- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | Fu Yue, Cui Guolong, Yu Xianxiang. Robust Design of Constant Modulus Sequence and Receiver Filter in the Presence of Signal-dependent Clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 292-299. doi: 10.12000/JR16158 |
Robust Design of Constant Modulus Sequence and Receiver Filter in the Presence of Signal-dependent Clutter
DOI: 10.12000/JR16158 CSTR: 32380.14.JR16158
-
Abstract
In this paper, we focus on the detection of a moving point-like target embedded in uncertain signal-dependent clutter and develop robust transmit-code and receive-filter designs in slow-time. First, based on the Worst-case Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (W-SINR) when the second-order clutter statistics are uncertain, we establish a high-dimensional transmit-receive optimization model that considers the constant modulus constraint with non-convexity. Next, we propose an Iterative Sequential Optimization (ISO) algorithm. At each iteration, it converts a high-dimensional optimization into multiple one-dimensional fractional programming problems that can be efficiently solved using Dinkelbach’s method. Finally, we use numerical examples to confirm that the ISO can resist the uncertain knowledge of signal-dependent clutter, which enables the radar system to adapt to complicated environments. Moreover, compared to Semi-Definite Relaxation (SDR)-related and randomization methods, the proposed algorithm is superior with respect to both optimized W-SINR and computational time. -

-
References
[1] Haykin S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2006, 23(1): 30–40. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2006.1593335[2] Guerci J R. Cognitive Radar: The Knowledge-aided Fully Adaptive Approach[M]. London: Artech House, 2010: 20–30.[3] 黎湘, 范梅梅. 认知雷达及其关键技术研究进展[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZZ201315020.htmLi Xiang and Fan Mei-mei. Research advance on cognitive radar and its key technology[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(9): 1863–1870. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZZ201315020.htm[4] 范梅梅. 认知雷达目标识别自适应波形设计技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012: 1–6.Fan Mei-mei. Adaptive waveform design for target recognition in cognitive radar[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012: 1–6.[5] Stoica P, Li Jian, and Xue Ming. Transmit codes and receive filters for radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(6): 94–109. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.929231[6] Aubry A, De Maio A, Piezzo M, et al.. Cognitive design of the receive filter and transmitted phase code in reverberating environment[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(9): 822–833.[7] 王璐璐, 王宏强, 王满喜, 等. 雷达目标检测的最优波形设计综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 487–498. http://radars.ie.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract378.shtmlWang Lu-lu, Wang Hong-qiang, Wang Man-xi, et al.. An overview of radar waveform optimization for target detection[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 487–498. http://radars.ie.ac.cn/CN/abstract/abstract378.shtml[8] Cui Guo-long, Li Hong-bin, and Rangaswamy M. MIMO radar waveform design with constant modulus and similarity constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(2): 343–353. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288086[9] Stoica P, He Hao, and Li Jian. Optimization of the receive filter and transmit sequence for active sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(4): 1730–1740. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2179652[10] 纠博, 刘宏伟, 李丽亚, 等. 雷达波形优化的特征互信息方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(1): 139–144. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD200901027.htmJiu Bo, Liu Hong-wei, Li Li-ya, et al.. Feature mutual information method for radar waveform optimization[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2009, 36(1): 139–144. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKD200901027.htm[11] Naghsh M M, Soltanalian M, Stoica P, et al.. A Doppler robust design of transmit sequence and receive filter in the presence of signal-dependent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(4): 772–785. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288082[12] Karbasi S M, Aubry A, Carotenuto V, et al.. Knowledge-based design of space-time transmit code and receive filter for a multiple-input-multiple-output radar in signal-dependent interference[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(8): 1124–1135.[13] Aubry A, De Maio A, and Naghsh M N. Optimizing radar waveform and Doppler filter bank via generalized fractional programming[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1387–1399. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469259[14] Zhu Wei and Tang Jun. Robust design of transmit waveform and receive filter for colocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(11): 2112–2116. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2461460[15] Aubry A, Demaio A, Farina A, et al.. Knowledge-aided (potentially cognitive) transmit signal and receive filter design in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 93–117.[16] He Hao, Li Jian, and Stoica P. Waveform Design for Active Sensing Systems—A Computational Approach[M]. Cambridge, U. K., Cambridge University Press, 2012: 2–6.[17] 倪国熙. 常用的矩阵理论和方法[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1984: 18–22.Ni Guo-xi. Common Matrix Theory and Method[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1984: 18–22.[18] 何子述, 夏威, 等. 现代数字信号处理及其应用[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2009: 100–106.He Zi-shu, Xia Wei, et al.. Advanced Digital Signal Processing and Application[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2009: 100–106.[19] Yu Xian-xiang, Cui Guo-long, Kong Ling-jiang, et al.. Space-time transmit code and receive filter design for colocated MIMO radar[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, 2016: 1–6.[20] Golub G H and Van Loan C F. Matrix computations[J]. The Mathematical Gazette, 1990, 74(469): 324–325. -
Proportional views

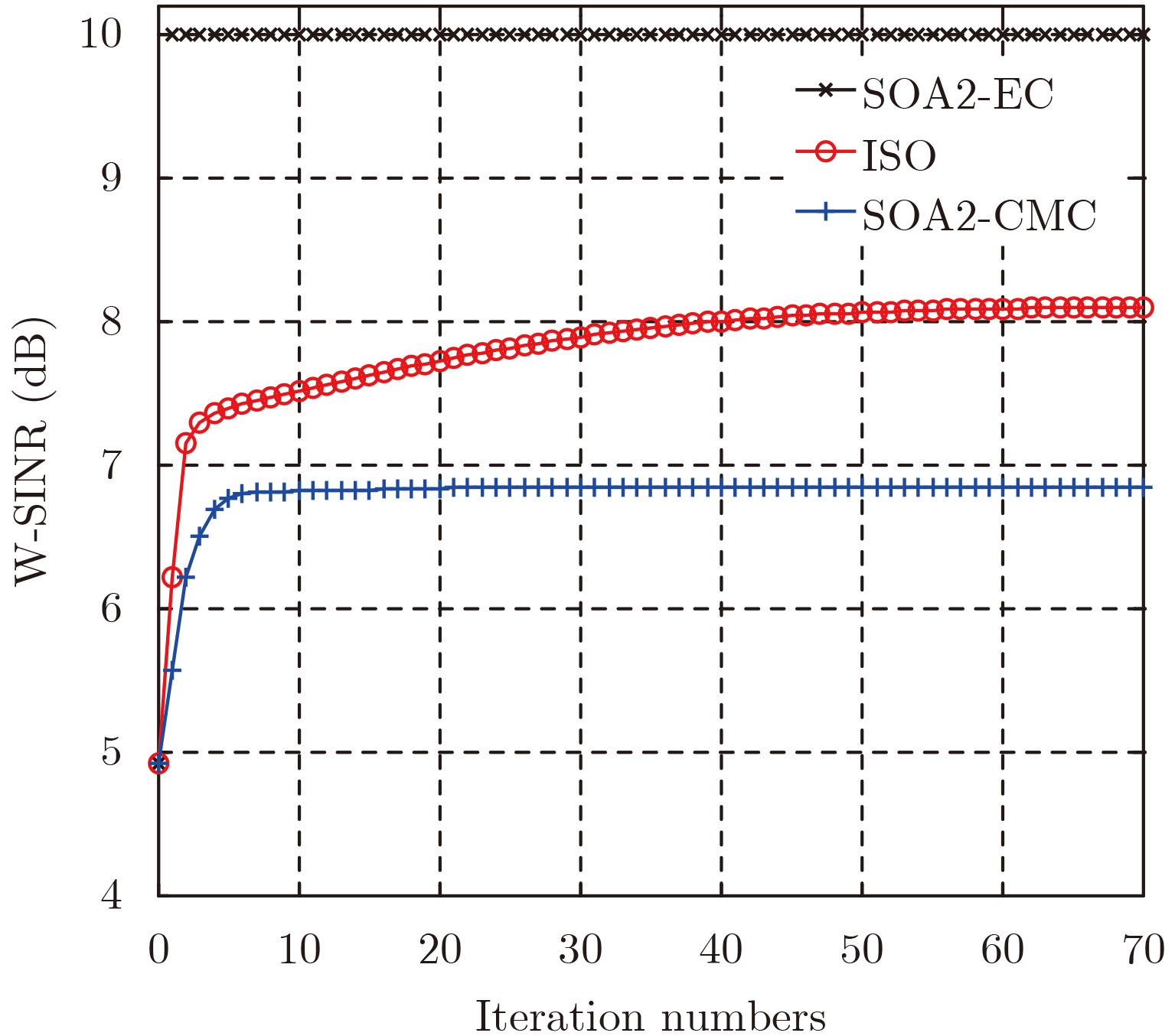
- Figure 1. W-SINR versus iteration number for SOA2-EC, ISO and SOA2-CMC
- Figure 2. Contour maps of CAF
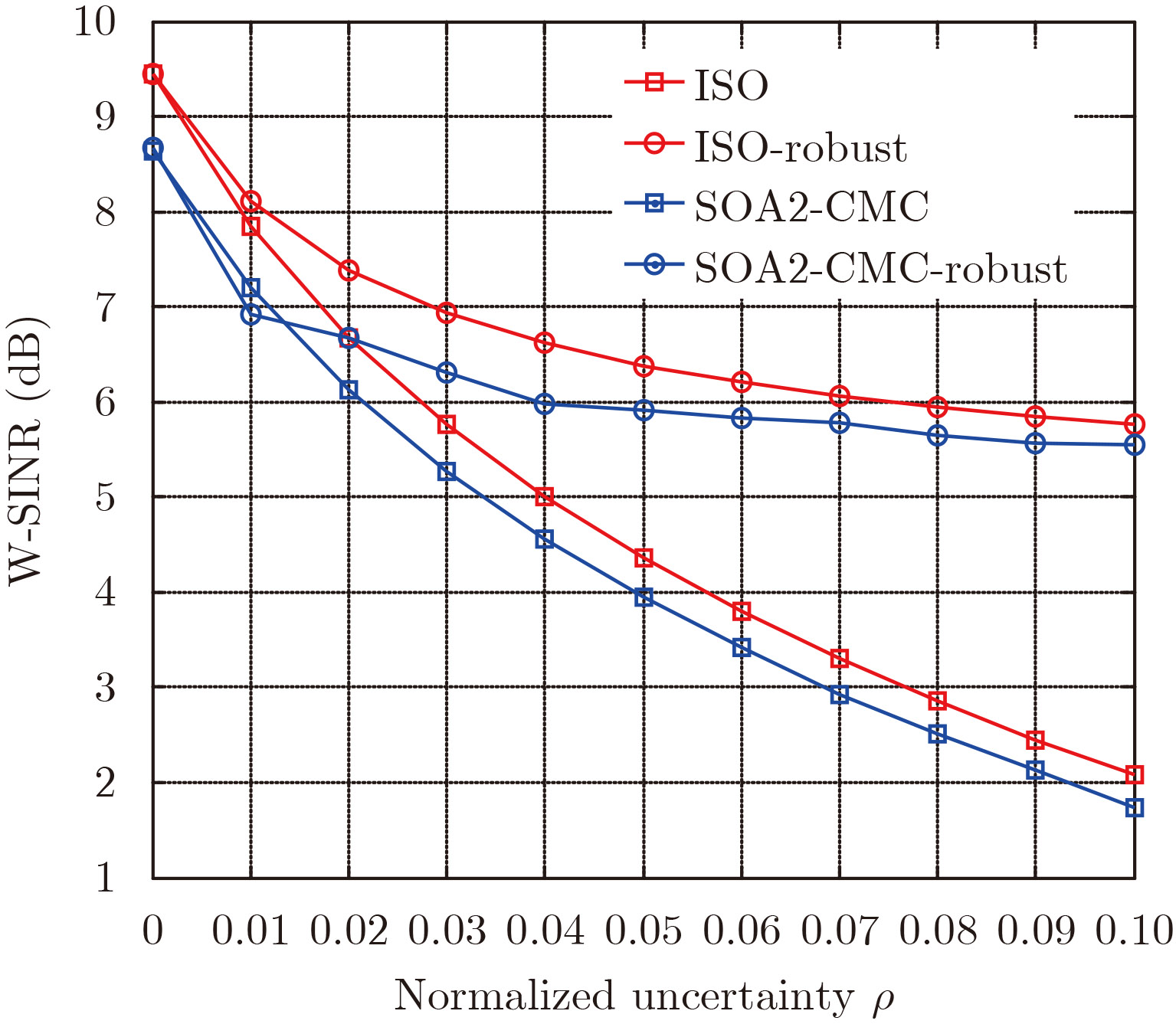
- Figure 3. W-SINR against the normalized uncertainty size for ISO and SOA2-CMC, associated with the nominal design and the robust design


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: