- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | |
Parametric SAR Imaging for Typical Lines and Surfaces
DOI: 10.12000/JR19077 CSTR: 32380.14.JR19077
More Information-
Abstract
In the Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) remote sensing imagery of complicated scenes (especially urban scenes), there are a large number of lines and surfaces, such as roads in urban areas and the surfaces of buildings. These microwave-signal-scattering features have strong directivity. Traditional SAR acquires the scattering information of a scene from a single observation, and traditional imaging algorithms are based on the point target model, which makes the main features of the lines and surfaces in traditional SAR images appear as a series of strong scattering points rather than line-scattering and surface-scattering features. This outcome ultimately causes the target to be discontinuous in the SAR image, thus making the SAR image difficult to interpret. Therefore, in this study, we conducted an in-depth and meticulous investigation of the SAR imaging mechanism for lines and surfaces by establishing a parametric echo model of typical lines and triangular surfaces. Based on the proposed parametric model, we performed parametric imaging of these lines and surfaces. Based on our results, we propose a parametric imaging method, in which the typical lines and surfaces are classified and determined based on Bayesian theory and the proposed parametric model. Then, an SAR image can be obtained that effectively characterizes the scattering features of the line and surface targets by visual imaging, which effectively facilitates SAR image interpretation. The results of our numerical simulation experiments verify the validity of the proposed method. -

-
References
[1] CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. New York, USA: Wiley, 1991.[2] ZENG Tao, LIU Luosi, and DING Zegang. Improved stepped-frequency SAR imaging algorithm with the range spectral-length extension strategy[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2012, 5(5): 1483–1494. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2012.2196681[3] DING Zegang, LIU Luosi, ZENG Tao, et al. Improved motion compensation approach for squint airborne SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4378–4387. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2265327[4] ZENG Tao, LI Yinghe, DING Zegang, et al. Subaperture approach based on azimuth-dependent range cell migration correction and azimuth focusing parameter equalization for maneuvering high-squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6718–6734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2447393[5] XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. Imaging simulation of polarimetric SAR for a comprehensive terrain scene using the mapping and projection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(11): 3219–3234. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.879544[6] GORHAM L A and MOORE L J. SAR image formation toolbox for MATLAB[C]. The SPIE 7699, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVII. Orlando, USA, 2010.[7] CUMMING I G and WONG F H C. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 3.[8] FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687[9] FARRELL T J, PATTERSON M S, and WILSON B. A diffusion theory model of spatially resolved, steady‐state diffuse reflectance for the noninvasive determination of tissue optical properties in vivo[J]. Medical Physics, 1992, 19(4): 879–888. doi: 10.1118/1.596777[10] MILLER E K and LAGER D L. Inversion of one-dimensional scattering data using Prony’s method[J]. Radio Science, 1982, 17(1): 211–217. doi: 10.1029/RS017i001p00211[11] POTTER L C, CHIANG D M, CARRIERE R, et al. A GTD-based parametric model for radar scattering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1995, 43(10): 1058–1067. doi: 10.1109/8.467641[12] GERRY M J, POTTER L C, GUPTA I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750[13] SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: Wiley, 1999.[14] ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734[15] Wei Y, Chen X, Fan Y, et al. Analysis and identification of continuous line target in SAR echo based on sidelobe features[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 5979–5981. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0327[16] BISHOP C M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning[M]. New York: Springer, 2006, 161–171.[17] 张连文, 郭海鹏. 贝叶斯网引论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006, 172–180.ZHANG Lianwen and GUO Haipeng. Introduction to Bayesian Networks[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006, 172–180. -
Proportional views

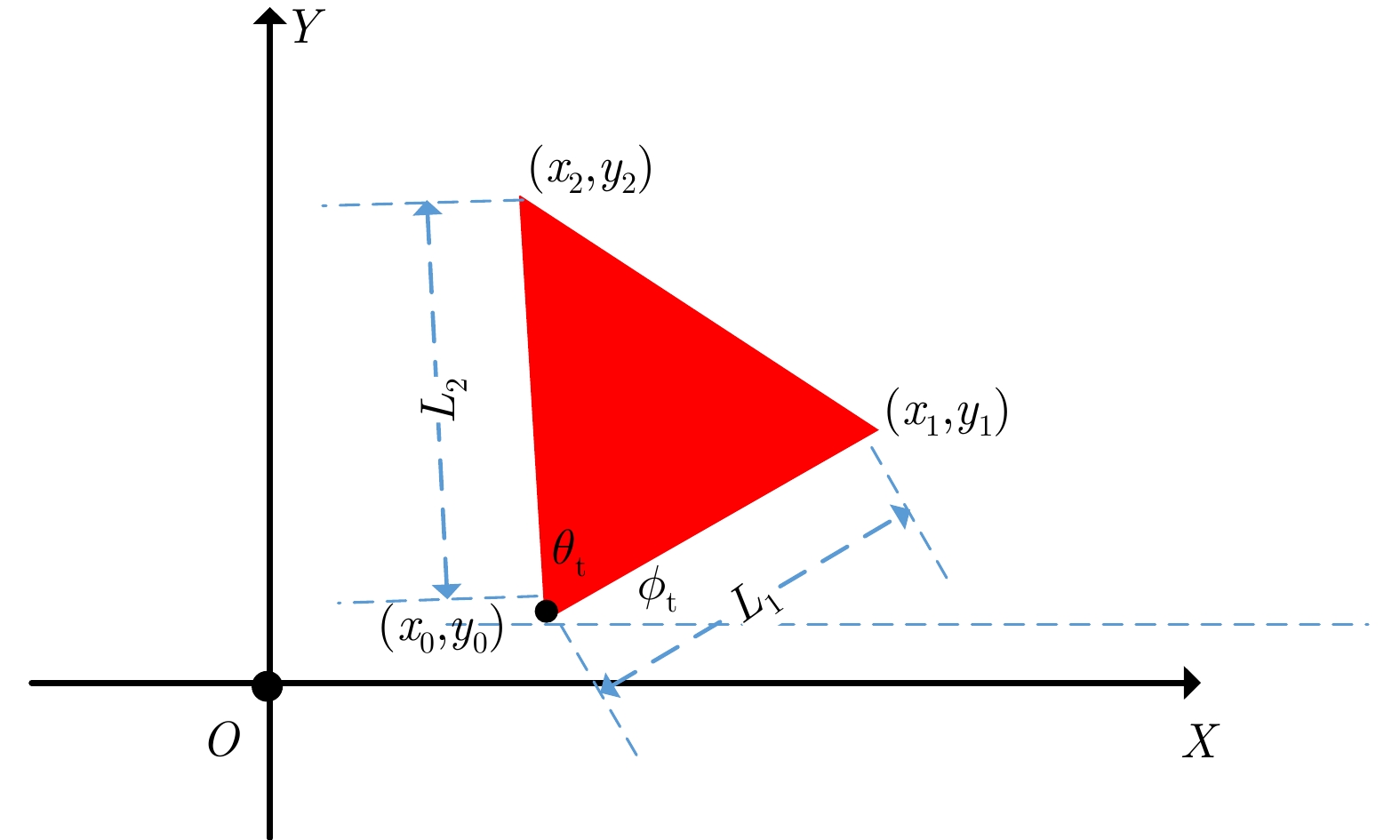
- Figure 1. Parametric line model
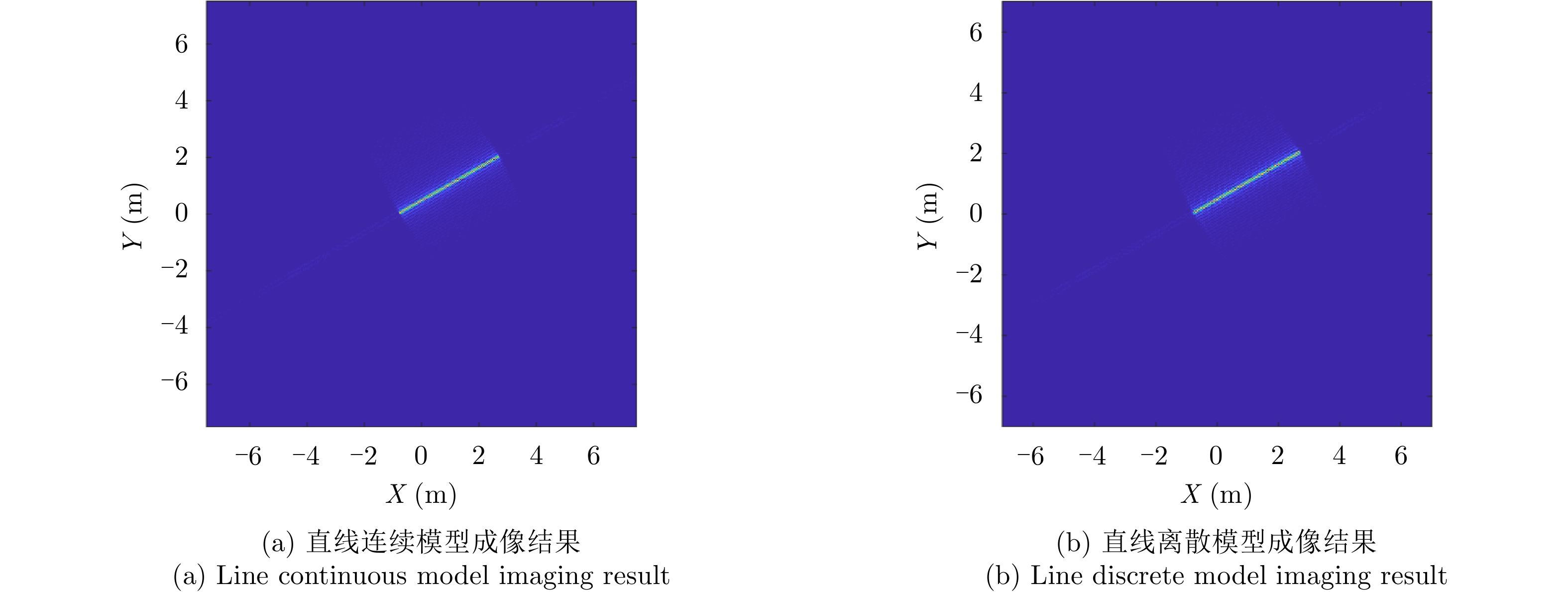
- Figure 2. Simulation of continuous and discrete lines
- Figure 3. Triangular face parameterization model
- Figure 4. Comparison of continuous and discrete models of triangular surface
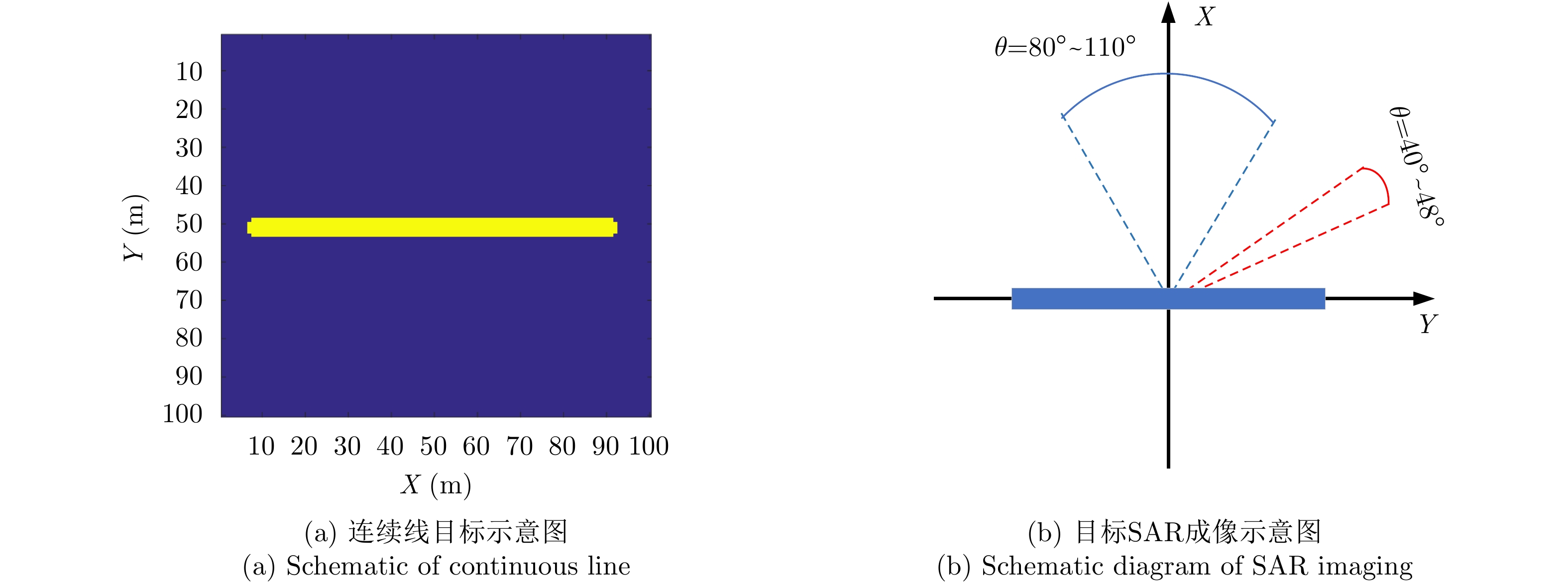
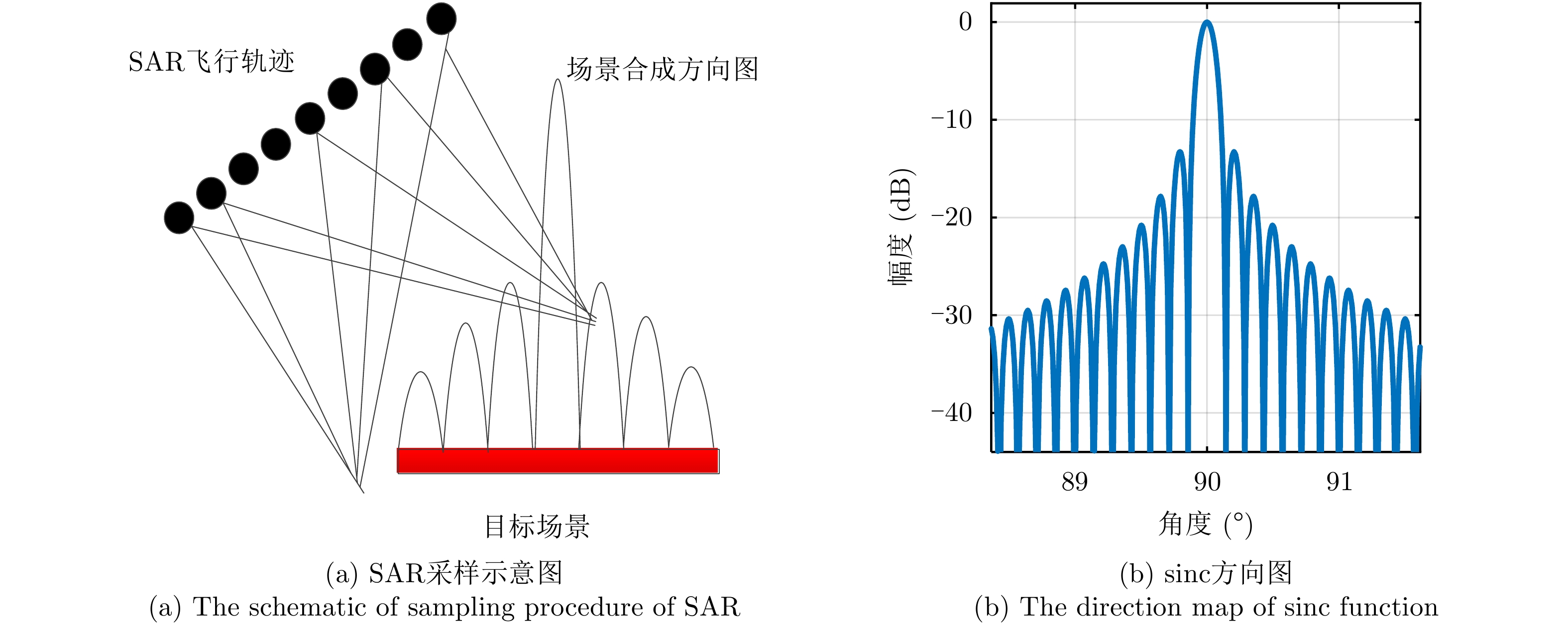
- Figure 5. Continuous target schematic and SAR imaging schematic
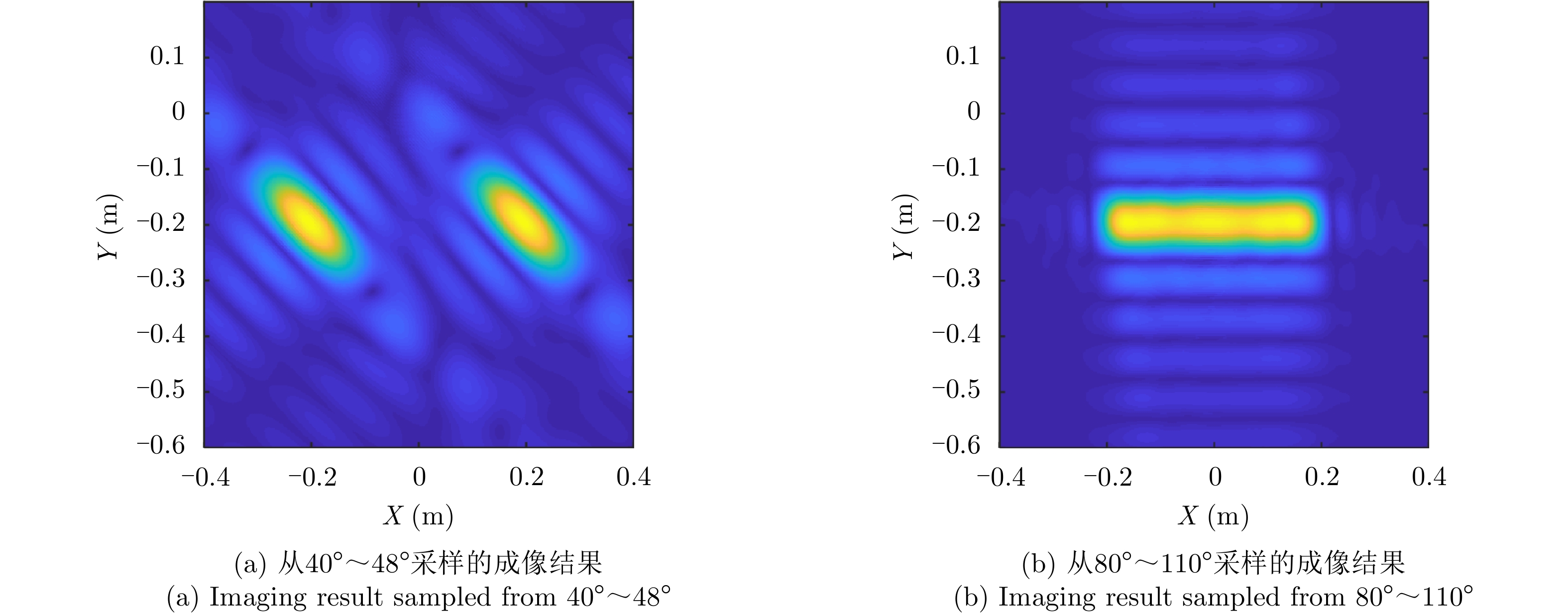
- Figure 6. SAR imaging results of continuous target under different angles of sampling
- Figure 7. SAR imaging results of triangular surface under different angle samplings
- Figure 8. Schematic relationship between radar system and signal spectrum
- Figure 9. Azimuth imaging model for line
- Figure 10. Parametric imaging flowchart
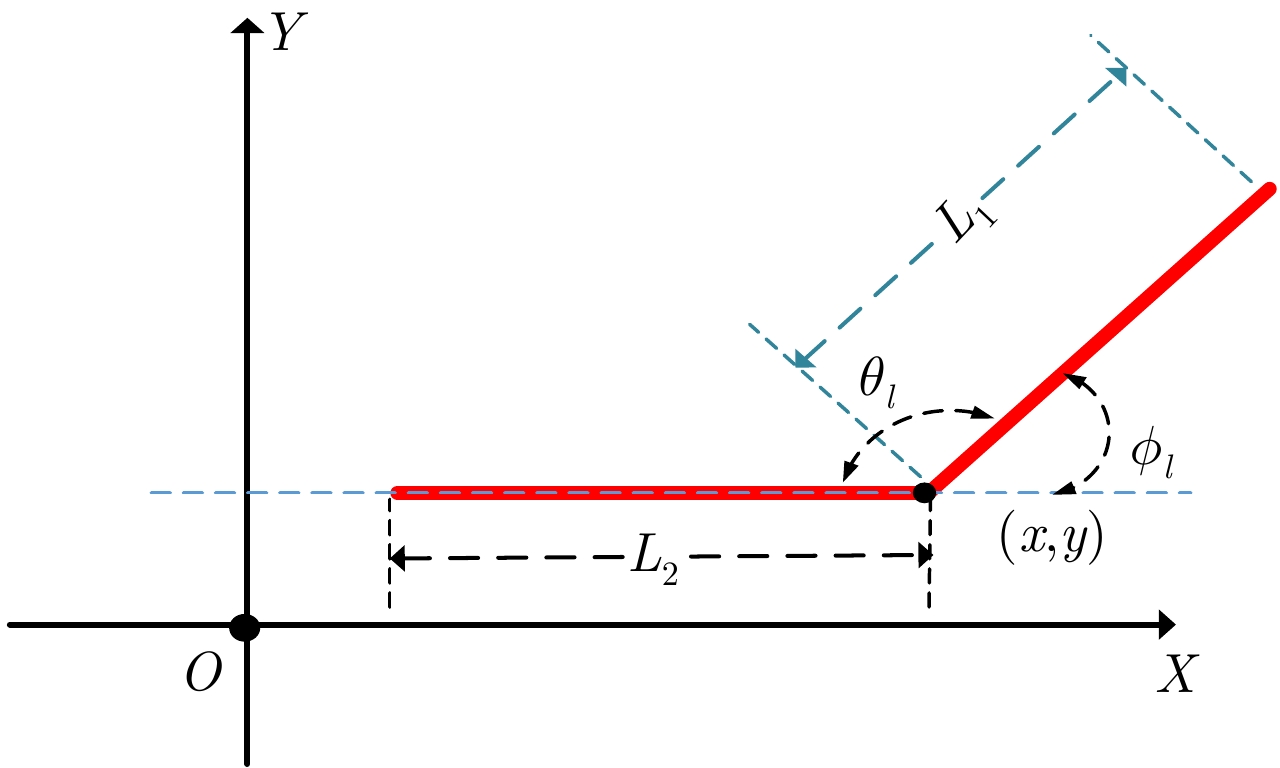
- Figure 11. Polyline geometry parameterization
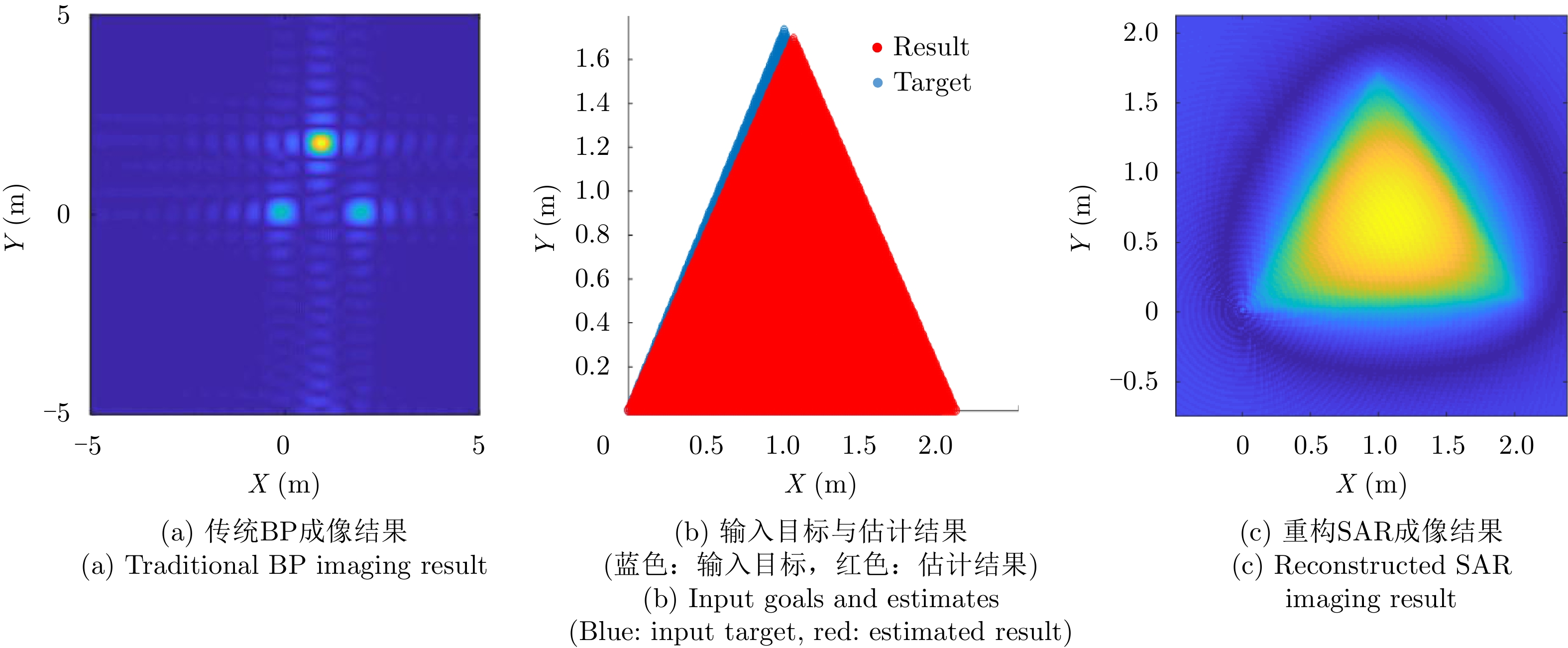
- Figure 12. Visualization of line
- Figure 13. Visualization of triangular surface


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: