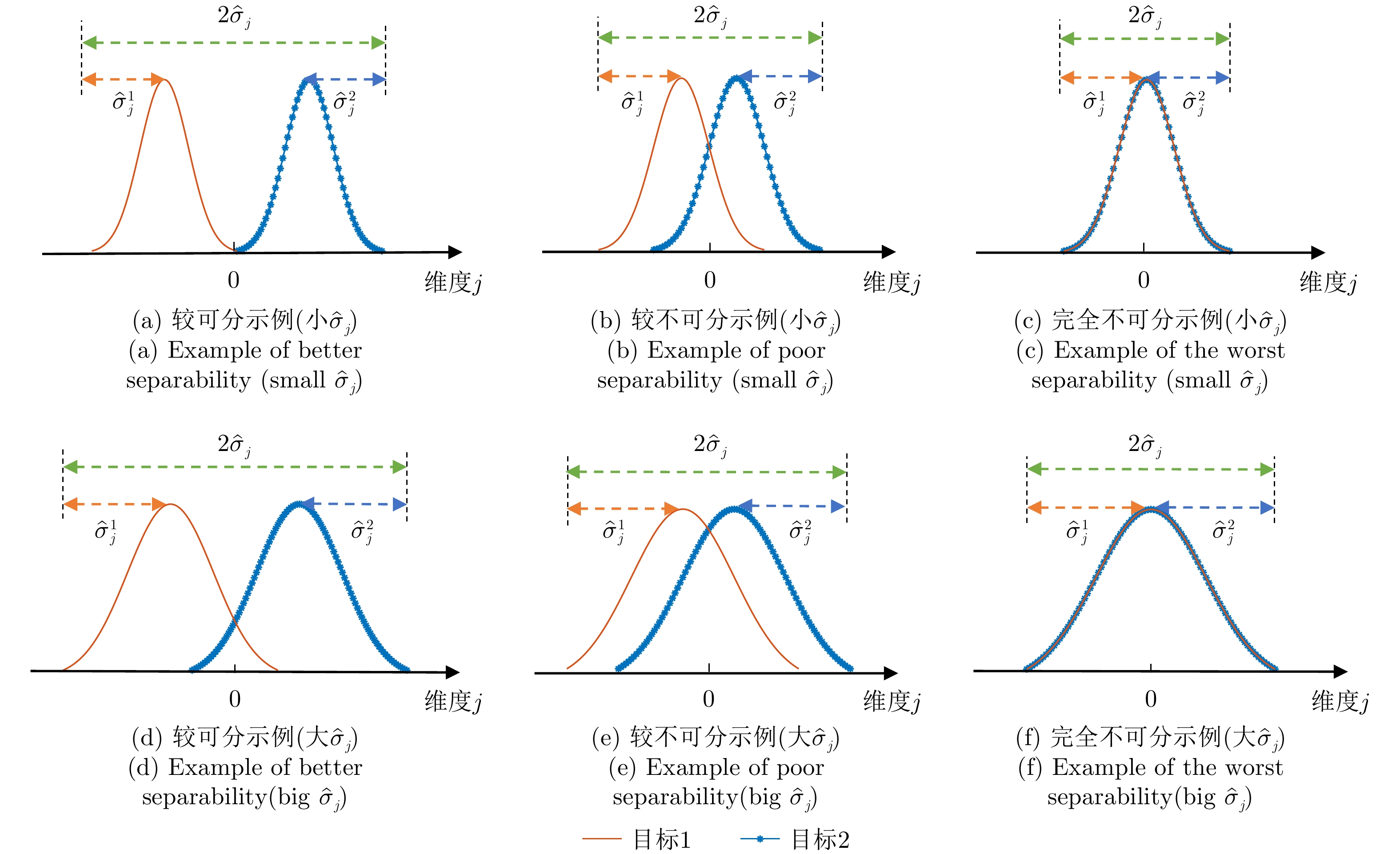
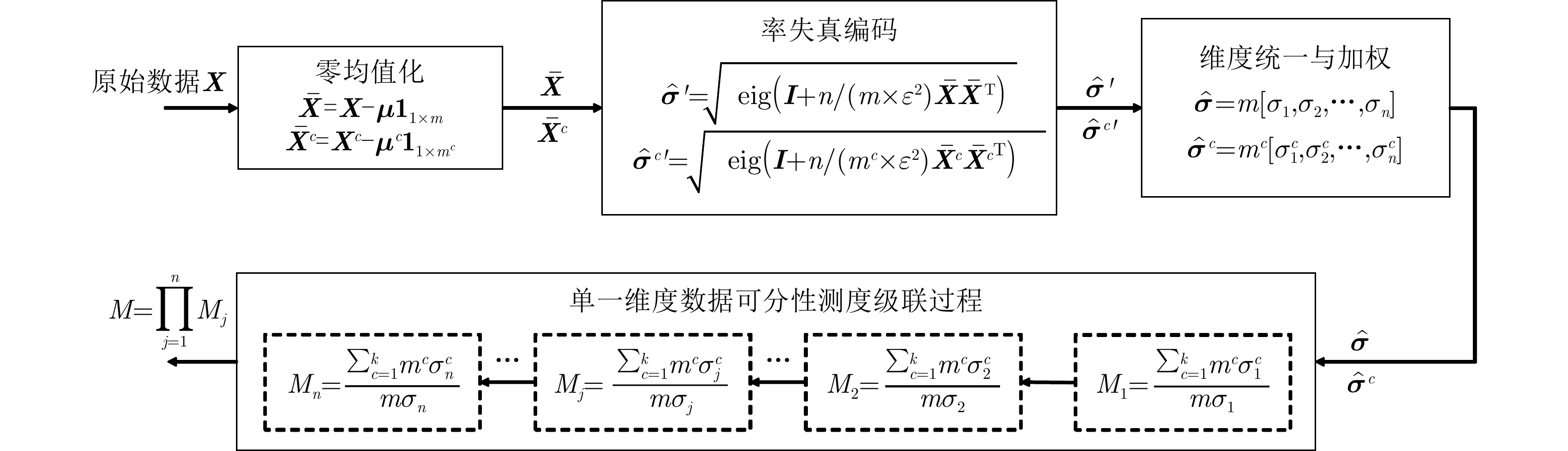
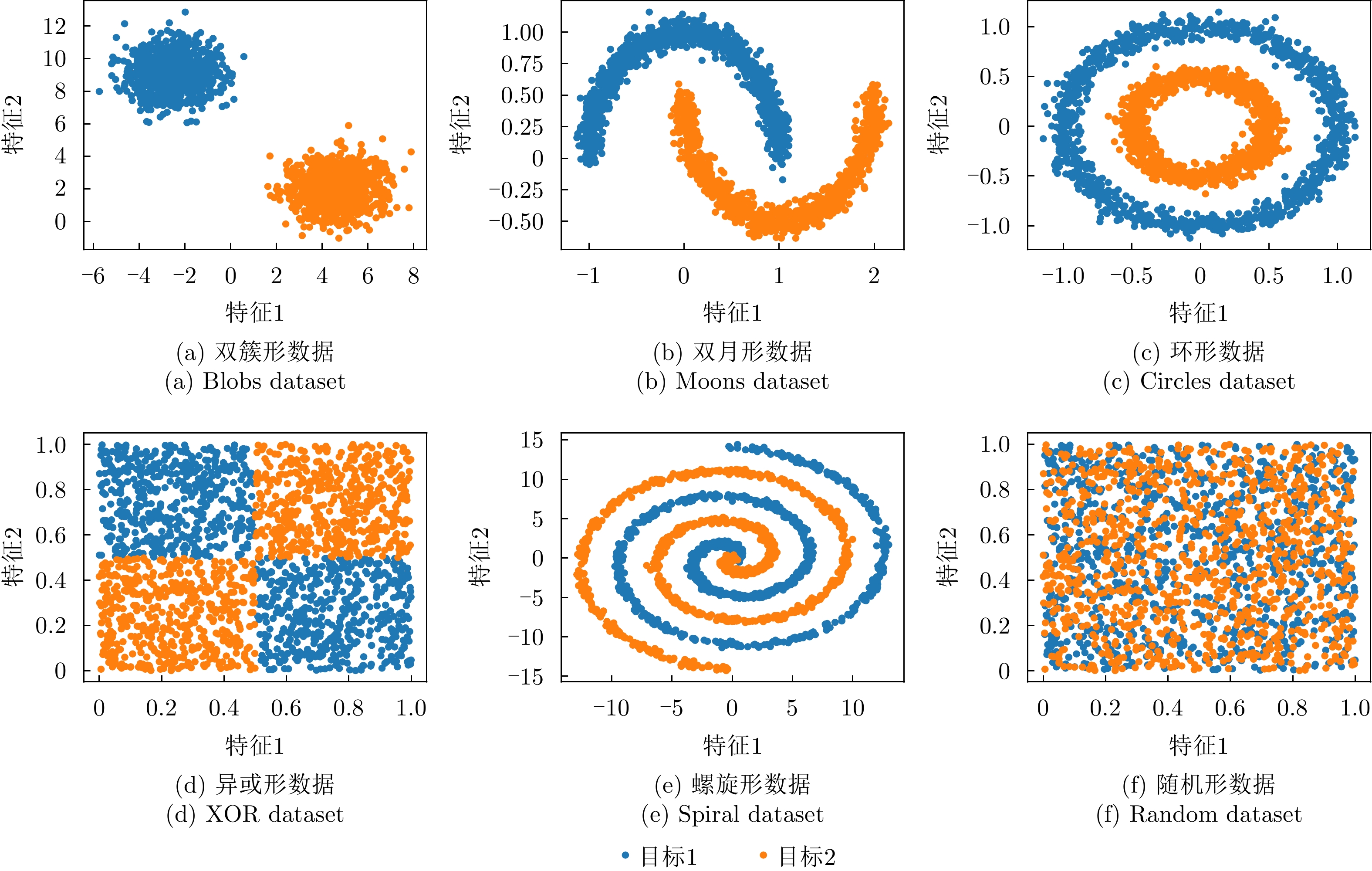
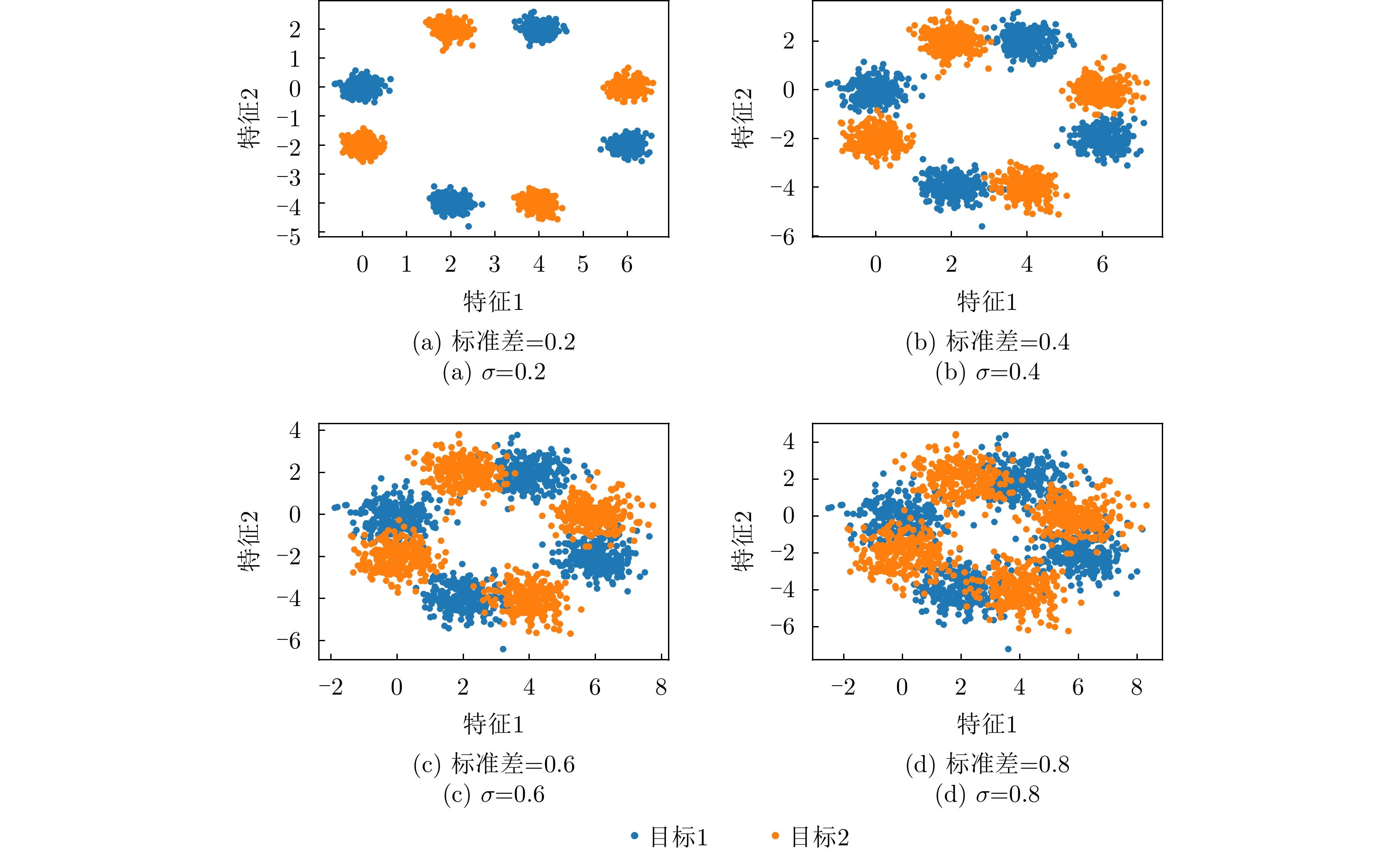
| [1] |
付强, 何峻. 自动目标识别评估方法及应用[M]. 北京, 科学出版社, 2013: 16–19.
FU Qiang and HE Jun. Automatic Target Recognition Evaluation Method and its Application[M]. Beijing, Science Press, 2013: 16–19.
|
| [2] |
YU Wenxian. Automatic target recognition from an engineering perspective[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 737–752. doi: 10.12000/JR22178 |
| [3] |
HOSSIN M and SULAIMAN M N. A review on evaluation metrics for data classification evaluations[J]. International Journal of Data Mining & Knowledge Management Process ( IJDKP), 2015, 5(2): 1–11. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3557376 |
| [4] |
ZHANG Chiyuan, BENGIO S, HARDT M, et al. Understanding deep learning (still) requires rethinking generalization[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2021, 64(3): 107–115. doi: 10.1145/3446776 |
| [5] |
OPREA M. A general framework and guidelines for benchmarking computational intelligence algorithms applied to forecasting problems derived from an application domain-oriented survey[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 89: 106103. doi: 10.1016/J.ASOC.2020.106103 |
| [6] |
YU Shuang, LI Xiongfei, FENG Yuncong, et al. An instance-oriented performance measure for classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 580: 598–619. doi: 10.1016/J.INS.2021.08.094 |
| [7] |
FERNÁNDEZ A, GARCÍA S, GALAR M, et al. Learning from Imbalanced Data Sets[M]. Cham: Springer, 2018: 253–277.
|
| [8] |
BELLO M, NÁPOLES G, VANHOOF K, et al. Data quality measures based on granular computing for multi-label classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 560: 51–57. doi: 10.1016/J.INS.2021.01.027 |
| [9] |
CANO J R. Analysis of data complexity measures for classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2013, 40(12): 4820–4831. doi: 10.1016/J.ESWA.2013.02.025 |
| [10] |
METZNER C, SCHILLING A, TRAXDORF M, et al. Classification at the accuracy limit: Facing the problem of data ambiguity[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 22121. doi: 10.1038/S41598-022-26498-Z |
| [11] |
XU Zongben. Ten fundamental problems for artificial intelligence: Mathematical and physical aspects[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2021, 51(12): 1967–1978. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0254 |
| [12] |
MISHRA A K. Separability indices and their use in radar signal based target recognition[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2009, 6(14): 1000–1005. doi: 10.1587/ELEX.6.1000 |
| [13] |
GUAN Shuyue and LOEW M. A novel intrinsic measure of data separability[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(15): 17734–17750. doi: 10.1007/S10489-022-03395-6 |
| [14] |
BRUN A L, BRITTO A S JR, OLIVEIRA L S, et al. A framework for dynamic classifier selection oriented by the classification problem difficulty[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 76: 175–190. doi: 10.1016/J.PATCOG.2017.10.038 |
| [15] |
CHARTE D, CHARTE F, and HERRERA F. Reducing data complexity using autoencoders with class-informed loss functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 9549–9560. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3127698 |
| [16] |
LORENA A C, GARCIA L P F, LEHMANN J, et al. How complex is your classification problem?: A survey on measuring classification complexity[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2020, 52(5): 107. doi: 10.1145/3347711 |
| [17] |
FERRARO M B and GIORDANI P. A review and proposal of (fuzzy) clustering for nonlinearly separable data[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2019, 115: 13–31. doi: 10.1016/J.IJAR.2019.09.004 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
COVER T M and THOMAS J A. Elements of Information Theory[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991: 301–332.
|
| [20] |
MADIMAN M, HARRISON M, and KONTOYIANNIS I. Minimum description length vs. maximum likelihood in lossy data compression[C]. 2004 International Symposium on Information Theory, Chicago, USA, 2004: 461.
|
| [21] |
MA Yi, DERKSEN H, HONG Wei, et al. Segmentation of multivariate mixed data via lossy data coding and compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(9): 1546–1562. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1085 |
| [22] |
MACDONALD J, WÄLDCHEN S, HAUCH S, et al. A rate-distortion framework for explaining neural network decisions[J]. arXiv: 1905.11092, 2019.
|
| [23] |
HAN Xiaotian, JIANG Zhimeng, LIU Ninghao, et al. Geometric graph representation learning via maximizing rate reduction[C]. ACM Web Conference, Lyon, France, 2022: 1226–1237.
|
| [24] |
CHOWDHURY S B R and CHATURVEDI S. Learning fair representations via rate-distortion maximization[J]. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2022, 10: 1159–1174. doi: 10.1162/TACL_A_00512 |
| [25] |
LICHMAN M E A. Uci machine learning reposit[EB/OL]. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/datasets, 2023.
|
| [26] |
HO T K and BASU M. Complexity measures of supervised classification problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(3): 289–300. doi: 10.1109/34.990132 |
| [27] |
LEYVA E, GONZÁLEZ A, and PÉREZ R. A set of complexity measures designed for applying meta-learning to instance selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27(2): 354–367. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2014.2327034 |
| [28] |
GARCIA L P F, DE CARVALHO A C P L F, and LORENA A C. Effect of label noise in the complexity of classification problems[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 160: 108–119. doi: 10.1016/J.NEUCOM.2014.10.085 |
| [29] |
AGGARWAL C C, HINNEBURG A, and KEIM D A. On the surprising behavior of distance metrics in high dimensional space[C]. 8th International Conference on Database Theory, London, UK, 2001: 420–434.
|
| [30] |
MILLER K, MAURO J, SETIADI J, et al. Graph-based active learning for semi-supervised classification of SAR data[C]. SPIE 12095, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXIX, Orlando, United States, 2022: 120950C.
|
| [31] |
雷禹, 冷祥光, 孙忠镇, 等. 宽幅SAR海上大型运动舰船目标数据集构建及识别性能分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 347–362. doi: 10.12000/JR21173LEI Yu, LENG Xiangguang, SUN Zhongzhen, et al. Construction and recognition performance analysis of wide-swath SAR maritime large moving ships dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 347–362. doi: 10.12000/JR21173 |
| [32] |
HOU Xiyue, AO Wei, SONG Qian, et al. FUSAR-Ship: Building a high-resolution SAR-AIS matchup dataset of Gaofen-3 for ship detection and recognition[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(4): 140303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2772-5 |
| [33] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 228–242.
|
| [34] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 |
| [35] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A novel deep learning network with HOG feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3082759 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: