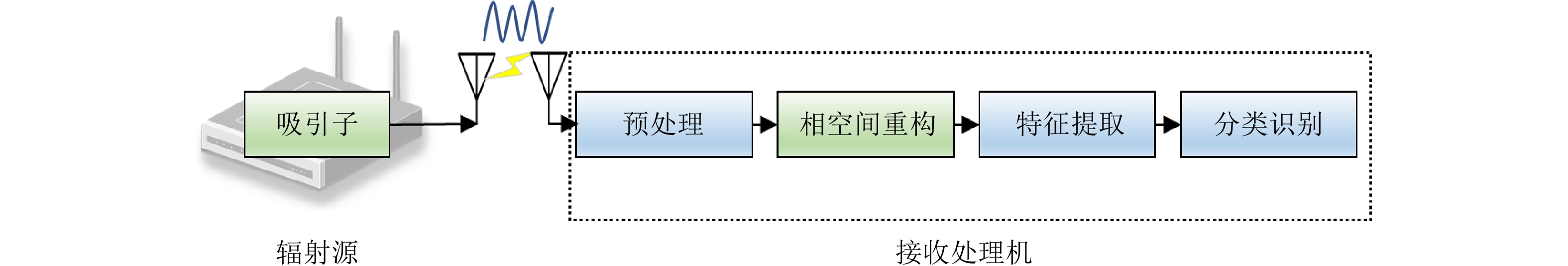
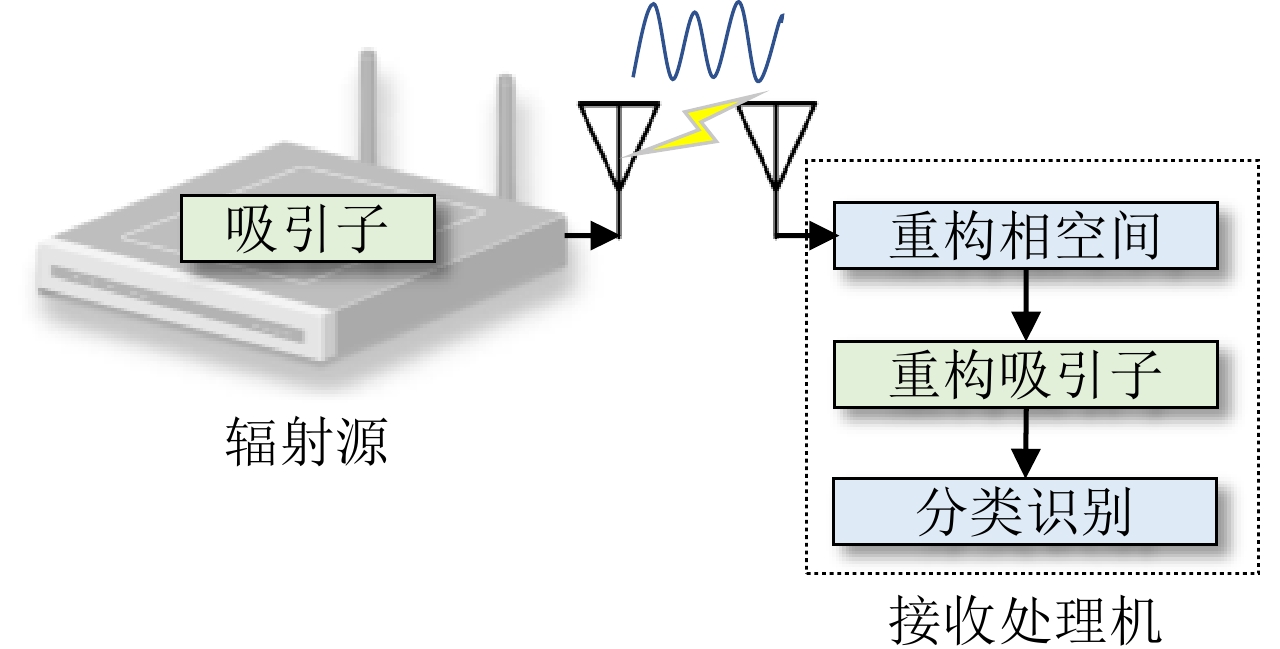
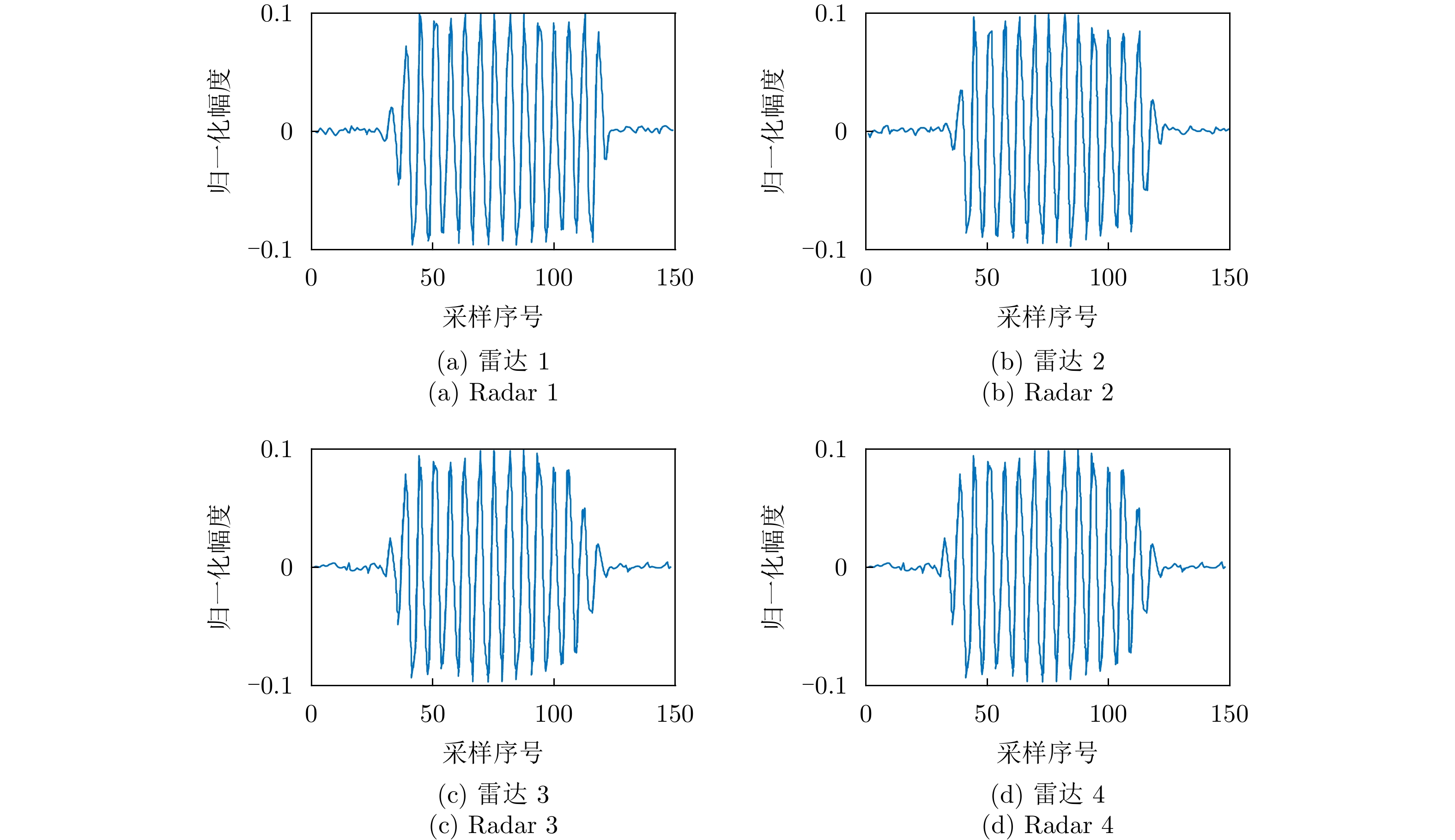
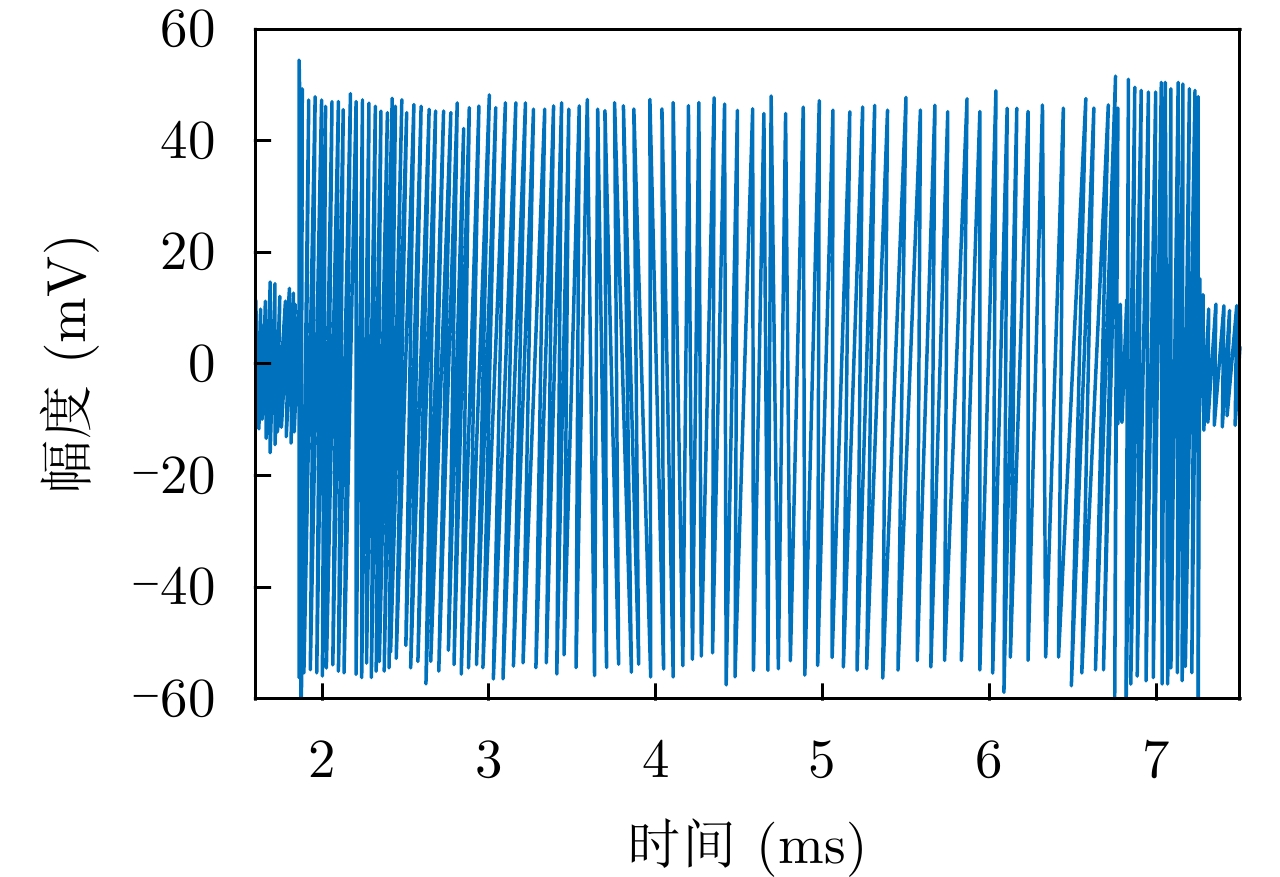
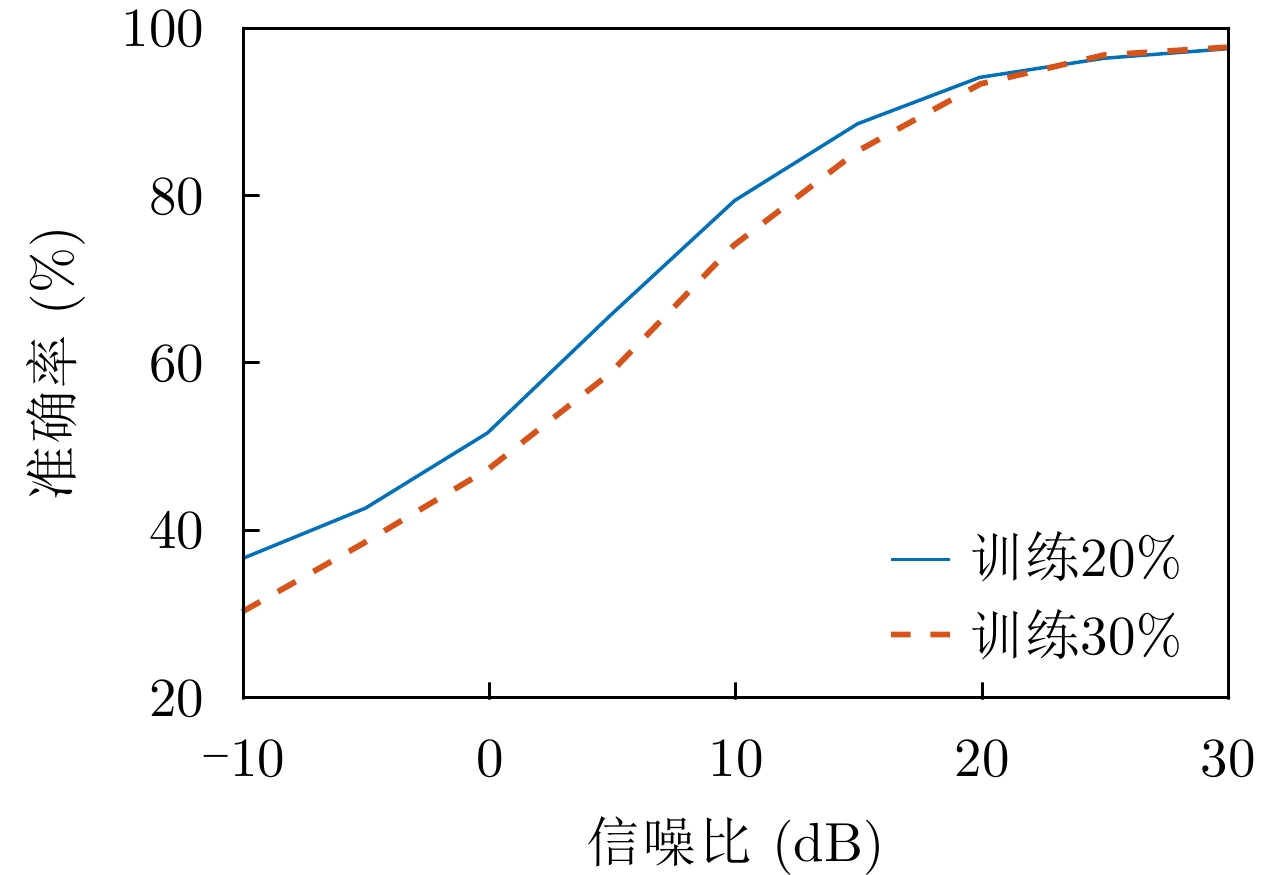
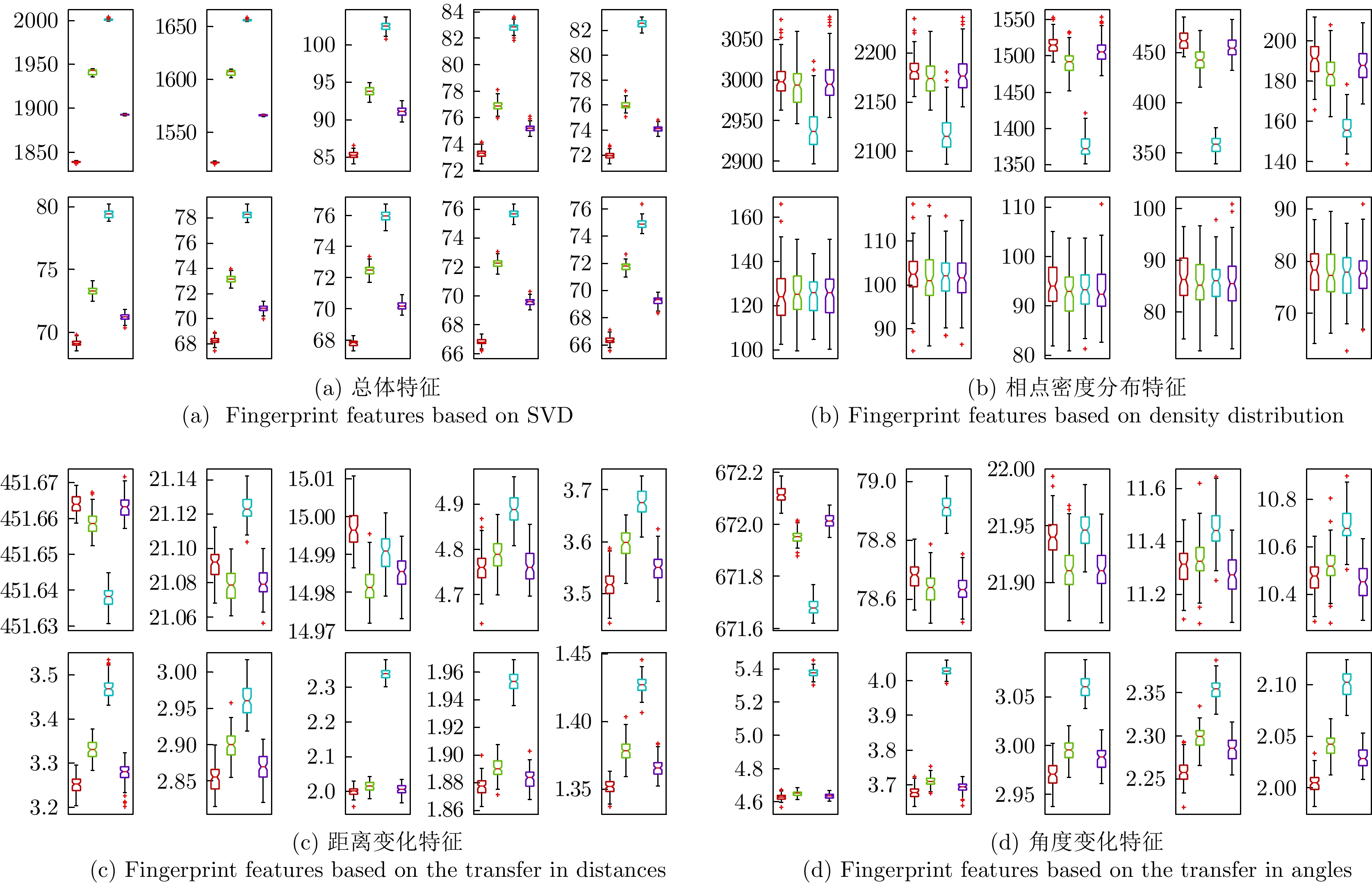
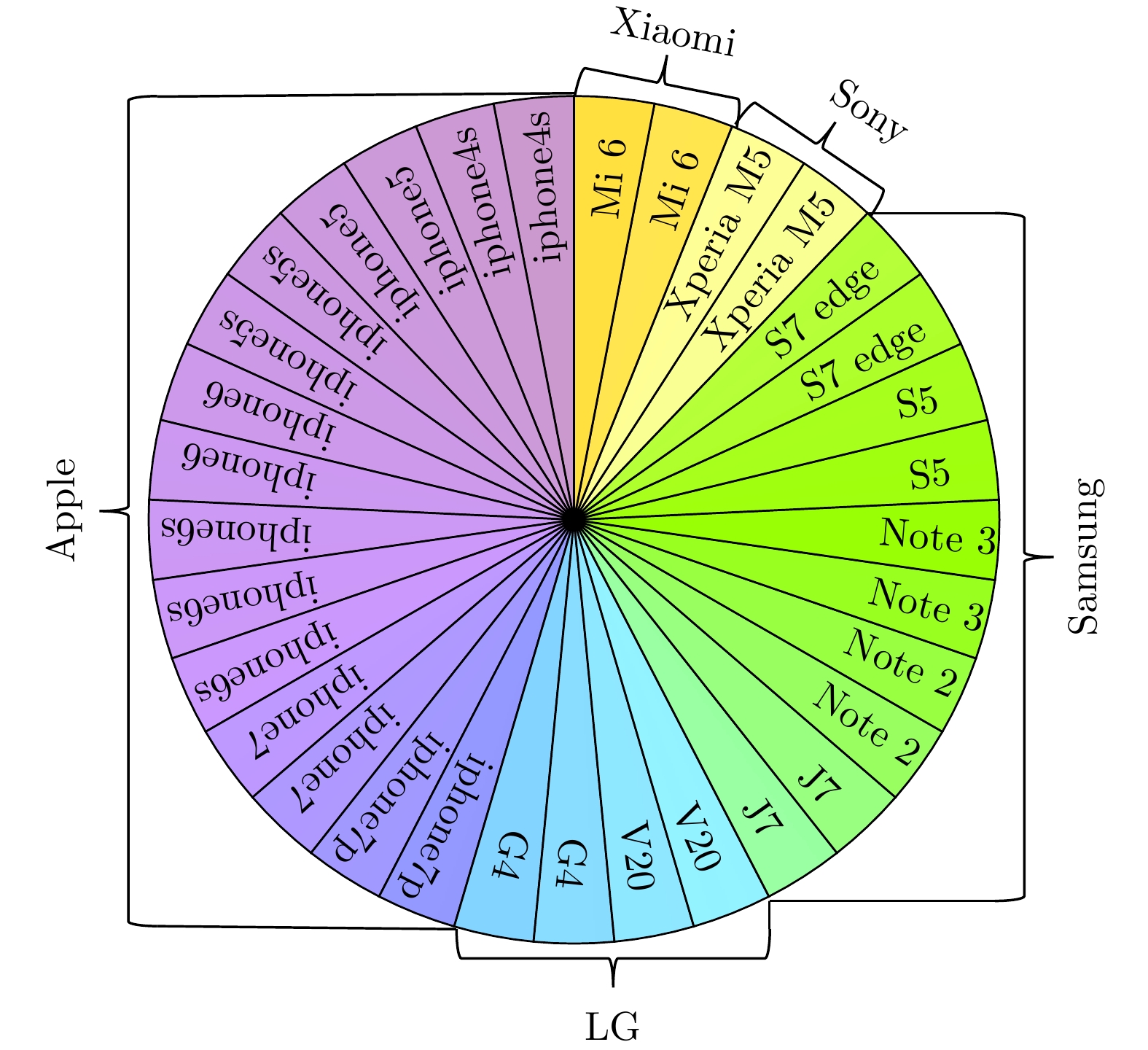
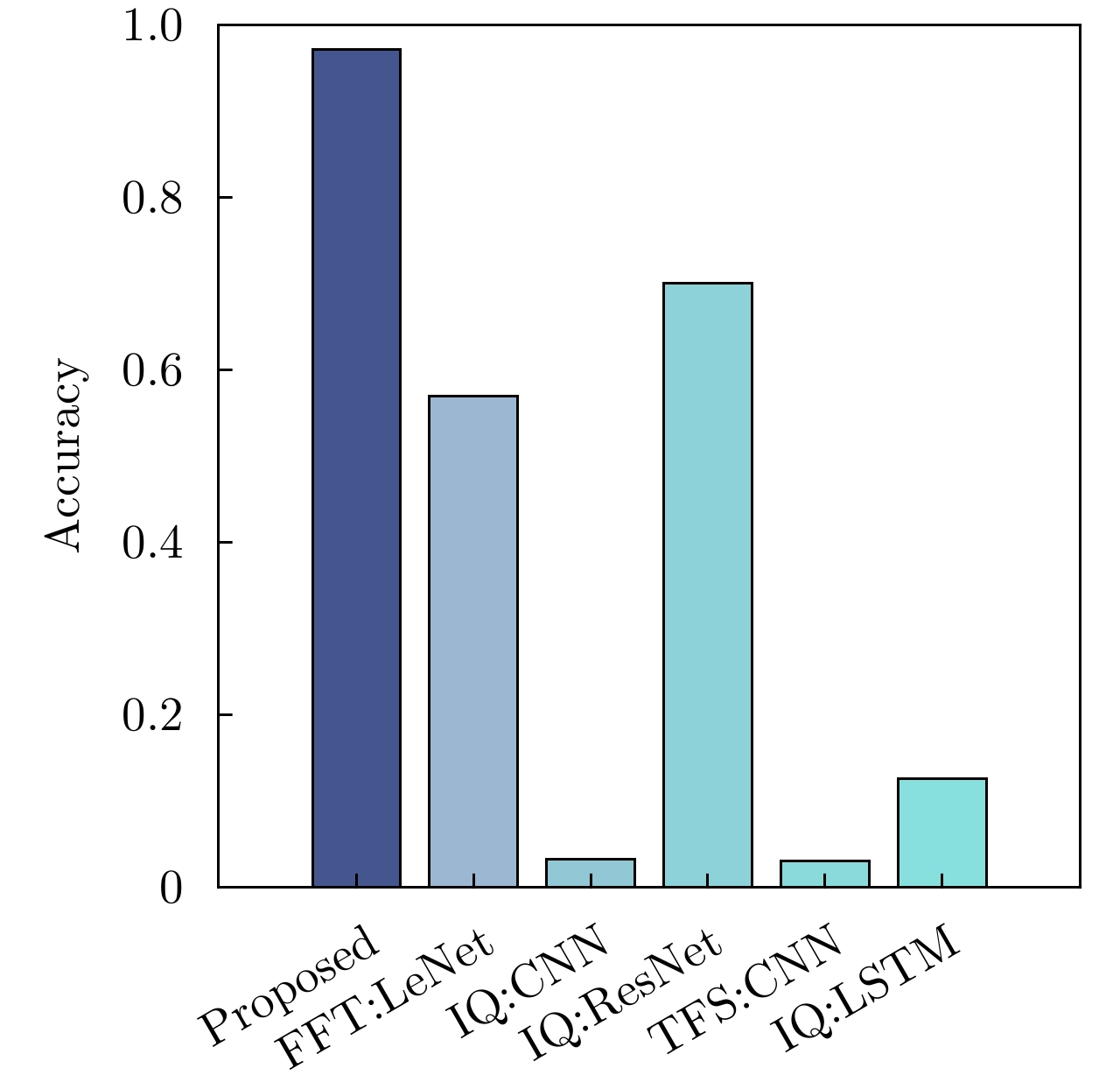
| [1] |
TALBOT K I, DULEY P R, HYATT M H, et al. Specific emitter identification and verification[J]. Technology Review, 2003, 32(1): 27–33.
|
| [2] |
JAGANNATH A, JAGANNATH J, and KUMAR P S P V. A comprehensive survey on radio frequency (RF) fingerprinting: Traditional approaches, deep learning, and open challenges[J]. Computer Networks, 2022, 219: 109455. doi: 10.1016/J.COMNET.2022.109455 |
| [3] |
SHI Ya, ZHANG Wenbo, ZHU Mingzhe, et al. Specific radar emitter identification: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 2216–2229. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210161 |
| [4] |
孙丽婷, 黄知涛, 王翔, 等. 辐射源指纹特征提取方法述评[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 1014–1031. doi: 10.12000/JR19115SUN Liting, HUANG Zhitao, WANG Xiang, et al. overview of radio frequency fingerprint extraction in specific emitter identification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 1014–1031. doi: 10.12000/JR19115 |
| [5] |
GOK G, ALP Y K, and ARIKAN O. A new method for specific emitter identification with results on real radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 3335–3346. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.2988558 |
| [6] |
LIU Zhangmeng. Multi-feature fusion for specific emitter identification via deep ensemble learning[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 110: 102939. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102939 |
| [7] |
ZHANG Zhen, JIA Jicheng, KANG Jian, et al. Overview of RF fingerprint identification technology methods[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2021, 47(3): 249–258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2021.03.001 |
| [8] |
GUO Shanzeng, AKHTAR S, and MELLA A. A method for radar model identification using time-domain transient signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 3132–3149. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3074129 |
| [9] |
SA Kejin, LANG Depeng, WANG Chenggang, et al. Specific emitter identification techniques for the internet of things[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 1644–1652. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962626 |
| [10] |
QIAN Yunhan, QI Jie, KUAI Xiaoyan, et al. Specific emitter identification based on multi-level sparse representation in automatic identification system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 2872–2884. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3068010 |
| [11] |
WANG Yu, GUI Guan, LIN Yun, et al. Few-shot specific emitter identification via deep metric ensemble learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(24): 24980–24994. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3194967 |
| [12] |
WANG Yu, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. An efficient specific emitter identification method based on complex-valued neural networks and network compression[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(8): 2305–2317. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3087243 |
| [13] |
FADUL M K M, REISING D R, and SARTIPI M. Identification of OFDM-based radios under Rayleigh fading using RF-DNA and deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 17100–17113. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053491 |
| [14] |
ZHANG Jingwen, WANG Fanggang, DOBRE O A, et al. Specific emitter identification via Hilbert-Huang transform in single-hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(6): 1192–1205. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2520908 |
| [15] |
ZHA Xiong, LI Tianyun, QIU Zhaoyang, et al. A novel anti-Doppler SEI algorithm based on the vector diagram decomposition[J]. Electronics Letters, 2021, 57(20): 785–787. doi: 10.1049/ell2.12257 |
| [16] |
ZHAO Yurui, WANG Xiang, SUN Liting, et al. A novel framework for extracting moment-based fingerprint features in specific emitter identification[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2023, 2023(1): 17. doi: 10.1186/S13634-023-00978-4 |
| [17] |
CARROLL T L. A nonlinear dynamics method for signal identification[J]. Chaos, 2007, 17(2): 023109. doi: 10.1063/1.2722870 |
| [18] |
熊小莉. 基于指纹特征提取的辐射源个体识别研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021.
XIONG Xiaoli. Research on individual radiation source identification based on fingerprint feature extraction[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021.
|
| [19] |
苏飞宇. 基于小波与混沌理论的辐射源个体识别方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.
SU Feiyu. Research on specific emitter identification method based on wavelet and chaos theory[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020.
|
| [20] |
张向前. 机器学习在辐射源信号指纹识别中的应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2018.
ZHANG Xiangqian. Study of machine learning in fingerprint identification of emitter signals. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018.
|
| [21] |
STROGATZ S H. Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: With Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press, 2019.
|
| [22] |
LI Cuiting and LIU Ke. Path signature-based phase space reconstruction for stock trend prediction[J]. International Journal of Data Science and Analytics, 2022, 14(3): 293–304. doi: 10.1007/s41060-022-00326-z |
| [23] |
LI Yue, CHEN Zengqiang, and CANG Shijian. Phase space reconstruction and time series prediction of a nonlinear financial system[C]. 2021 IEEE 10th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS), Suzhou, China, 2021: 23–28.
|
| [24] |
聂振华. 基于重构相空间的结构损伤检测方法及可视化研究[D]. [博士论文], 暨南大学, 2012.
NIE Zhenhua. Structural damage detection based on reconstructed phase space and the visualization of damage information[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Jinan University, 2012.
|
| [25] |
郑卉. 基于相空间重构的结构损伤识别方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.
ZHENG Hui. Study on structural damage identification based on phase space reconstruction[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013.
|
| [26] |
PACKARD N H, CRUTCHFIELD J P, FARMER J D, et al. Geometry from a time series[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1980, 45(9): 712–716. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.45.712 |
| [27] |
TAKENS F. Detecting strange attractors in turbulence[C]. Dynamical Systems and Turbulence, Warwick 1980, Coventry, UK, 2006: 366–381.
|
| [28] |
NOAKES L. The Takens embedding theorem[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 1991, 1(4): 867–872. doi: 10.1142/S0218127491000634 |
| [29] |
GIBSON J F, DOYNE FARMER J, CASDAGLI M, et al. An analytic approach to practical state space reconstruction[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 57(1/2): 1–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90085-2 |
| [30] |
ROSENSTEIN M T, COLLINS J J, and DE LUCA C J. A practical method for calculating Largest Lyapunov Exponents from small data sets[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1993, 65(1/2): 117–134. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(93)90009-P |
| [31] |
ROSENSTEIN M T, COLLINS J J, and DE LUCA C J. Reconstruction expansion as a geometry-based framework for choosing proper delay times[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1994, 73(1/2): 82–98. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(94)90226-7 |
| [32] |
FRASER A M and SWINNEY H L. Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information[J]. Physical Review A, 1986, 33(2): 1134–1140. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.33.1134 |
| [33] |
ZHANG Yu and REN Chenglong. The methods to confirm the dimension of re-constructed phase space[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2005, 27(6): 101–105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2005.06.022 |
| [34] |
KENNEL M B, BROWN R, and ABARBANEL H D I. Determining embedding dimension for phase-space reconstruction using a geometrical construction[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(6): 3403–3411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.3403 |
| [35] |
CAO Liangyue. Practical method for determining the minimum embedding dimension of a scalar time series[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1997, 110(1/2): 43–50. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(97)00118-8 |
| [36] |
BROOMHEAD D S and KING G P. Extracting qualitative dynamics from experimental data[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1986, 20(2/3): 217–236. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(86)90031-X |
| [37] |
KUGIUMTZIS D. State space reconstruction parameters in the analysis of chaotic time series—the role of the time window length[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1996, 95(1): 13–28. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(96)00054-1 |
| [38] |
KIM H S, EYKHOLT R, and SALAS J D. Nonlinear dynamics, delay times, and embedding windows[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1999, 127(1/2): 48–60. doi: 10.1016/S0167-2789(98)00240-1 |
| [39] |
KENINGTON P B. High-Linearity RF Amplifier Design[M]. Boston, USA: Artech House, 2000.
|
| [40] |
QIN Xin, HUANG Jie, WANG Jiantao, et al. Radar emitter identification based on unintentional phase modulation on pulse characteristic[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(5): 104–111. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020084 |
| [41] |
郭辉明. 水声通信辐射源指纹特征提取方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 厦门大学, 2018.
GUO Huiming. The study of the method for emitter fingerprint feature extraction in underwater acoustic communication[D]. [Master dissertation], Xiamen University, 2018.
|
| [42] |
毛毅, 胡远泽, 王景琳, 等. 基于相空间重构的未知辐射源信号特征提取与盲聚类[C]. 第十届中国指挥控制大会论文集, 北京, 2022.
MAO Yi, HU Yuanze, WANG Jinglin, et al. Feature extraction and blind clustering of unknown radiation sources based on phase space reconstruction[C]. 10th China Conference on Command and Control, Beijing, China, 2022.
|
| [43] |
REN Dongfang, ZHANG Tao, and HAN Jie. Approach of specific communication emitter identification combining ITD and nonlinear analysis[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(3): 331–339. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.03.010 |
| [44] |
YU Qin, CHENG Wei, and YANG Ruijuan. Specific emitter identification based on extraction of permutation entropy and fractal dimension[J]. Journal of Air Force Early Warning Academy, 2017, 31(3): 184–189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5839.2017.03.007 |
| [45] |
DENG Shouyun, HUANG Zhitao, WANG Xiang, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multidimension permutation entropy[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 2017: 1538728. doi: 10.1155/2017/1538728 |
| [46] |
SUN Liting, WANG Xiang, YANG Afeng, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multi-dimension approximate entropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 471–475. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2978333 |
| [47] |
YUAN Yingjun, HUANG Zhitao, WANG Fenghua, et al. Radio specific emitter identification based on nonlinear characteristics of signal[C]. 2015 IEEE International Black Sea Conference on Communications and Networking (BlackSeaCom), Constanta, Romania, 2015: 77–81.
|
| [48] |
袁英俊. 通信辐射源个体识别关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2014.
YUAN Yingjun. Research on key technologies of communication specific emitter identification[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2014.
|
| [49] |
眭萍, 郭英, 李红光, 等. 基于混沌吸引子重构和Low-rank聚类的跳频信号电台分选[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(12): 2965–2971. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180947SUI Ping, GUO Ying, LI Hongguang, et al. Frequency-hopping transmitter classification based on chaotic attractor reconstruction and low-rank clustering[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(12): 2965–2971. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180947 |
| [50] |
杨立波. 雷达辐射源无意调制特征提取算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2014.
YANG Libo. Research on unintentional modulation feature extraction for radar emitter[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2014.
|
| [51] |
许丹. 辐射源指纹机理及识别方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2008.
XU Dan. Research on mechanism and methodology of specific emitter identification[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2008.
|
| [52] |
ZHAO Yurui, WANG Xiang, and HUANG Zhitao. Concentrate on hardware imperfection via aligning reconstructed States[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(12): 2934–2938. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3204170 |
| [53] |
赵雨睿, 宋川江, 王翔, 等. 采用重构吸引子的辐射源个体识别技术[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 待出版.
ZHAO Yurui, SONG Chuanjiang, WANG Xiang, et al. Specific emitter identification using reconstructed attractors[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, in press.
|
| [54] |
ZHAO Yurui, WANG Xiang, SUN Liting, et al. A novel signal representation in SEI: Manifold[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2023, 360(7): 5292–5318. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2023.03.010 |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
UZUNDURUKAN E, DALVEREN Y, and KARA A. A database for the radio frequency fingerprinting of bluetooth devices[J]. Data, 2020, 5(2): 55. doi: 10.3390/data5020055 |
| [57] |
MERCHANT K, REVAY S, STANTCHEV G, et al. Deep learning for RF device fingerprinting in cognitive communication networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 160–167. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2796446 |
| [58] |
WENG Lintianran, PENG Jinlin, HE Yuan, et al. Specific emitter identification of ADS-B signal based on deep residual network[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2021, 28(4): 24–29. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2020.0095 |
| [59] |
XIAO Yao and WEI Xizhang. Specific emitter identification of radar based on one dimensional convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1550: 032114. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1550/3/032114 |
| [60] |
BITAR N, MUHAMMAD S, and REFAI H H. Wireless technology identification using deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Montreal, Canada, 2017: 1–6.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: