- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | HUANG Yan, ZHANG Hui, LAN Lyuhongkang, et al. Overview of signal processing techniques for automotive millimeter-wave radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(5): 923–970. doi: 10.12000/JR23119 |
Overview of Signal Processing Techniques for Automotive Millimeter-wave Radar(in English)
DOI: 10.12000/JR23119 CSTR: 32380.14.jr23119
More Information-
Abstract
As one of the core components of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), automotive millimeter-wave radar has become the focus of scholars and manufacturers at home and abroad because it has the advantages of all-day and all-weather operation, miniaturization, high integration, and key sensing capabilities. The core performance indicators of the automotive millimeter-wave radar are distance, speed, angular resolution, and field of view. Accuracy, cost, real-time and detection performance, and volume are the key issues to be considered. The increasing performance requirements pose several challenges for the signal processing of millimeter-wave radar systems. Radar signal processing technology is crucial for improving radar performance to meet more stringent requirements. Obtaining dense radar point clouds, generating accurate radar imaging results, and mitigating mutual interference among multiple radar systems are the key points and the foundation for subsequent tracking, recognition, and other applications. Therefore, this paper discusses the practical application of the automotive millimeter-wave radar system based on the key technologies of signal processing, summarizes relevant research results, and mainly discusses the topics of point cloud imaging processing, synthetic aperture radar imaging processing, and interference suppression. Finally, herein, we summarize the research status at home and abroad. Moreover, future development trends for automotive millimeter-wave radar systems are forecast with the hope of enlightening readers in related fields.
-

-
References
[1] 黄乐平, 陈旭东. 4D毫米波雷达: 智驾普及的新路径[EB/OL]. https://xueqiu.com/3161724413/247489207, 2023.HUANG Leping and CHEN Xudong. 4D millimeter-wave radar: A new path to the popularization of smart driving[EB/OL]. https://xueqiu.com/3161724413/247489207, 2023.[2] LI Gang, SIT Y L, MANCHALA S, et al. Novel 4D 79 GHz radar concept for object detection and active safety applications[C]. The 2019 12th German Microwave Conference(GeMiC), Stuttgart, Germany, 2019: 87–90. doi: 10.23919/GEMIC.2019.8698172.[3] QIAN Kun, HE Zhaoyuan, and ZHANG Xinyu. 3D point cloud generation with millimeter-wave radar[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2020, 4(4): 148. doi: 10.1145/3432221.[4] ENGELS F, HEIDENREICH P, WINTERMANTEL M, et al. Automotive radar signal processing: Research directions and practical challenges[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 865–878. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3063666.[5] 林凤泰, 严蘋蘋, 张慧, 等. 基于最近迭代点的毫米波雷达点云数据处理方法[J]. 信号处理, 2023, 39(2): 288–297. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.02.010.LIN Fengtai, YAN Pinpin, ZHANG Hui, et al. Iterative closest point method for point cloud data processing of millimeter wave radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2023, 39(2): 288–297. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2023.02.010.[6] WEISHAUPT F, APPENRODT N, TILLY J F, et al. PreCFAR gridmaps for automotive radar[C]. The 2021 18th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), London, United Kingdom, 2022: 161–164. doi: 10.23919/EuRAD50154.2022.9784455.[7] WEI Ziping, LI Bin, FENG Tao, et al. Area-based CFAR target detection for automotive millimeter-wave radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(3): 2891–2906. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3216013.[8] 兰吕鸿康, 黄岩, 郑凯航, 等. 毫米波雷达自适应门限点云成像方法研究[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(10): 2009–2020. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.10.002.LAN Lühongkang, HUANG Yan, ZHENG Kaihang, et al. Research on adaptive threshold point cloud imaging method of millimeter-wave radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(10): 2009–2020. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.10.002.[9] DANZER A, GRIEBEL T, BACH M, et al. 2D car detection in radar data with pointnets[C]. 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 2019: 61–66. doi: 10.1109/ITSC.2019.8917000.[10] JIN Feng, SENGUPTA A, CAO Siyang, et al. Mmwave radar point cloud segmentation using GMM in multimodal traffic monitoring[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference(RADAR), Washington, USA, 2020: 732–737. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114662.[11] XU Fenglei, WANG Huan, HU Bingwen, et al. Road boundaries detection based on modified occupancy grid map using millimeter-wave radar[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020, 25(4): 1496–1503. doi: 10.1007/s11036-019-01378-5.[12] JIN Yi, PROPHET R, DELIGIANNIS A, et al. Point-cloud-based road course estimation on automotive radar data[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Antennas, Communications and Electronic Systems (COMCAS), Tel Aviv, Israel, 2021: 29–34. doi: 10.1109/COMCAS52219.2021.9629037.[13] CHENG Yuwei, SU Jingran, CHEN Hongyu, et al. A new automotive radar 4D point clouds detector by using deep learning[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, Canada, 2021: 8398–8402. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9413682.[14] CHENG Yuwei, SU Jingran, JIANG Mengxin, et al. A novel radar point cloud generation method for robot environment perception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(6): 3754–3773. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2022.3185831.[15] JIANG Mengjie, XU Gang, PEI Hao, et al. 4D high-resolution imagery of point clouds for automotive mmWave radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3258688.[16] FRANCESCHI R and RACHKOV D. Deep learning-based radar detector for complex automotive scenarios[C]. 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Aachen, Germany, 2022: 303–308. doi: 10.1109/IV51971.2022.9827045.[17] TAN Bin, MA Zhixiong, ZHU Xichan, et al. 3-D object detection for multiframe 4-D automotive millimeter-wave radar point cloud[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(11): 11125–11138. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3219643.[18] SUN Yue, HUANG Zhuoming, ZHANG Honggang, et al. 3DRIMR: 3D reconstruction and imaging via mmWave radar based on deep learning[C]. 2021 IEEE International Performance, Computing, and Communications Conference (IPCCC), Austin, USA, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/IPCCC51483.2021.9679394.[19] SUN Yue, ZHANG Honggang, HUANG Zhuoming, et al. DeepPoint: A deep learning model for 3D reconstruction in point clouds via mmWave radar[J]. arXiv: 2109.09188, 2021. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2109.09188.[20] HUANG Yan, ZHANG Hui, GUO Kunpeng, et al. Density-based vehicle detection approach for automotive millimeter-wave radar[C]. The 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Shenzhen, China, 2020: 534–537. doi: 10.1109/ICEICT51264.2020.9334238.[21] DREHER M, ERÇELIK E, BÄNZIGE T, et al. Radar-based 2D car detection using deep neural networks[C]. The 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rhodes, Greece, 2020: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ITSC45102.2020.9294546.[22] XU Baowei, ZHANG Xinyu, WANG Li, et al. RPFA-Net: A 4D RaDAR pillar feature attention network for 3D object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, USA, 2021: 3061–3066. doi: 10.1109/ITSC48978.2021.9564754.[23] LANG A H, VORA S, CAESAR H, et al. PointPillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12689–12697. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.01298.[24] MEYER M and KUSCHK G. Automotive radar dataset for deep learning based 3D object detection[C]. The 2019 16th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Paris, France, 2019: 129–132.[25] OUAKNINE A, NEWSON A, REBUT J, et al. CARRADA dataset: Camera and automotive radar with range-angle-Doppler annotations[C]. The 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 5068–5075, doi: 10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9413181.[26] CAESAR H, BANKITI V, LANG A H, et al. NuScenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11618–11628. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01164.[27] KRAMER A, HARLOW K, WILLIAMS C, et al. ColoRadar: The direct 3D millimeter wave radar dataset[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2022, 41(4): 351–360. doi: 10.1177/02783649211068535.[28] WANG Yizhou, JIANG Zhongyu, LI Yudong, et al. RODNet: A real-time radar object detection network cross-supervised by camera-radar fused object 3D localization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 954–967. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3058895.[29] BIJELIC M, GRUBER T, MANNAN F, et al. Seeing through fog without seeing fog: Deep multimodal sensor fusion in unseen adverse weather[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11679–11689. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01170.[30] PALFFY A, POOL E, BARATAM S, et al. Multi-class road user detection with 3+1D radar in the View-of-Delft dataset[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 4961–4968. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3147324.[31] PAEK D H, KONG S H, and WIJAYA K T. K-Radar: 4D radar object detection for autonomous driving in various weather conditions[C]. The 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 3819–3829.[32] SCHUMANN O, HAHN M, SCHEINER N, et al. RadarScenes: A real-world radar point cloud data set for automotive applications[C]. The 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Sun City, South Africa, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION49465.2021.9627037.[33] ZHENG Lianqing, MA Zhixiong, ZHU Xichan, et al. TJ4DRadSet: A 4D radar dataset for autonomous driving[C]. The 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 2022: 493–498. doi: 10.1109/ITSC55140.2022.9922539.[34] MEYER M and KUSCHK G. Deep learning based 3D object detection for automotive radar and camera[C]. The 2019 16th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Paris, France, 2019: 133–136.[35] NABATI R and QI Hairong. RRPN: Radar region proposal network for object detection in autonomous vehicles[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, China, 2019: 3093–3097. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803392.[36] JHA H, LODHI V, and CHAKRAVARTY D. Object detection and identification using vision and radar data fusion system for ground-based navigation[C]. The 2019 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 2019: 590–593. doi: 10.1109/SPIN.2019.8711717.[37] NOBIS F, GEISSLINGER M, WEBER M, et al. A deep learning-based radar and camera sensor fusion architecture for object detection[J]. 2019 Sensor Data Fusion: Trends, Solutions, Applications (SDF), Bonn, Germany, 2019: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/SDF.2019.8916629.[38] CUI Hang, WU Junzhe, ZHANG Jiaming, et al. 3D detection and tracking for on-road vehicles with a monovision camera and dual low-cost 4D mmWave radars[C]. 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, USA, 2021: 2931–2937. doi: 10.1109/ITSC48978.2021.9564904.[39] NABATI R and QI Hairong. Centerfusion: Center-based radar and camera fusion for 3D object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision(WACV), Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 1526–1535. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00157.[40] JOHN V, NITHILAN M K, MITA S, et al. So-Net: Joint semantic segmentation and obstacle detection using deep fusion of monocular camera and radar[C]. Pacific-Rim Symposium on Image and Video Technology (PSIVT), Sydney, Australia, 2020: 138–148. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-39770-8_11.[41] CHANG Shuo, ZHANG Yifan, ZHANG Fan, et al. Spatial attention fusion for obstacle detection using mmWave radar and vision sensor[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(4): 956. doi: 10.3390/s20040956.[42] BANSAL K, RUNGTA K, and BHARADIA D. RadSegNet: A reliable approach to radar camera fusion[J]. arXiv: 2208.03849, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2208.03849.[43] LO C C and VANDEWALLE P. RCDPT: Radar-camera fusion dense prediction transformer[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10096129.[44] WU Zizhang, CHEN Guilian, GAN Yuanzhu, et al. MVFusion: Multi-view 3D object detection with semantic-aligned radar and camera fusion[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, London, UK, 2023: 2766–2773. doi: 10.1109/ICRA48891.2023.10161329.[45] SENGUPTA A, CHENG Lei, and CAO Siyang. Robust multiobject tracking using mmwave radar-camera sensor fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2022, 6(10): 5501304. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2022.3213529.[46] ZHOU Taohua, JIANG Kun, WANG Sijia, et al. 3D multiple object tracking with multi-modal fusion of low-cost sensors for autonomous driving[C]. The 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 2022: 1750–1757. doi: 10.1109/ITSC55140.2022.9921854.[47] BAI Jie, LI Sen, HUANG Libo, et al. Robust detection and tracking method for moving object based on radar and camera data fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(9): 10761–10774. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3049449.[48] SENGUPTA A, YOSHIZAWA A, and CAO Siyang. Automatic radar-camera dataset generation for sensor-fusion applications[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 2875–2882. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3144524.[49] DONG Xu, ZHUANG Binnan, MAO Yunxiang, et al. Radar camera fusion via representation learning in autonomous driving[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, USA, 2021: 1672–1681. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW53098.2021.00183.[50] FEIL P, KRAUS T, and MENZEL W. Short range mm-Wave SAR for surveillance and security applications[C]. The 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 1–4.[51] IQBAL H, SAJJAD M B, MUELLER M, et al. SAR imaging in an automotive scenario[C]. The 2015 IEEE 15th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Lecce, Italy, 2015: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/MMS.2015.7375430.[52] JIANG Chenghao, TANG Shiyang, ZHANG Linrang, et al. Real data imaging approach design for automotive SAR experiments[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 386–388. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028054.[53] XU Gang, PEI Hao, JIANG Mengjie, et al. High-resolution mmWave SAR imagery for automotive parking assistance[J]. IEEE Journal on Miniaturization for Air and Space Systems, 2023, 4(1): 54–61. doi: 10.1109/JMASS.2022.3226771.[54] WU Huaming and ZWICK T. Automotive SAR for parking lot detection[C]. 2009 German Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 2009: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/GEMIC.2009.4815910.[55] GUMBMANN F, TRAN H P, WEINZIERL J, et al. Optimization of a fast scanning millimetre-wave short range SAR imaging system[C]. 2007 European Radar Conference, Munich, Germany, 2007: 24–27. doi: 10.1109/EURAD.2007.4404927.[56] SRIHARSHA NAG T S, VANDANA G S, PARDHASARADHI B, et al. SAR imaging with automotive radar: Range migration algorithm, experiment, and future directions in automotive vehicle[C]. The 2022 IEEE 7th International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Mangalore, India, 2022: 382–387. doi: 10.1109/ICRAIE56454.2022.10054316.[57] ZHANG Yan, ZHAO Jie, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. RMA-based azimuth-range decouple method for automotive SAR sparse imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 3480–3492. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3226161.[58] LEE S, JUNG Y, LEE M, et al. Compressive sensing-based SAR image reconstruction from sparse radar sensor data acquisition in automotive FMCW radar system[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(21): 7283. doi: 10.3390/s21217283.[59] IQBAL H, SCHARTEL M, ROOS F, et al. Implementation of a SAR demonstrator for automotive imaging[C]. The 2018 18th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Istanbul, Turkey, 2018: 240–243. doi: 10.1109/MMS.2018.8611814.[60] ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734.[61] GISDER T, HARRER F, and BIEBL E. Application of a stream-based SAR-backprojection approach for automotive environment perception[C]. The 2018 19th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2018.8447924.[62] FARHADI M, FEGER R, FINK J, et al. Adaption of fast factorized back-projection to automotive SAR applications[C]. The 2019 16th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Paris, France, 2019: 261–264.[63] FARHADI M, FEGER R, FINK J, et al. Synthetic aperture radar imaging of moving targets for automotive applications[C]. The 2021 18th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), London, United Kingdom, 2022: 453–456. doi: 10.23919/EuRAD50154.2022.9784564.[64] MANZONI M, TEBALDINI S, MONTI-GUARNIERI A V, et al. Multipath in automotive MIMO SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5202612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3240705.[65] RIZZI M, MANZONI M, TEBALDINI S, et al. Multi-beam automotive SAR imaging in urban scenarios[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764331.[66] WRIGHT D, GISHKORI S, DANIEL L, et al. Adaptive integration time in automotive SAR[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266411.[67] TAGLIAFERRI D, RIZZI M, TEBALDINI S, et al. Cooperative synthetic aperture radar in an urban connected car scenario[C]. The 2021 1st IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications & Sensing (JC&S), Dresden, Germany, 2021: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/JCS52304.2021.9376348.[68] FEGER R, HADERER A, and STELZER A. Experimental verification of a 77-GHz synthetic aperture radar system for automotive applications[C]. 2017 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Nagoya, Japan, 2017: 111–114. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM.2017.7918869.[69] TAGLIAFERRI D, RIZZI M, NICOLI M, et al. Navigation-aided automotive SAR for high-resolution imaging of driving environments[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 35599–35615. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3062084.[70] WU Huaming and ZWICK T. A novel motion compensation algorithm for automotive SAR: Simulations and experiments[C]. German Microwave Conference Digest of Papers, Berlin, Germany, 2010: 222–226.[71] WU Huaming, ZWIRELLO L, LI Xuyang, et al. Motion compensation with one-axis gyroscope and two-axis accelerometer for automotive SAR[C]. 2011 German Microwave Conference, Darmstadt, Germany, 2011: 1–4.[72] IQBAL H, LÖFFLER A, MEJDOUB M N, et al. Realistic SAR implementation for automotive applications[C]. The 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 306–309. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00085.[73] STEINER M, GREBNER T, and WALDSCHMIDT C. Millimeter-wave SAR-imaging with radar networks based on radar self-localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(11): 4652–4661. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2020.2995225.[74] FARHADI M, FEGER R, FINK J, et al. Phase error estimation for automotive SAR[C]. 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Linz, Austria, 2020: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM48759.2020.9298998.[75] FARHADI M, FEGER R, FINK J, et al. Space-variant phase error estimation and correction for automotive SAR[C]. The 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 310–313. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00086.[76] MANZONI M, RIZZI M, TEBALDINI S, et al. Residual motion compensation in automotive MIMO SAR imaging[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764310.[77] MANZONI M, TAGLIAFERRI D, RIZZI M, et al. Motion estimation and compensation in automotive MIMO SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(2): 1756–1772. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3219542.[78] HU Ruizhi, RAO B S M R, MURTADA A, et al. Automotive squint-forward-looking SAR: High resolution and early warning[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 904–912. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3064175.[79] WANG Jianqiu, LIU Kang, LIU Qingping, et al. Azimuth improved radar imaging with virtual array in the forward-looking sight[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(19): 18867–18879. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3163163.[80] GISHKORI S, WRIGHT D, DANIEL L, et al. Imaging moving targets for a forward-scanning automotive SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 56(2): 1106–1119. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2925446.[81] GAO Xiangyu, ROY S, and XING Guanbin. MIMO-SAR: A hierarchical high-resolution imaging algorithm for mmWave FMCW radar in autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7322–7334. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3092355.[82] ZHANG Bangjie, XU Gang, ZHOU Rui, et al. Multi-channel back-projection algorithm for mmWave automotive MIMO SAR imaging with Doppler-division multiplexing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2023, 17(2): 445–457. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3207902.[83] FARHADI M, FEGER R, FINK J, et al. Automotive synthetic aperture radar imaging using TDM-MIMO[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2147009.2021.9455230.[84] SOMMER A, NGO T T, and OSTERMANN J. 3D multiple input single output near field automotive synthetic aperture radar[C]. The 2017 18th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2017: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2017.8008121.[85] TEBALDINI S, MANZONI M, TAGLIAFERRI D, et al. Sensing the urban environment by automotive SAR imaging: Potentials and challenges[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(15): 3602. doi: 10.3390/rs14153602.[86] MANZONI M, TEBALDINI S, MONTI-GUARNIERI A V, et al. A comparison of processing schemes for automotive MIMO SAR imaging[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(19): 4696. doi: 10.3390/rs14194696.[87] TEBALDINI S, RIZZI M, MANZONI M, et al. SAR imaging in automotive scenarios[C]. 2022 Microwave Mediterranean Symposium (MMS), Pizzo Calabro, Italy, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/MMS55062.2022.9825599.[88] ALBABA A, SAKHNINI A, SAHLI H, et al. Forward-looking MIMO-SAR for enhanced angular resolution[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764255.[89] ALBABA A, BAUDUIN M, SAHLI H, et al. Low-complexity forward-looking volumetric SAR for high resolution 3-D radar imaging[C]. 2023 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf23), San Antonio, USA, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2351548.2023.10149651.[90] HAKOBYAN G and YANG Bin. High-performance automotive radar: A review of signal processing algorithms and modulation schemes[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36(5): 32–44. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2911722.[91] ALLAND S, STARK W, ALI M, et al. Interference in automotive radar systems: Characteristics, mitigation techniques, and current and future research[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36(5): 45–59. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2019.2908214.[92] XU Zhihuo. Bi-level l1 optimization-based interference reduction for millimeter wave radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(1): 728–738. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3215636.[93] KIM Y. Identification of FMCW radar in mutual interference environments using frequency ramp modulation[C]. The 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Davos, Switzerland, 2016: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/EuCAP.2016.7481567.[94] KITSUKAWA Y, MITSUMOTO M, MIZUTANI H, et al. An interference suppression method by transmission chirp waveform with random repetition interval in fast-chirp FMCW radar[C]. The 2019 16th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Paris, France, 2019: 165–168.[95] BECHTER J, SIPPEL C, and WALDSCHMIDT C. Bats-inspired frequency hopping for mitigation of interference between automotive radars[C]. 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), San Diego, USA, 2016: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM.2016.7533928.[96] HOSSAIN A, ELSHAFIEY I, and AL-SANIE A. Mutual interference mitigation in automotive radars under realistic road environments[C]. The 2017 8th International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), Amman, Jordan, 2017: 895–900. doi: 10.1109/ICITECH.2017.8079965.[97] LUO Tangnian, WU C H E, and CHEN Y J E. A 77-GHz CMOS automotive radar transceiver with anti-interference function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2013, 60(12): 3247–3255. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2013.2265974.[98] YANG Xiaokang, ZHANG Kunfan, WANG Ting, et al. Anti-interference waveform design for automotive radar[C]. The 2017 IEEE 2nd Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 2017: 14–17. doi: 10.1109/IAEAC.2017.8053967.[99] UYSAL F. Phase-coded FMCW automotive radar: System design and interference mitigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(1): 270–281. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2953305.[100] LIU T H, HSU M L, and TSAI Z M. Mutual interference of pseudorandom noise radar in automotive collision avoidance application at 24 GHz[C]. The 2016 IEEE 5th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics, Kyoto, Japan, 2016: 1–2. doi: 10.1109/GCCE.2016.7800400.[101] XU Zhihuo and SHI Quan. Interference mitigation for automotive radar using orthogonal noise waveforms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 137–141. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2777962.[102] HAKOBYAN G, ARMANIOUS K, and YANG Bin. Interference-aware cognitive radar: A remedy to the automotive interference problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2326–2339. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2947973.[103] BASIREDDY A and MORADI H. OFDM waveform design for interference resistant automotive radars[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(14): 15670–15678. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3057119.[104] BOURDOUX A and BAUDUIN M. PMCW waveform cross-correlation characterization and interference mitigation[C]. The 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 164–167. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00051.[105] KHOURY J, RAMANATHAN R, MCCLOSKEY D, et al. RadarMAC: Mitigating radar interference in self-driving cars[C]. The 2016 13th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), London, UK, 2016: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/SAHCN.2016.7733011.[106] MAZHER K U, HEATH R W, GULATI K, et al. Automotive radar interference characterization and reduction by partial coordination[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266425.[107] AYDOGDU C, GARCIA N, HAMMARSTRAND L, et al. Radar communications for combating mutual interference of FMCW radars[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2019.8835744.[108] AYDOGDU C, KESKIN M F, GARCIA N, et al. RadChat: Spectrum sharing for automotive radar interference mitigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(1): 416–429. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2959881.[109] AYDOGDU C, KESKIN M F, and WYMEERSCH H. Automotive radar interference mitigation via multi - hop cooperative radar communications[C]. The 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 270–273. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00076.[110] JIN Feng and CAO Siyang. Automotive radar interference mitigation using adaptive noise canceller[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3747–3754. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2901493.[111] WAGNER M, SULEJMANI F, MELZER A, et al. Threshold-free interference cancellation method for automotive FMCW radar systems[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2018.8351077.[112] BECHTER J, EID K, ROOS F, et al. Digital beamforming to mitigate automotive radar interference[C]. 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), San Diego, USA, 2016: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM.2016.7533914.[113] ARTYUKHIN I, ERMOLAEV V, FLAKSMAN A, et al. Development of effective anti-interference primary signal processing for mmWave automotive radar[C]. 2019 International Conference on Engineering and Telecommunication (EnT), Dolgoprudny, Russia, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/EnT47717.2019.9030561.[114] BECHTER J, RAMEEZ M, and WALDSCHMIDT C. Analytical and experimental investigations on mitigation of interference in a DBF MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(5): 1727–1734. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2668404.[115] RAMEEZ M, DAHL M, and PETTERSSON M I. Adaptive digital beamforming for interference suppression in automotive FMCW radars[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 252–256. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378566.[116] NOZAWA T, MAKINO Y, TAKAYA N, et al. An anti-collision automotive FMCW radar using time-domain interference detection and suppression[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems (Radar 2017), Belfast, Ireland, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/cp.2017.0366.[117] BARJENBRUCH M, KELLNER D, DIETMAYER K, et al. A method for interference cancellation in automotive radar[C]. 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Heidelberg, Germany, 2015: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM.2015.7117925.[118] CHOI J H, LEE H B, CHOI J W, et al. Mutual interference suppression using clipping and weighted-envelope normalization for automotive FMCW radar systems[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2016, E99.B(1): 280–287. doi: 10.1587/transcom.2015EBP3152.[119] BECHTER J, ROOS F, RAHMAN M, et al. Automotive radar interference mitigation using a sparse sampling approach[C]. 2017 European Radar Conference (EURAD), Nuremberg, Germany, 2017: 90–93. doi: 10.23919/EURAD.2017.8249154.[120] UMEHIRA M, NOZAWA T, MAKINO Y, et al. A novel iterative inter-radar interference reduction scheme for densely deployed automotive FMCW radars[C]. The 2018 19th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2018.8448223.[121] NEEMAT S, KRASNOV O, and YAROVOY A. An interference mitigation technique for FMCW radar using beat-frequencies interpolation in the STFT domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2019, 67(3): 1207–1220. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2018.2881154.[122] LIU Zhenyu, LU Wei, WU Jiayan, et al. A PELT-KCN algorithm for FMCW radar interference suppression based on signal reconstruction[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 45108–45118. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2977098.[123] JUNG J, LIM S, KIM J, et al. Interference suppression and signal restoration using kalman filter in automotive radar systems[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, USA, 2020: 726–731. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114723.[124] ALHUMAIDI M and WINTERMANTEL M. Interference avoidance and mitigation in automotive radar[C]. The 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 172–175. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00053.[125] WANG Jianping. CFAR-based interference mitigation for FMCW automotive radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(8): 12229–12238. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3111514.[126] WANG Jianping, DING Min, and YAROVOY A. Matrix-pencil approach-based interference mitigation for FMCW radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 5099–5115. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3090798.[127] RAMEEZ M, DAHL M, and PETTERSSON M I. Autoregressive model-based signal reconstruction for automotive radar interference mitigation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(5): 6575–6586. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3042061.[128] FEI Tai, GUANG Honghao, SUN Yuliang, et al. An efficient sparse sensing based interference mitigation approach for automotive radar[C]. The 2020 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 274–277. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00077.[129] YANG Shuai and SHANG Xiaolei. Iterative approaches to interference mitigation for automotive radar[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf22), New York City, USA, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9764221.[130] UYSAL F and SANKA S. Mitigation of automotive radar interference[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 405–410. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378593.[131] WU Jiayan, YANG Siyuan, LU Wei, et al. Iterative modified threshold method based on EMD for interference suppression in FMCW radars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(8): 1219–1228. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2020.0092.[132] LEE S, LEE J Y, and KIM S C. Mutual interference suppression using wavelet denoising in automotive FMCW radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(2): 887–897. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2961235.[133] CORREAS-SERRANO A and GONZALEZ-HUICI M A. Sparse reconstruction of chirplets for automotive FMCW radar interference mitigation[C]. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Conference on Microwaves for Intelligent Mobility (ICMIM), Detroit, USA, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMIM.2019.8726758.[134] WANG Jianping, DING Min, and YAROVOY A. Interference mitigation for FMCW radar with sparse and low-rank hankel matrix decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 822–834. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3147863.[135] LIU Zhenyu, WU Jiayan, YANG Siyuan, et al. DOA estimation method based on EMD and MUSIC for mutual interference in FMCW automotive radars[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3504005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3058729.[136] XU Zhihuo and YUAN Min. An interference mitigation technique for automotive millimeter wave radars in the tunable Q-factor wavelet transform domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(12): 5270–5283. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3121322.[137] LEE W H and LEE S. Geometric sequence decomposition-based interference cancellation in automotive radar systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 4318–4327. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3141543.[138] WANG Yunxuan, HUANG Yan, WEN Cai, et al. Mutual interference mitigation for automotive FMCW radar with time and frequency domain decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3275816.[139] MUN J, KIM H, and LEE J. A deep learning approach for automotive radar interference mitigation[C]. The 2018 IEEE 88th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Chicago, USA, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2018.8690848.[140] ROCK J, TOTH M, MESSNER E, et al. Complex signal denoising and interference mitigation for automotive radar using convolutional neural networks[C]. The 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION43075.2019.9011164.[141] MUN J, HA S, and LEE J. Automotive radar signal interference mitigation using RNN with self attention[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 3802–3806. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053013.[142] RISTEA N C, ANGHEL A, and IONESCU R T. Fully convolutional neural networks for automotive radar interference mitigation[C]. The 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, Canada, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2020-Fall49728.2020.9348690.[143] FUCHS J, DUBEY A, LÜBKE M, et al. Automotive radar interference mitigation using a convolutional autoencoder[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, USA, 2020: 315–320. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114641.[144] ROCK J, ROTH W, TOTH M, et al. Resource-efficient deep neural networks for automotive radar interference mitigation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 927–940. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3062452. -
Proportional views

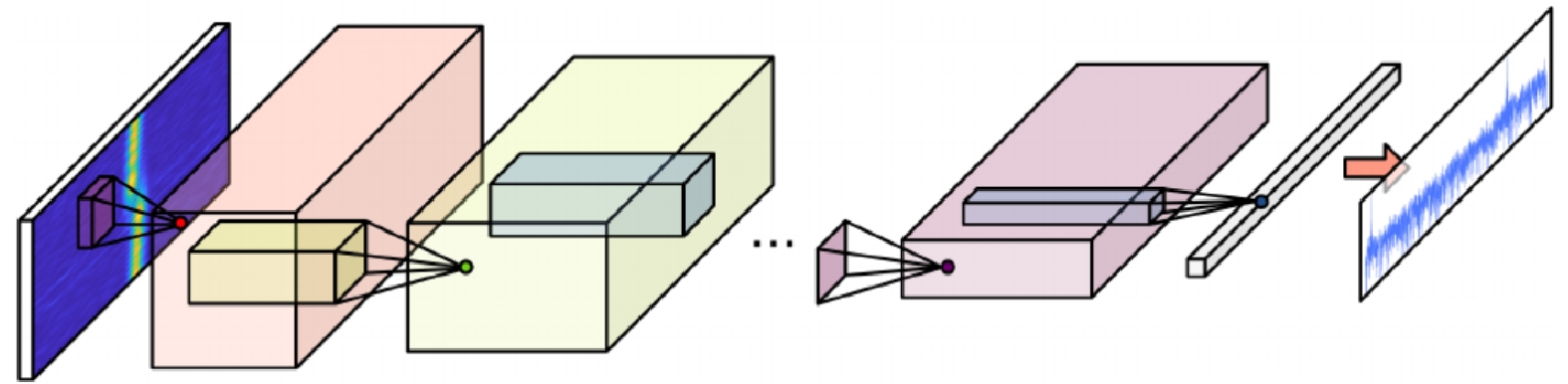
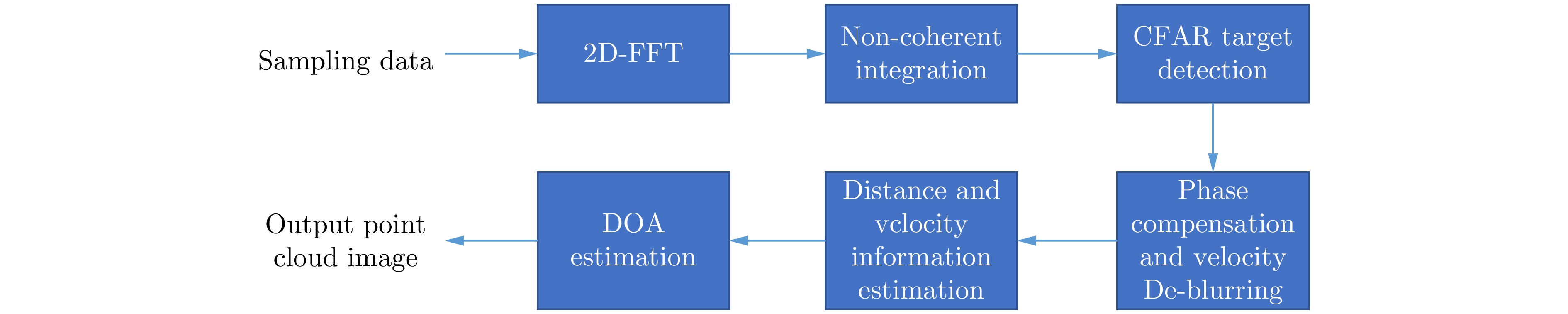
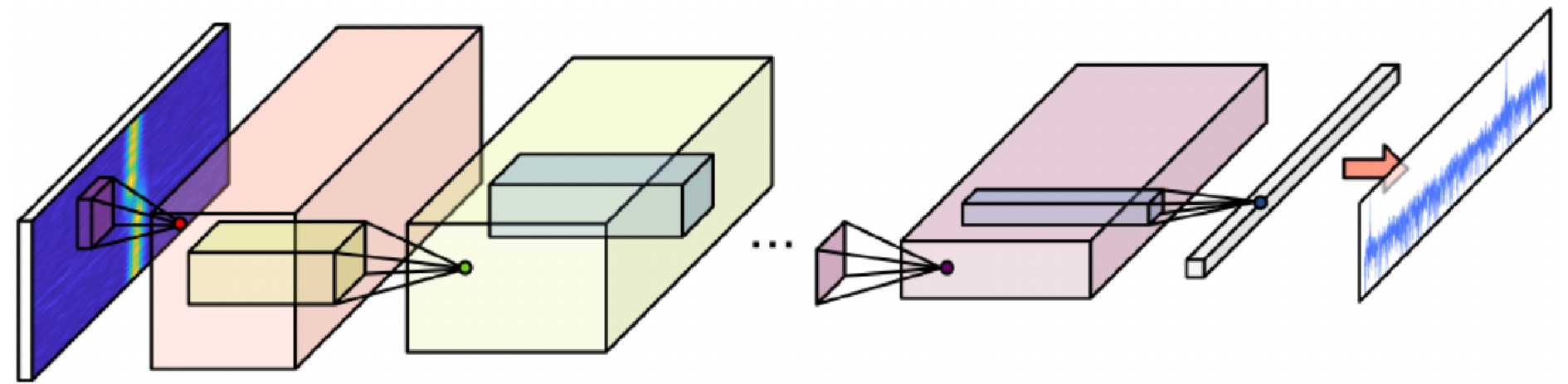
- Figure 1. The processing flow of millimeter-wave radar point cloud imaging algorithm
- Figure 2. MIMO-FMCW 4D radar imaging based on BPSK orthogonal waveform[2]
- Figure 3. The 3D point cloud generated by MilliPoint system[3]
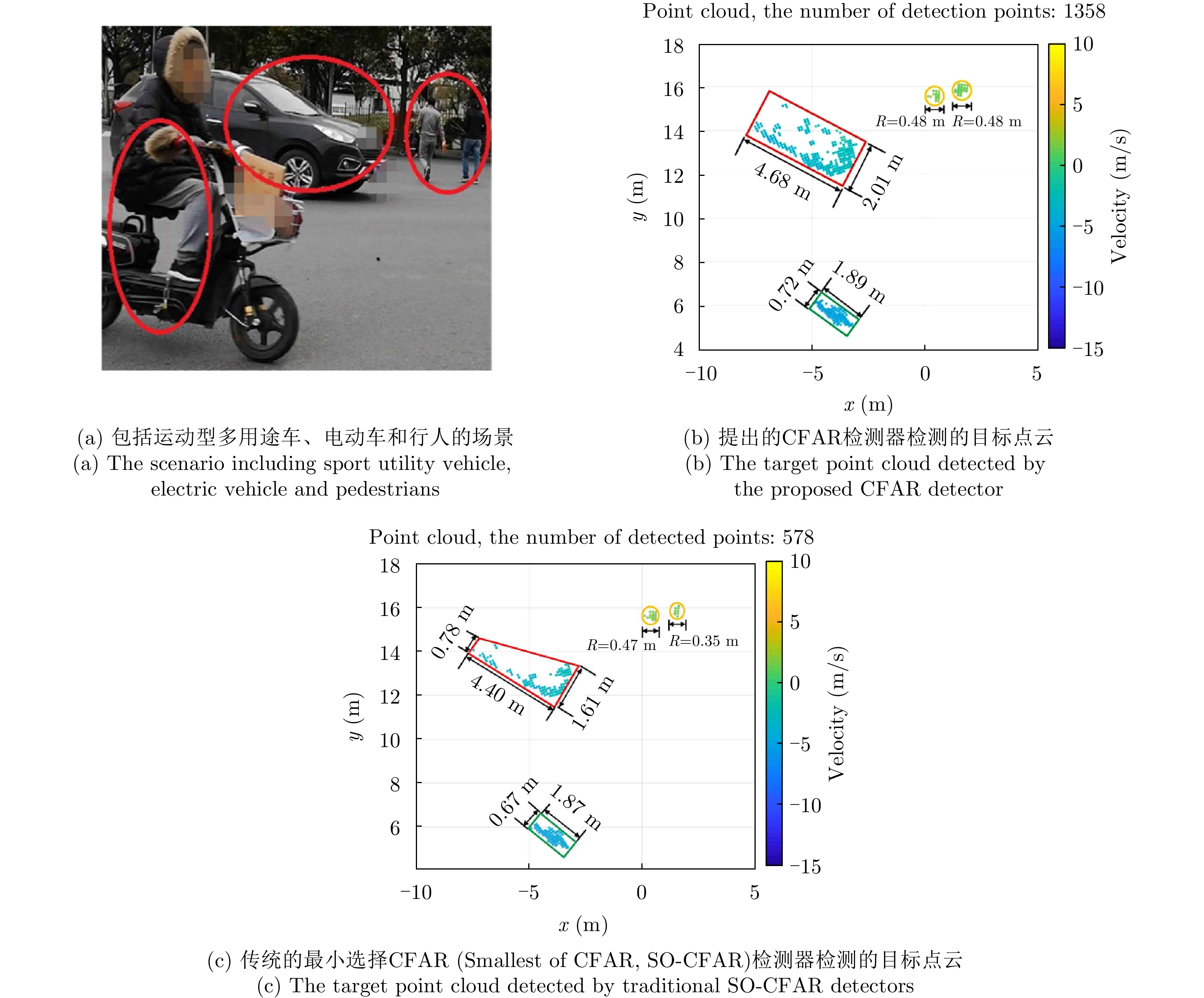
- Figure 4. Comparison of the number of point clouds generated by PreCFAR method proposed in Ref. [7] and the traditional SO-CFAR method
- Figure 5. 3D point cloud imaging results in Ref. [8]
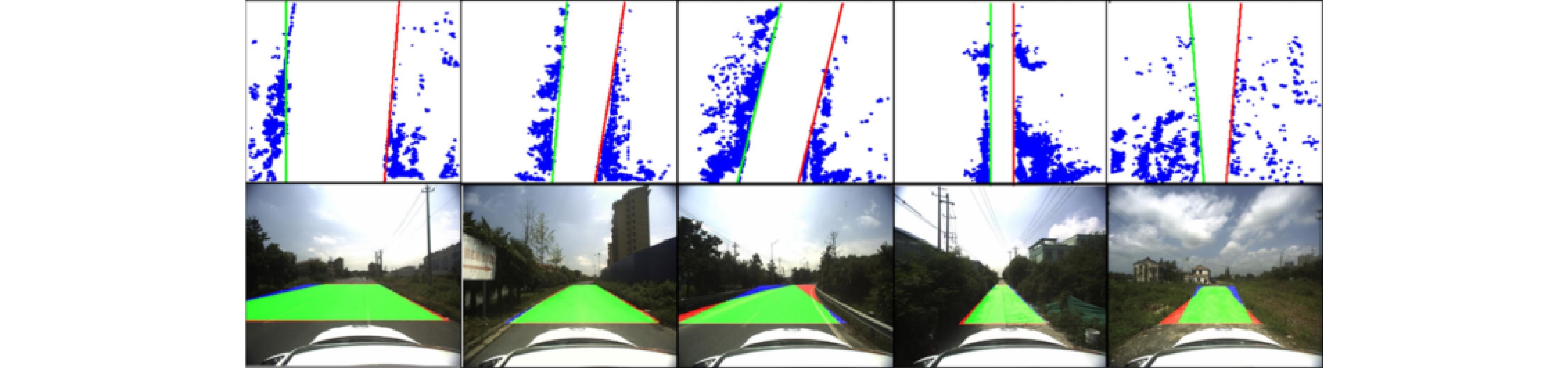
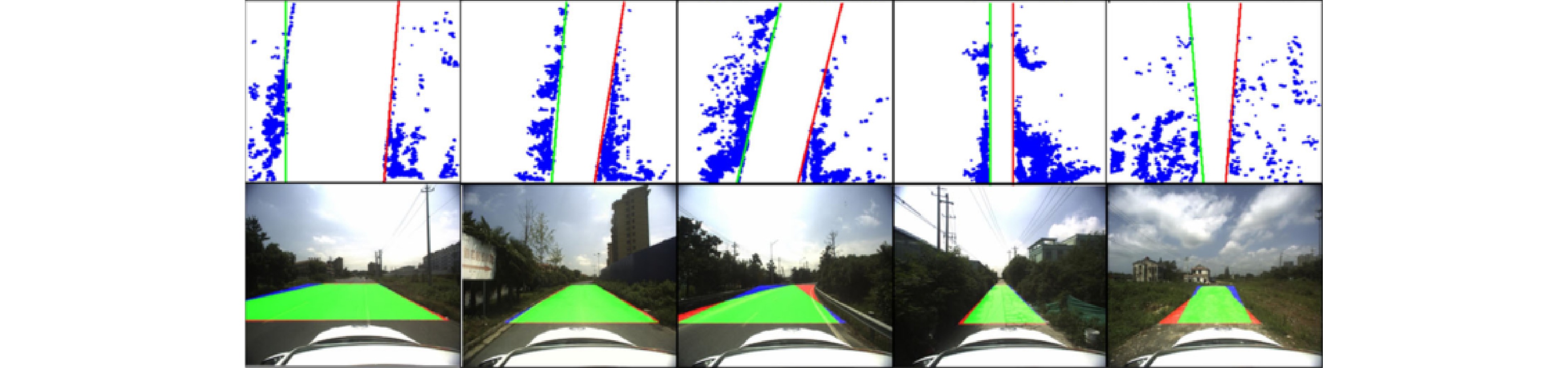
- Figure 6. Road boundary detection based on RANSAC algorithm[11]
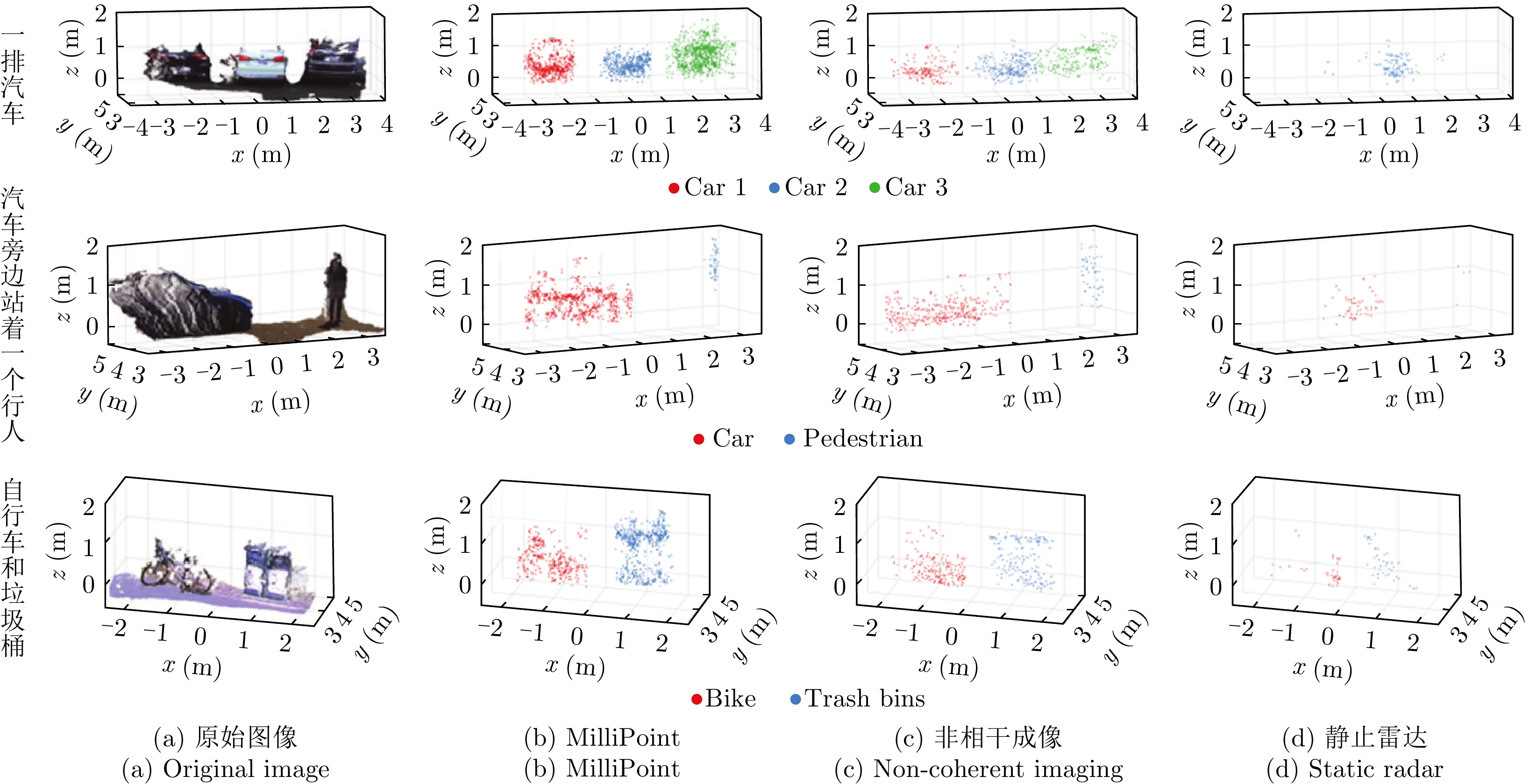
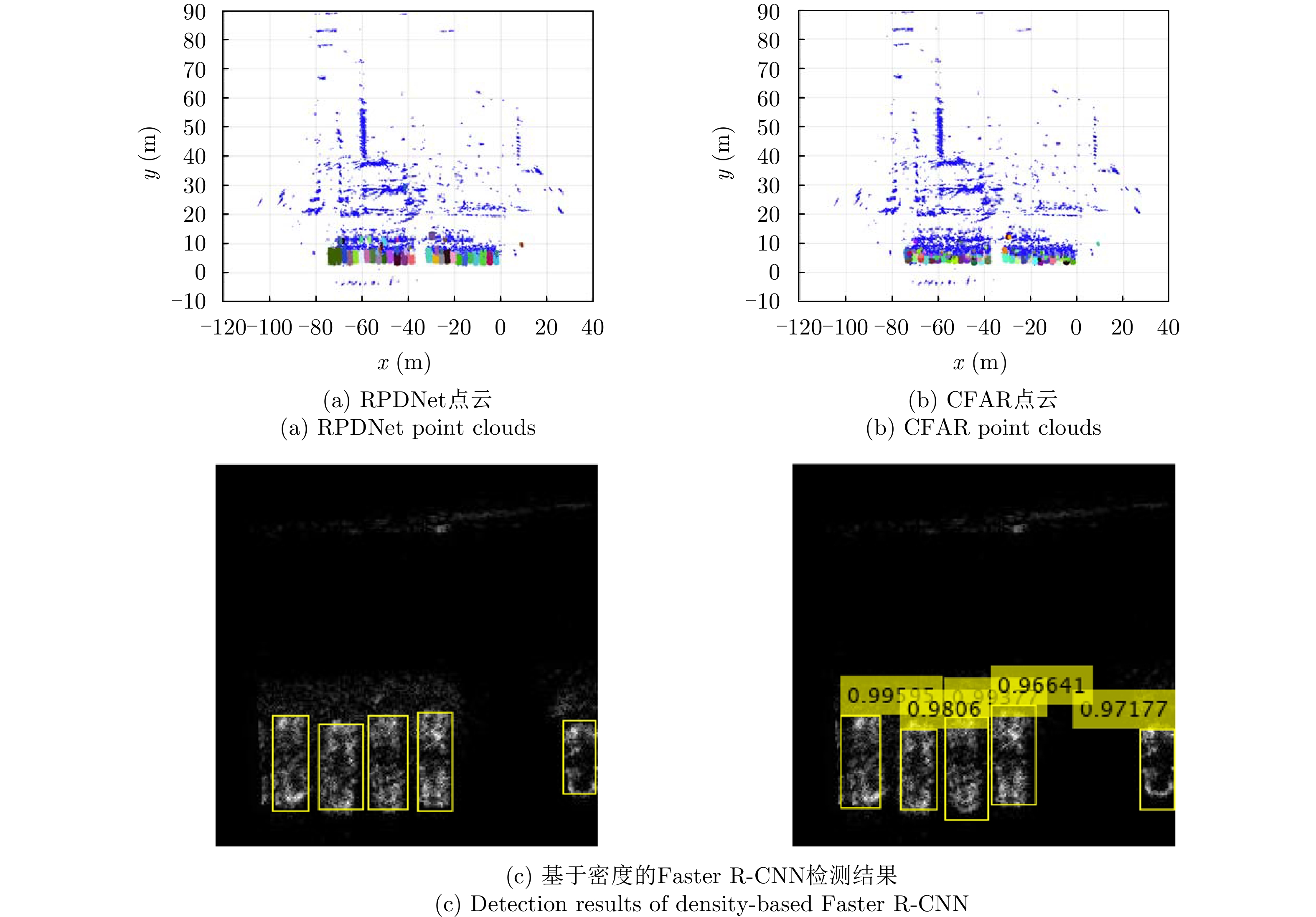
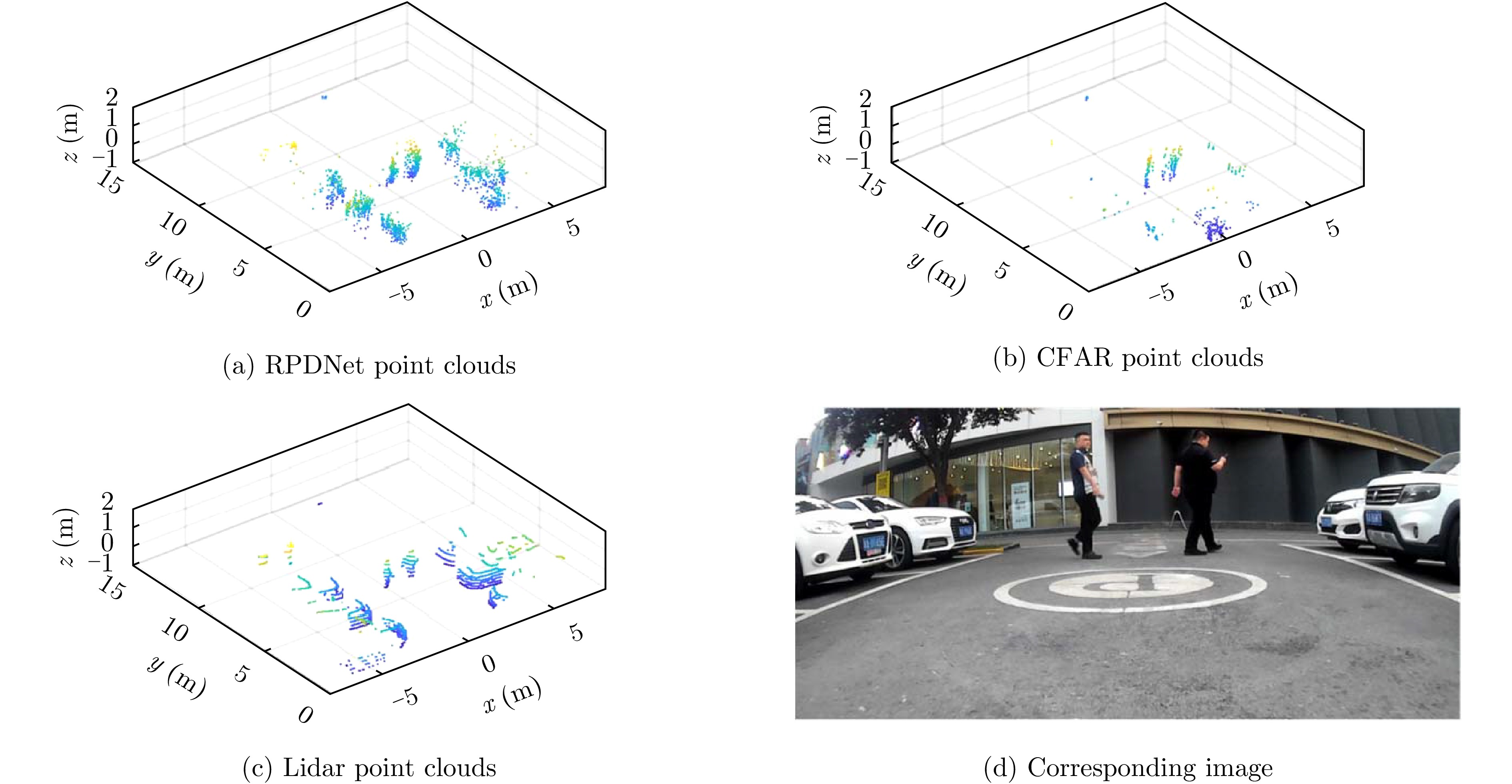
- Figure 7. Comparison of point cloud image generated by RPDNet[13,14] with CFAR and Lidar
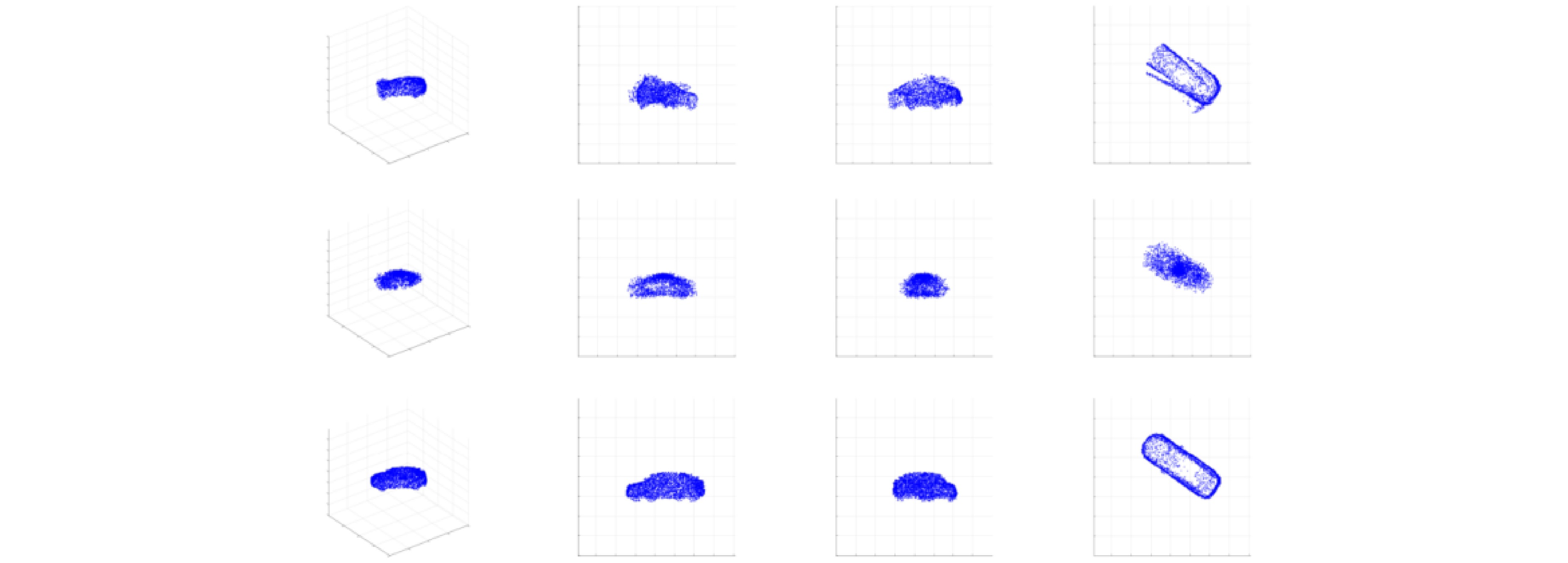
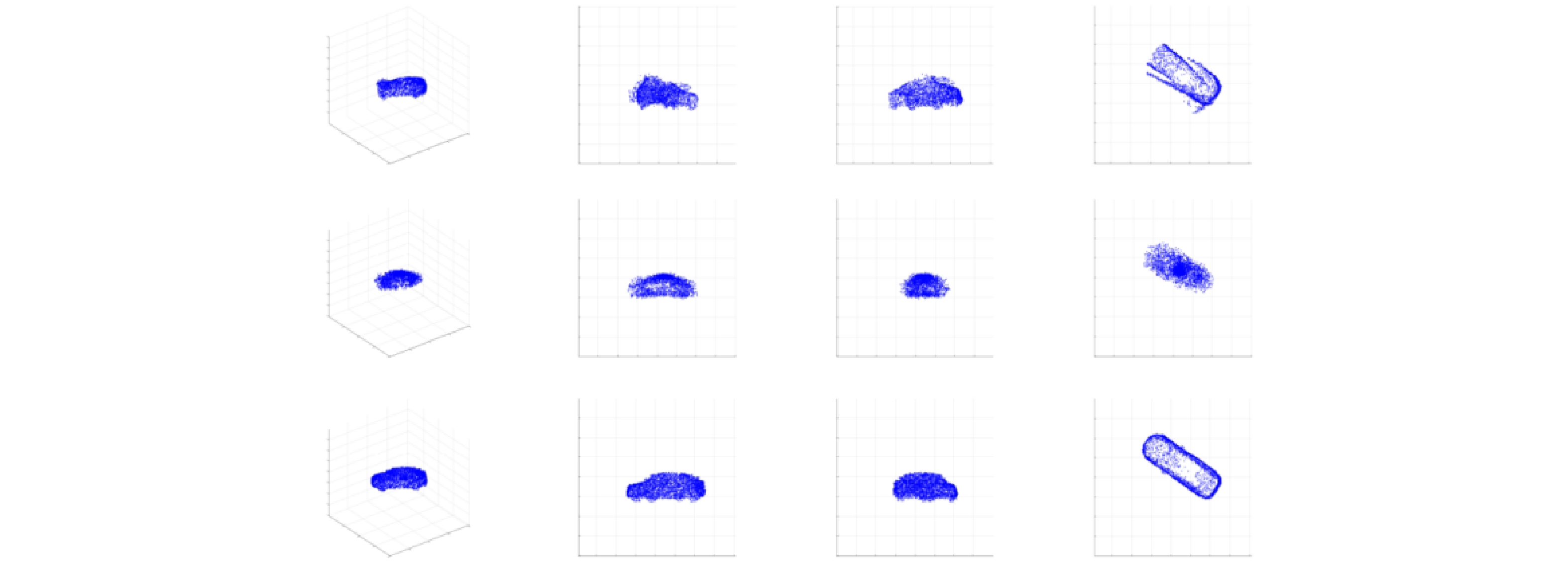
- Figure 8. 3DRIMR[18,19] used to reconstruct the three-dimensional shape of the car in point cloud form
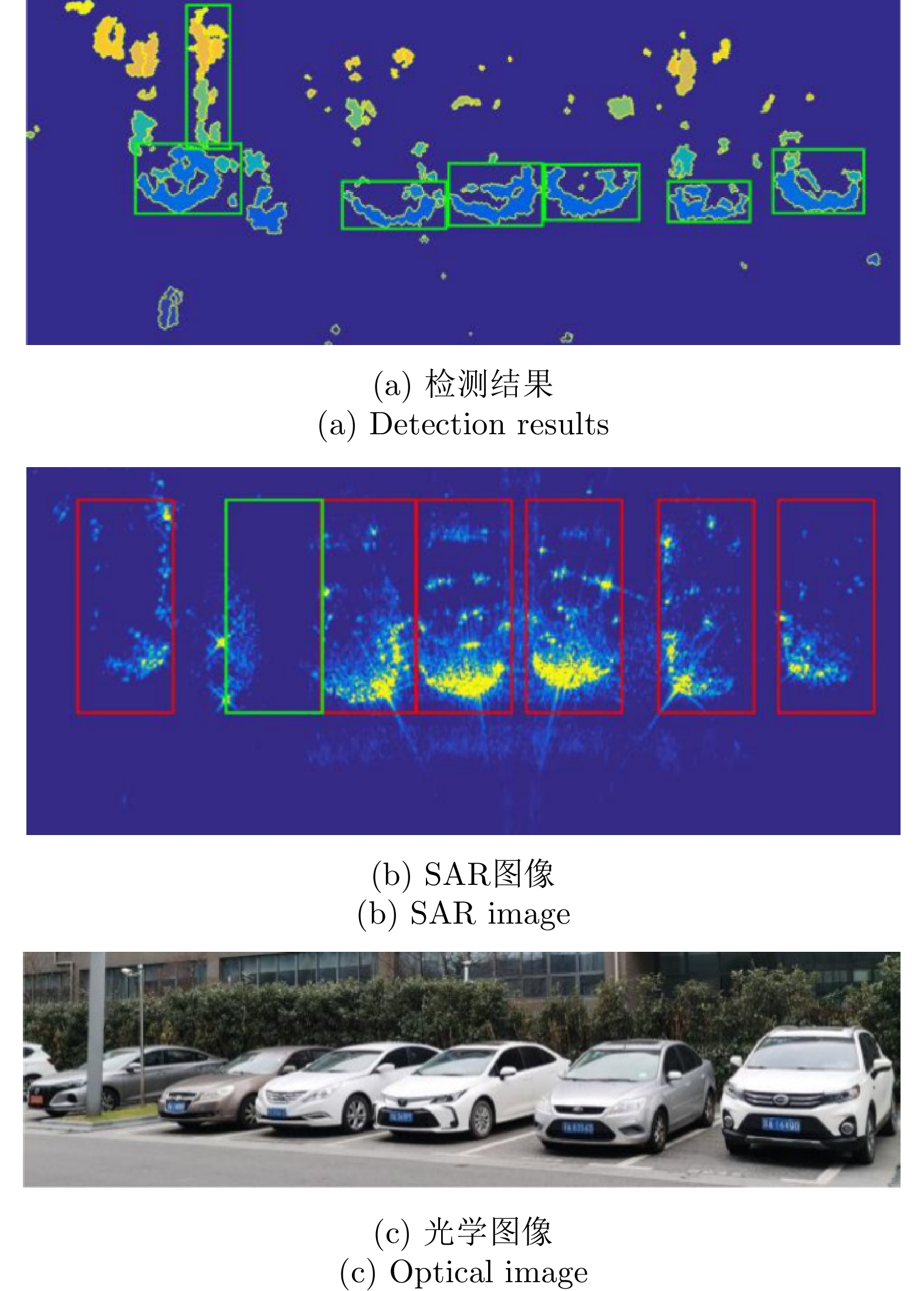
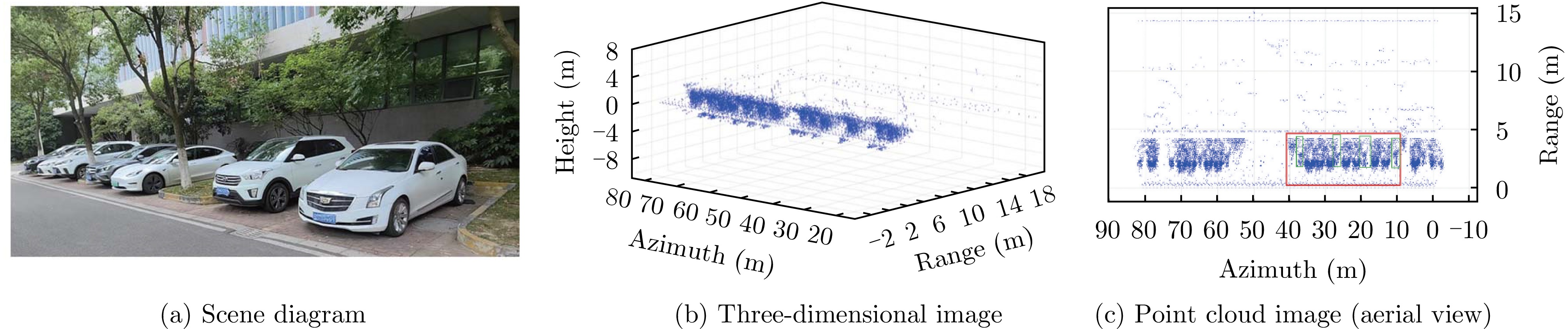
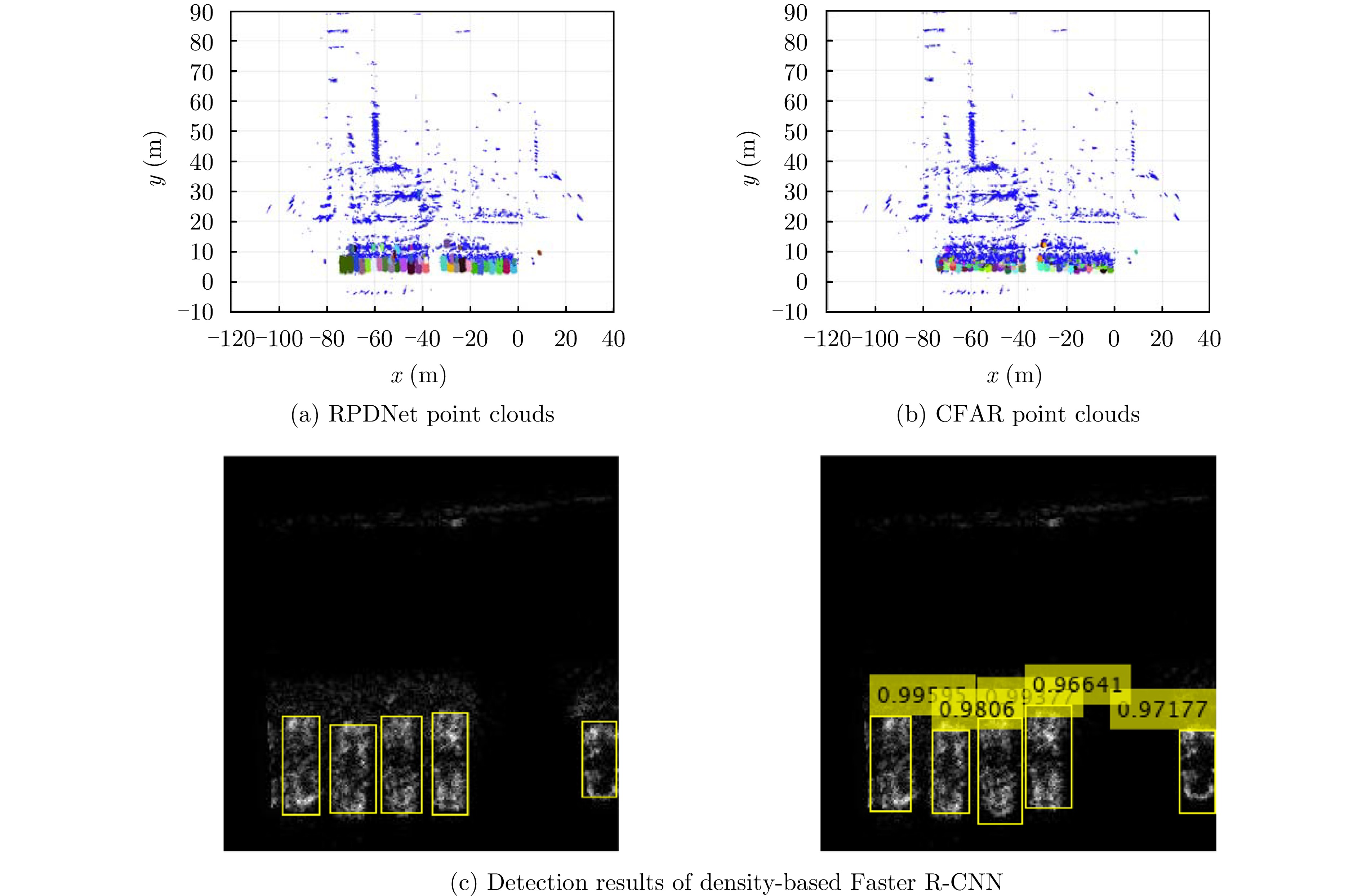
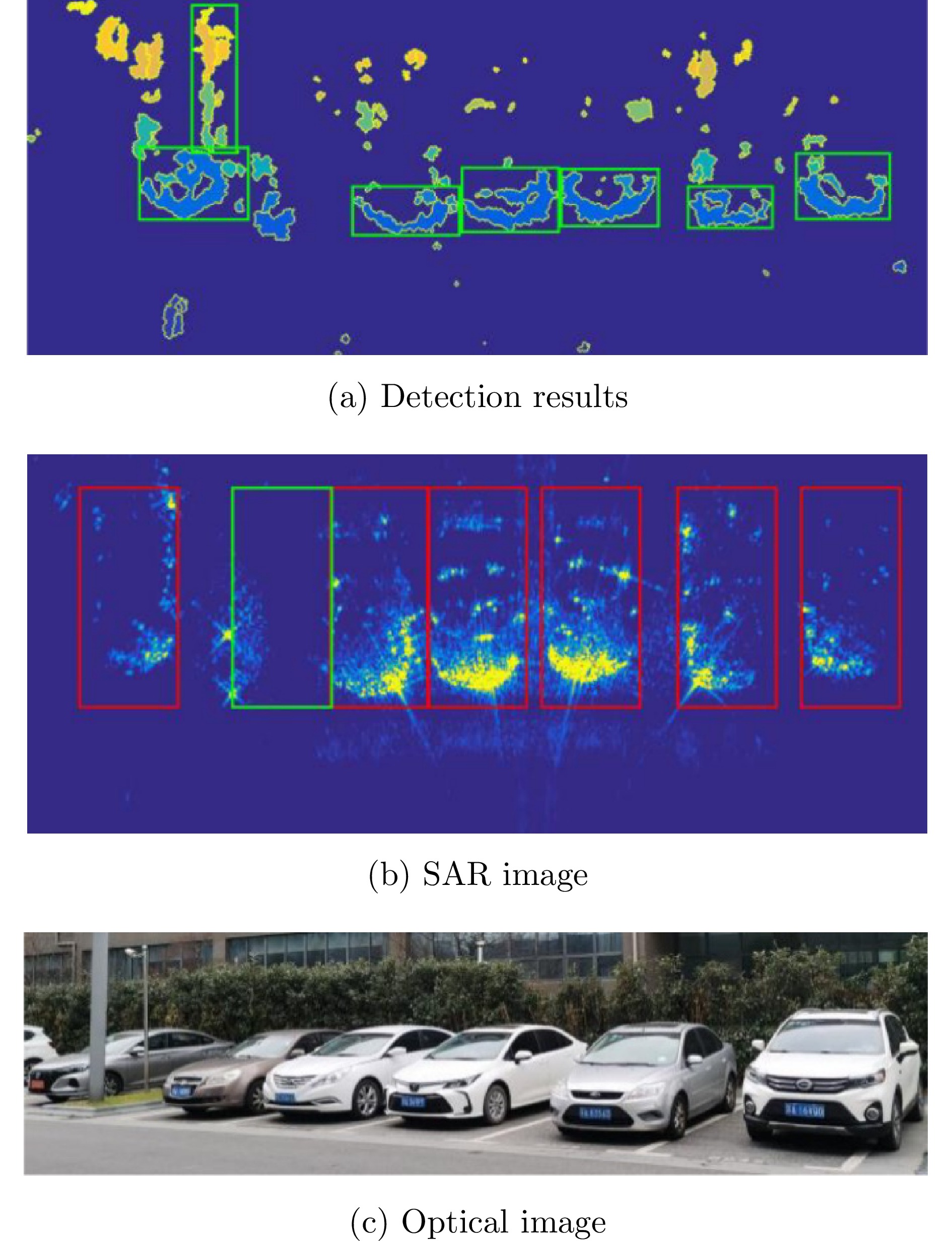
- Figure 9. Detection results of the method proposed in Ref. [20]
- Figure 10. Test results of RPFA-Net[22] and PointPillars[23] in AstyxHiRes dataset
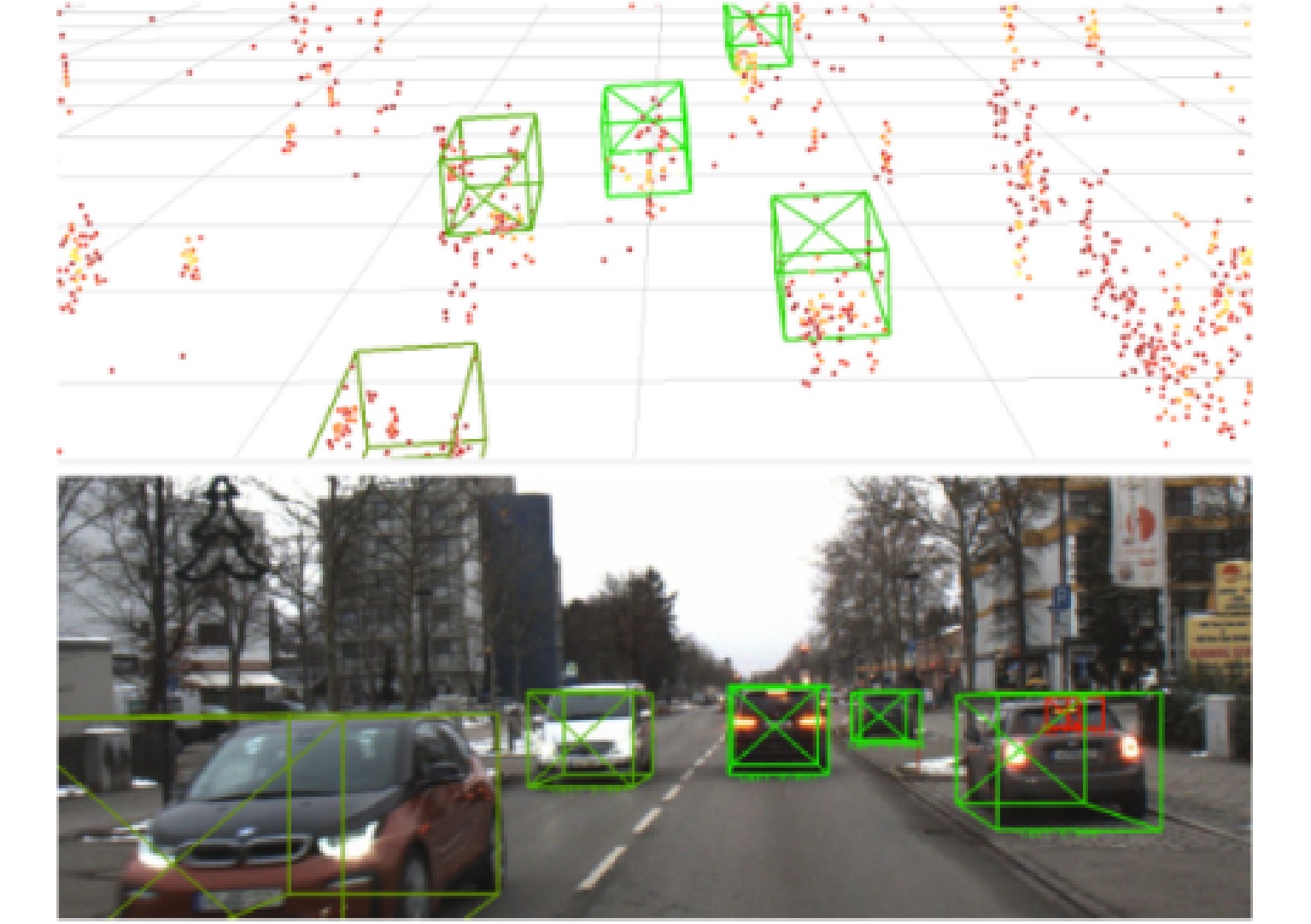
- Figure 11. 3D target detection results based on AstyxHiRes dataset in Ref. [34]
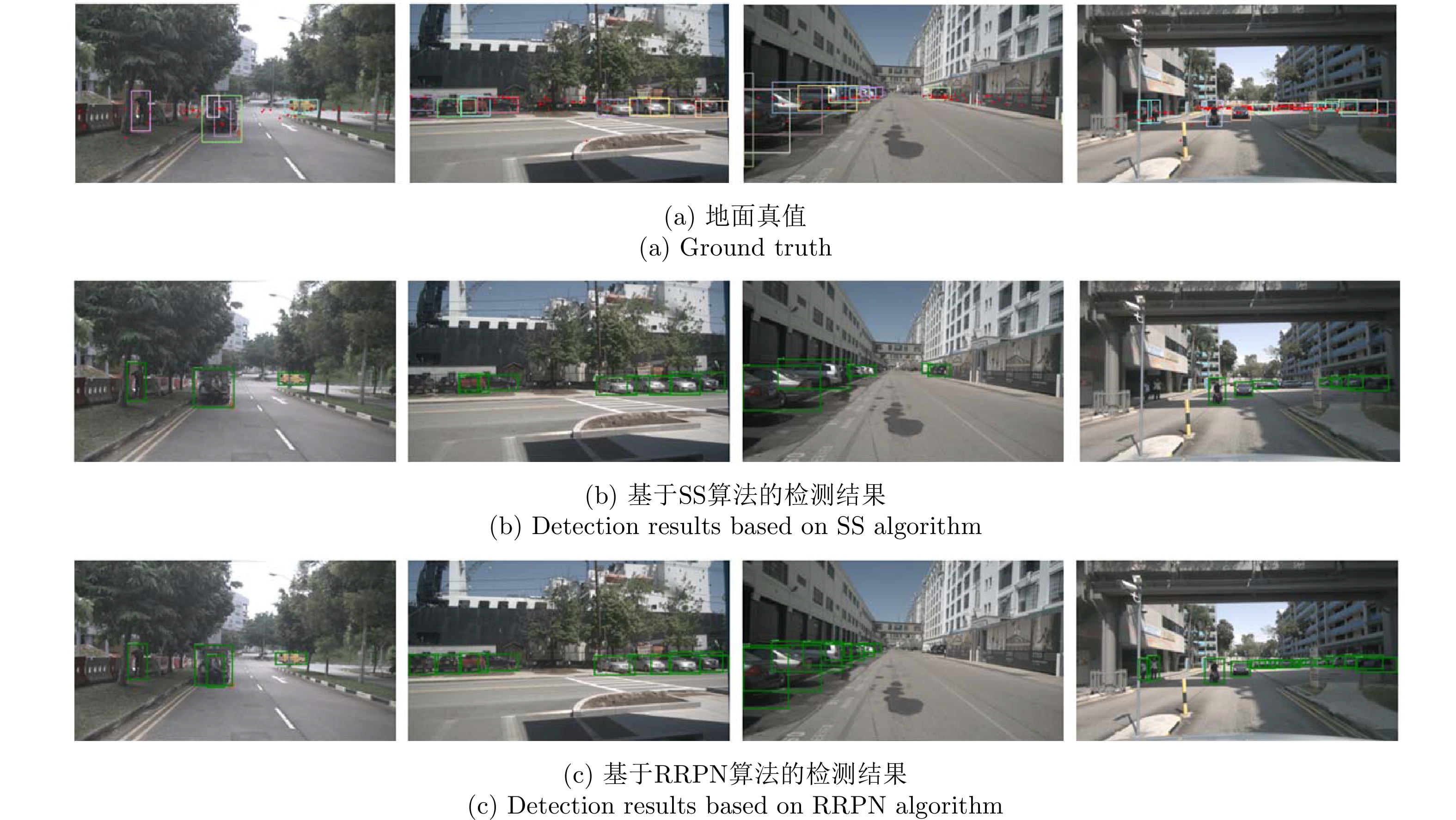
- Figure 12. Detection results of SS method and RRPN[35] method
- Figure 13. Three-dimensional detection in different scenarios results of CenterFusion[39] on the NuScenes dataset
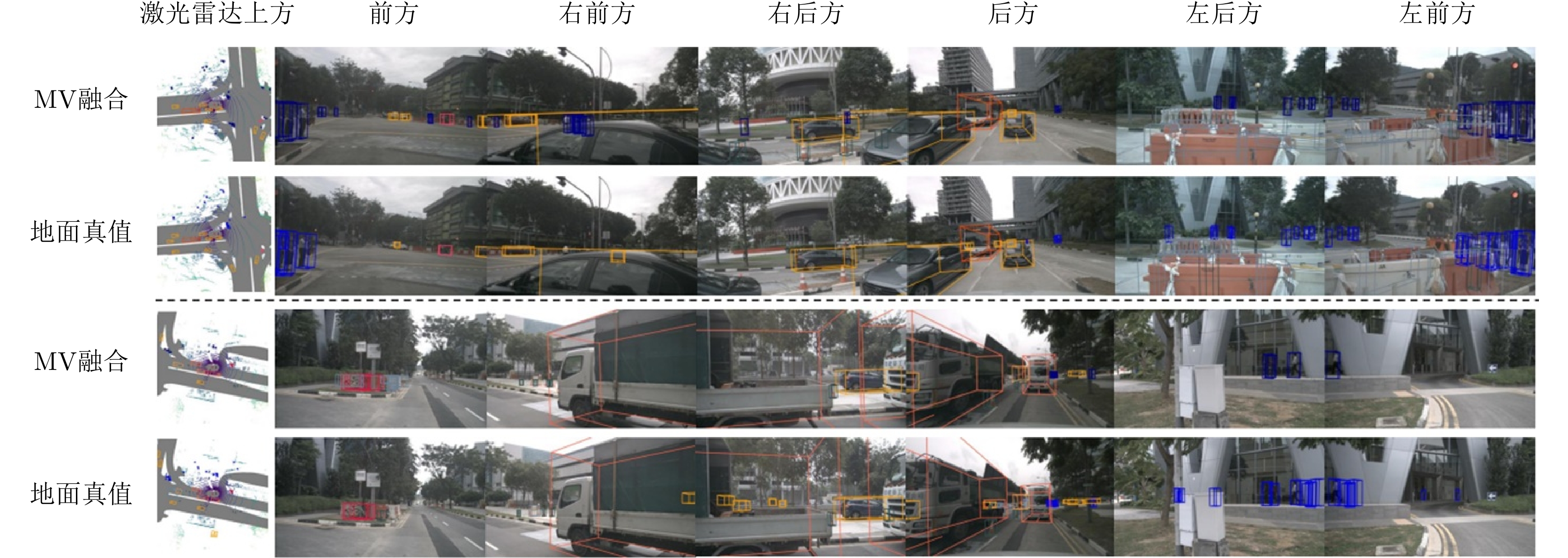
- Figure 14. 3D detection results of MVFusion[44] on the NuScenes dataset
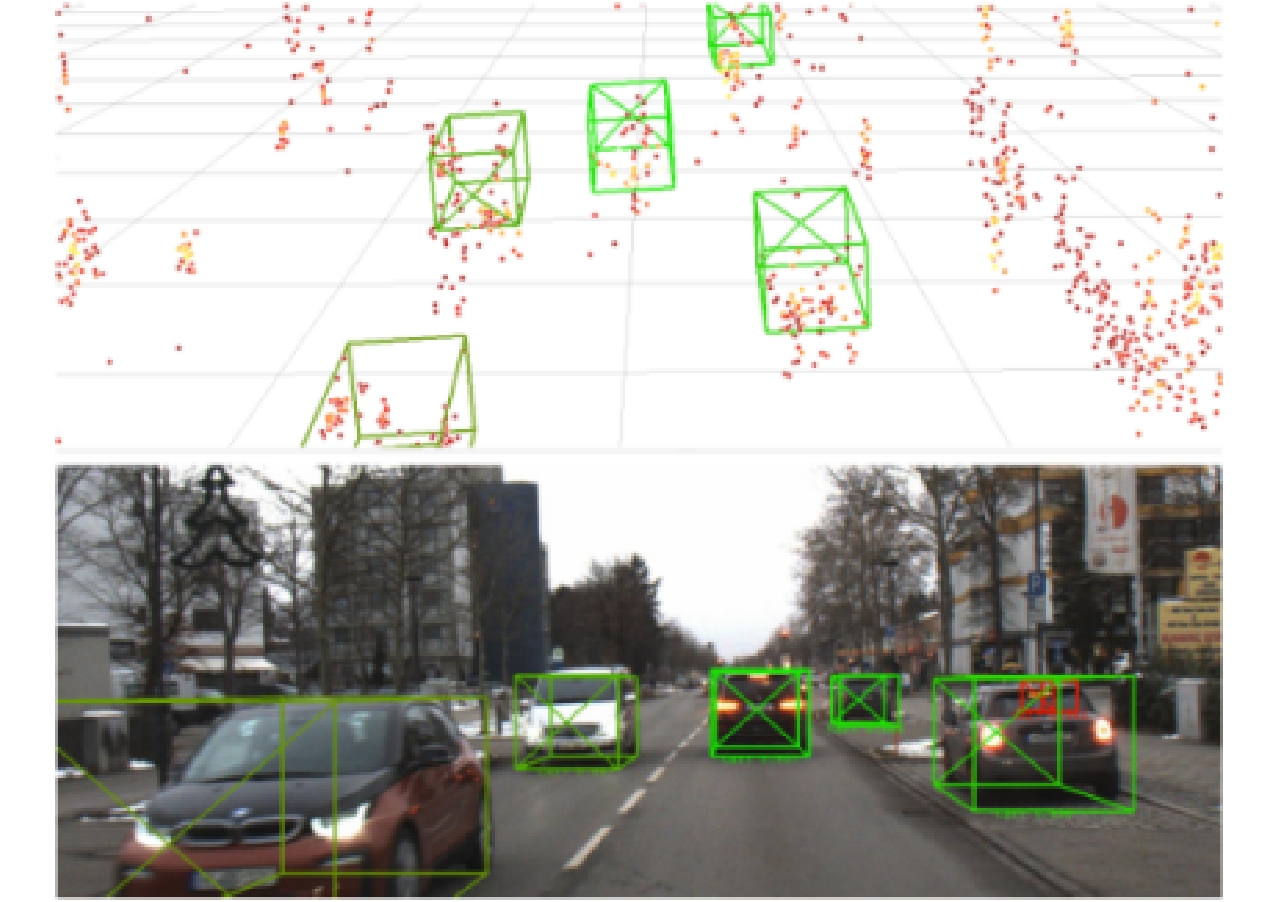
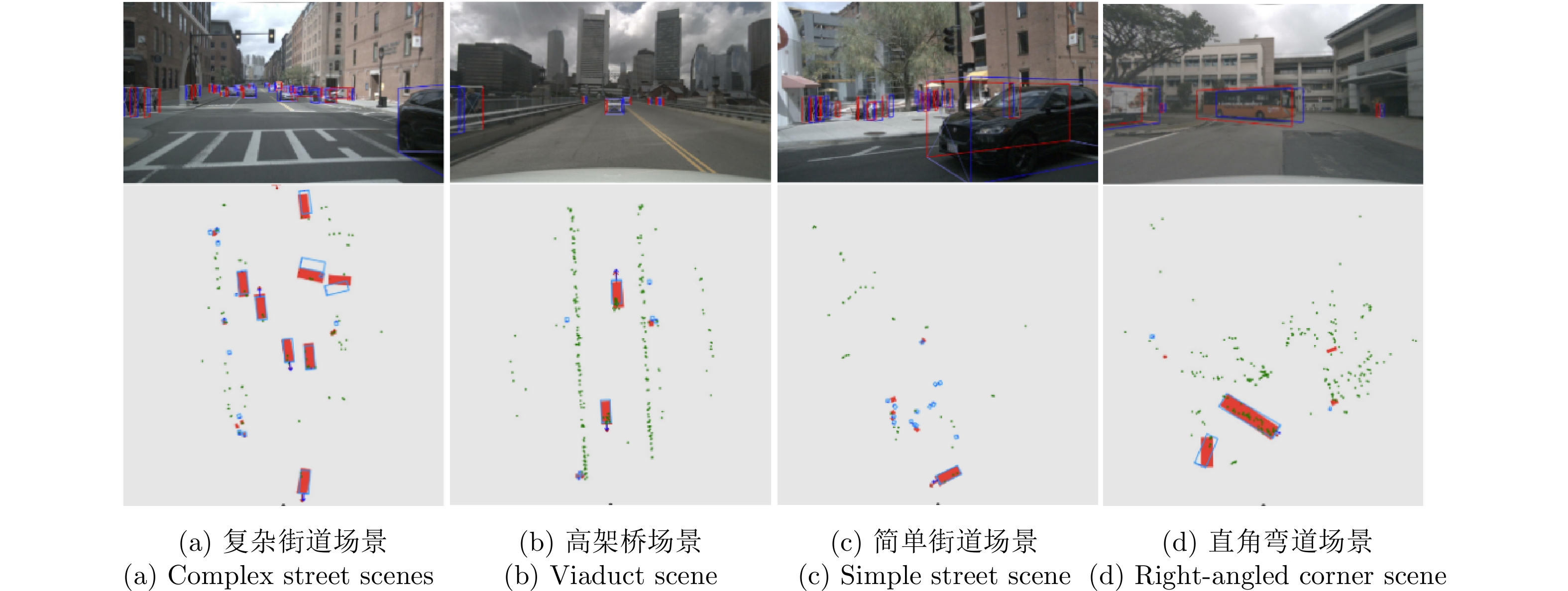
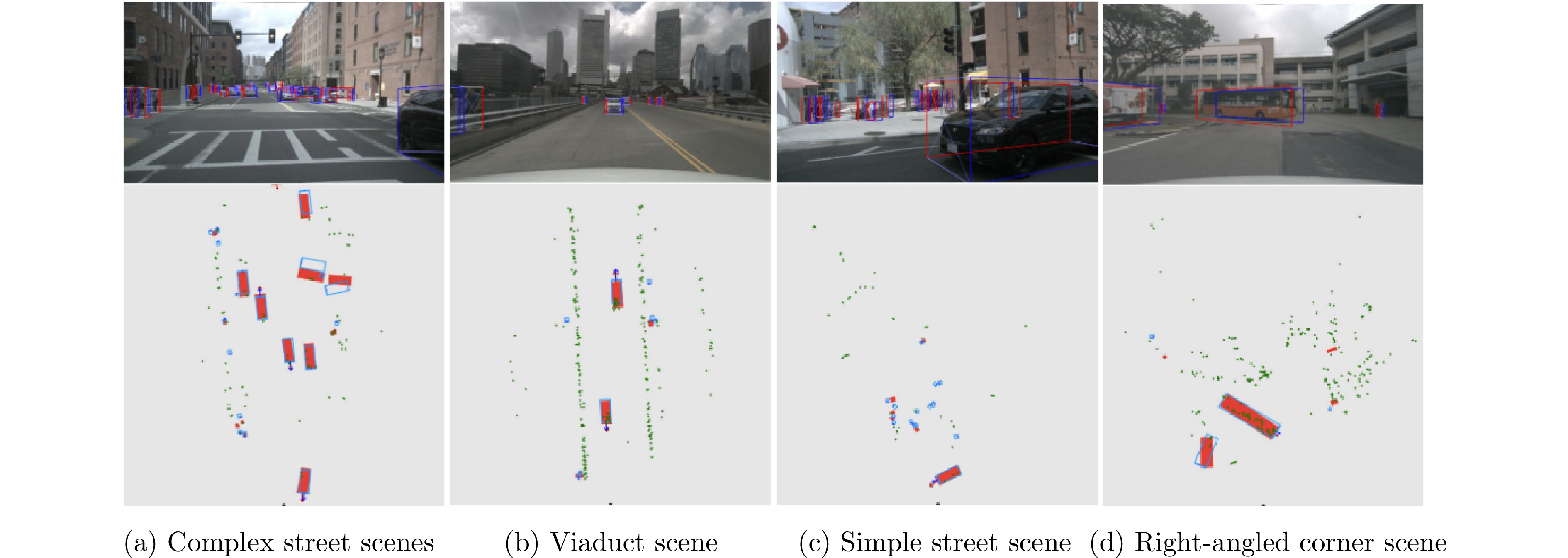
- Figure 15. Three scenes tested in Ref. [46] and 3D tracking results
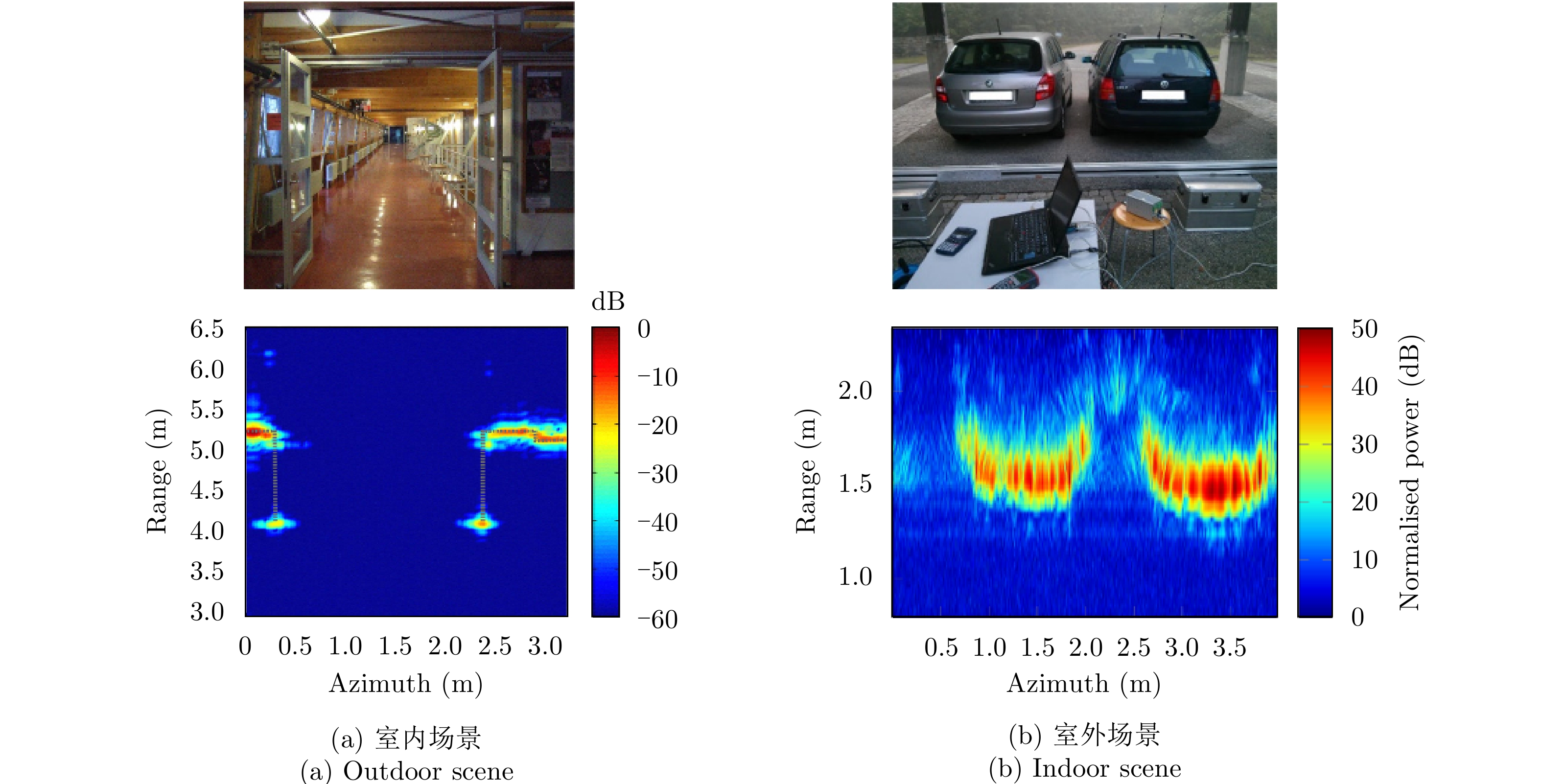
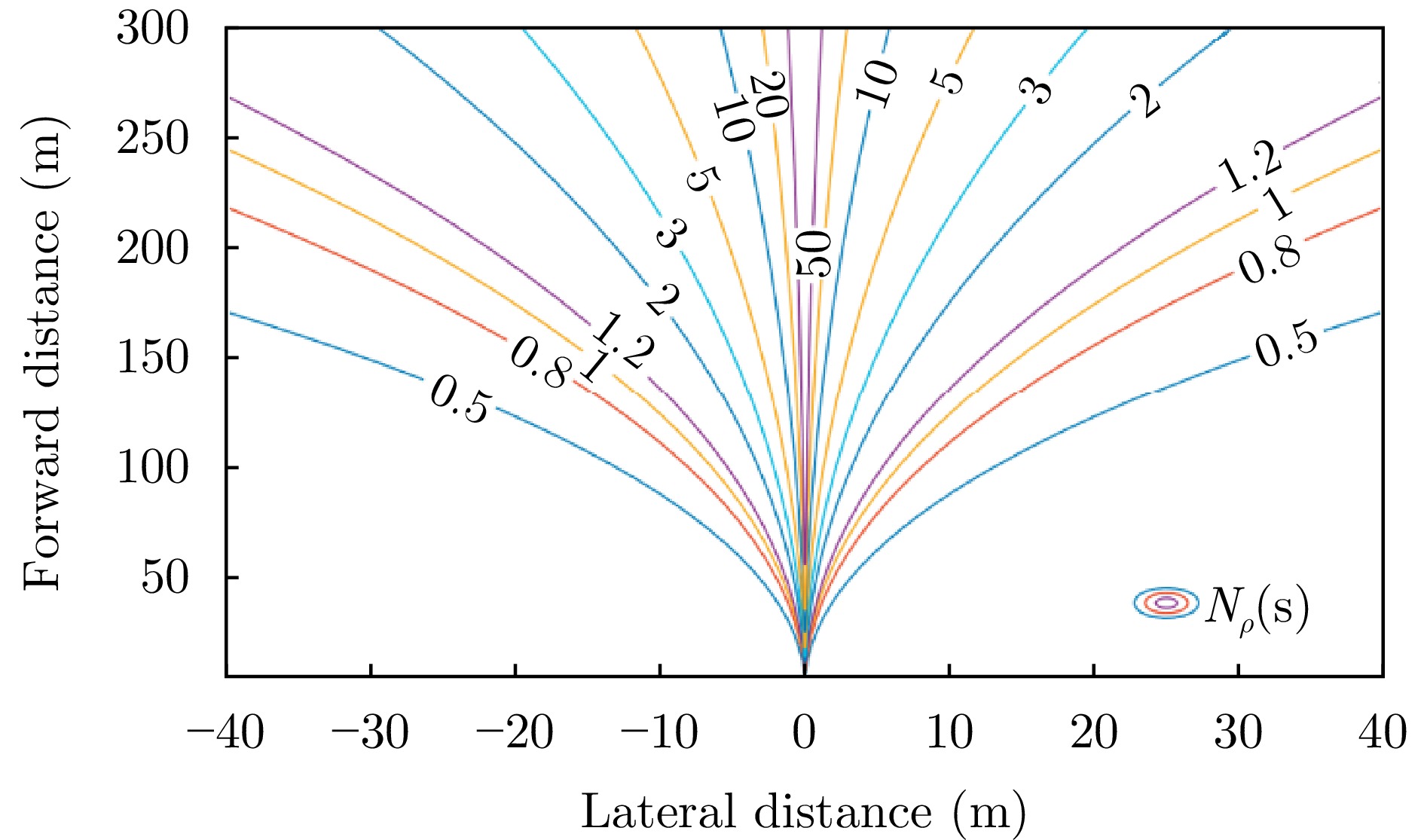
- Figure 16. The verification of RDA near-field scene SAR imaging[50,51]
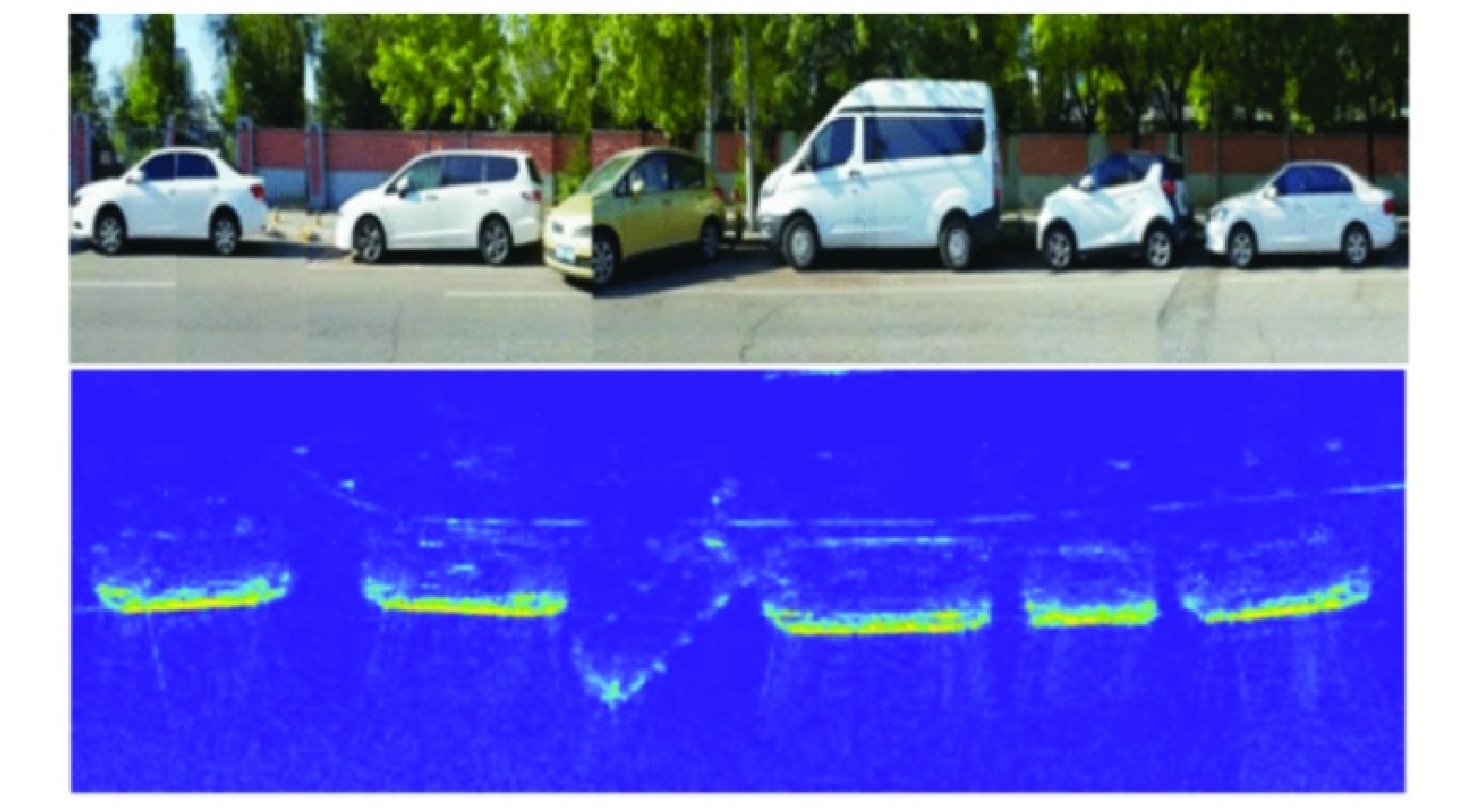
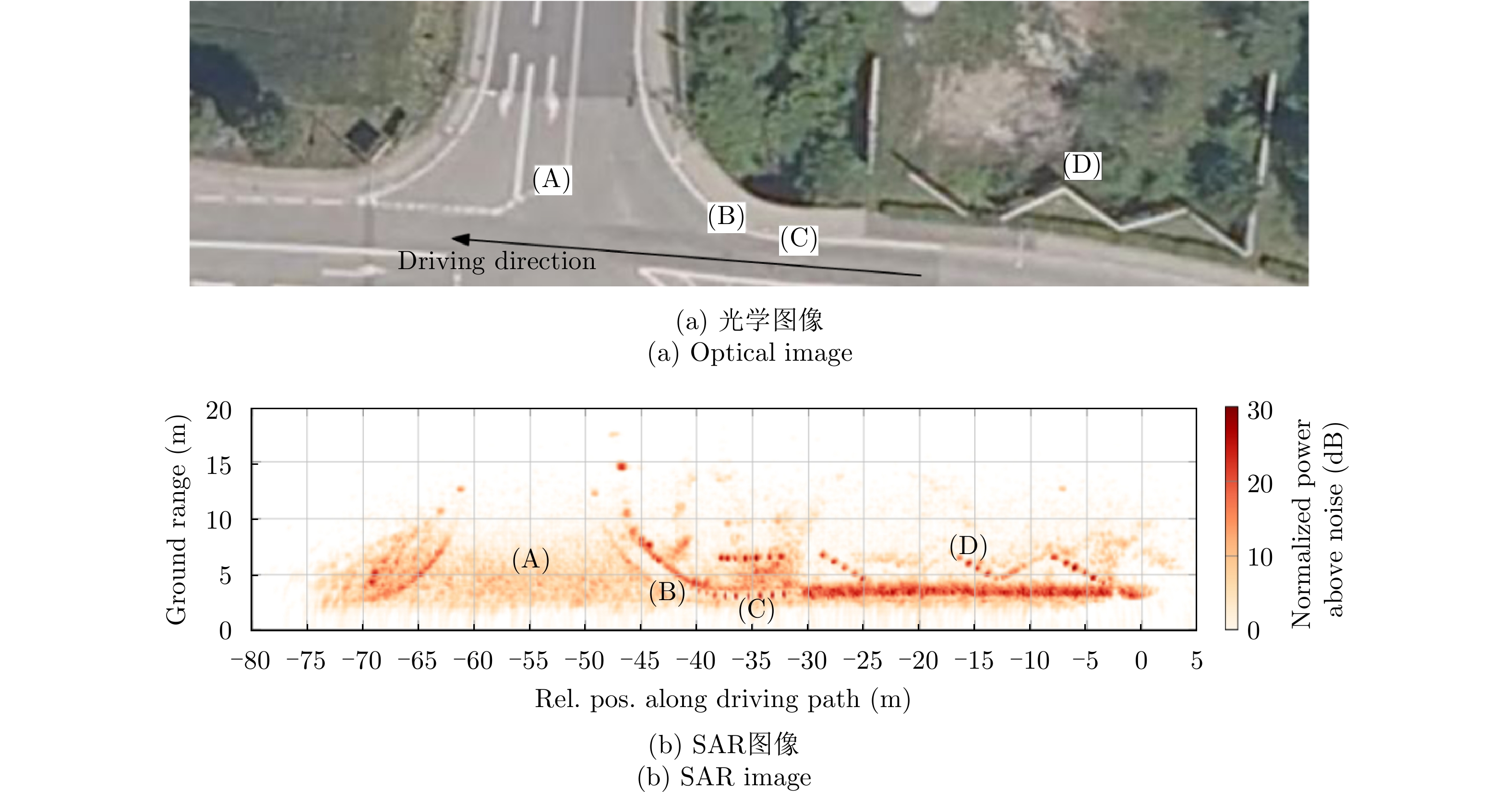
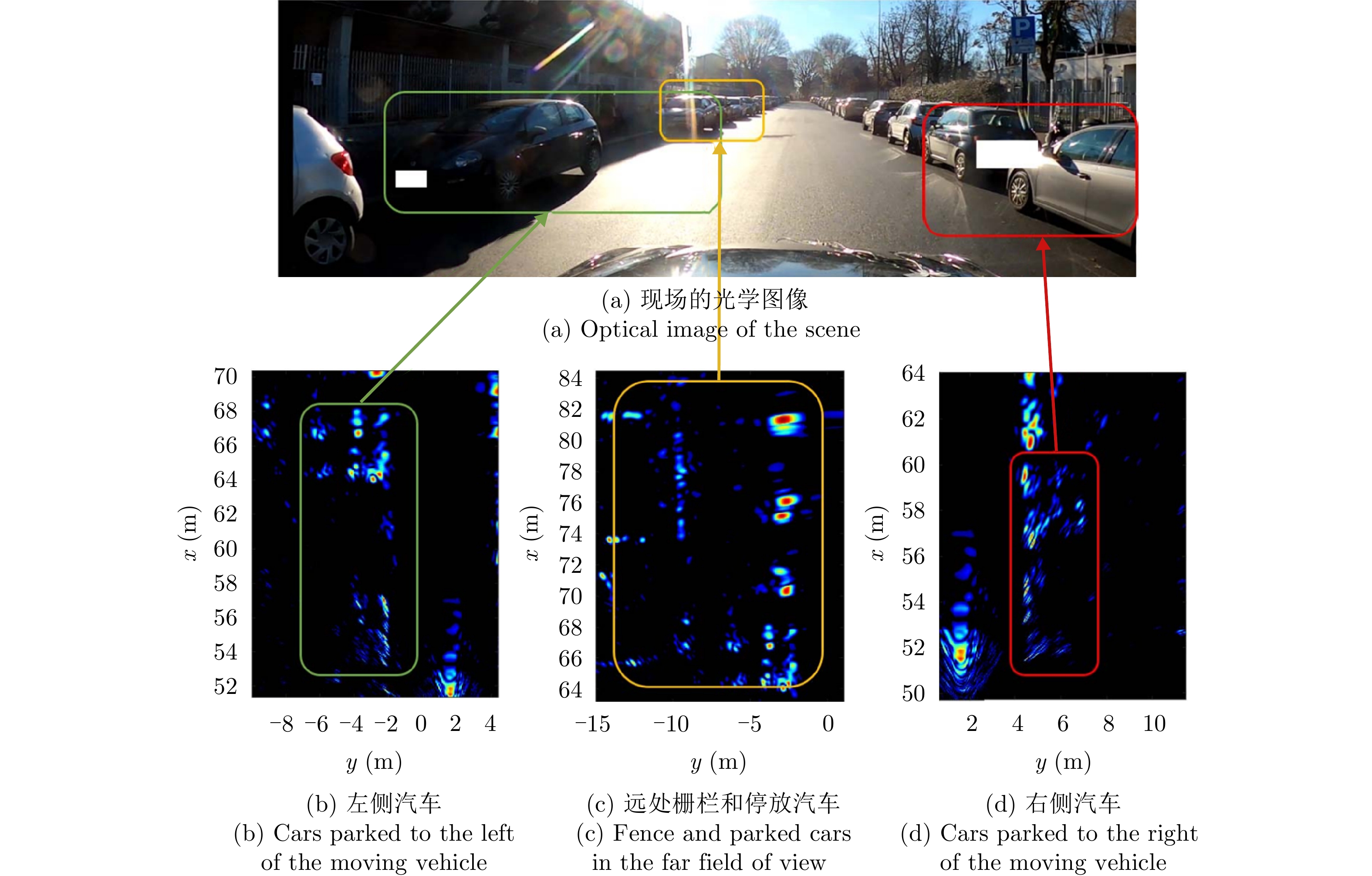
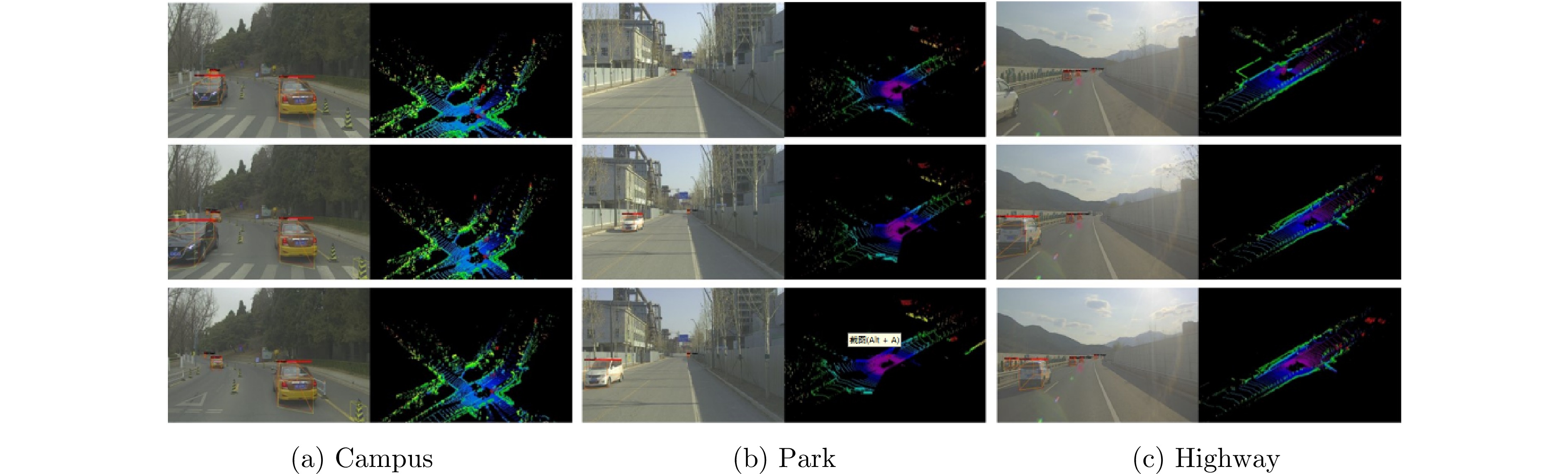
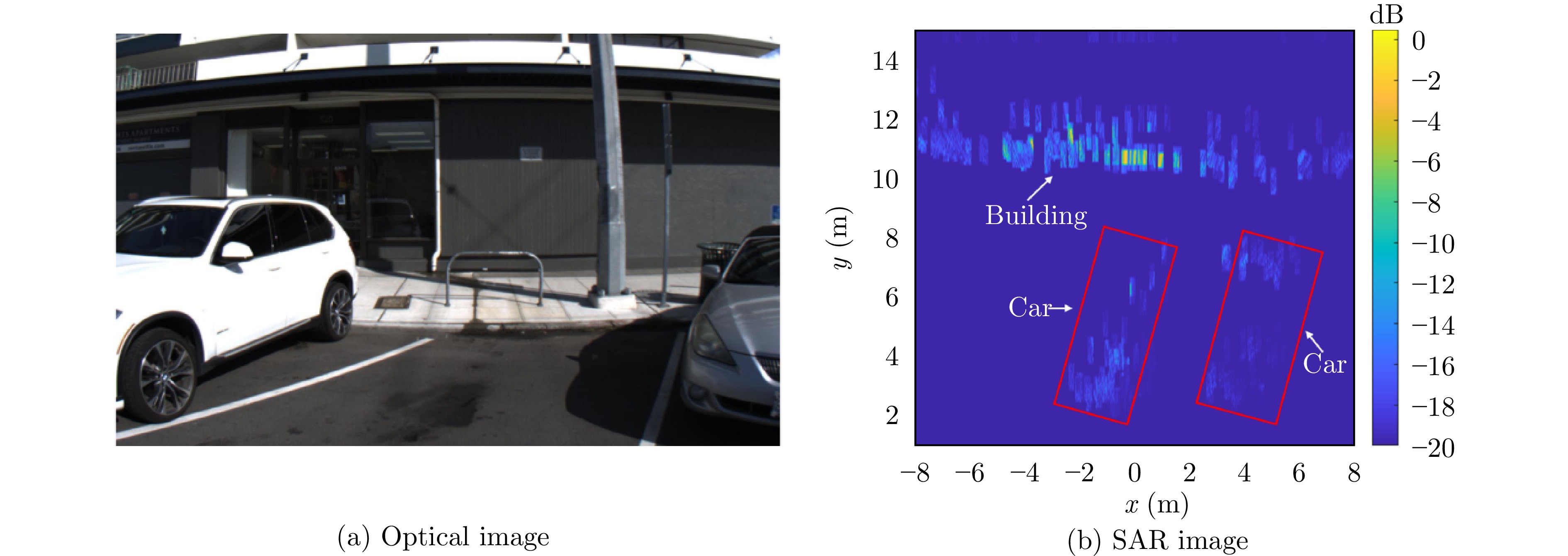
- Figure 17. RDA imaging for automotive scenes[52]
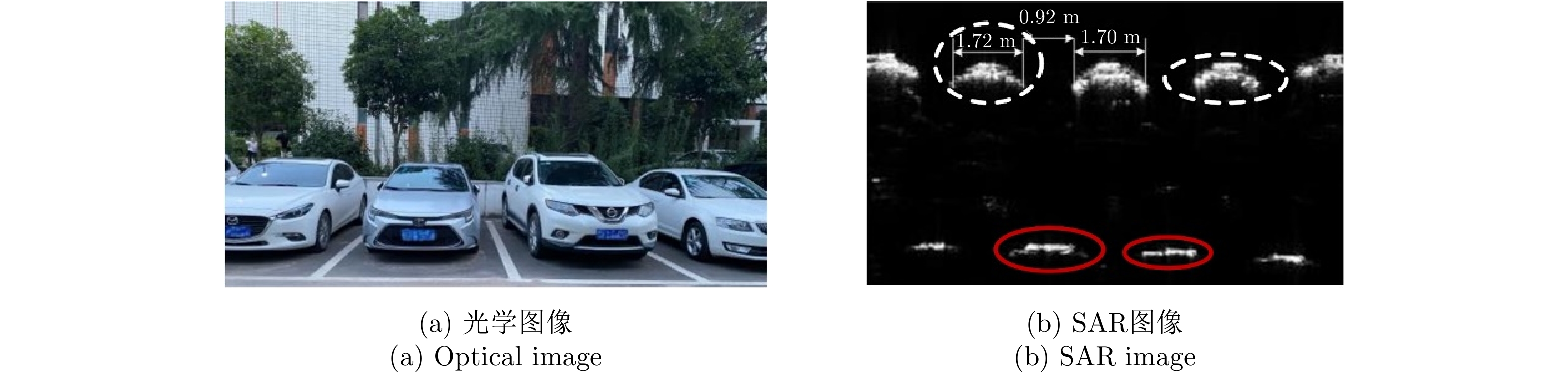
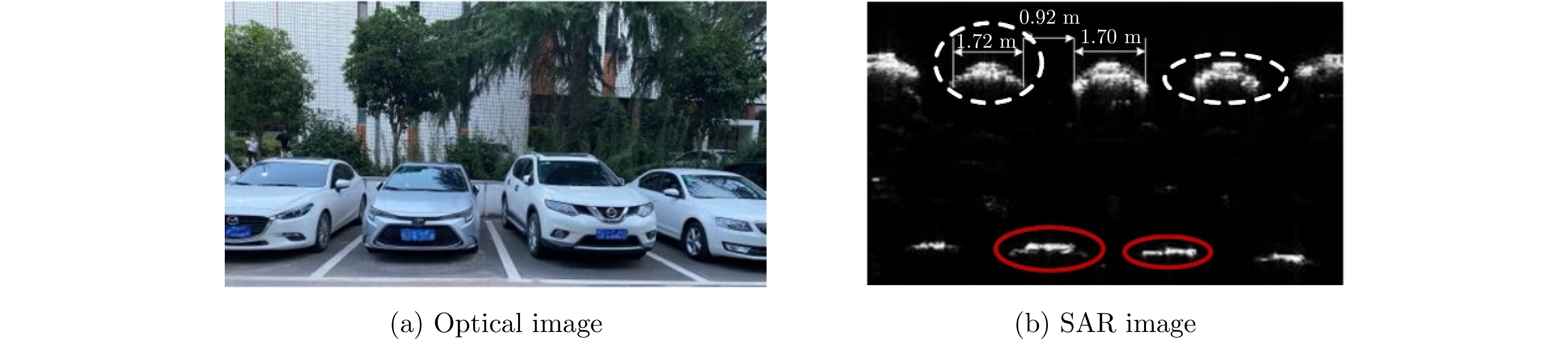
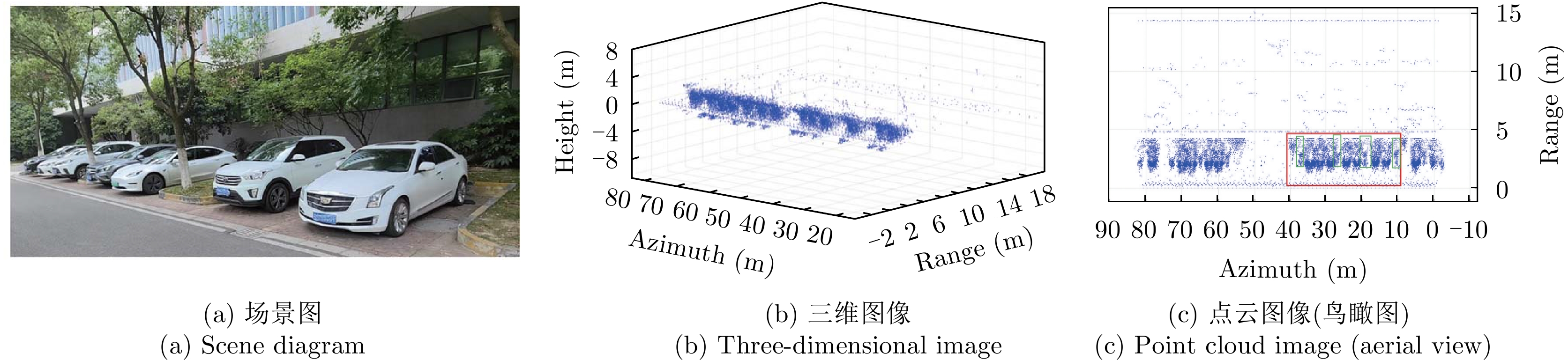
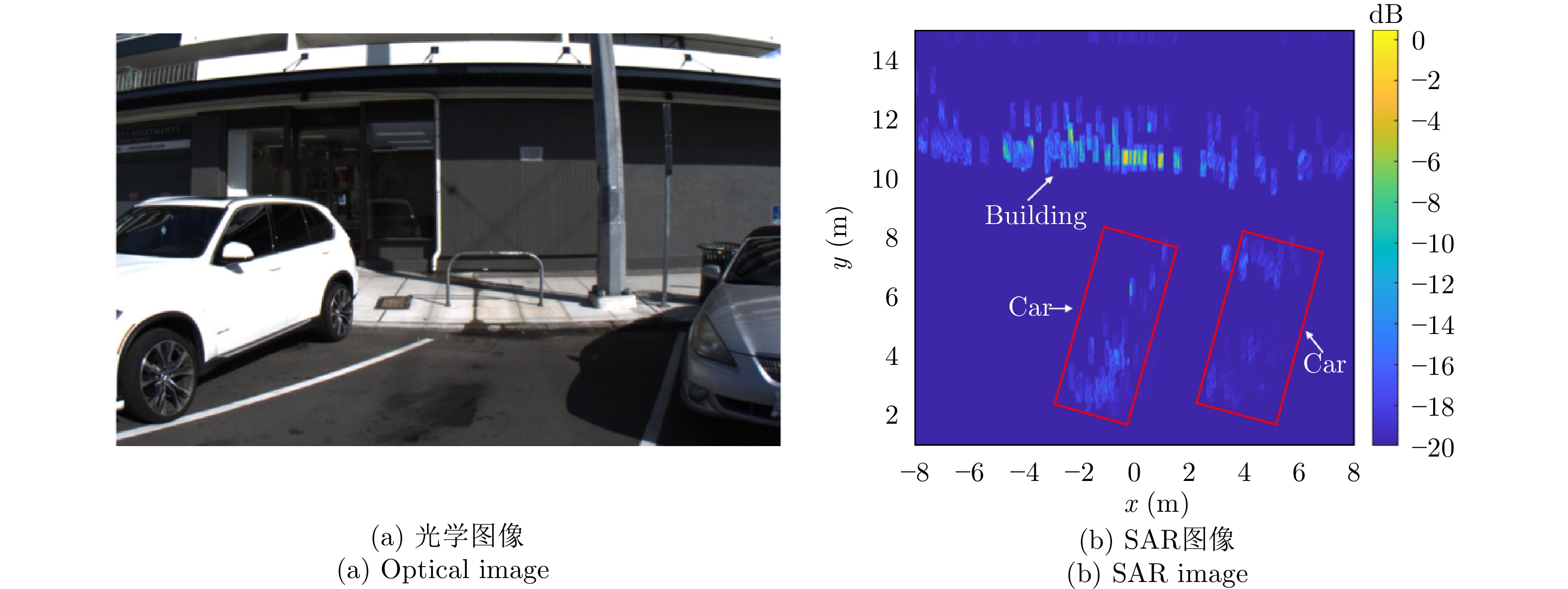
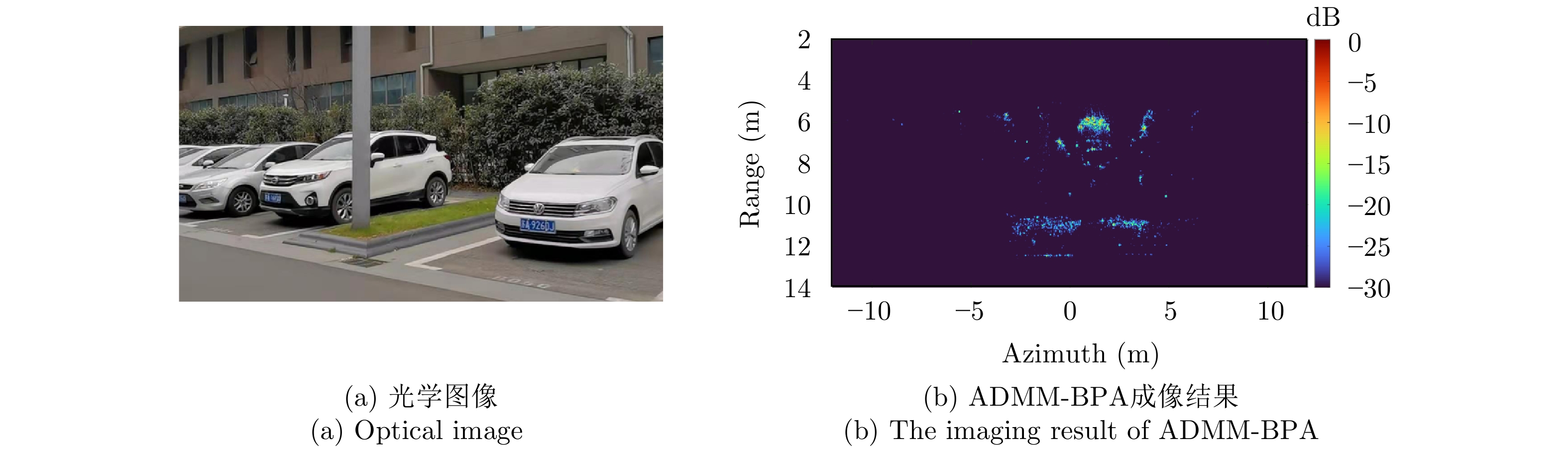
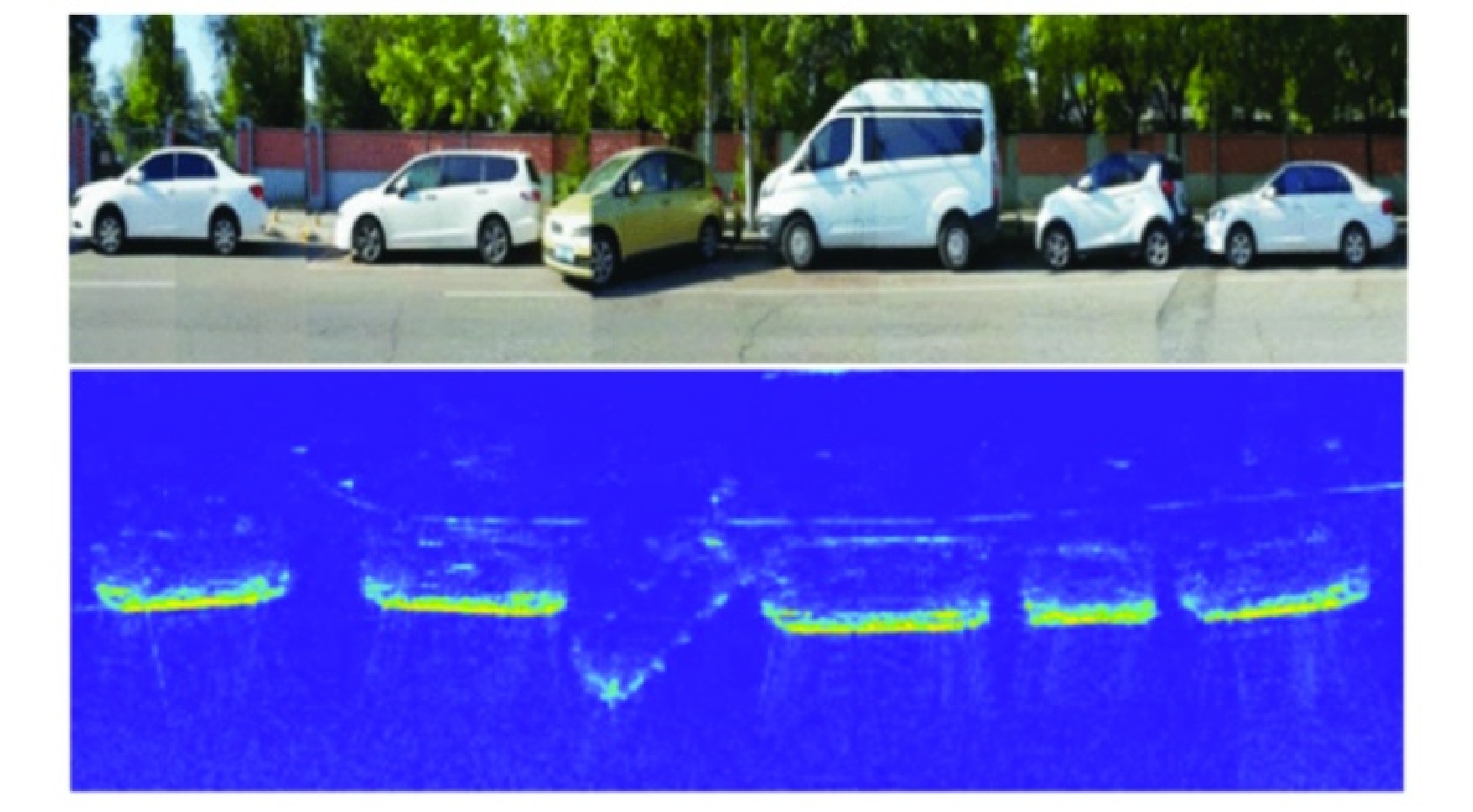
- Figure 18. Parking space detection and recognition[53]
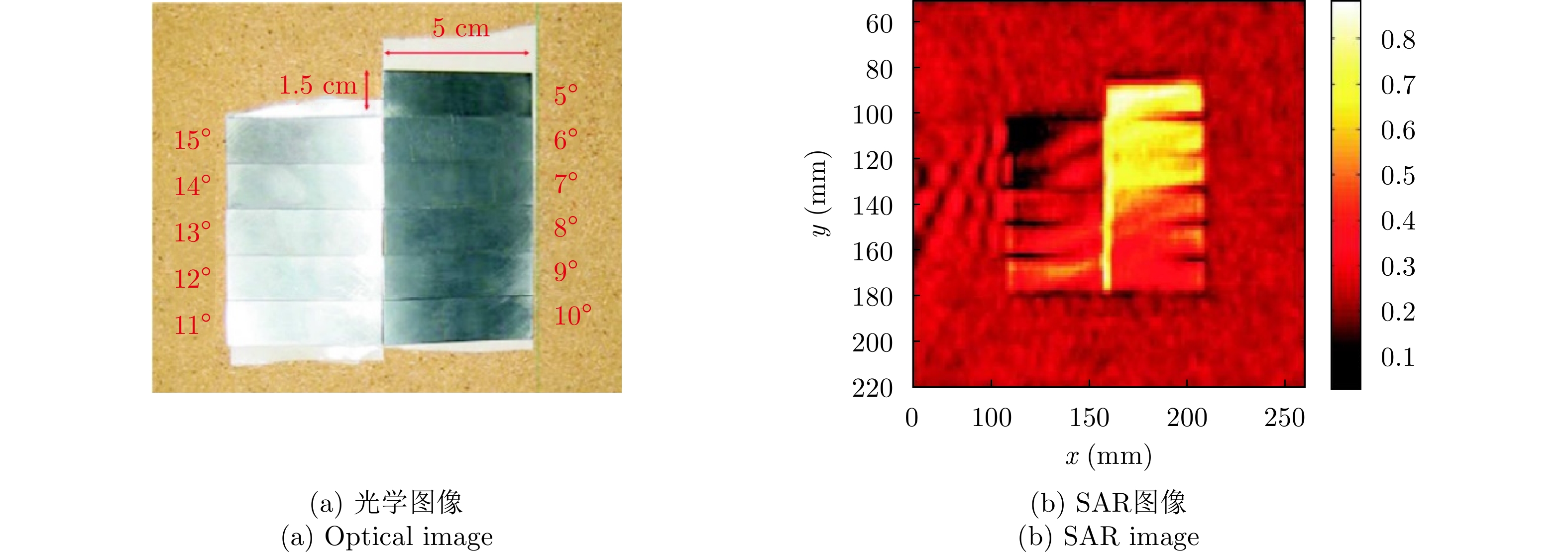
- Figure 19. 94 GHz millimeter-wave SAR imaging results of polyethylene cylinders with different tilting degrees[55]
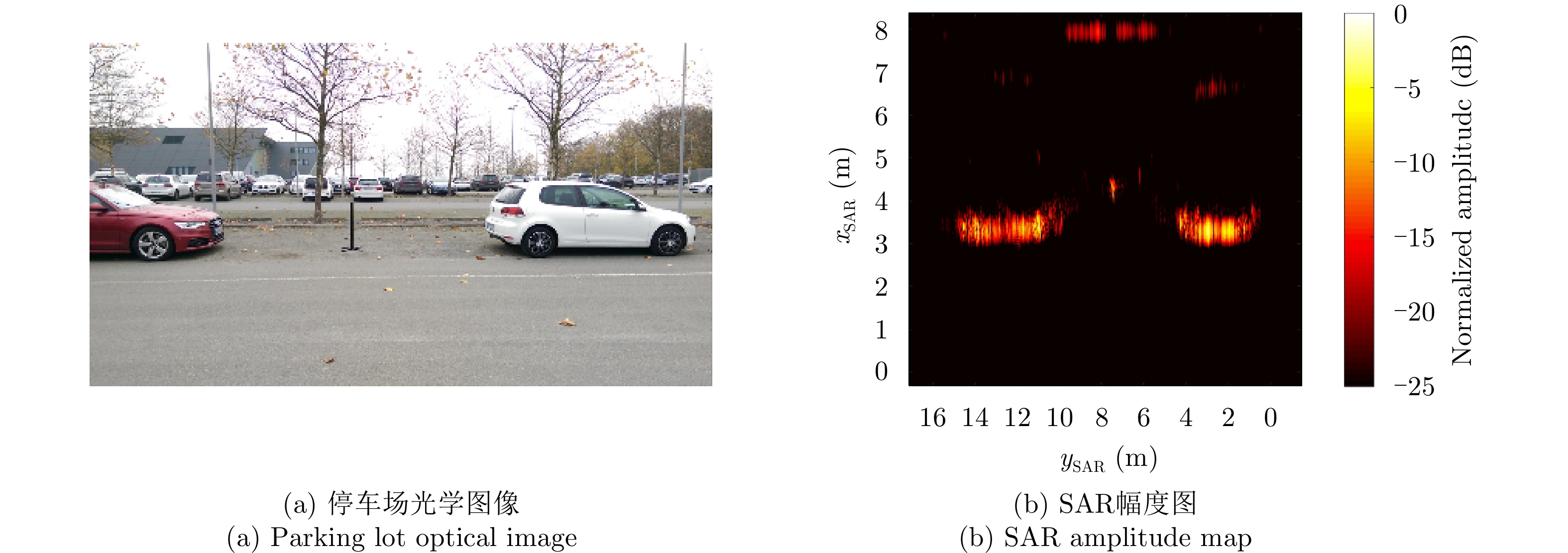
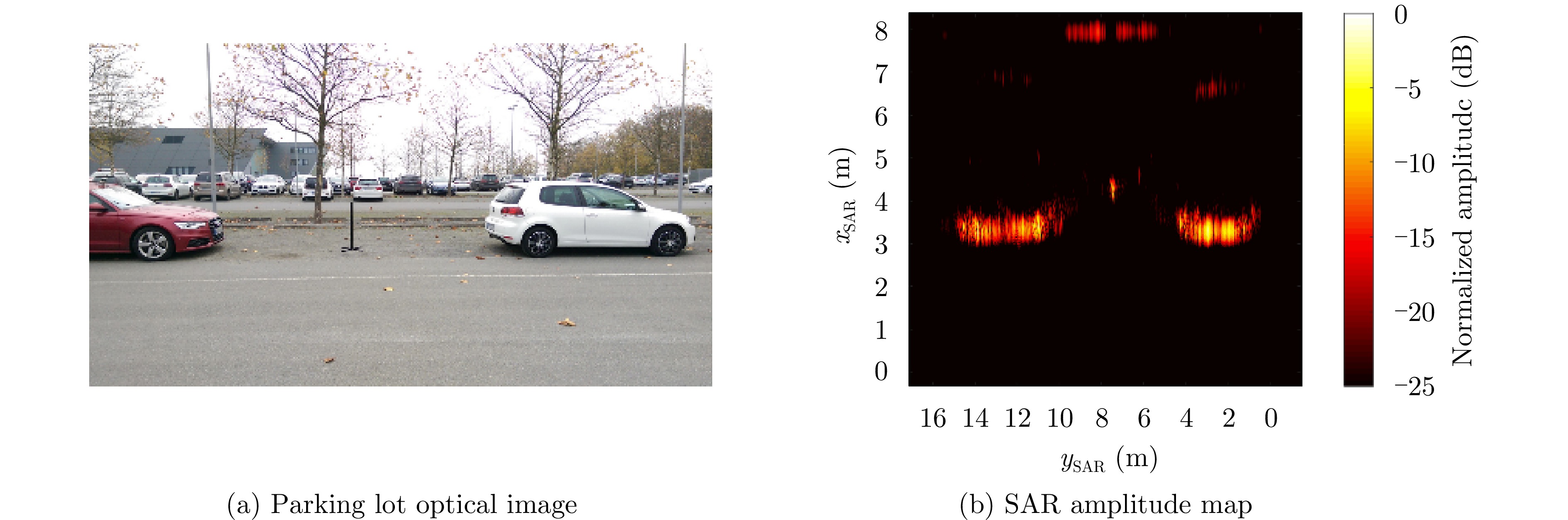
- Figure 20. Parking lots SISO-RMA SAR image[56]
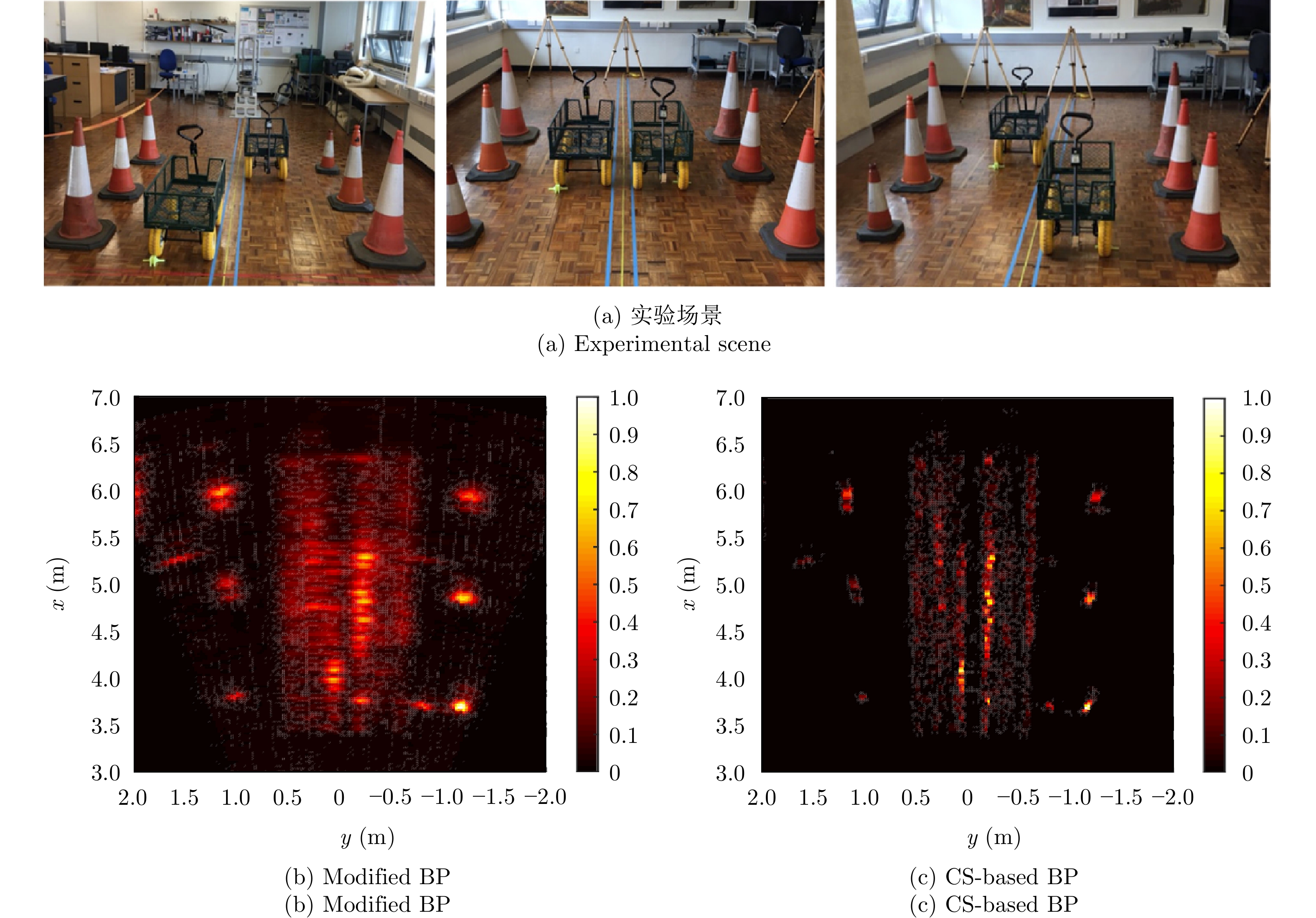
- Figure 21. SAR images using RMA & CS[57]
- Figure 22. Modified RMA imaging[59]
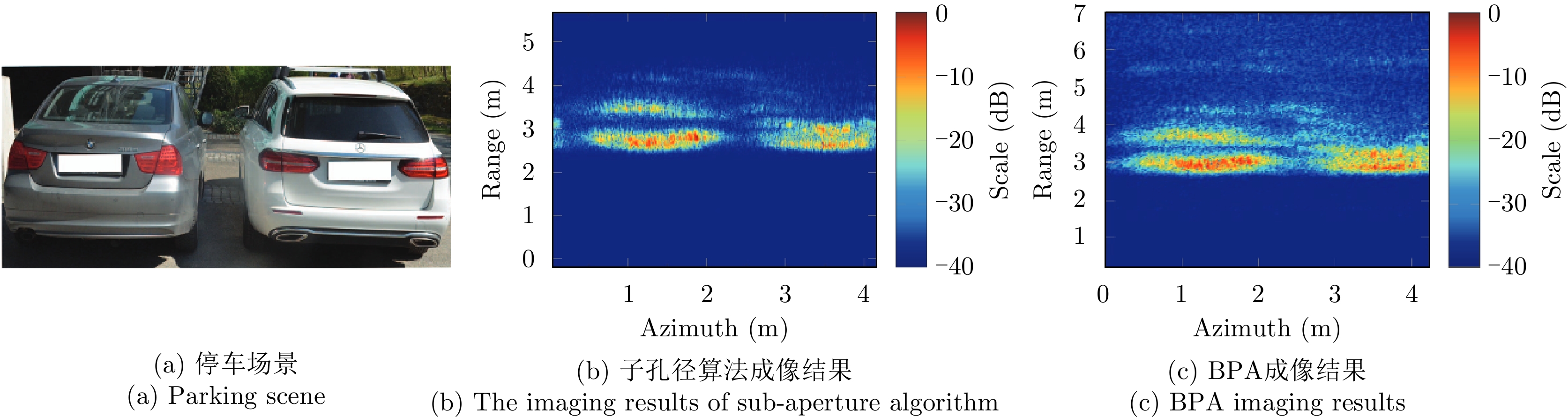
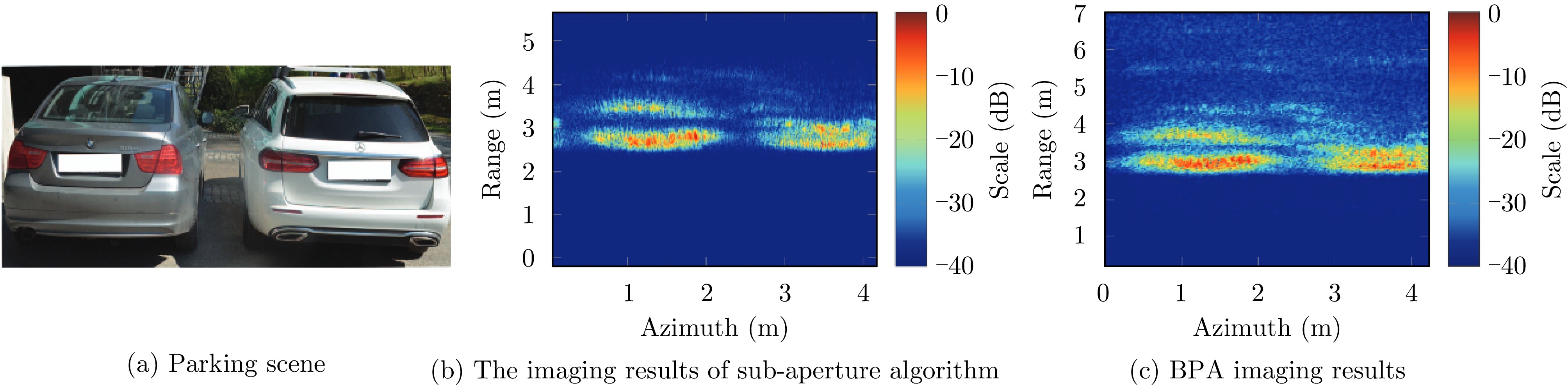
- Figure 23. The test scene of BP algorithm flow processing scheme[61]
- Figure 24. Moving Target Imaging (MTI) base on BP algorithm[63]
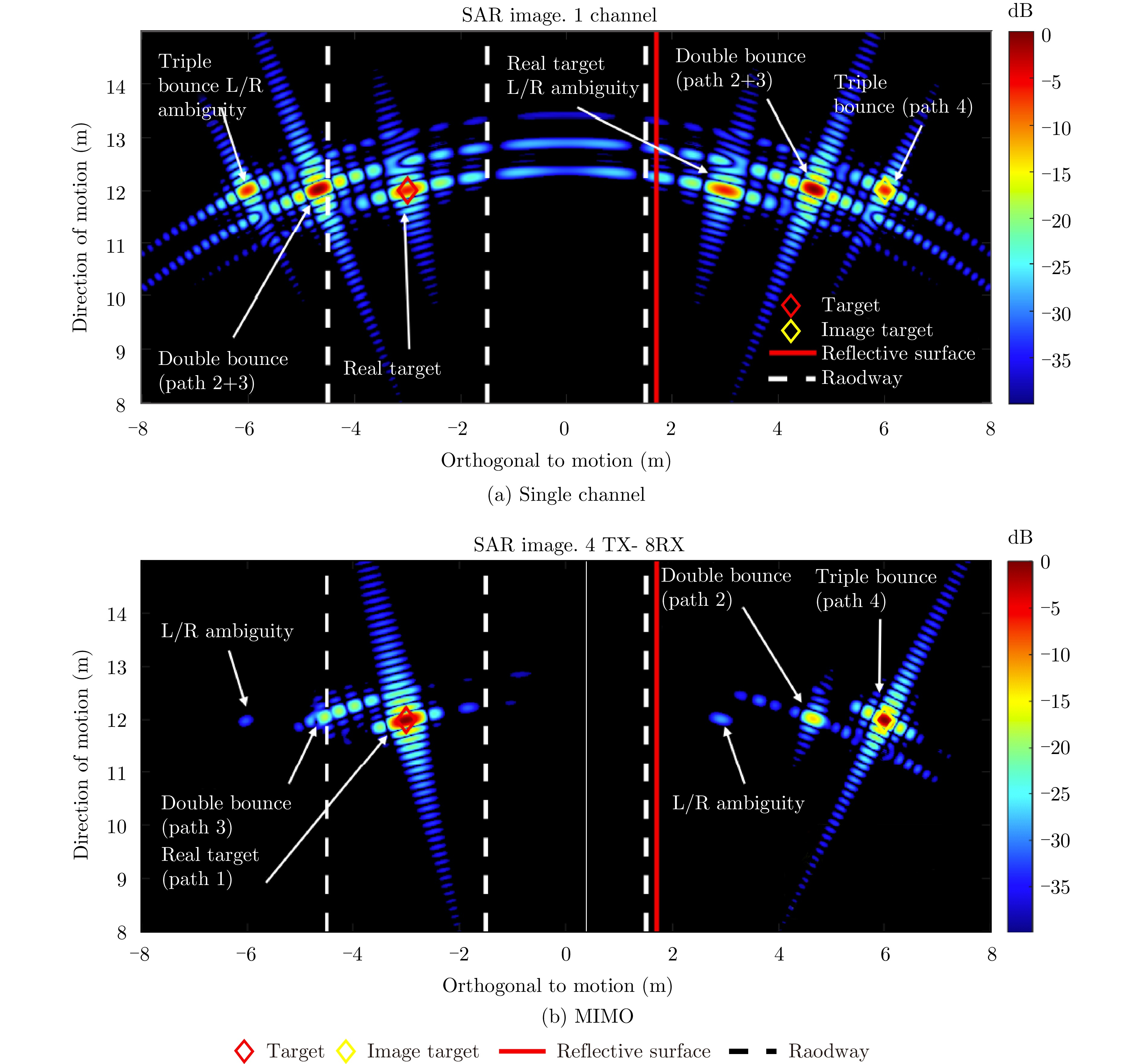
- Figure 25. Multipath interference suppression comparison chart[64]
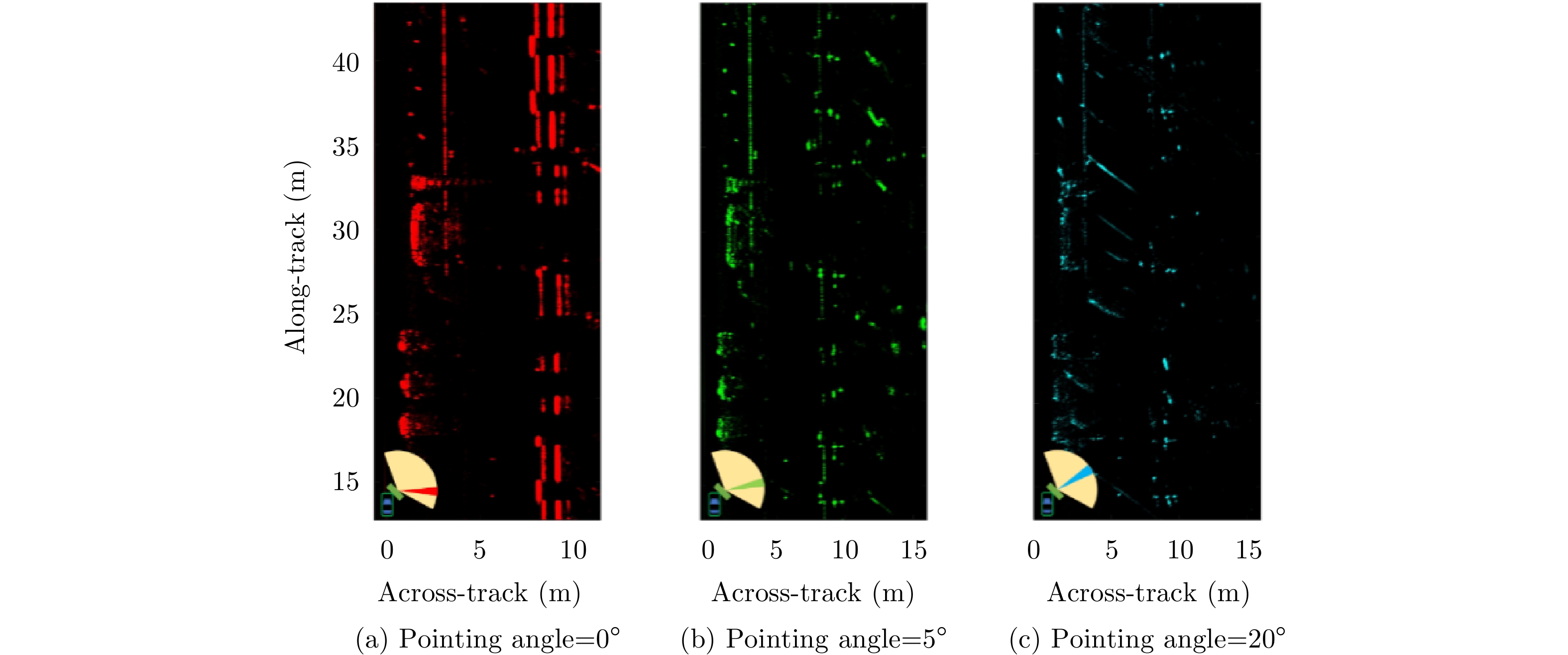
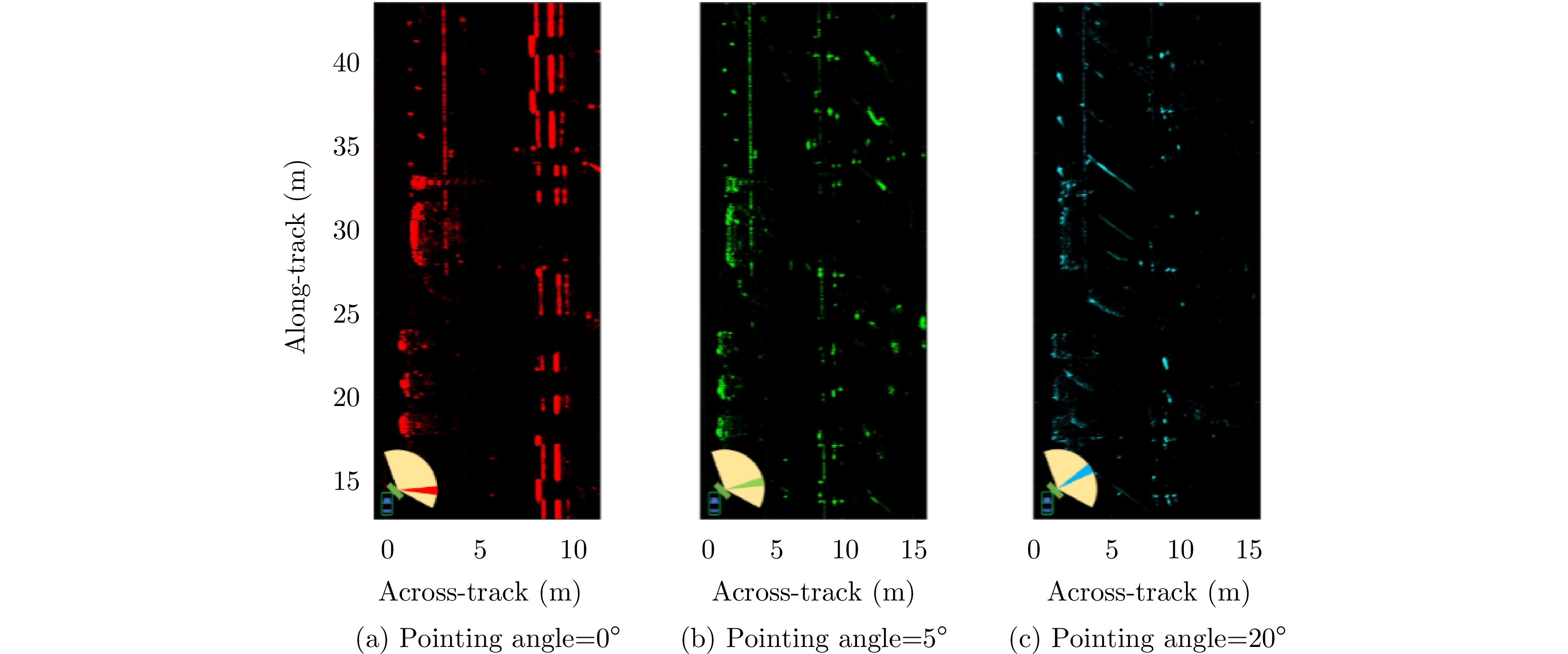
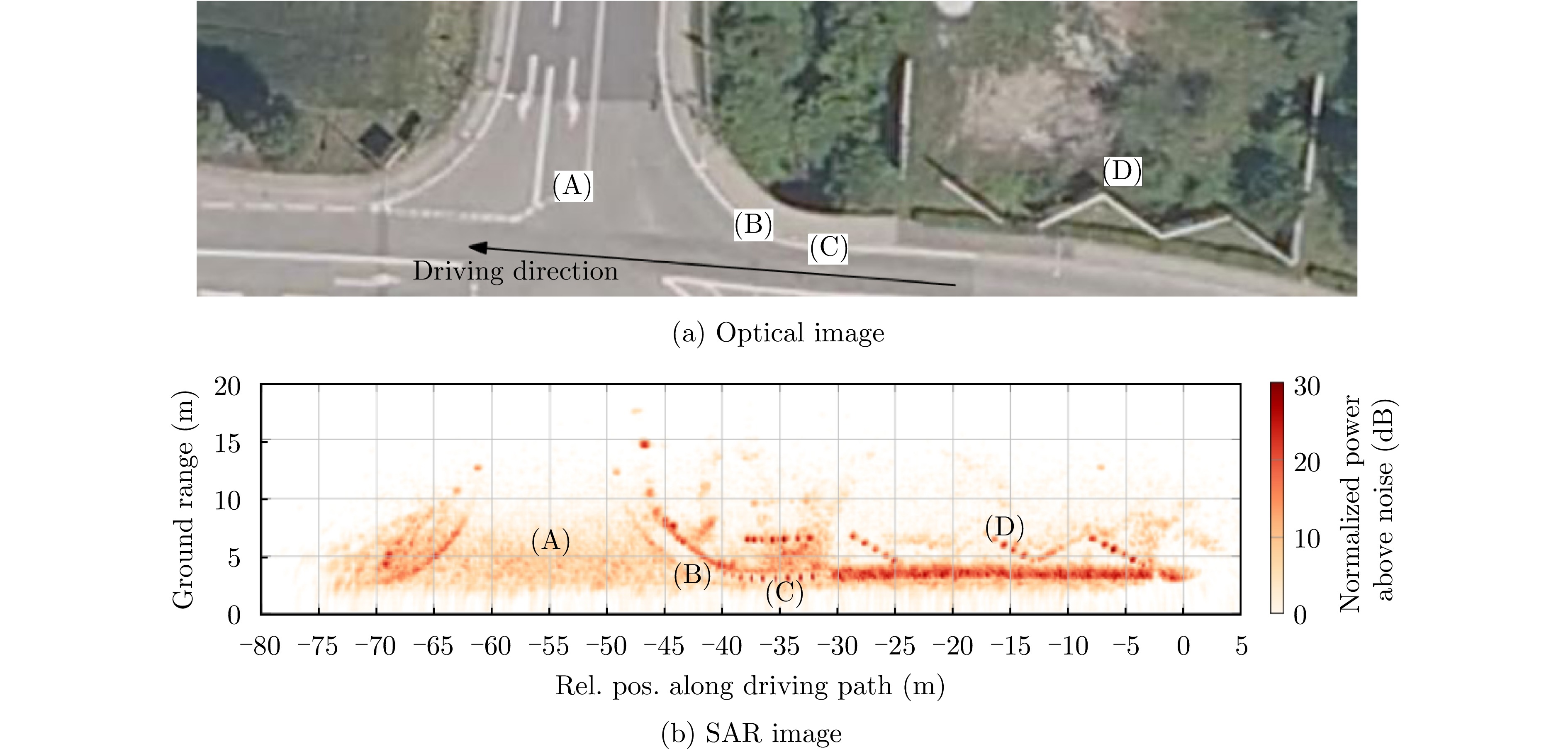
- Figure 26. Imaging results of automotive SAR at different beam angles[65]
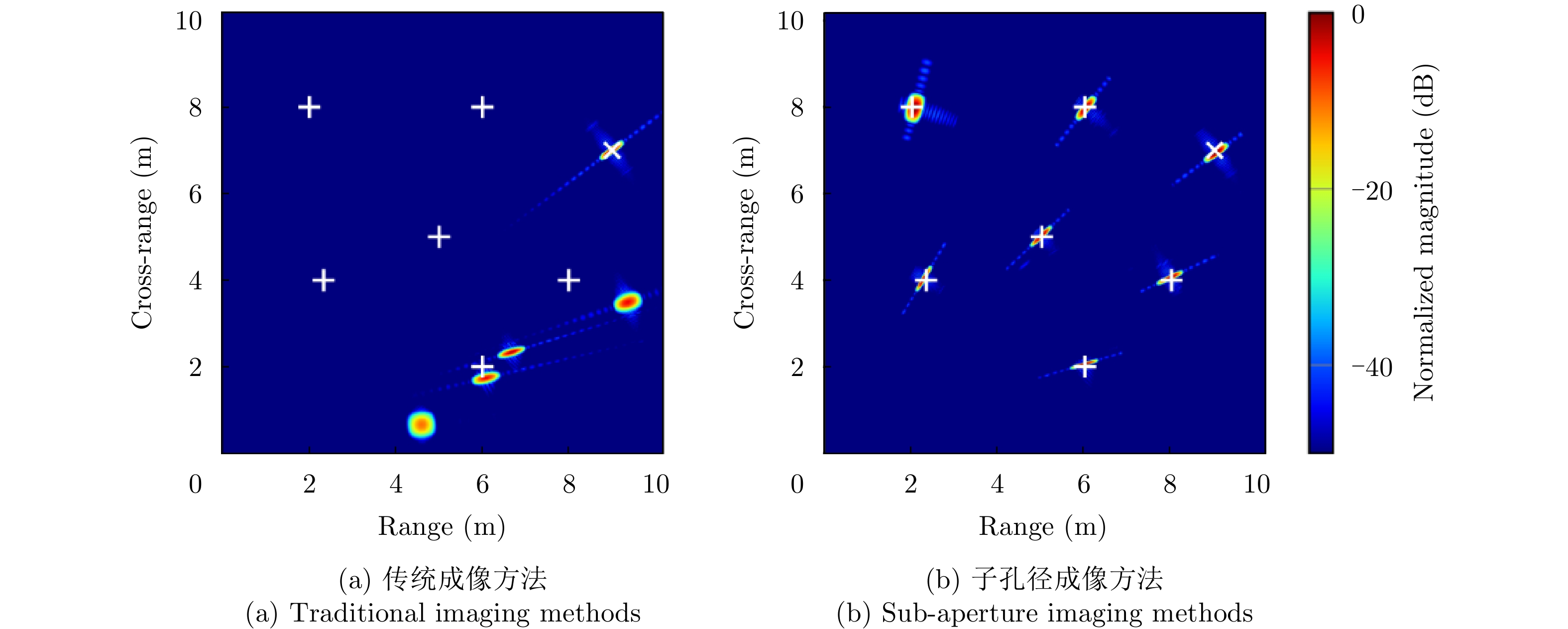
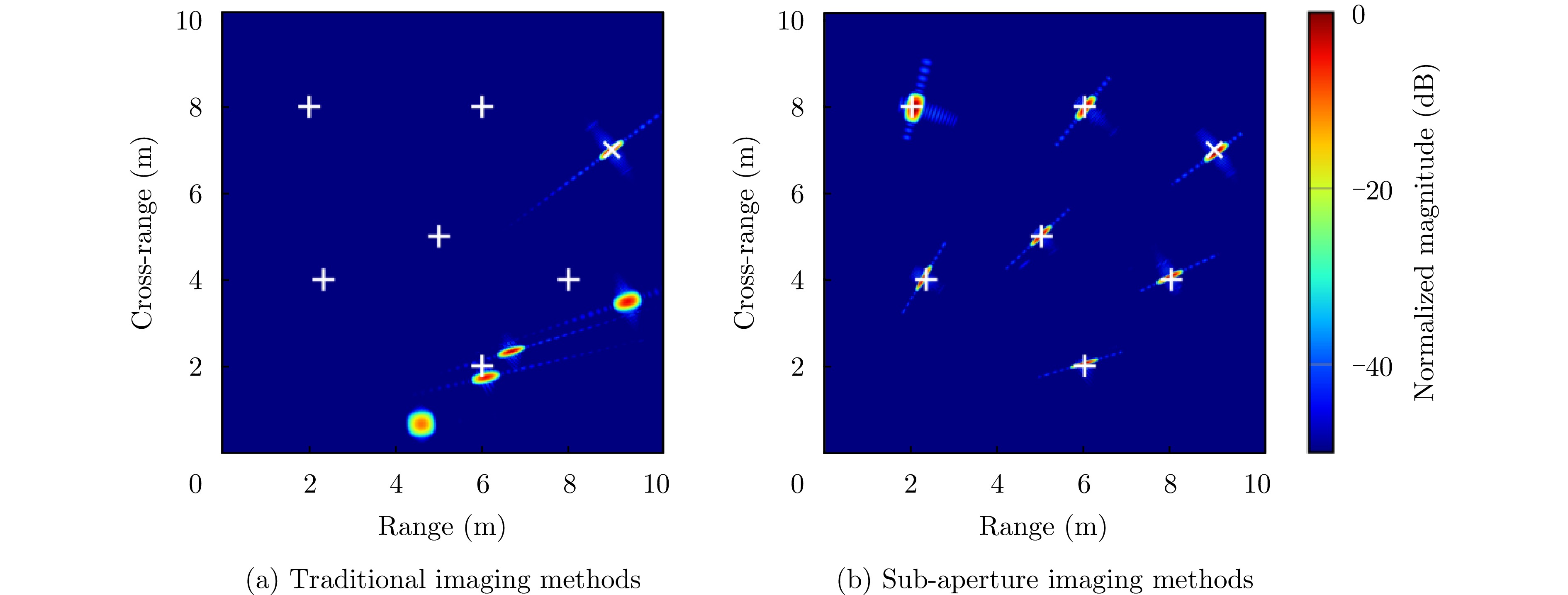
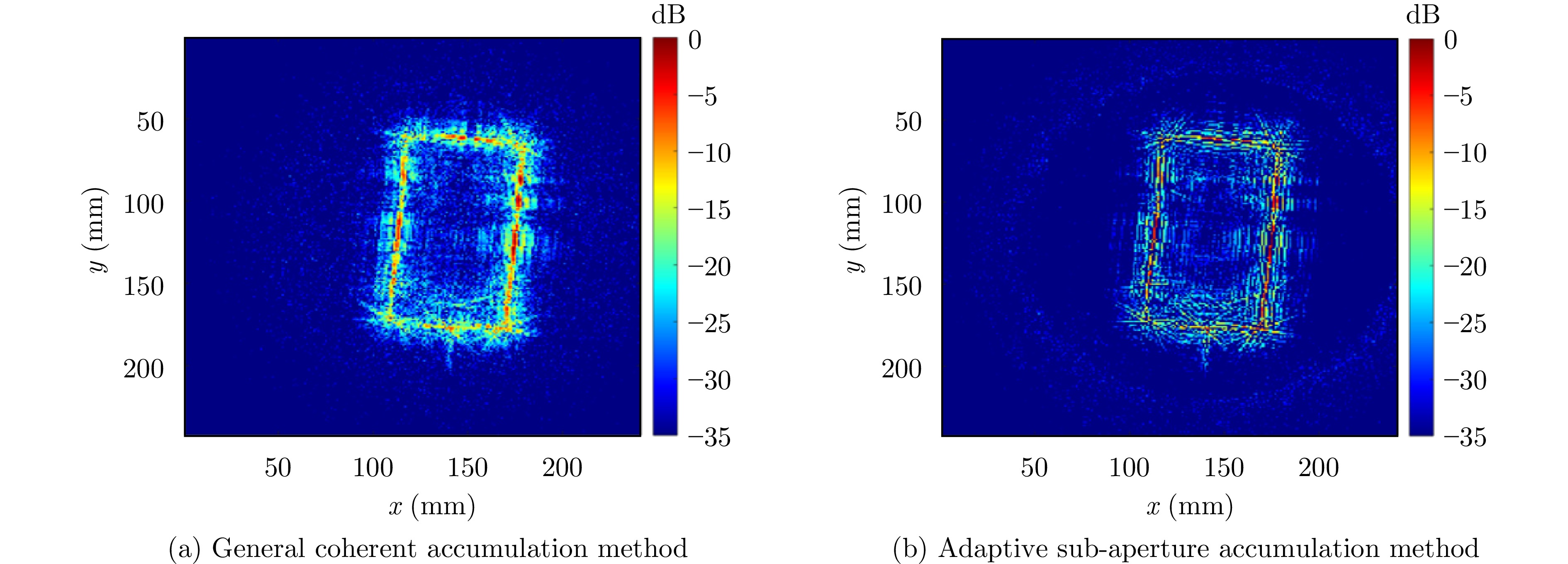
- Figure 27. Image enhancement by adaptive sub-aperture accumulation[66]
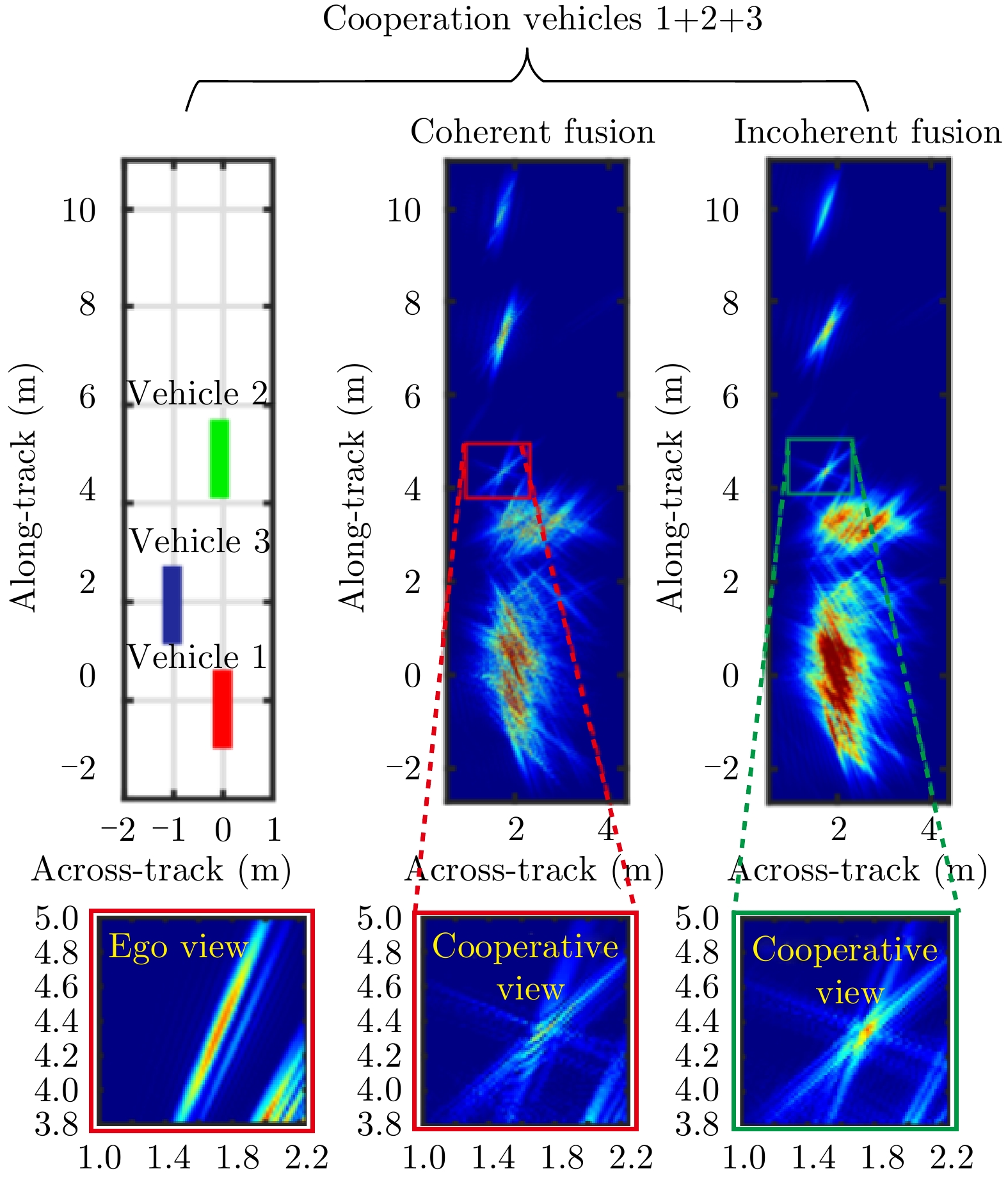
- Figure 28. Comparison of improving range-direction resolution in multi-vehicle collaboration[67]
- Figure 29. 77 GHz automotive SAR system[68]
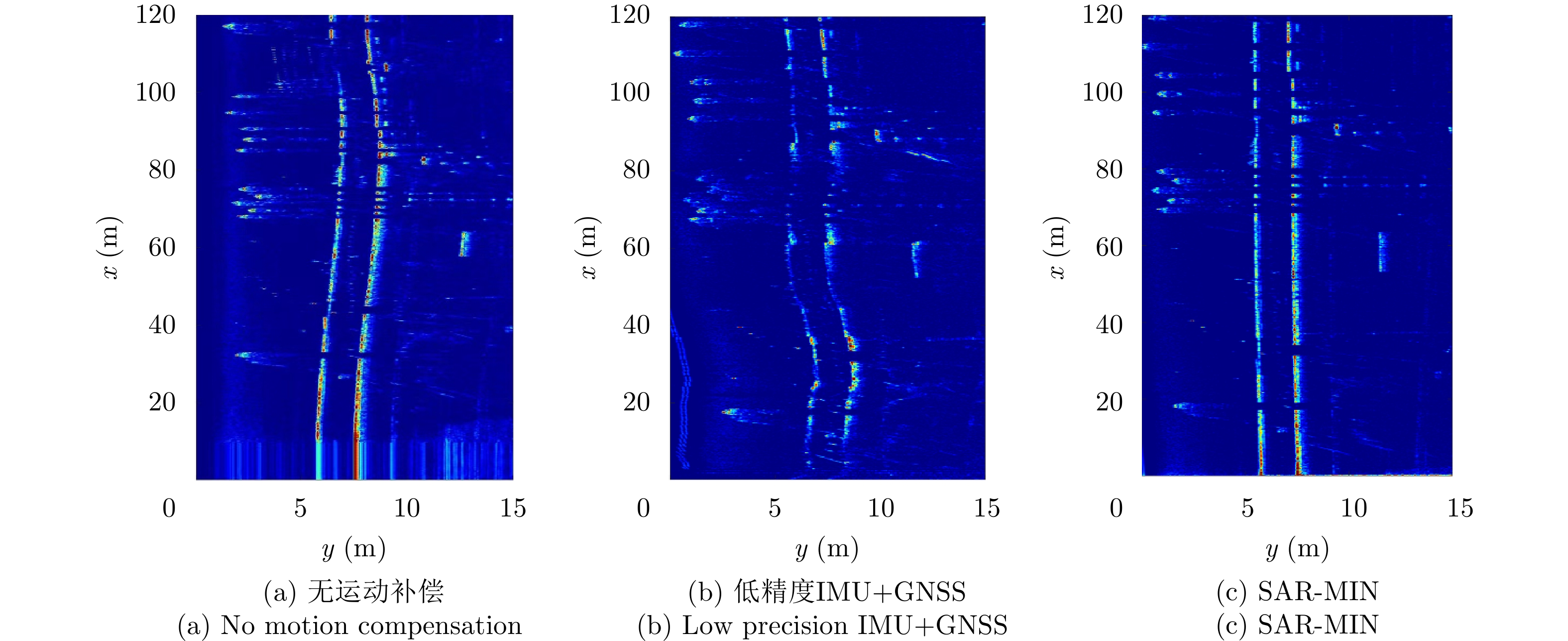
- Figure 30. Comprehensive motion compensation method[69]
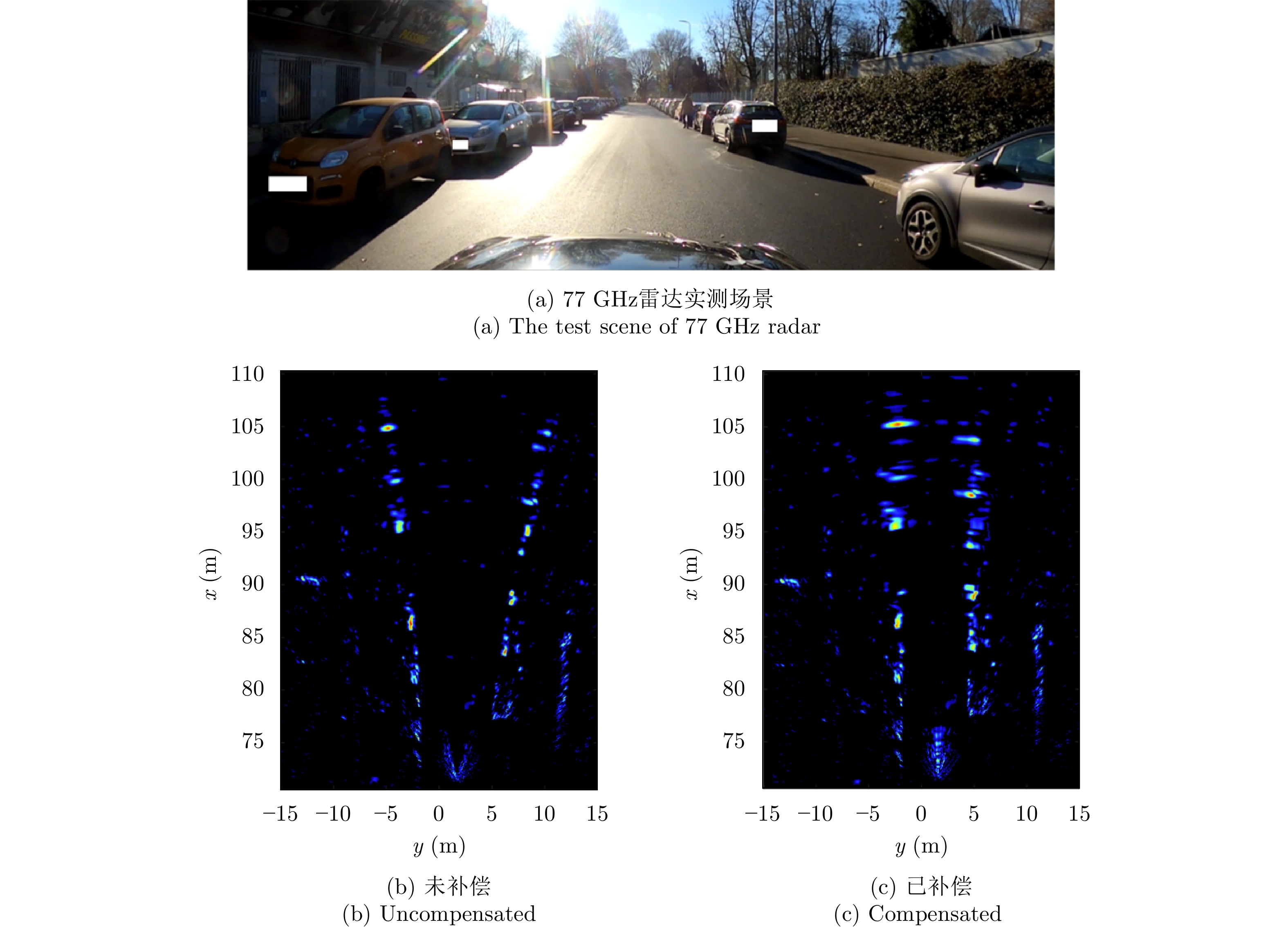
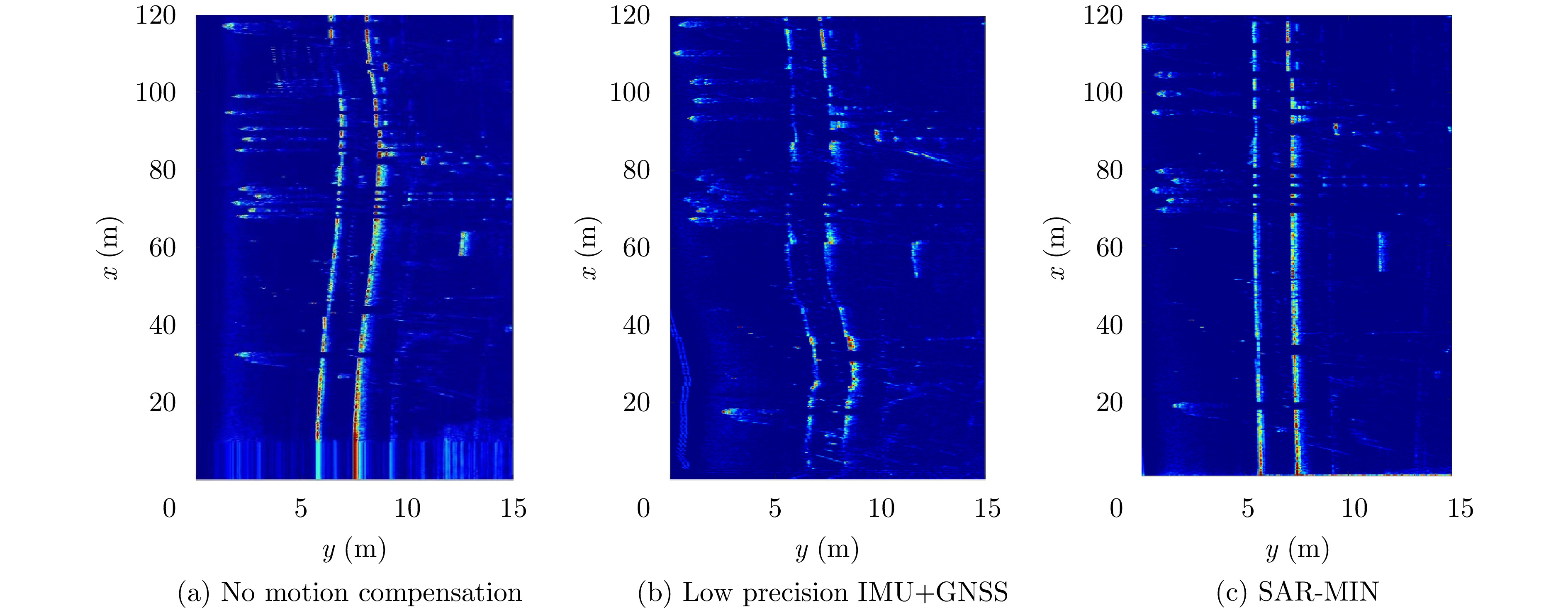
- Figure 31. Motion compensation by multi-radar system [72,73]
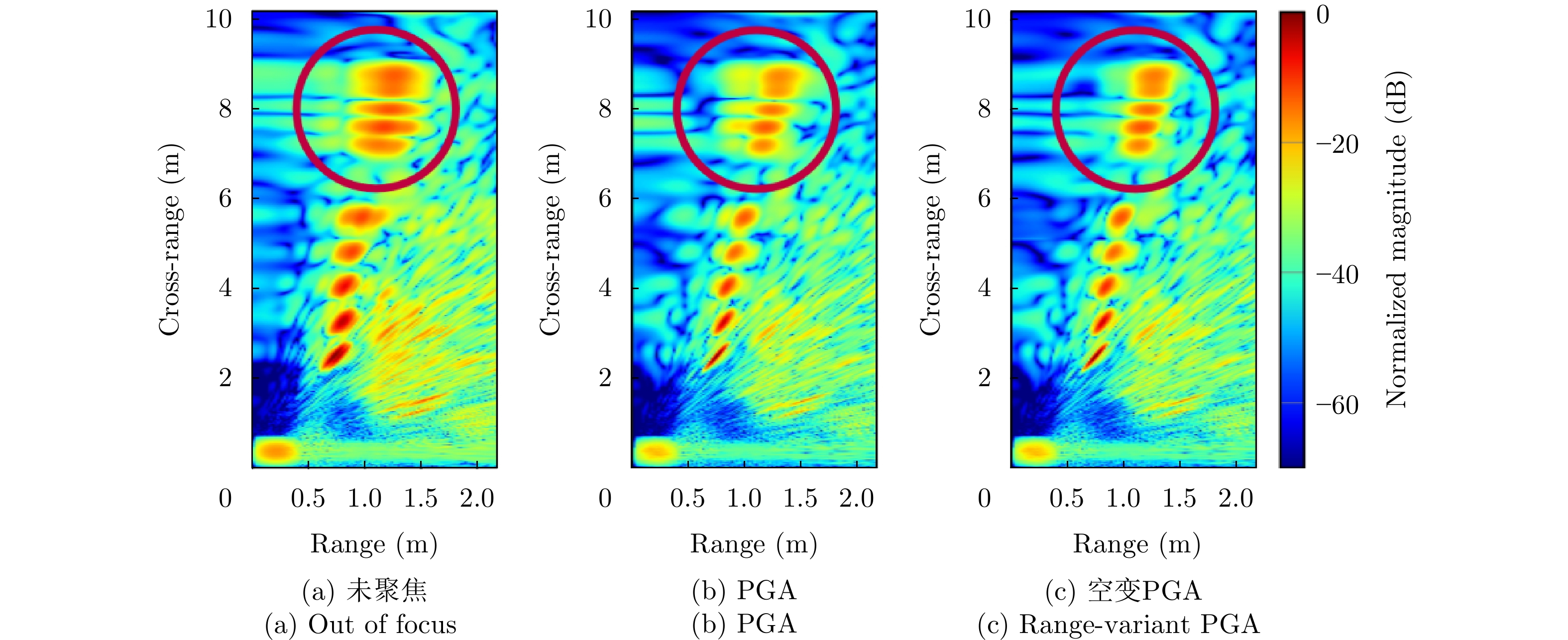
- Figure 32. PGA motion compensation[74,75]
- Figure 33. Residual Doppler method[76]
- Figure 34. MIMO-SAR motion compensation[77]
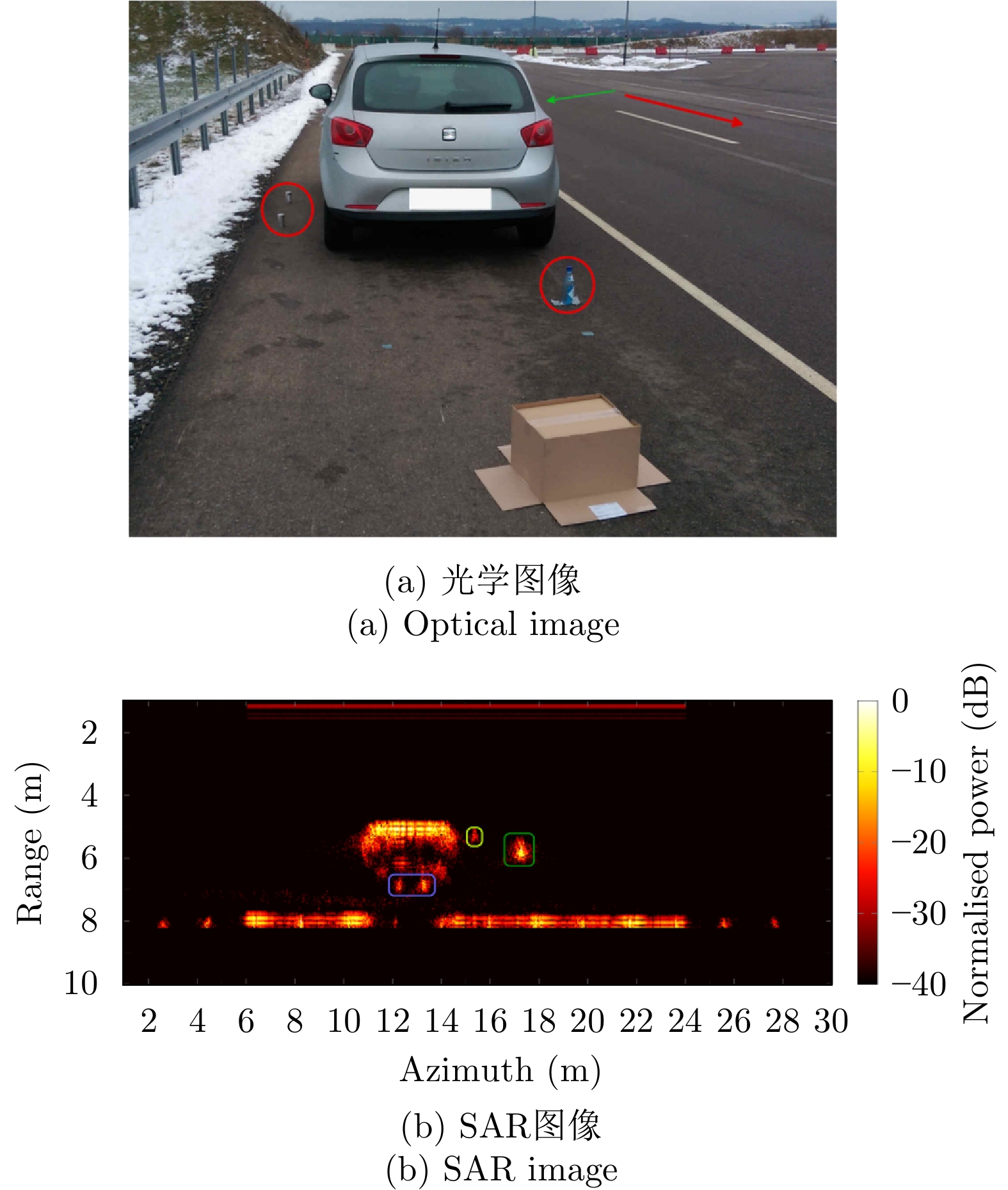
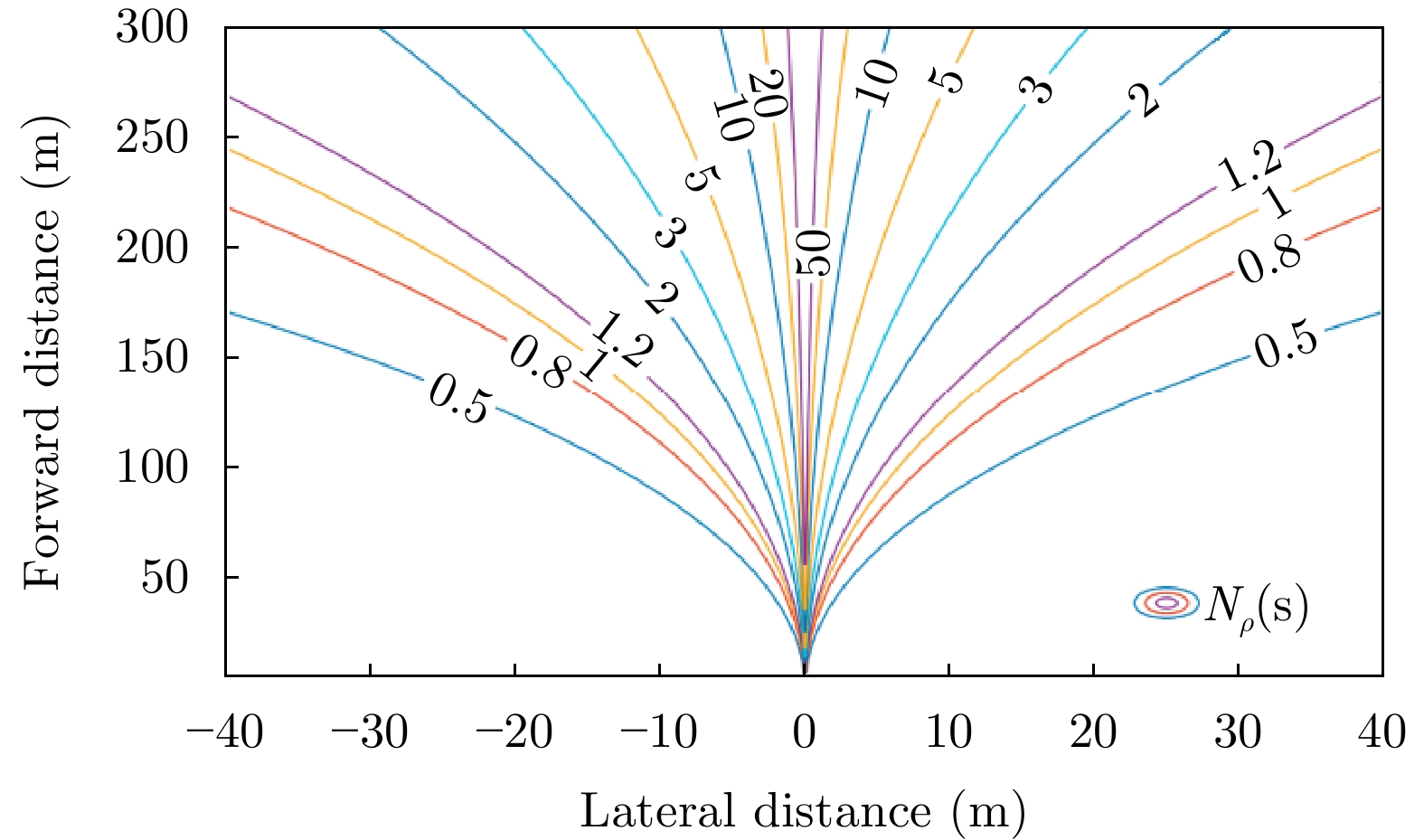
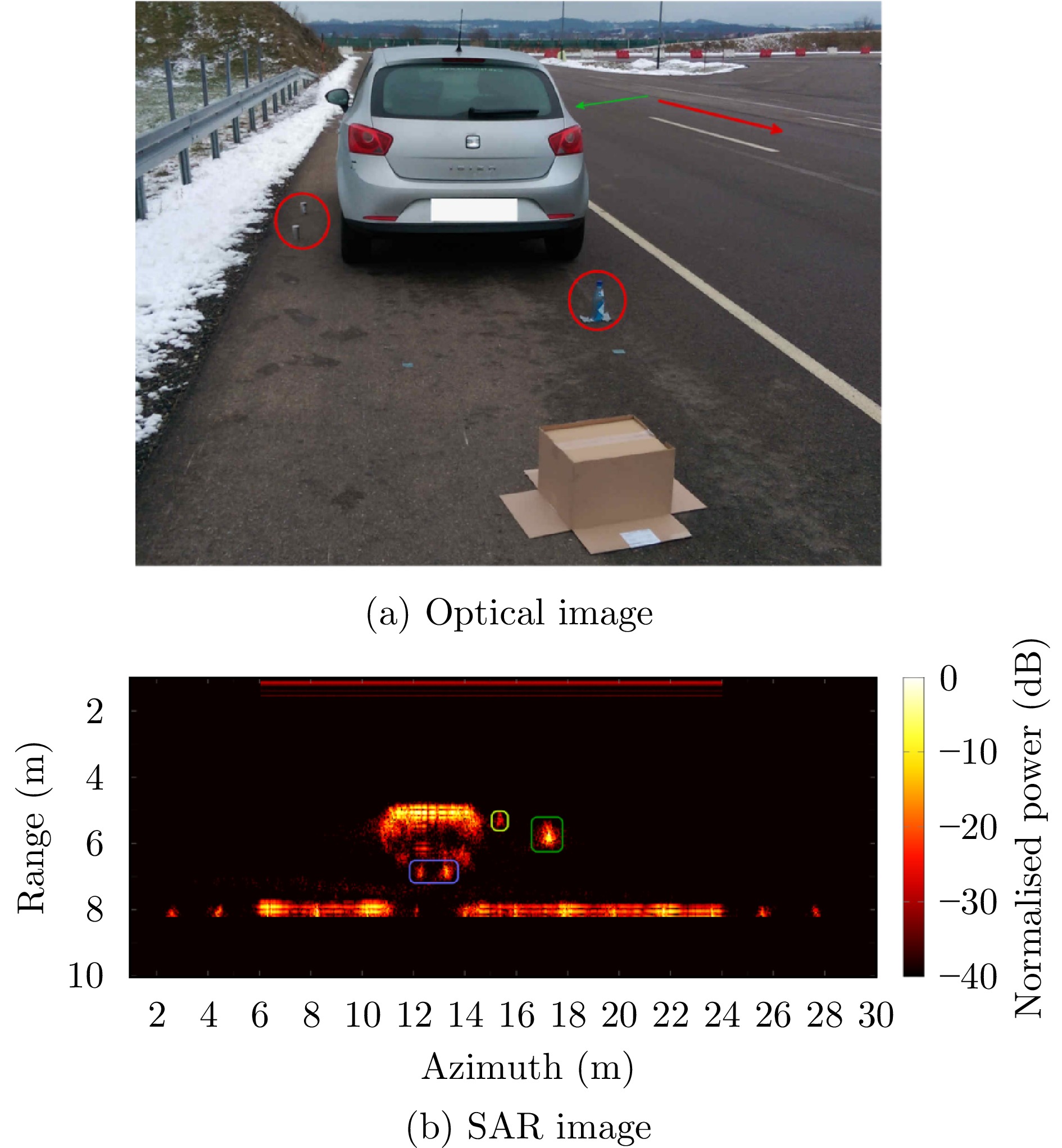
- Figure 35. 2D resolution of vehicle front view scene[78]
- Figure 36. Forward scanning SAR imaging[80]
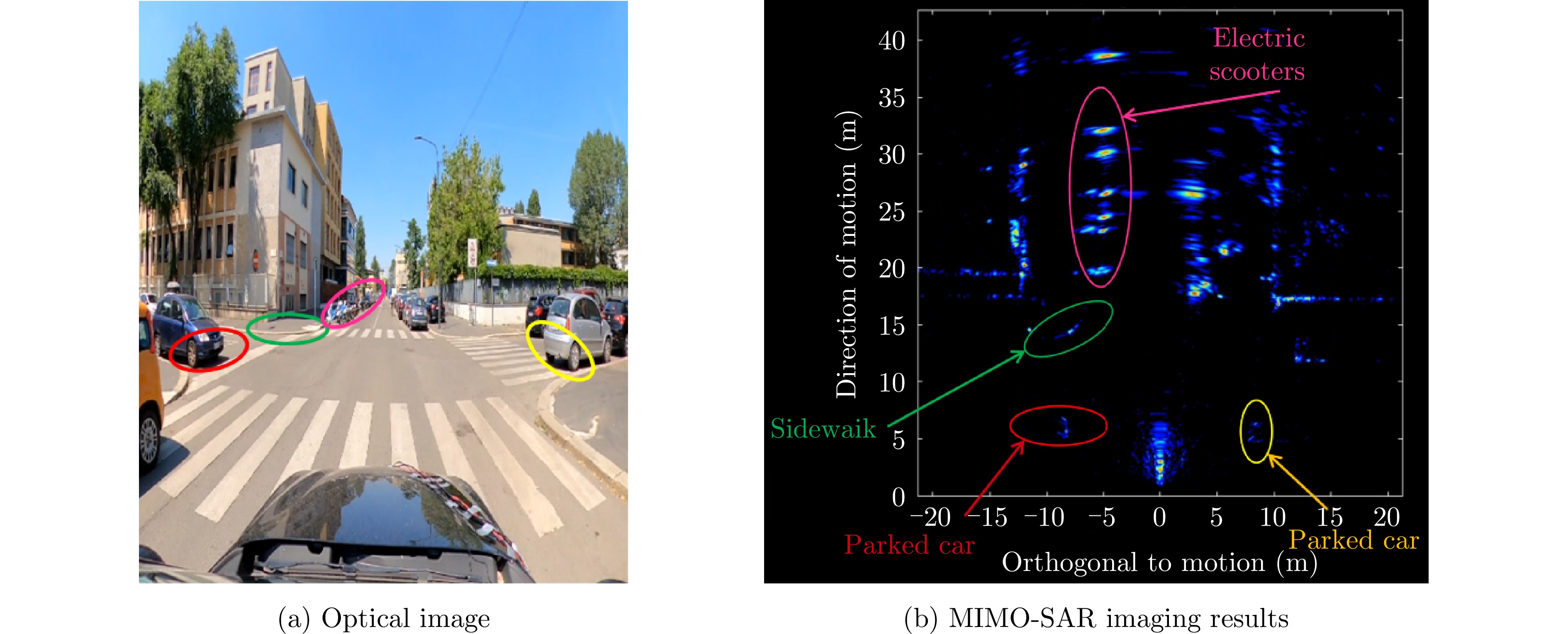
- Figure 37. Hierarchical MIMO-SAR imaging[81]
- Figure 38. Doppler multiplexing MIMO-SAR imaging[82]
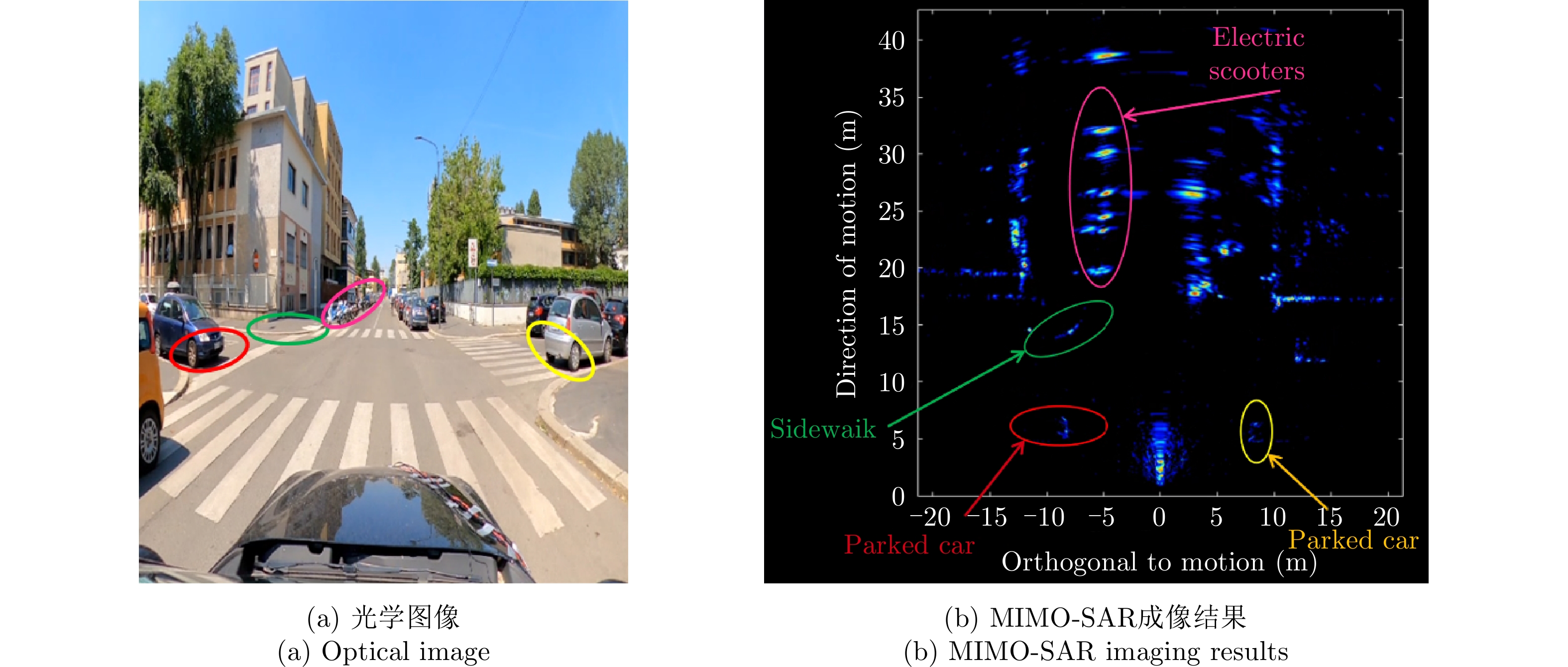
- Figure 39. 77 GHz forward-looking MIMO-SAR system[85–87]
- Figure 40. Forward-looking SAR imaging[88]
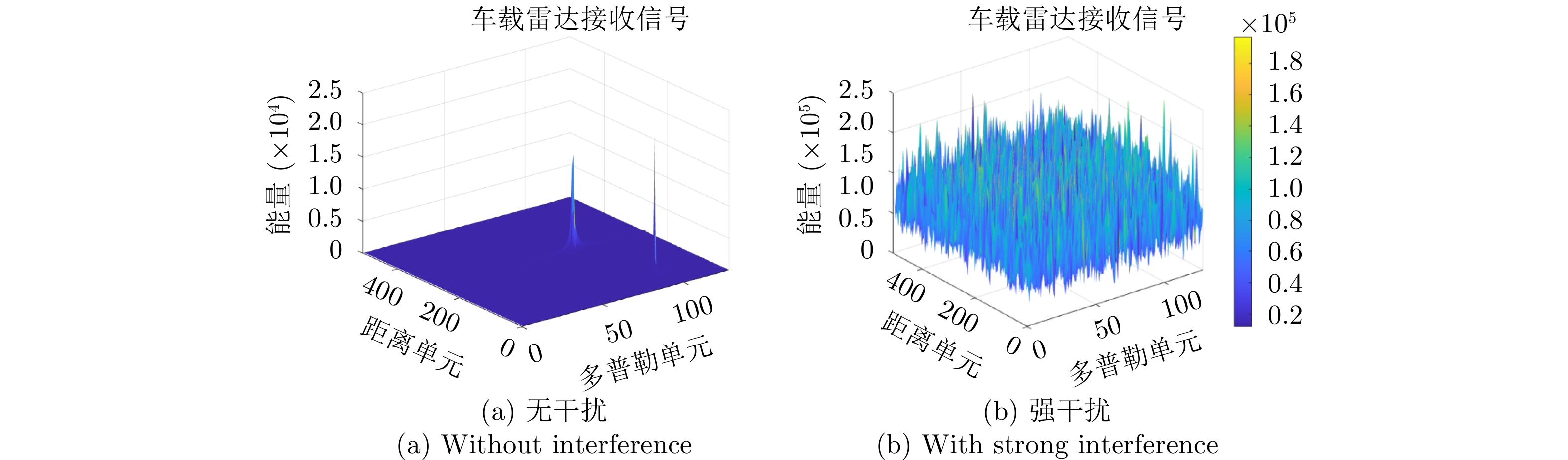
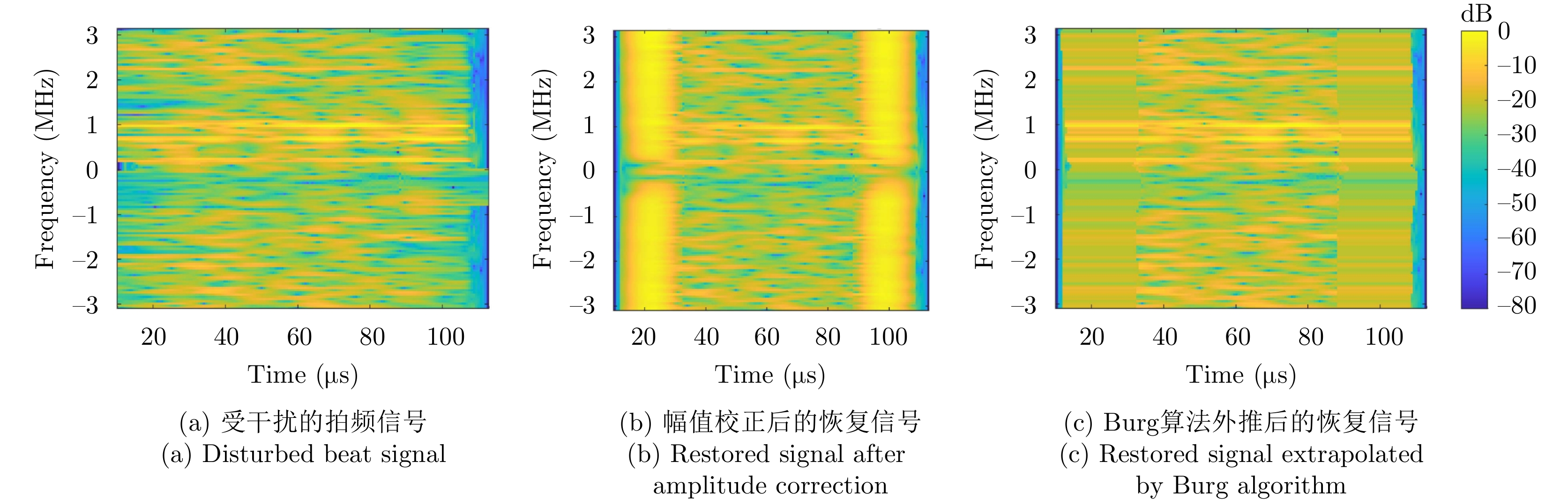
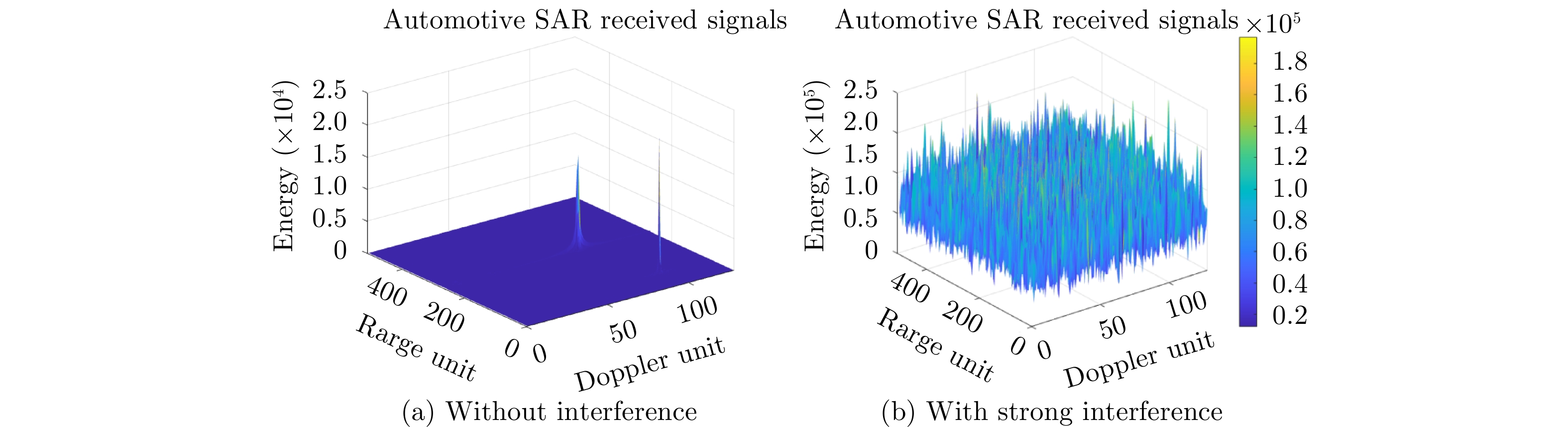
- Figure 41. Range Doppler images without interference and with strong interference[92]
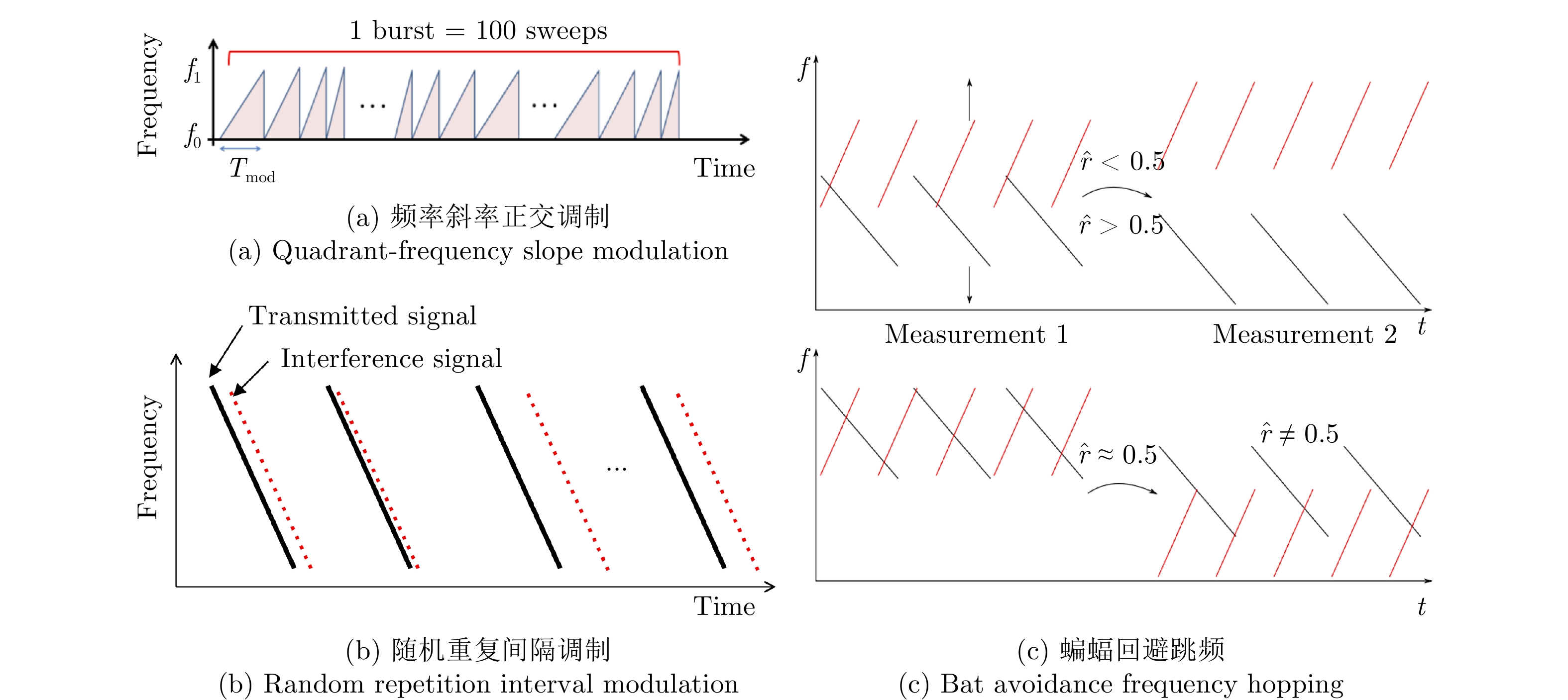
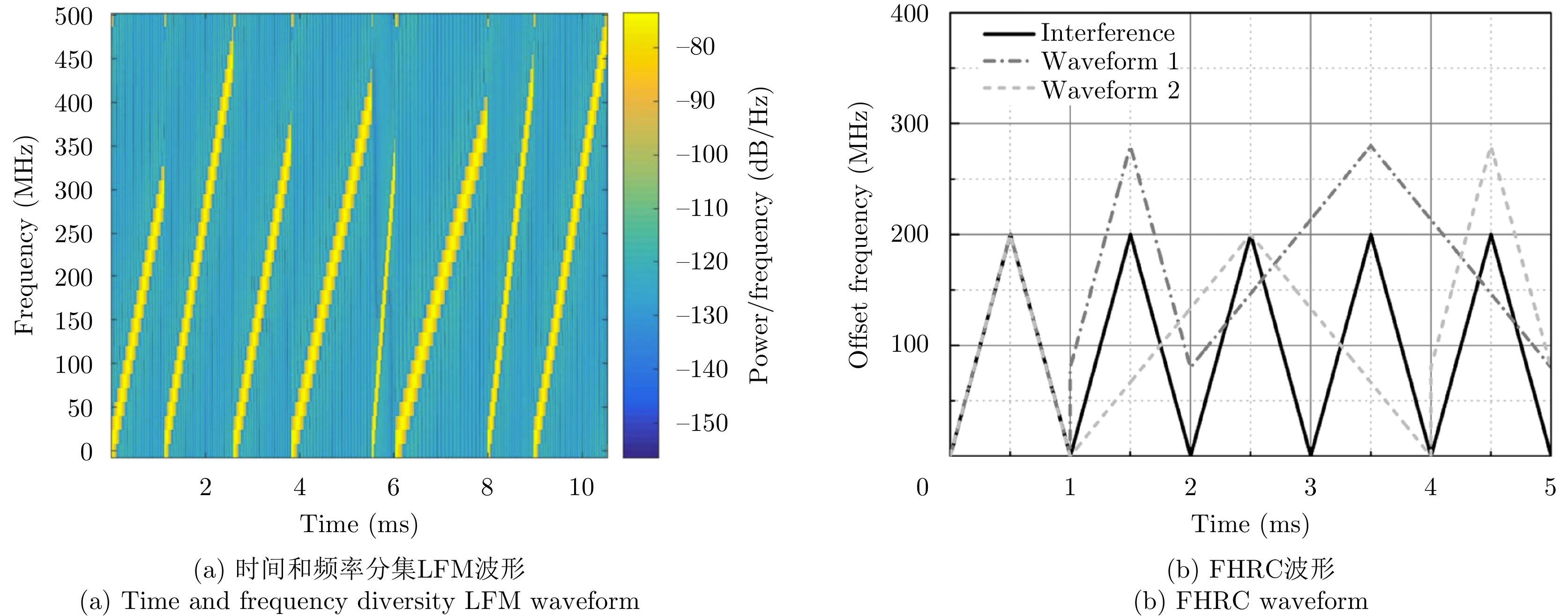
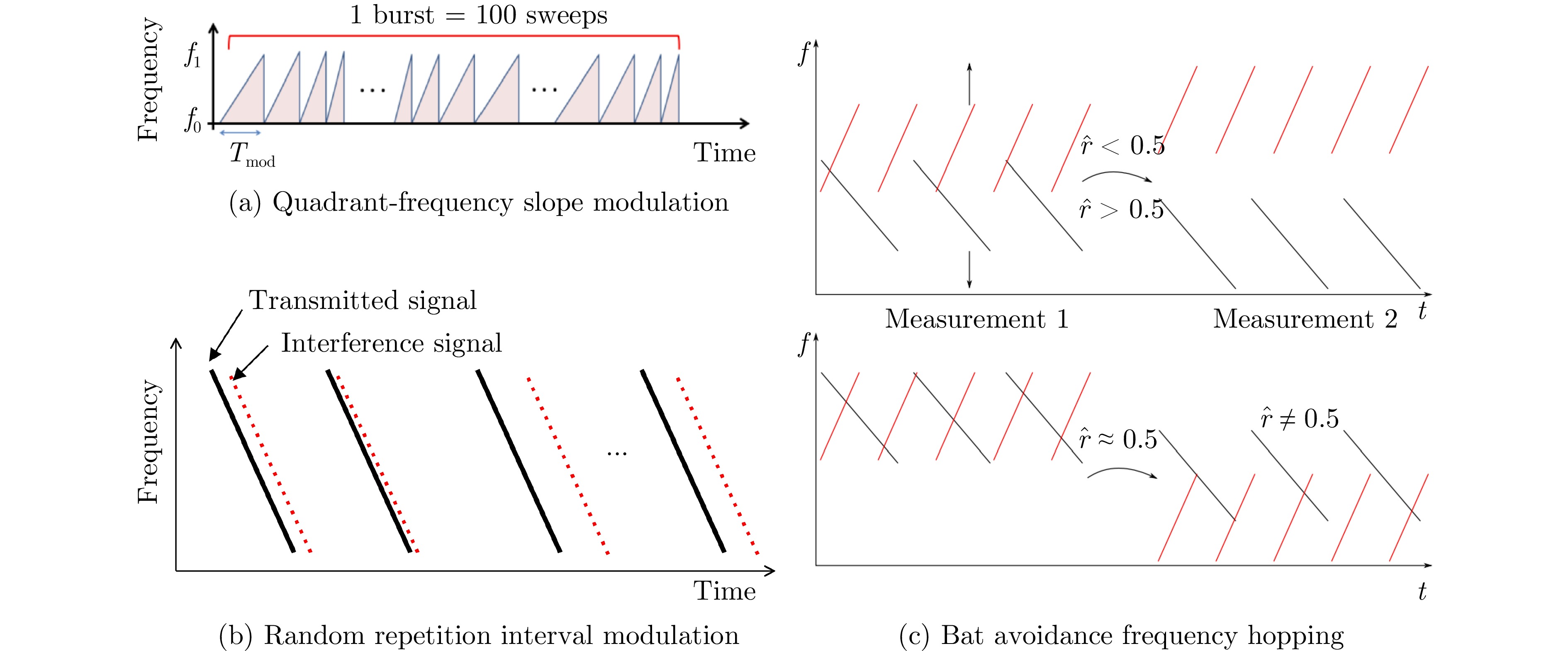
- Figure 42. Simple anti-interference improved FMCW waveform[93–95]
- Figure 43. FMCW waveform improved by anti-interference adjustment of multiple parameters[96,97]
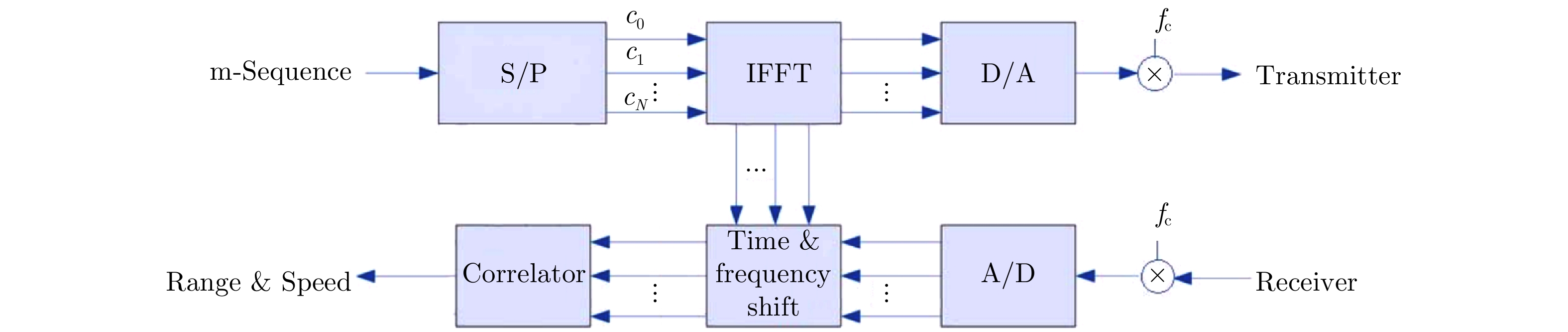
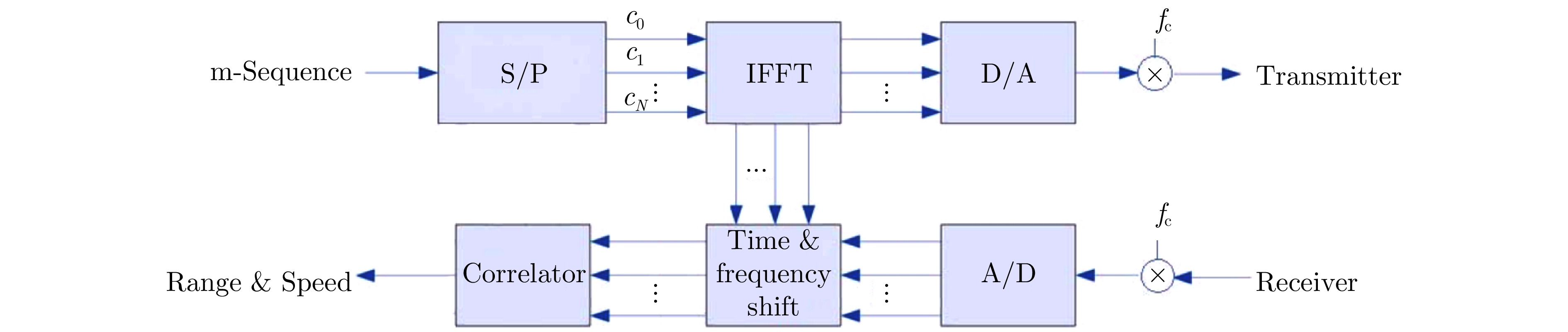
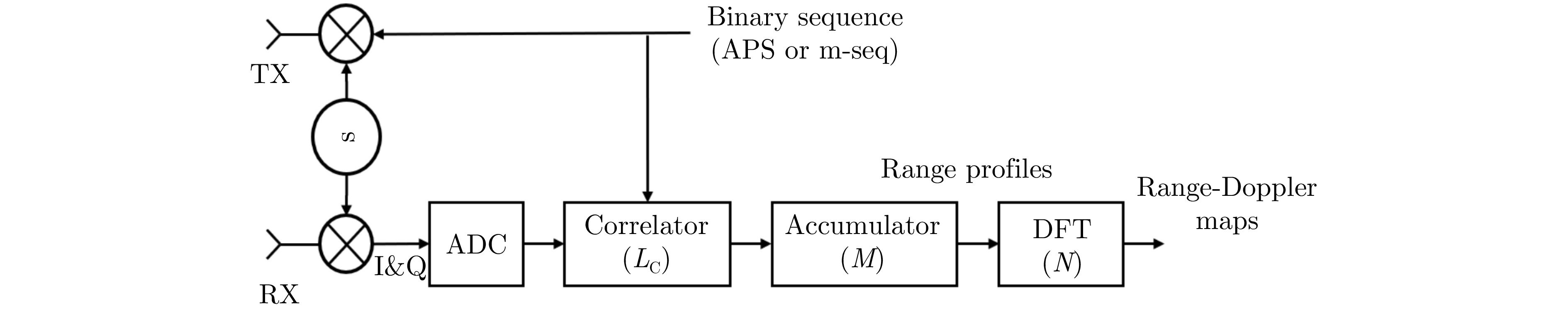
- Figure 44. OFDM radar based on m-sequence[103]
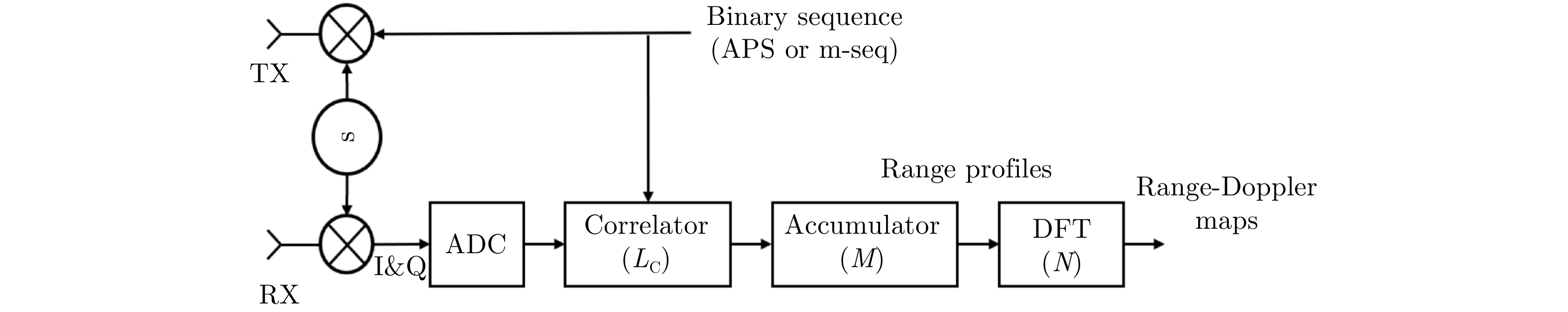
- Figure 45. PMCW radar block diagram[104]
- Figure 46. System coordination and policy anti-interference architecture[105–107]
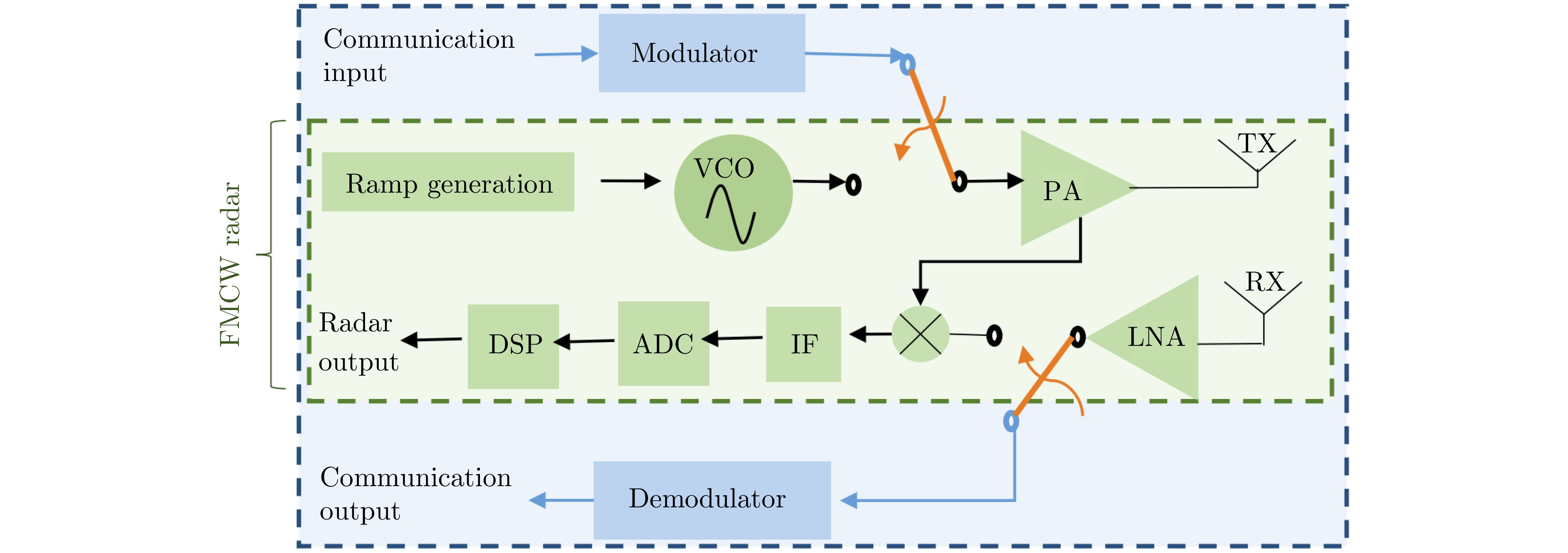
- Figure 47. The system composition of RadChat[108]
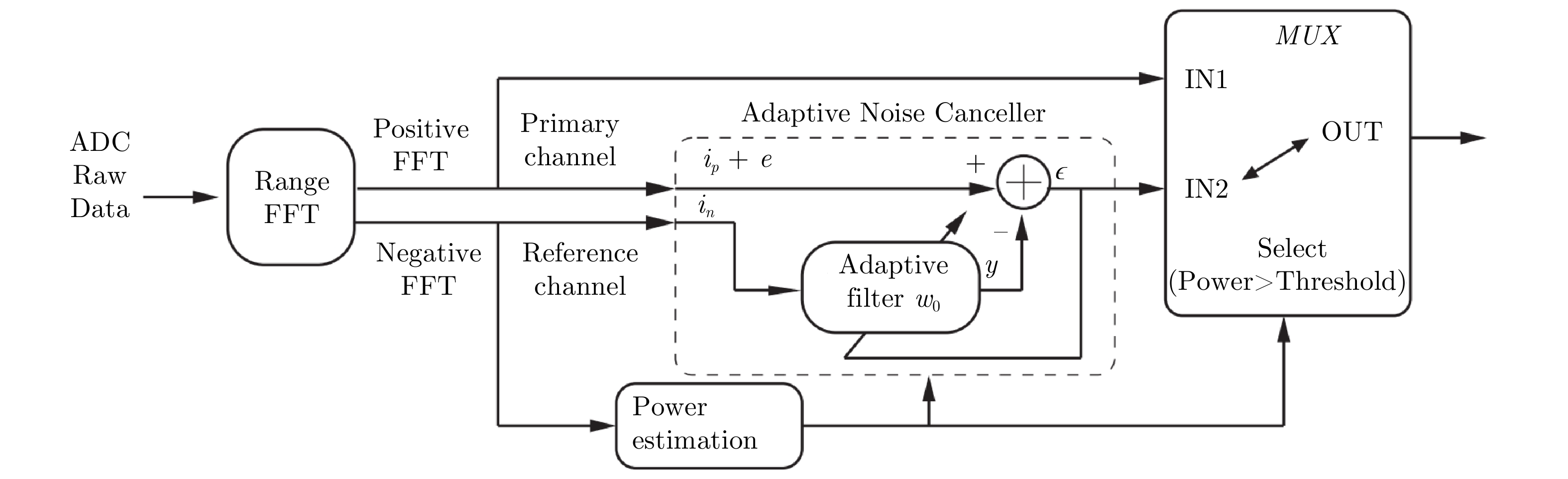
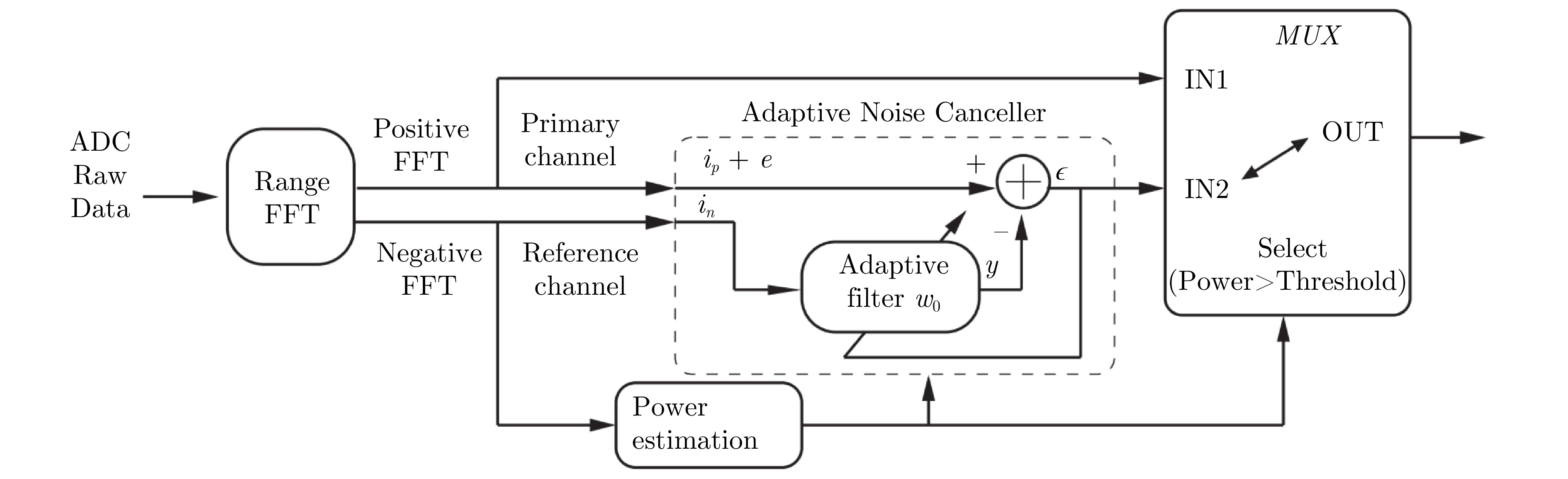
- Figure 48. Adaptive noise canceller used to suppress interference[110]
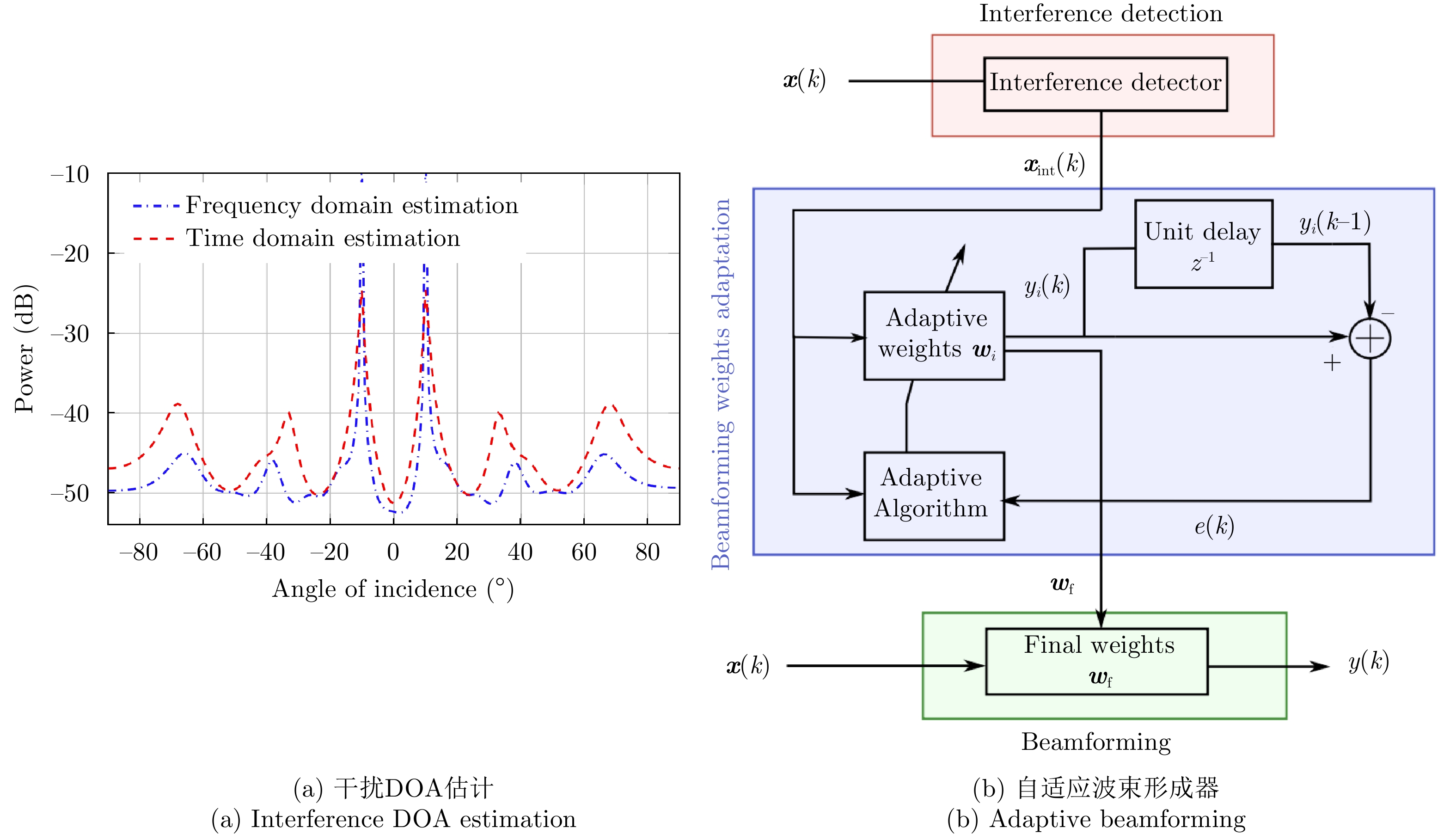
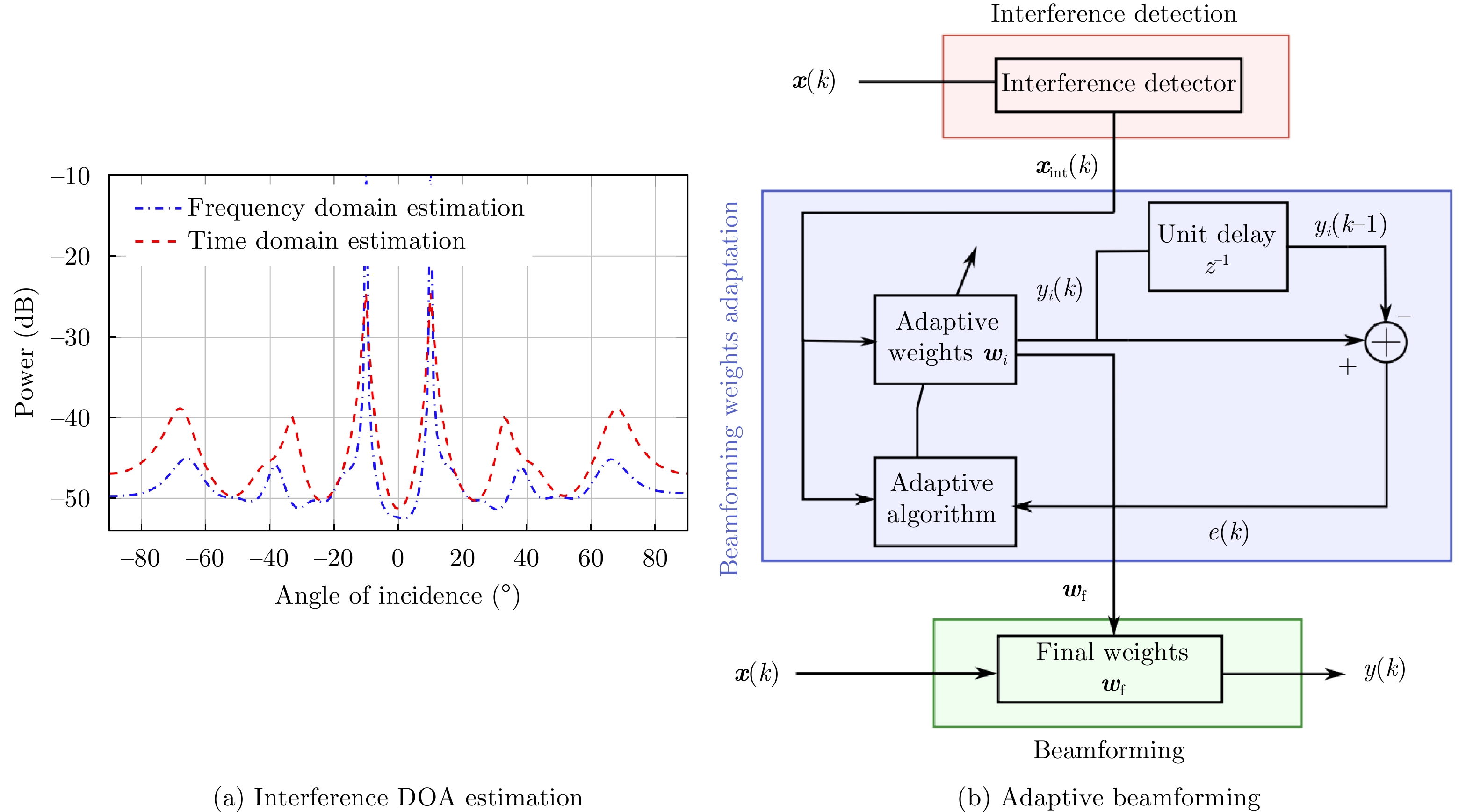
- Figure 49. Adaptive DBF for interference suppression[112,115]
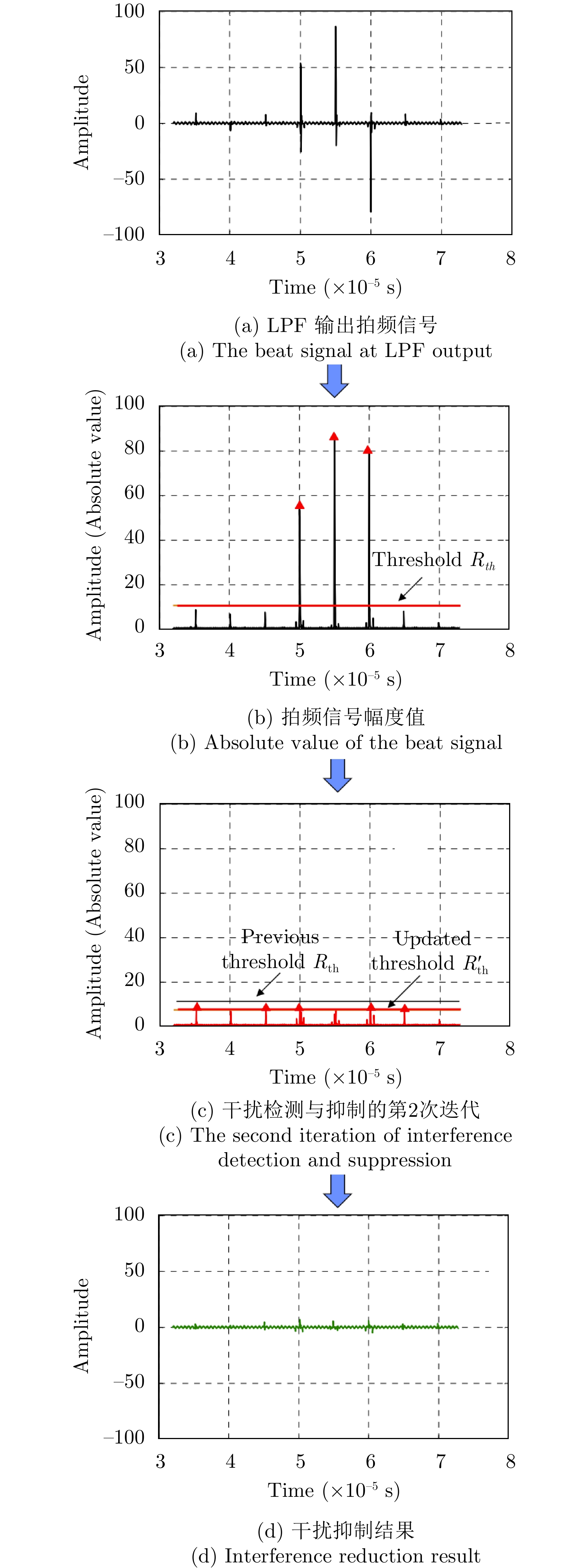
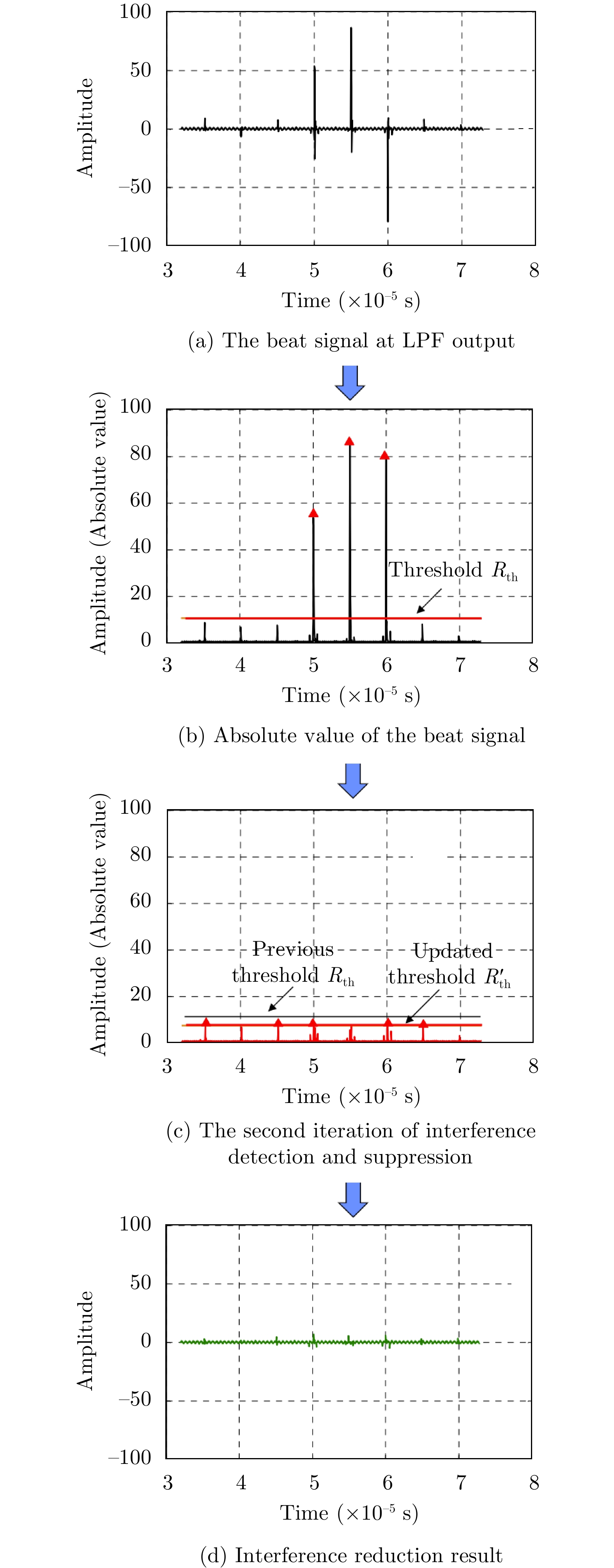
- Figure 50. Iterative threshold interference detection in time domain[120]
- Figure 51. Beat interpolation in STFT domain[121]
- Figure 52. Beat signal in the time-frequency domain[125]
- Figure 53. IMIA algorithm[129]
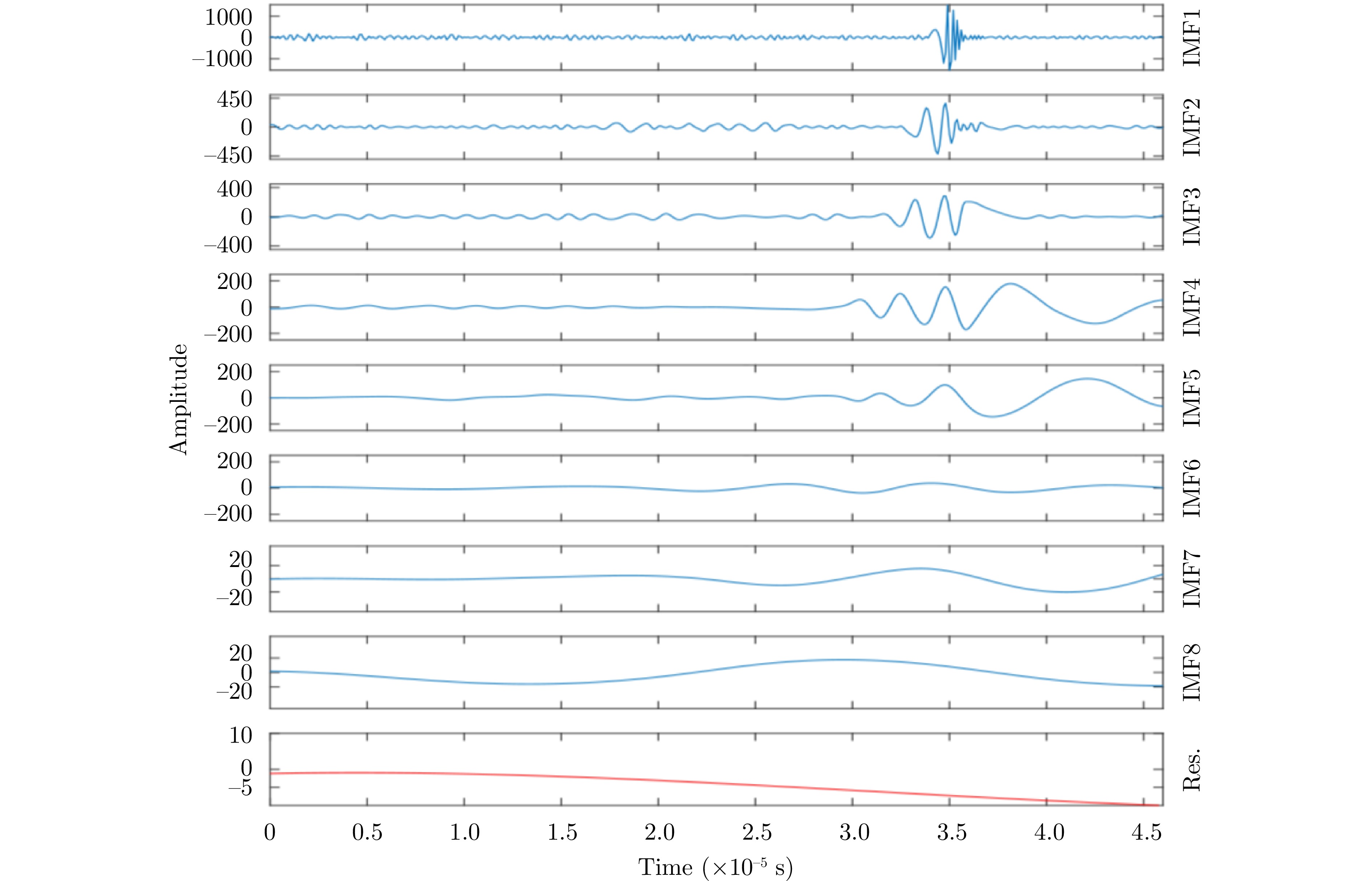
- Figure 54. Time domain signal EMD[131]
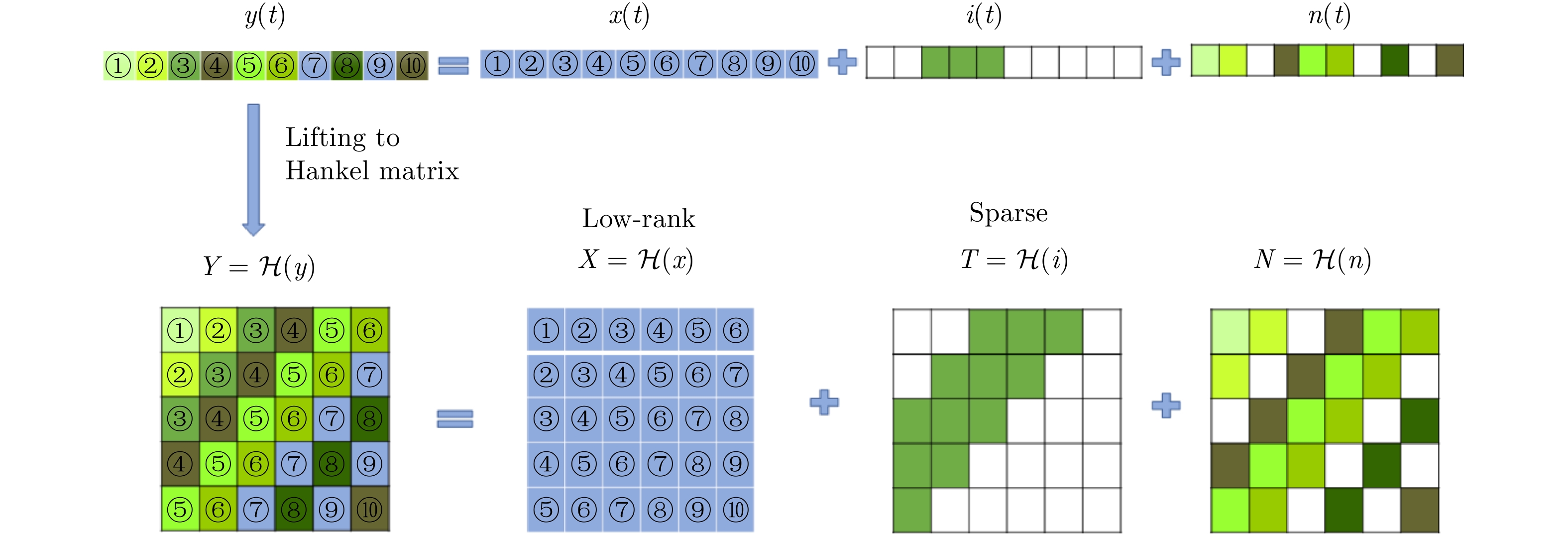
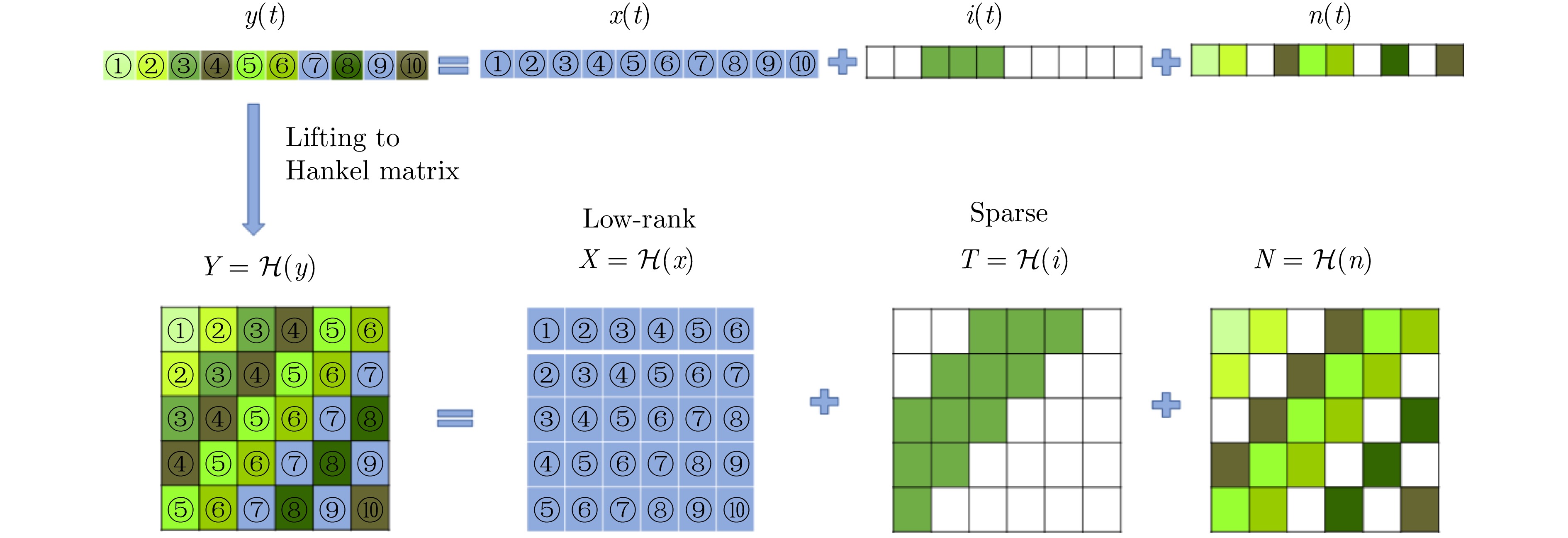
- Figure 55. Sparse low-rank decomposition of Hankel matrix[134]
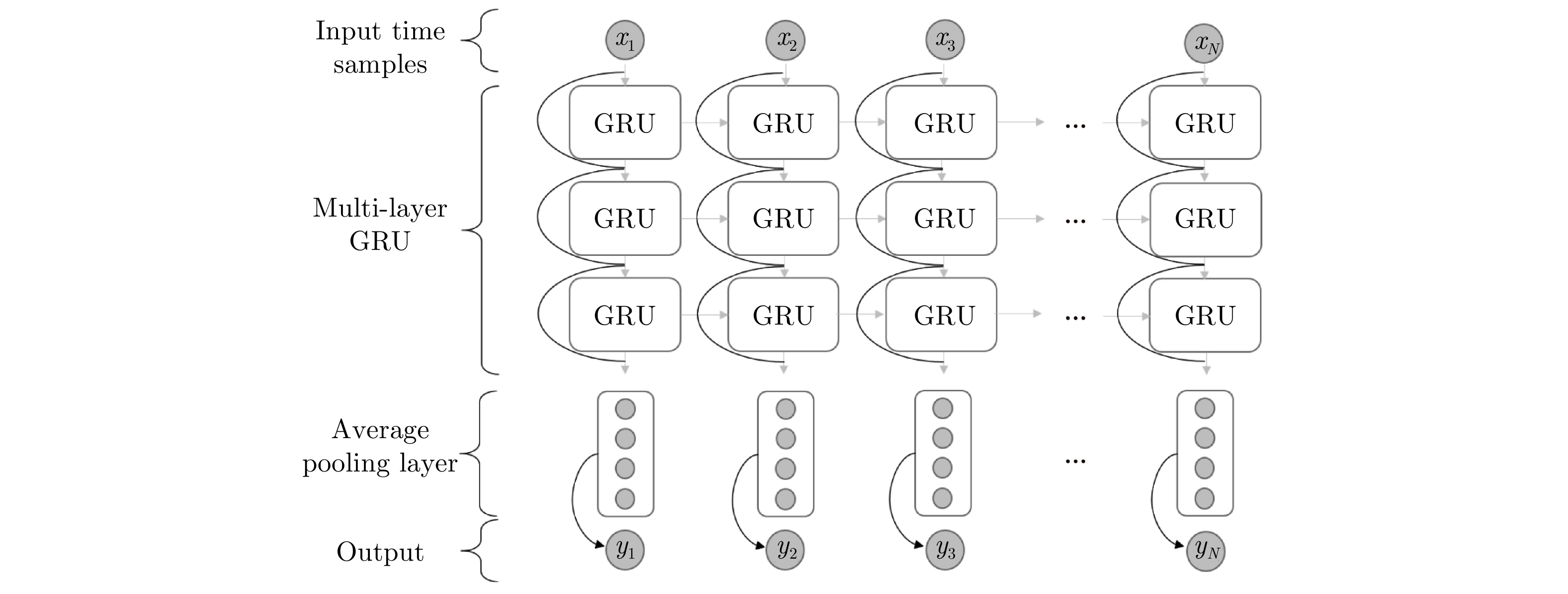
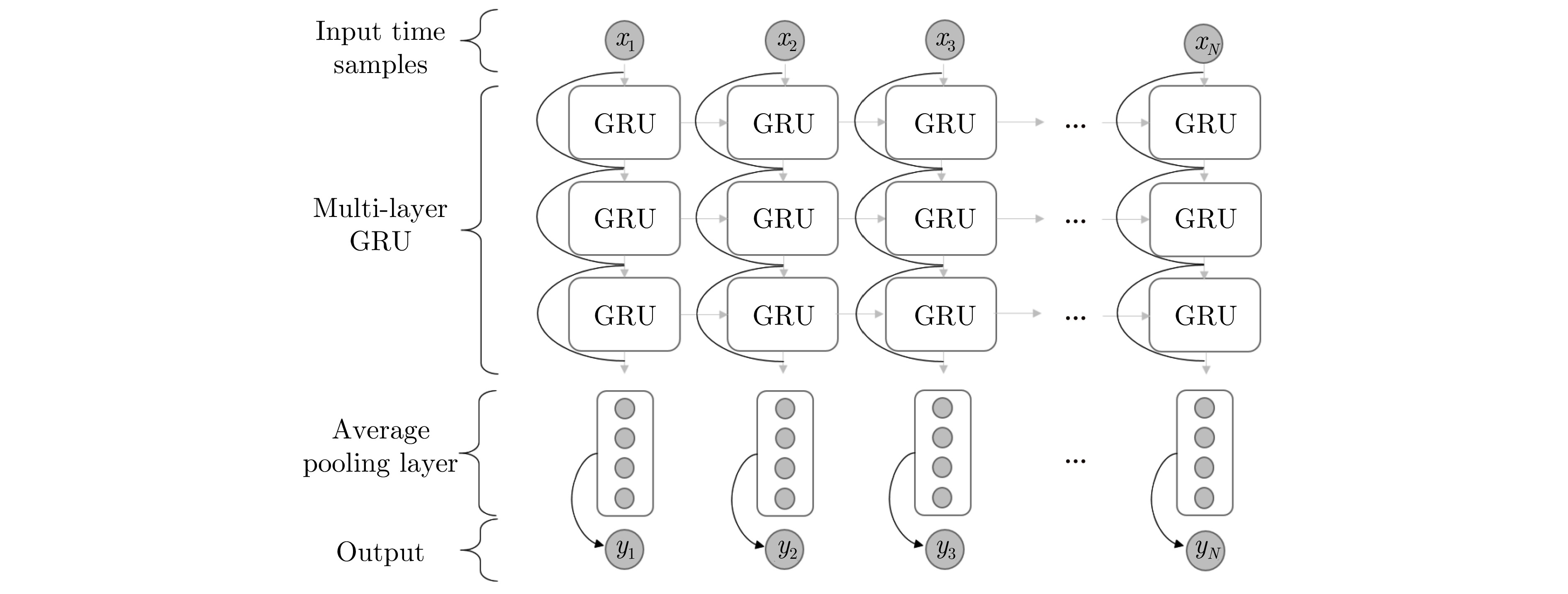
- Figure 56. RNN model with GRUs[139]
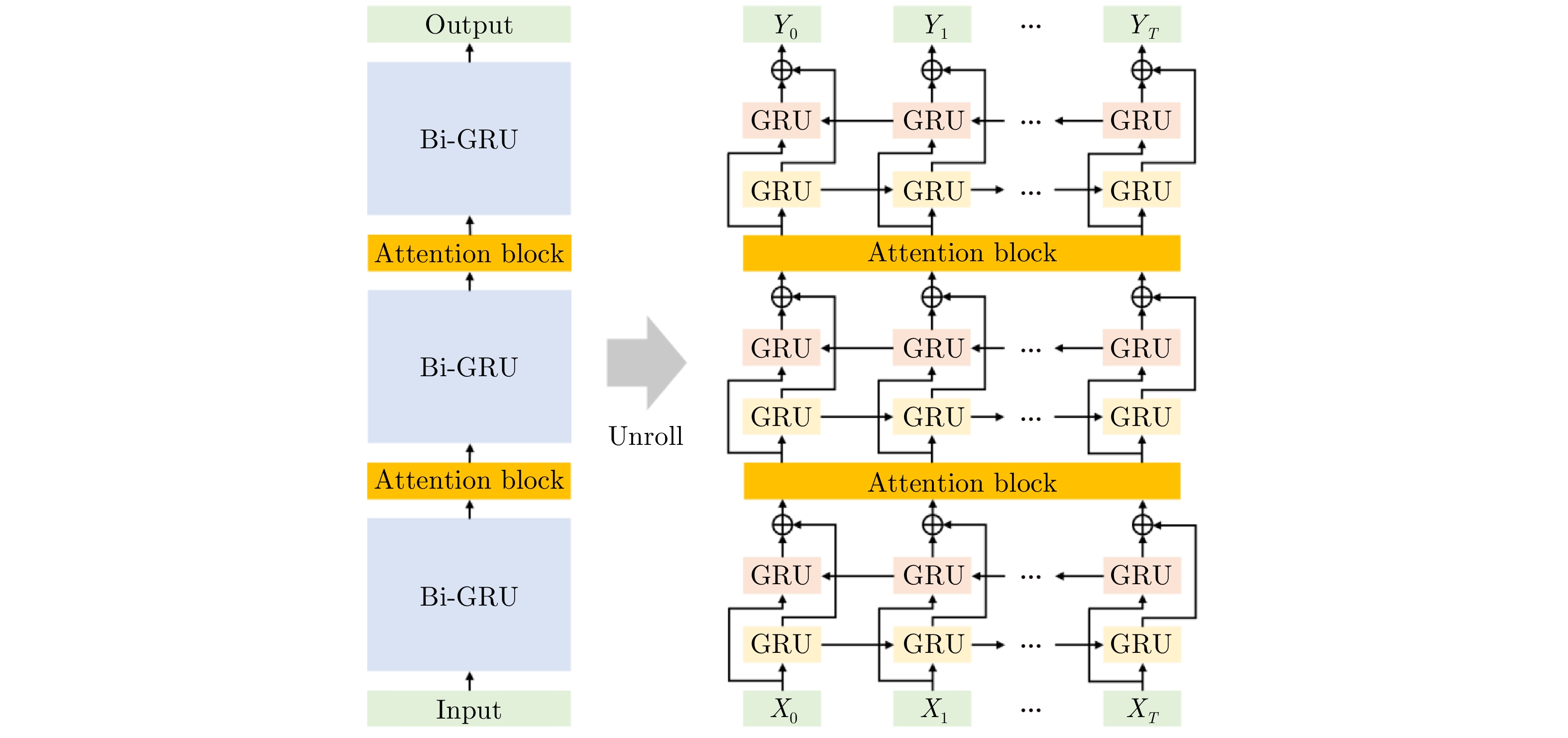
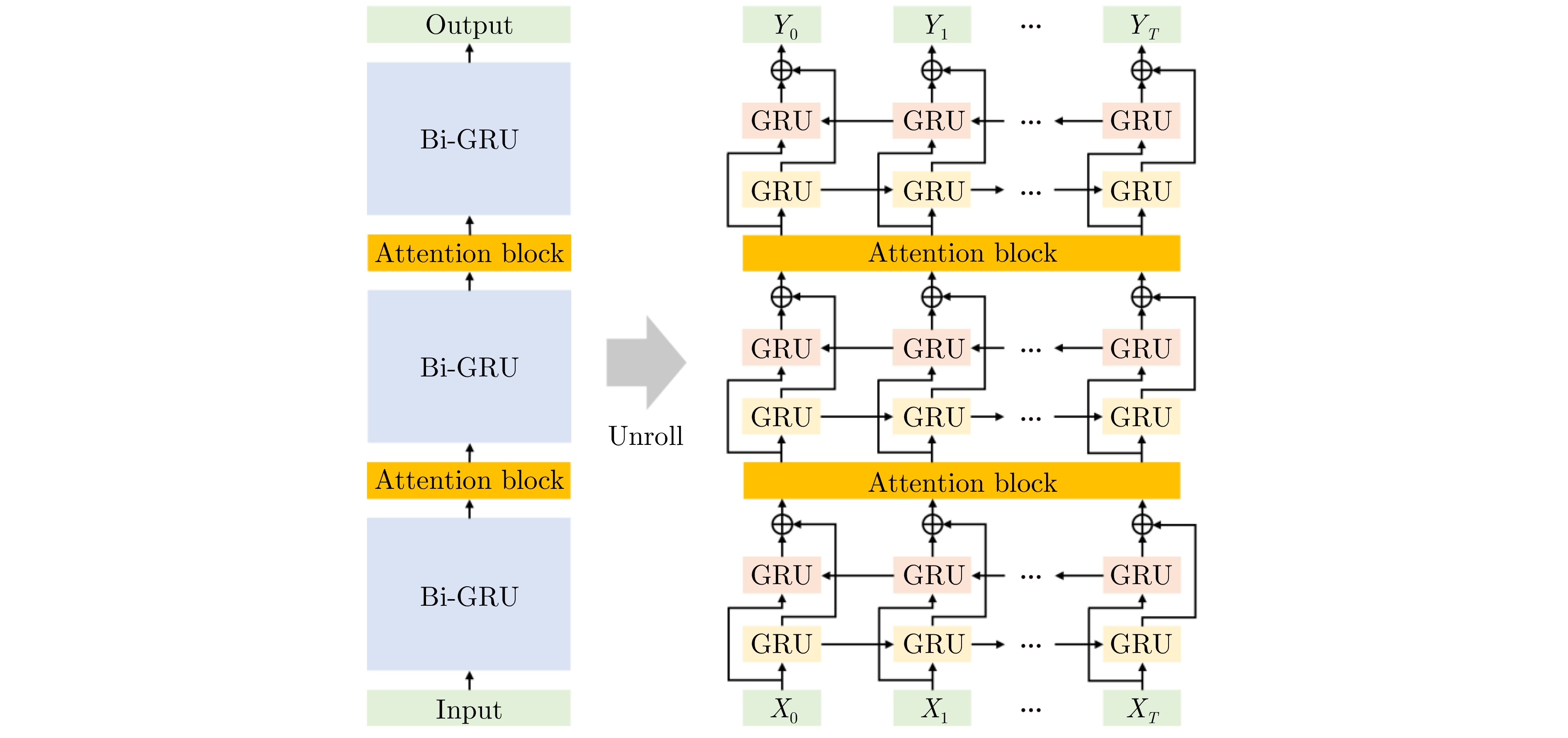
- Figure 57. RNN models with self-attention mechanisms[141]
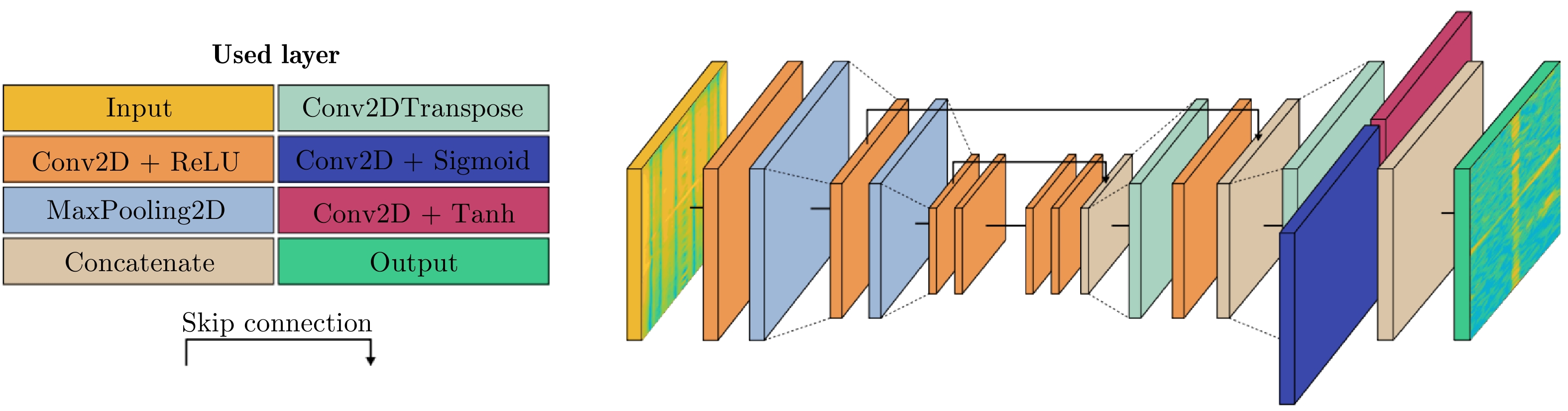
- Figure 58. General architecture of the FCN model[142]
- Figure 59. CNN model architecture based on AE[143]
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
- Figure 6.
- Figure 7.
- Figure 8.
- Figure 9.
- Figure 10.
- Figure 11.
- Figure 12.
- Figure 13.
- Figure 14.
- Figure 15.
- Figure 16.
- Figure 17.
- Figure 18.
- Figure 19.
- Figure 20.
- Figure 21.
- Figure 22.
- Figure 23.
- Figure 24.
- Figure 25.
- Figure 26.
- Figure 27.
- Figure 28.
- Figure 29.
- Figure 30.
- Figure 31.
- Figure 32.
- Figure 33.
- Figure 34.
- Figure 35.
- Figure 36.
- Figure 37.
- Figure 38.
- Figure 39.
- Figure 40.
- Figure 41.
- Figure 42.
- Figure 43.
- Figure 44.
- Figure 45.
- Figure 46.
- Figure 47.
- Figure 48.
- Figure 49.
- Figure 50.
- Figure 51.
- Figure 52.
- Figure 53.
- Figure 54.
- Figure 55.
- Figure 56.
- Figure 57.
- Figure 58.
- Figure 59.


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: