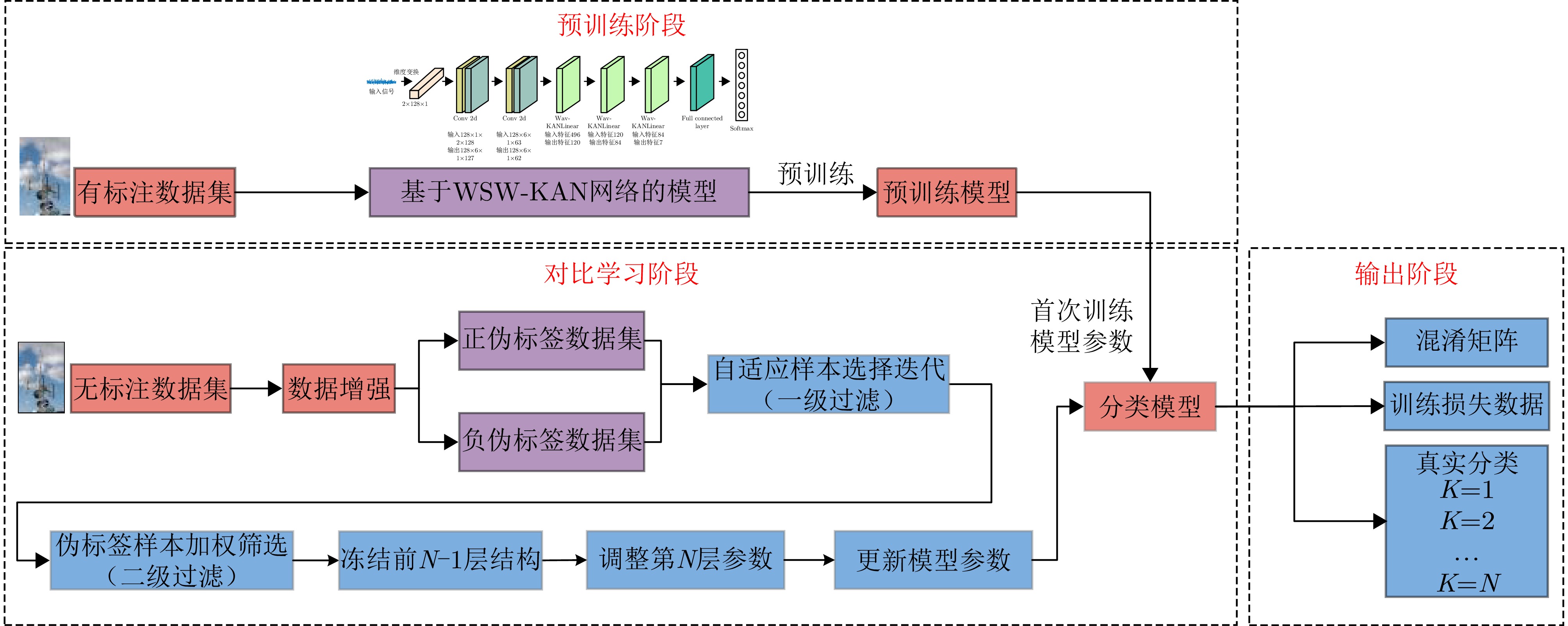
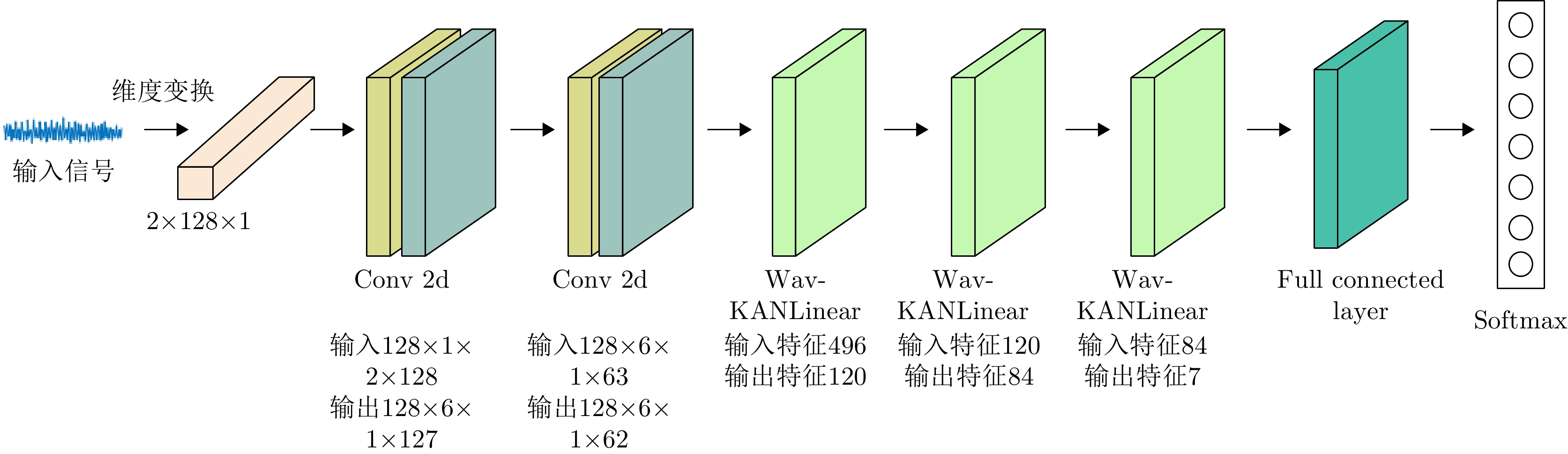
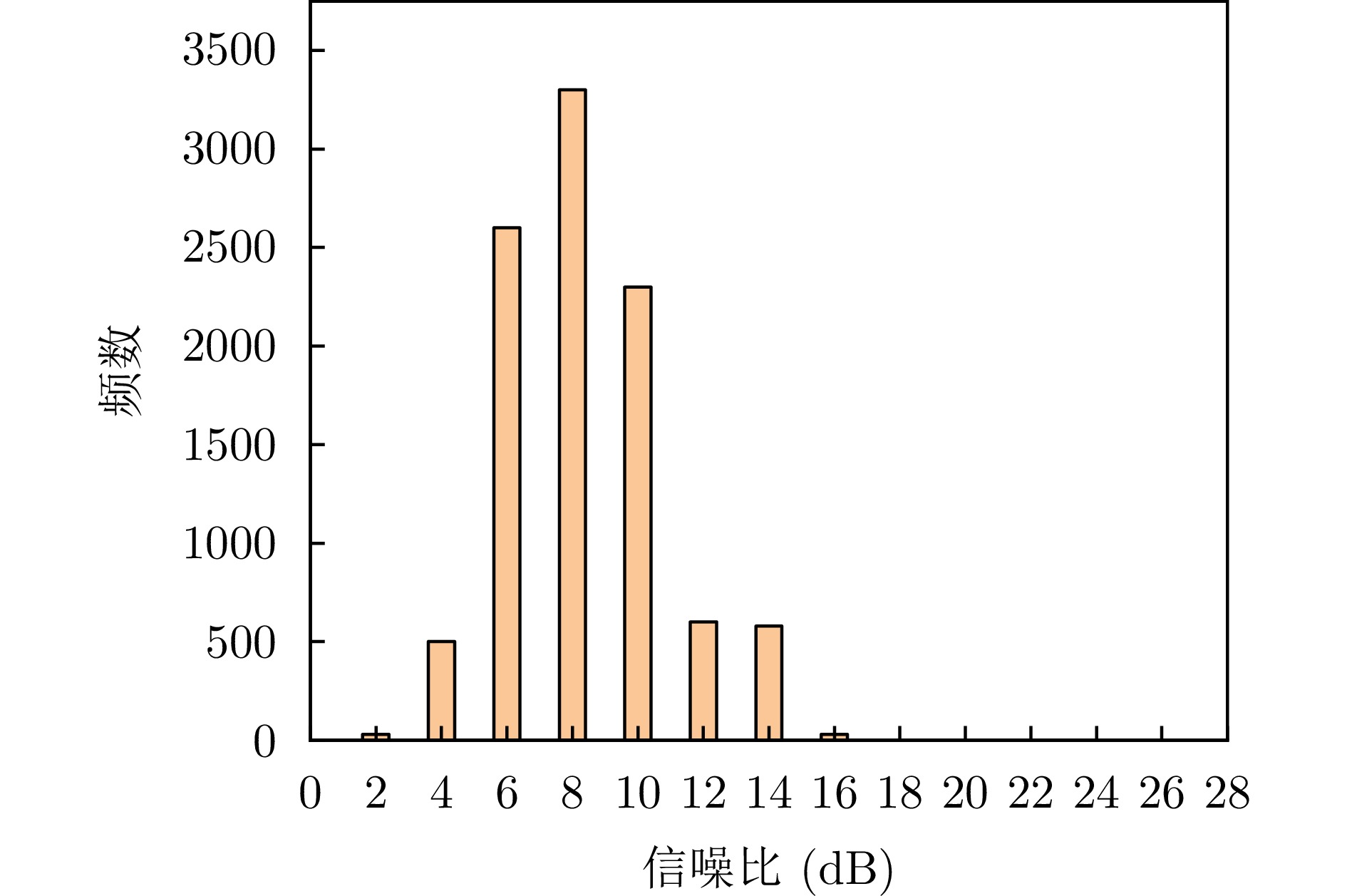
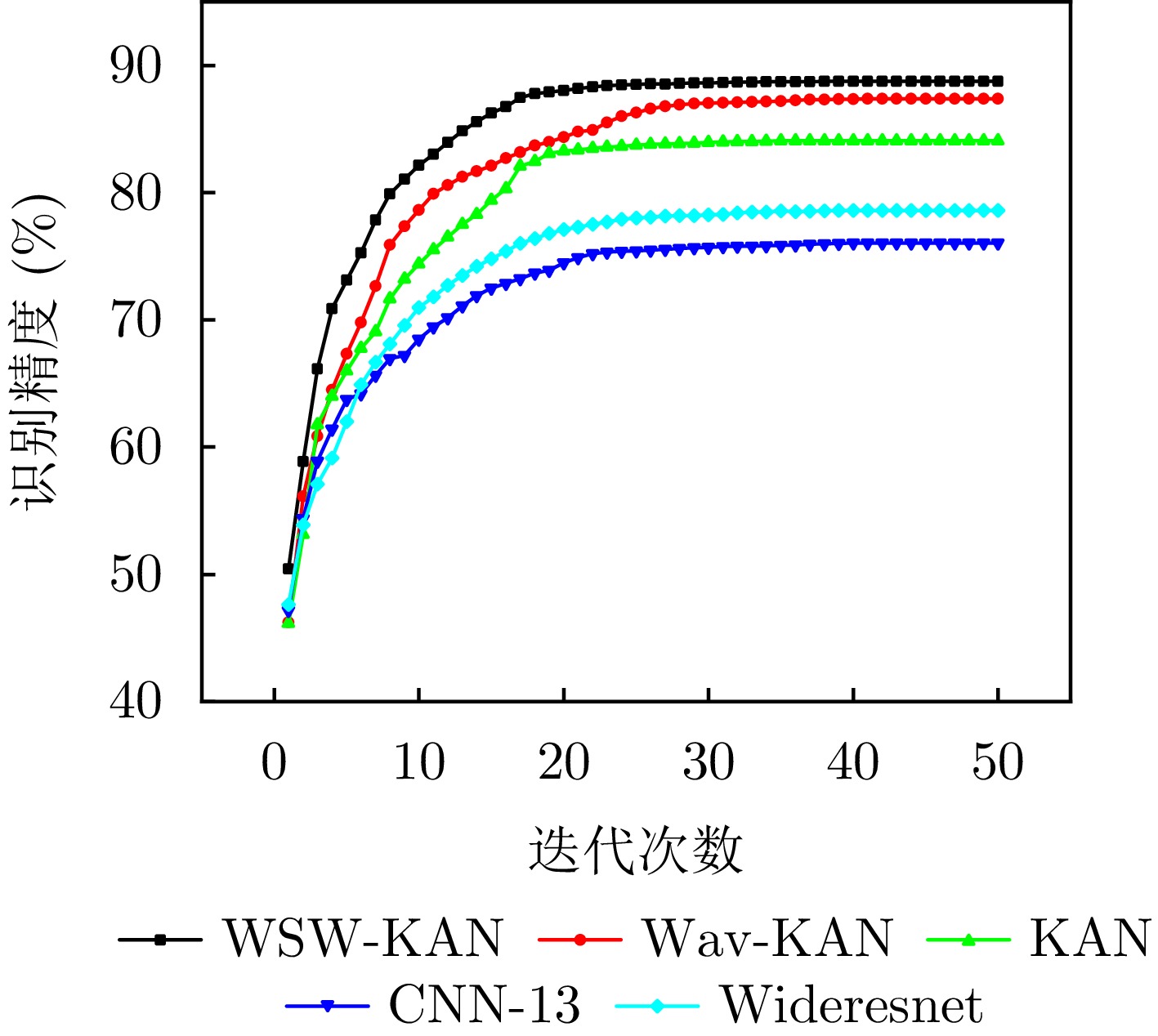
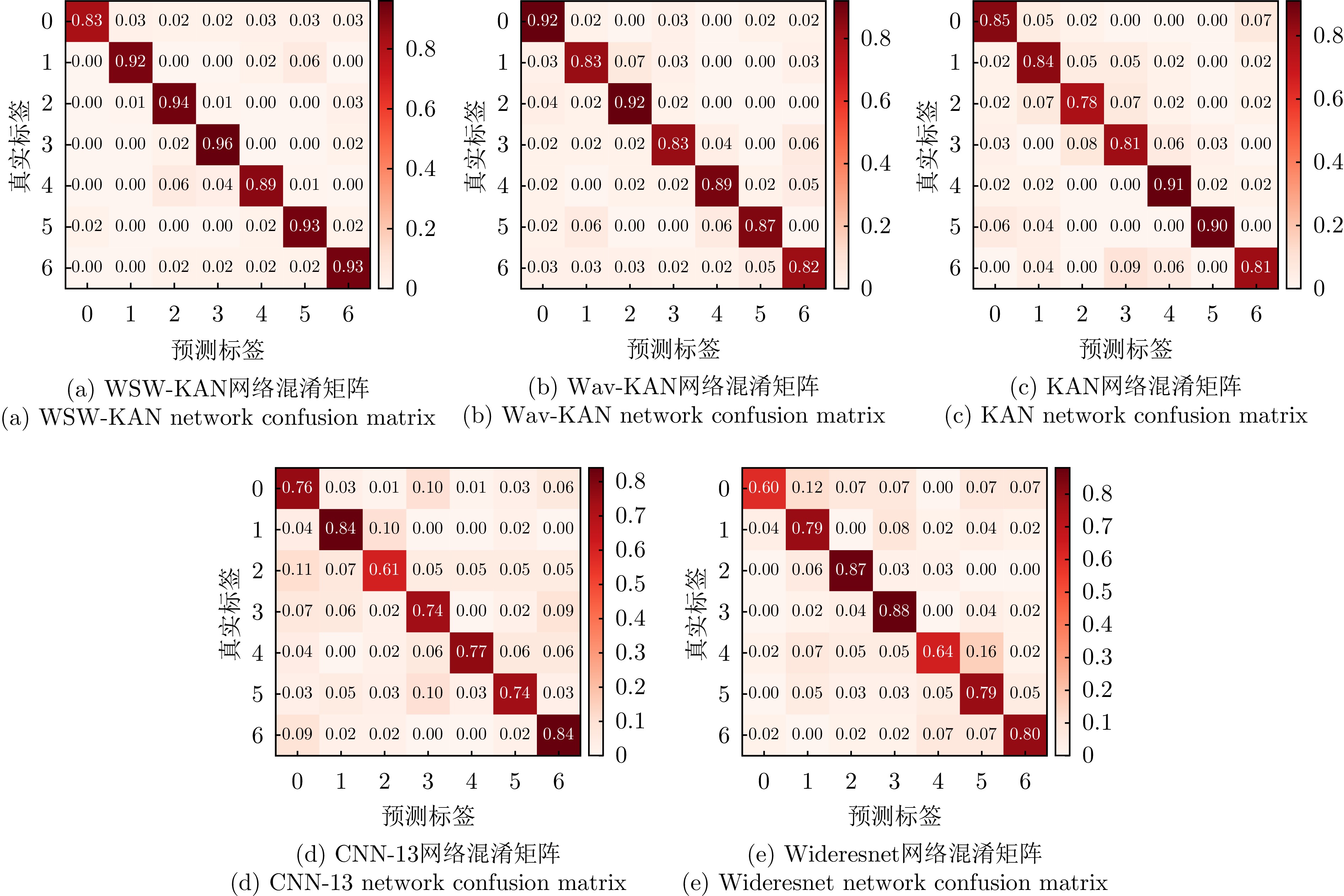
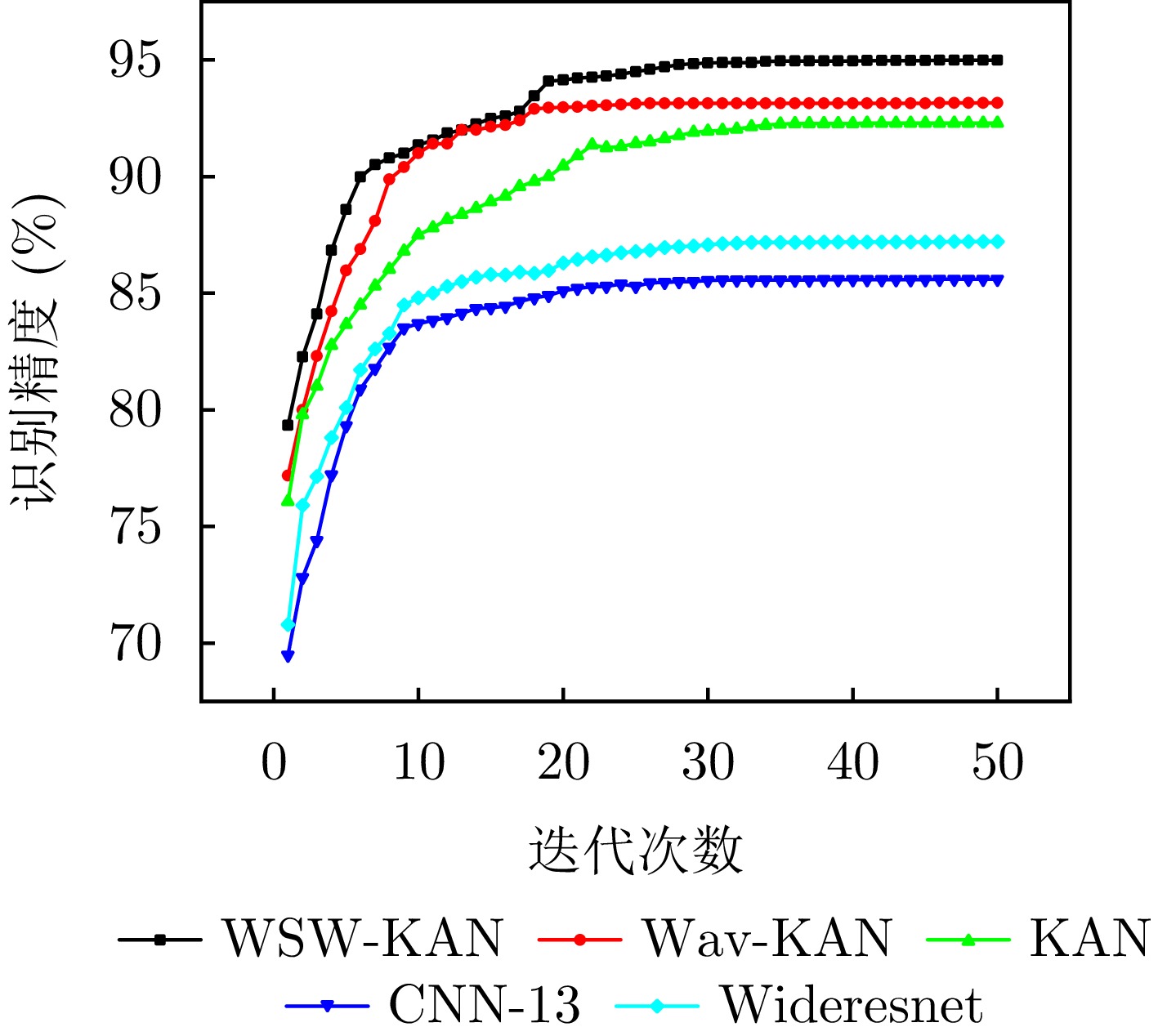
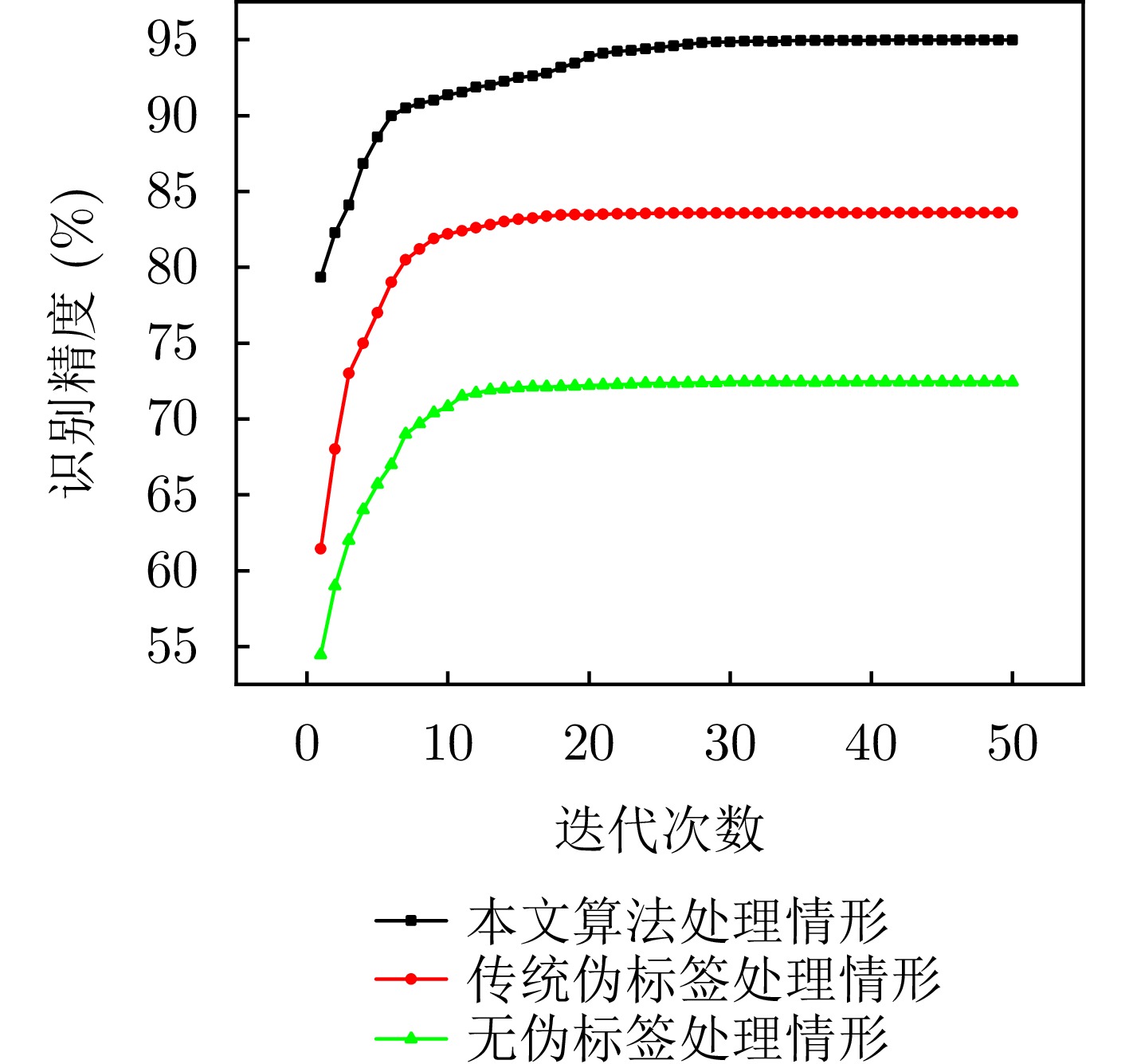
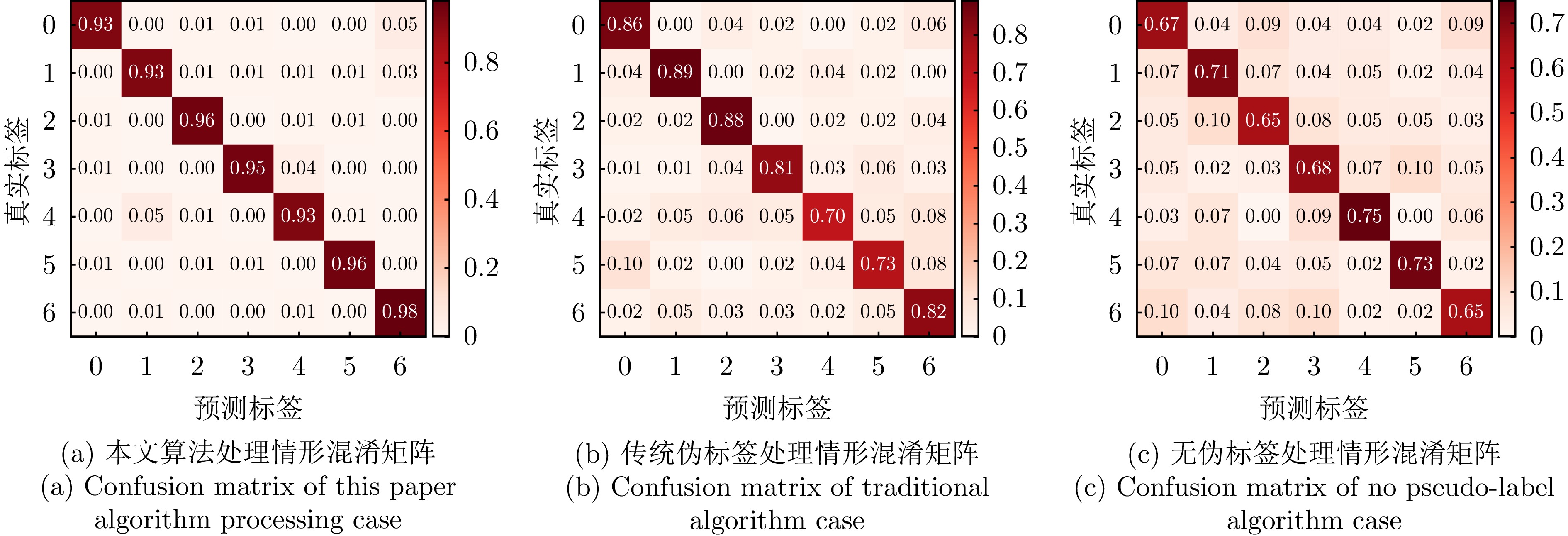
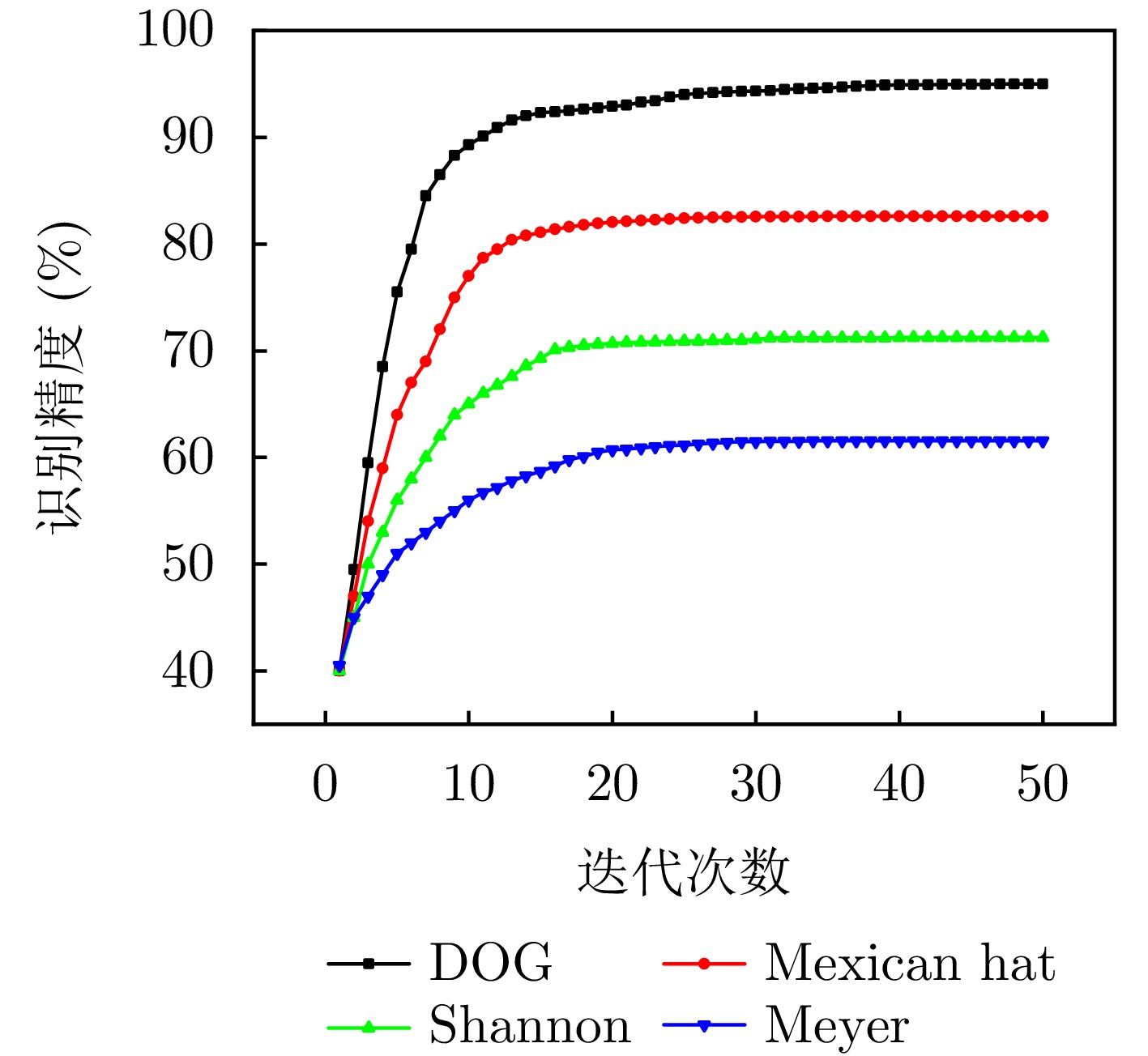
| [1] |
WU Qiong. Research on radar emitter recognition algorithm based on improved CNN[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.7666/d.D01905147. |
| [2] |
TAN Kaiwen, YAN Wenjun, ZHANG Limin, et al. Specific emitter identification based on software-defined radio and decision fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 86217–86229. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3088542. |
| [3] |
WANG Yihui, YAN Wenjun, LING Qing, et al. Low labeling rate specific emitter identification algorithm based on confidence learning[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2024, 45(5): 267–275. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2024.05.037. |
| [4] |
ZHANG Shunsheng, DING Huancheng, and WANG Wenqin. Multi-scale feature extraction and feature selection network for radiation source identification[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2024, 46(6): 141–148. doi: 10.11887/j.cn.202406015. |
| [5] |
XING Yuexiu, HU Aiqun, ZHANG Junqing, et al. Design of a robust radio-frequency fingerprint identification scheme for multimode LFM radar[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(10): 10581–10593. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3003692. |
| [6] |
LI Xin. Research on individual communication transmitter identification based on unsupervised learning[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2019: 1–10. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2019.000718. |
| [7] |
CHEN Qi, YANG Lingxiao, LAI Jianhuang, et al. Self-supervised image-specific prototype exploration for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 4278–4288. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00425. |
| [8] |
DU Ye, FU Zehua, LIU Qingjie, et al. Weakly supervised semantic segmentation by pixel-to-prototype contrast[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 4310–4319. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00428. |
| [9] |
JIANG Pengtao, YANG Yuqi, HOU Qibin, et al. L2G: A simple local-to-global knowledge transfer framework for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 16865–16875. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01638. |
| [10] |
LEE J, KIM E, and YOON S. Anti-adversarially manipulated attributions for weakly and semi-supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 4070–4078. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00406. |
| [11] |
LEE S, LEE M, LEE J, et al. Railroad is not a train: Saliency as pseudo-pixel supervision for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 5491–5501. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00545. |
| [12] |
ZHOU Tianfei, ZHANG Meijie, ZHAO Fand, et al. Regional semantic contrast and aggregation for weakly supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 4289–4299. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00426. |
| [13] |
HE Kaiming, FAN Haoqi, WU Yuxin, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 9726–9735. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00975. |
| [14] |
PENG Yang, HOU Changbo, ZHANG Yibin, et al. Supervised contrastive learning for RFF identification with limited samples[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(19): 17293–17306. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3272628. |
| [15] |
CHEN Jun, WONG W K, and HAMDAOUI B. Unsupervised contrastive learning for robust RF device fingerprinting under time-domain shift[C]. ICC 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Denver, USA, 2024: 3567–3572. doi: 10.1109/ICC51166.2024.10622173. |
| [16] |
ZHAN Mengqi, LI Yang, CUI Huajun, et al. MCRFF: A meta-contrastive learning-based RF fingerprinting method[C]. MILCOM 2023 - 2023 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Boston, USA, 2023: 391–396. doi: 10.1109/MILCOM58377.2023.10356211. |
| [17] |
DU Mingyang, PAN Jifei, and BI Daping. A contrastive learner for automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, in press. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3532438. |
| [18] |
LIU Ziming, WANG Yixuan, VAIDYA S, et al. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756, 2024.
|
| [19] |
BOZORGASL Z and CHEN Hao. Wav-KAN: Wavelet Kolmogorov-Arnold networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.12832, 2024.
|
| [20] |
PERSONS J B, WONG L J, MOORE M O, et al. Classification of radio signals using truncated Gaussian discriminant analysis of convolutional neural network-derived features[C]. MILCOM 2022 - 2022 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Rockville, USA, 2022: 304–310. doi: 10.1109/MILCOM55135.2022.10017724. |
| [21] |
ZHENG Qinghe, ZHAO Penghui, LI Yang, et al. Spectrum interference-based two-level data augmentation method in deep learning for automatic modulation classification[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(13): 7723–7745. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05514-1. |
| [22] |
CHEN Xi, YANG Haosen, ZHANG Huicong, et al. Uncertainty-aware pseudo-label filtering for source-free unsupervised domain adaptation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 575: 127190. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.127190. |
| [23] |
刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011. |
| [24] |
ALBATINEH A N, BOUBAKARI I, and KIBRIA B M G. New confidence interval estimator of the signal-to-noise ratio based on asymptotic sampling distribution[J]. Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods, 2017, 46(2): 574–590. doi: 10.1080/03610926.2014.1000498. |
| [25] |
ZAGORUYKO S and KOMODAKIS N. Wide residual networks[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2016, York, UK, 2016.
|
| [26] |
谭凯文, 张立民, 闫文君, 等. 面向非均衡类别的半监督辐射源识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 713–727. doi: 10.12000/JR22043. TAN Kaiwen, ZHANG Limin, YAN Wenjun, et al. A semi-supervised emitter identification method for imbalanced category[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 713–727. doi: 10.12000/JR22043. |
| [27] |
WANG Chengyu, LING Qing, and YAN Wenjun. Individual identification algorithm for radar emitter signal based on DCGAN[J]. Measurement and Control Technology, 2024, 43(7): 17–22, 64. doi: 10.19708/j.ckjs.2024.04.222. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

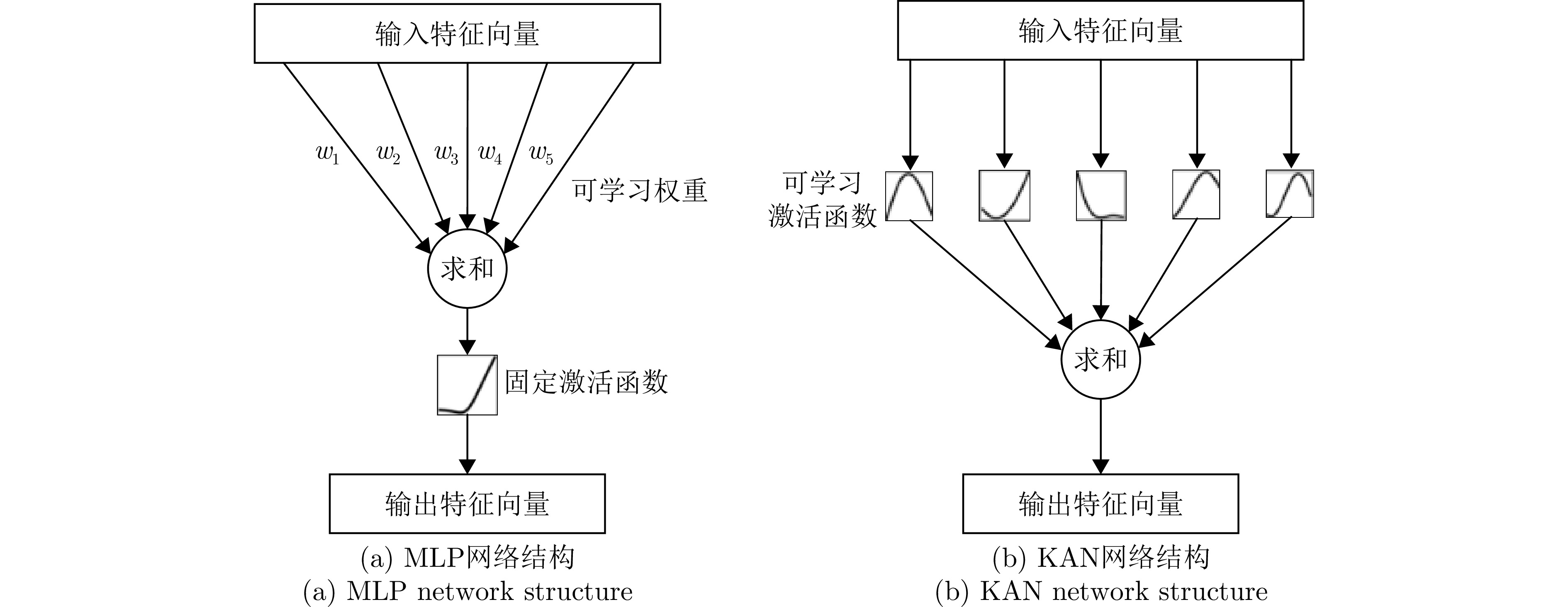



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: