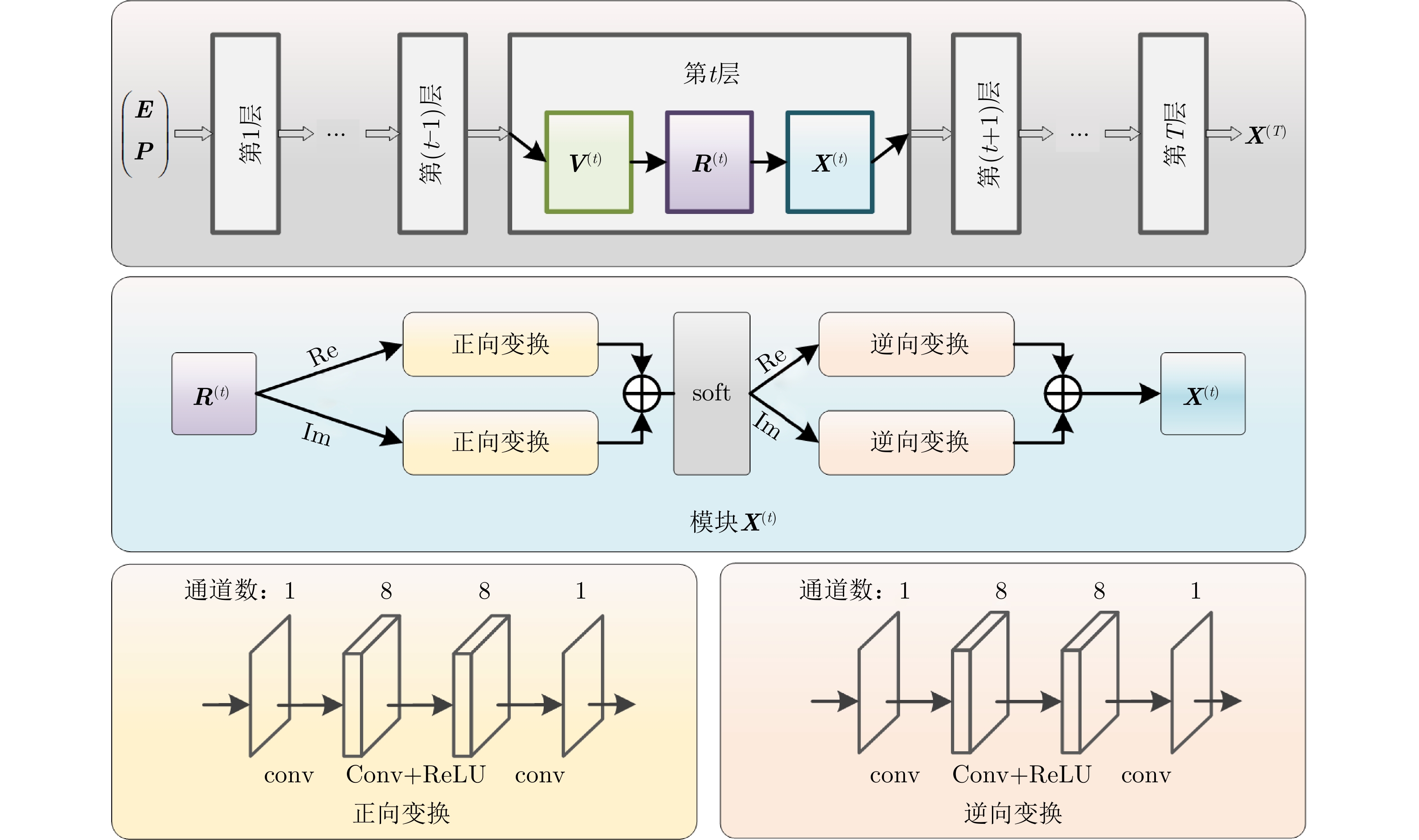
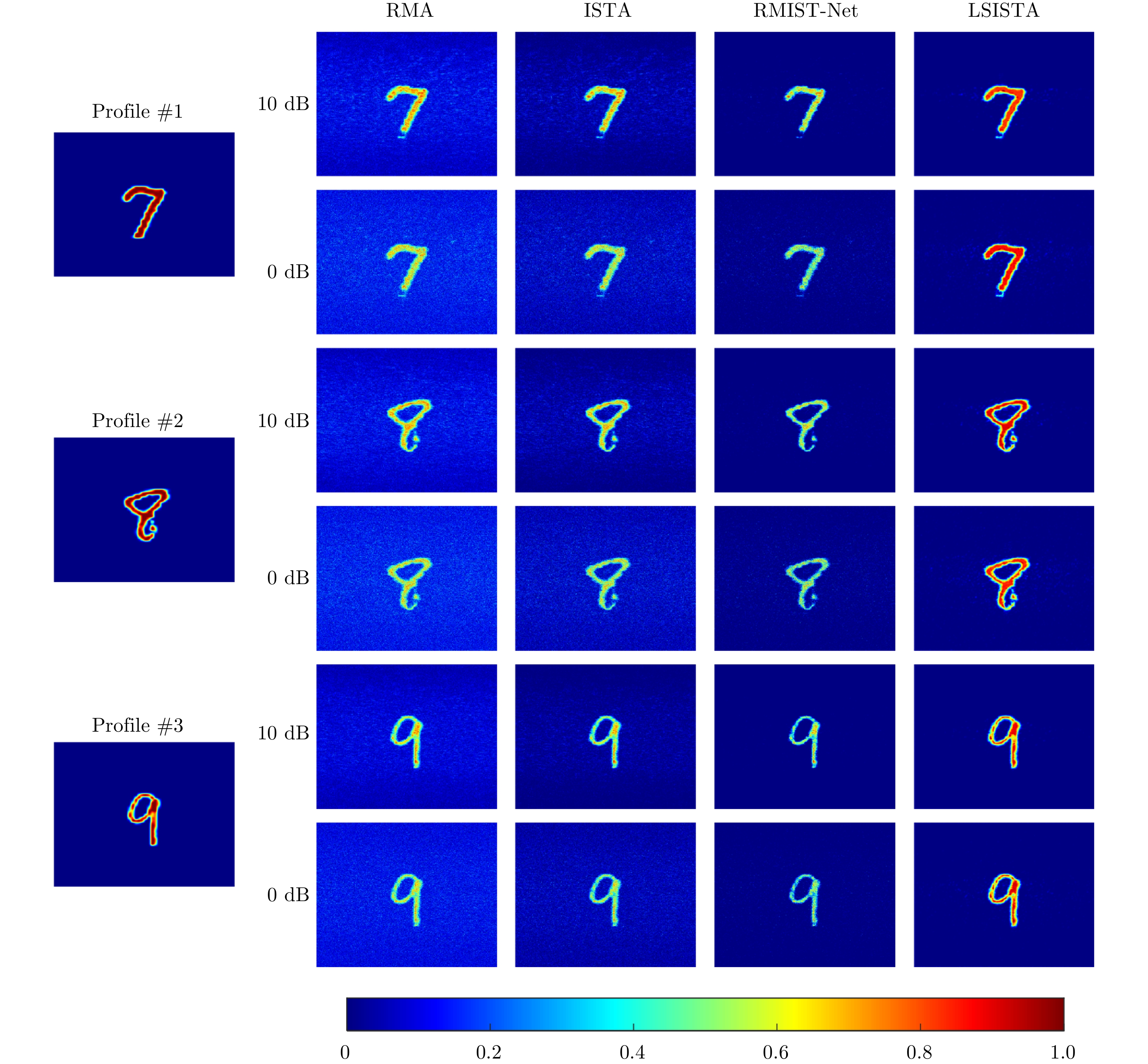
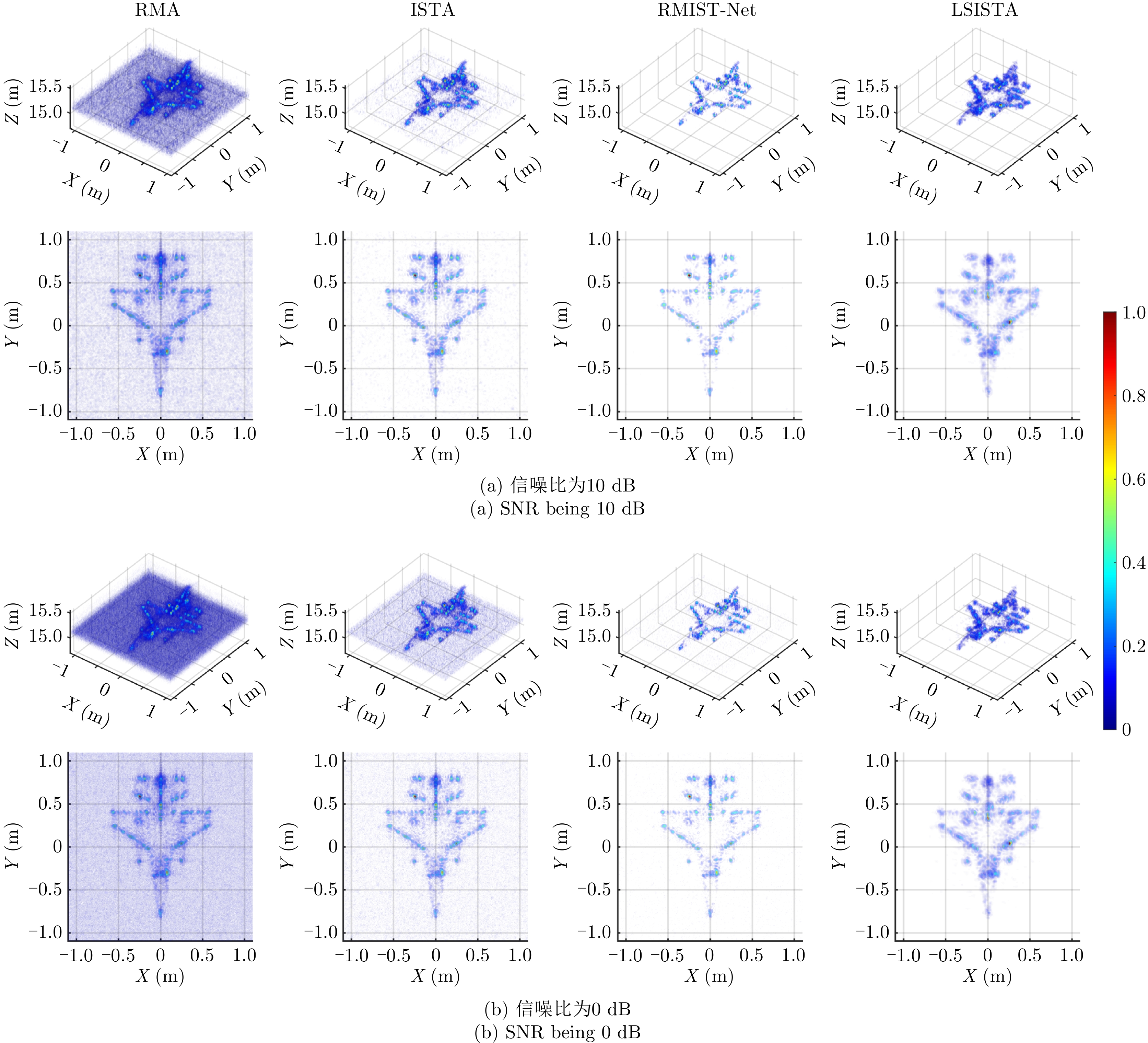
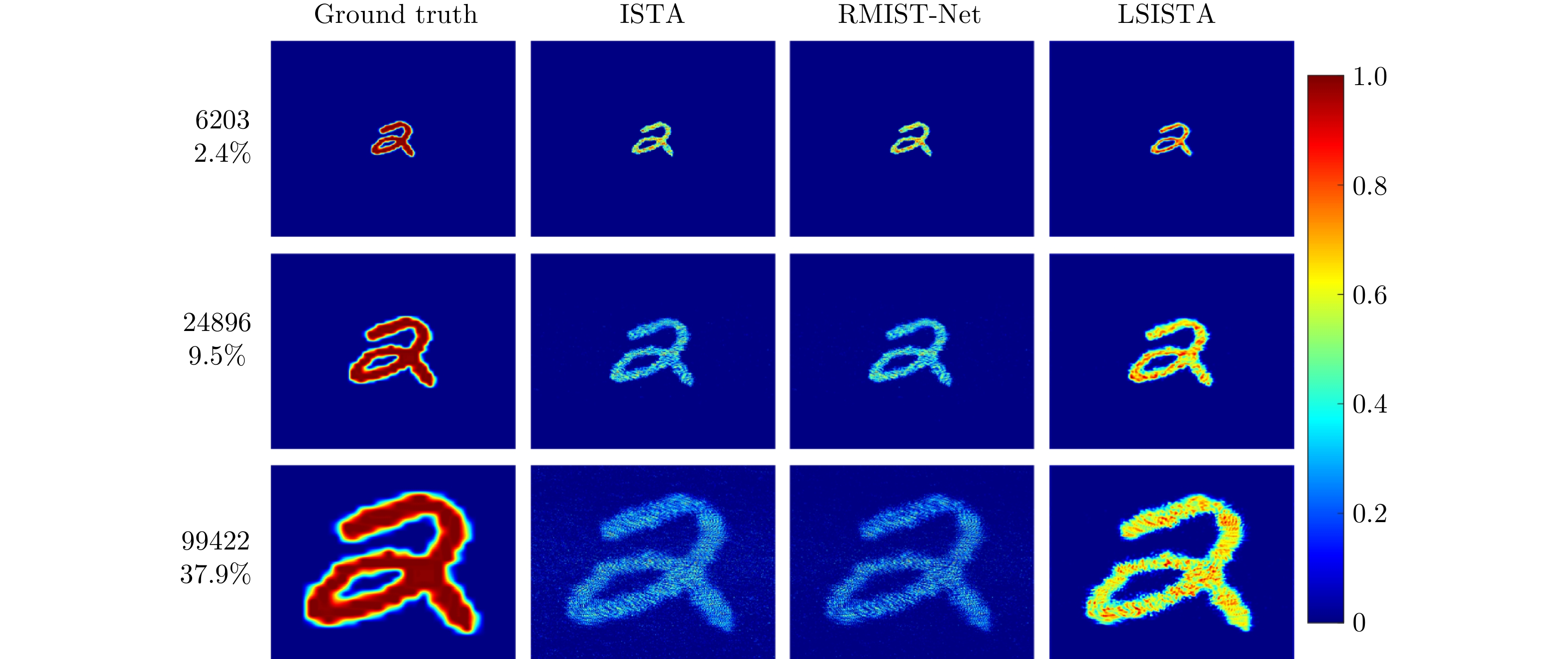
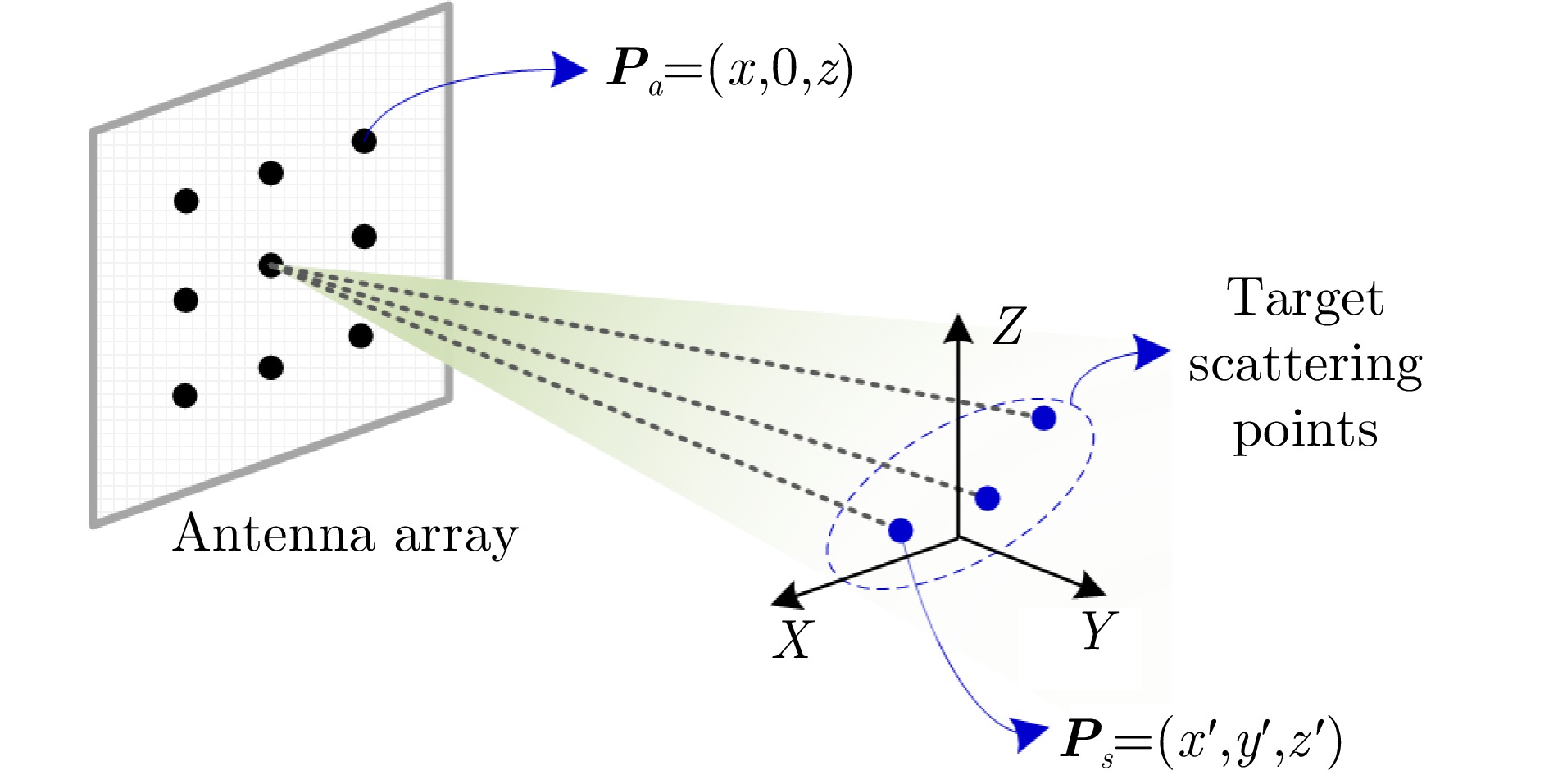
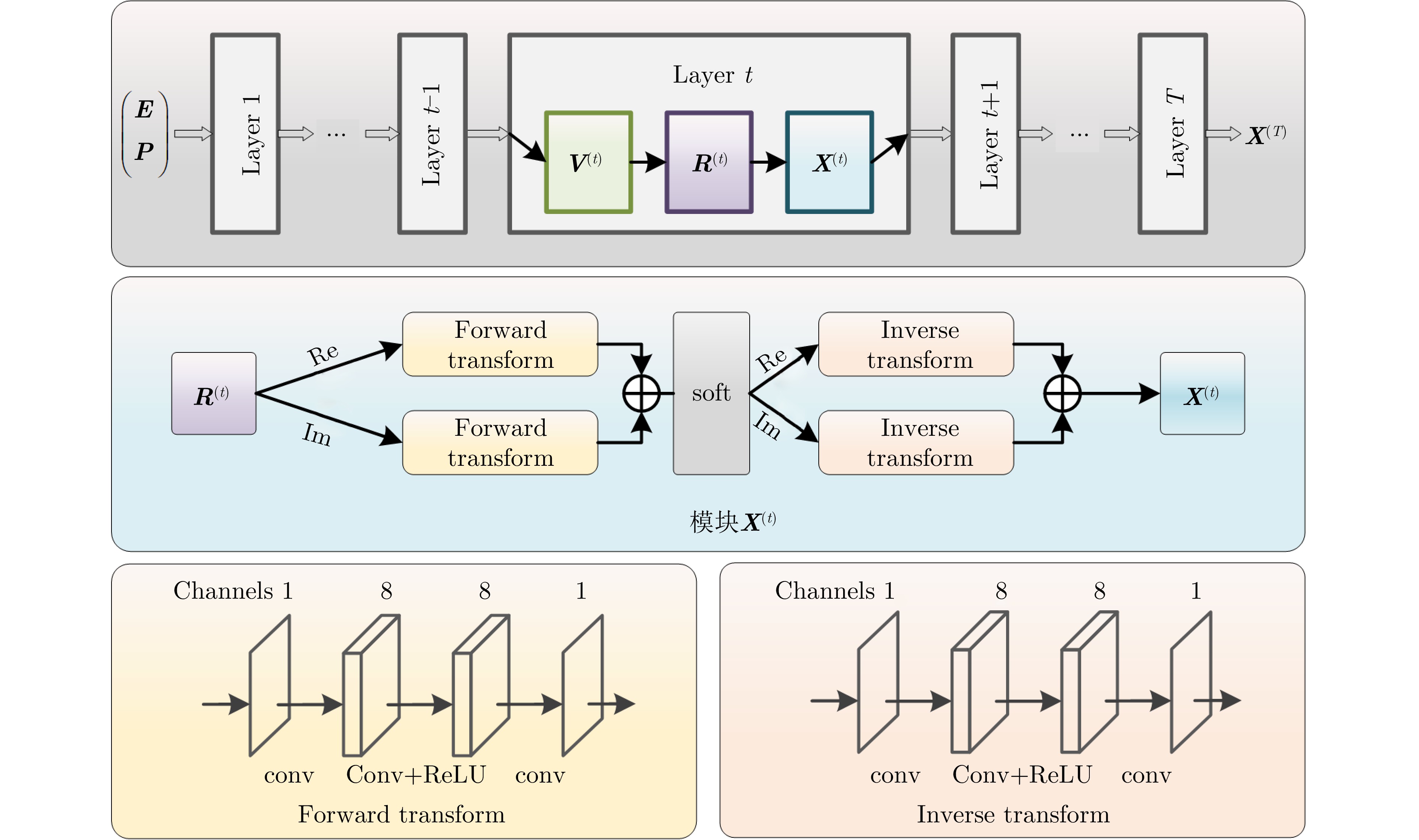
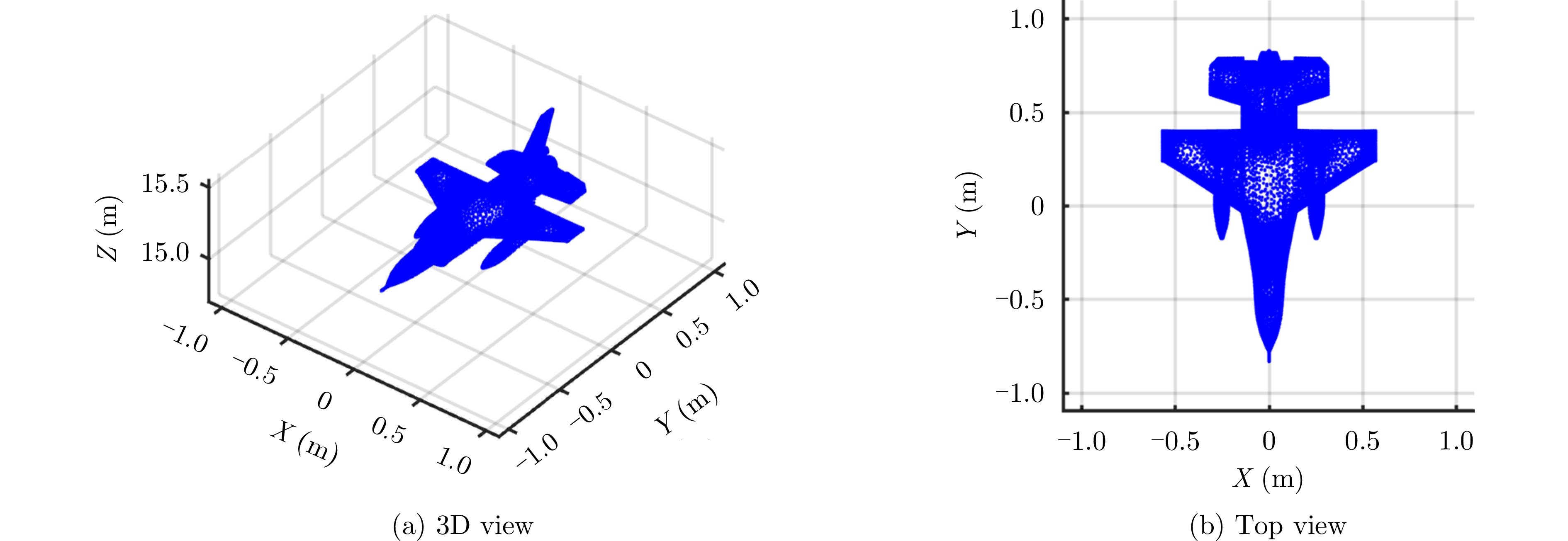
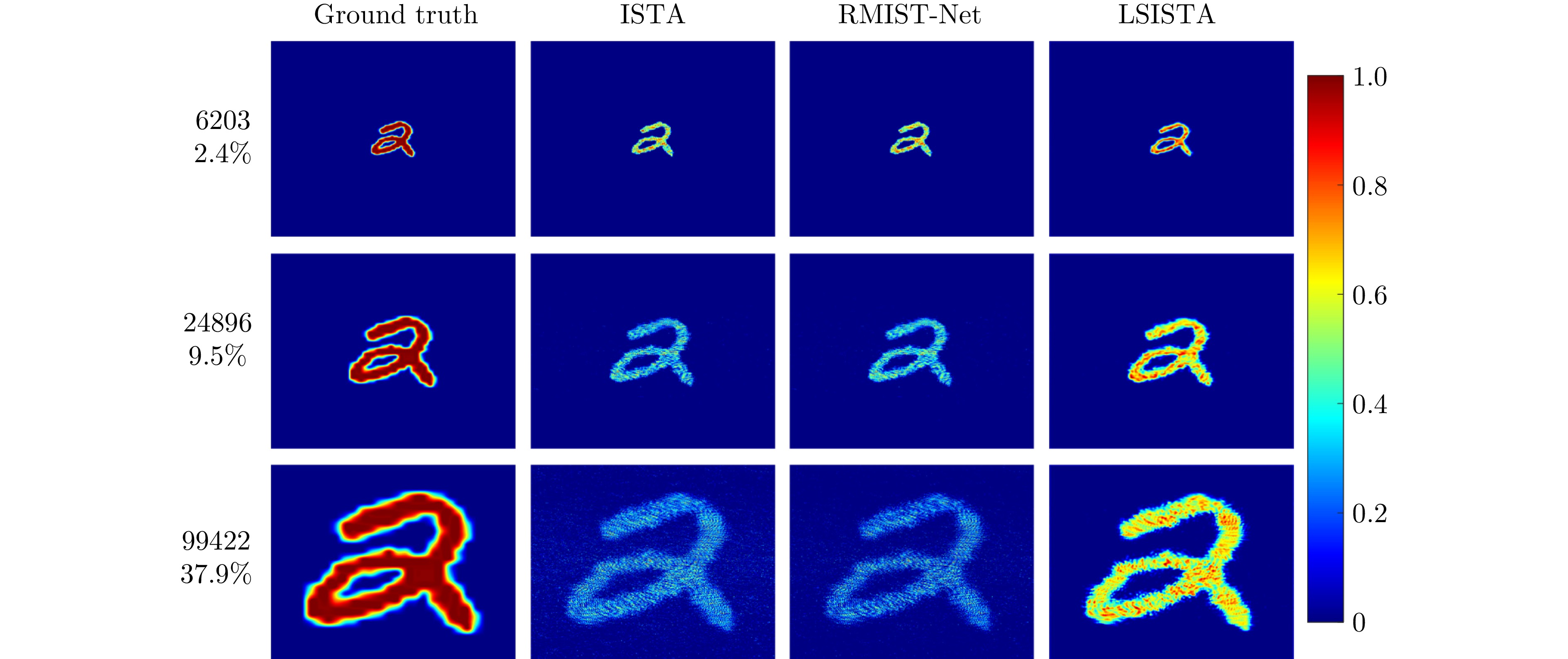
| [1] |
YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099. |
| [2] |
WU Yirong and ZHU Minhui. The developing status and trends of synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2000, 15(2): 121–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012. |
| [3] |
CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991.
|
| [4] |
DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582. |
| [5] |
SHI Wuzhen, JIANG Feng, LIU Shaohui, et al. Image compressed sensing using convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 375–388. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2928136. |
| [6] |
YANG Xianjun, TAO Xiaofeng, DUTKIEWICZ E, et al. Energy-efficient distributed data storage for wireless sensor networks based on compressed sensing and network coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(10): 5087–5099. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.090313.121804. |
| [7] |
POTTER L C, ERTIN E, PARKER J T, et al. Sparsity and compressed sensing in radar imaging[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(6): 1006–1020. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2037526. |
| [8] |
CAMLICA S, GURBUZ A C, and ARIKAN O. Autofocused spotlight SAR image reconstruction of off-grid sparse scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(4): 1880–1892. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2675138. |
| [9] |
PU Wei and WU Junjie. OSRanP: A novel way for radar imaging utilizing joint sparsity and low-rankness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 868–882. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2020.2993170. |
| [10] |
DONOHO D L, MALEKI A, and MONTANARI A. Message-passing algorithms for compressed sensing[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(45): 18914–18919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909892106. |
| [11] |
BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016. |
| [12] |
BECK A and TEBOULLE M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183–202. doi: 10.1137/080716542. |
| [13] |
ZHAO Lifan, WANG Lu, YANG Lei, et al. The race to improve radar imagery: An overview of recent progress in statistical sparsity-based techniques[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(6): 85–102. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2573847. |
| [14] |
FANG Jian, XU Zongben, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Fast compressed sensing SAR imaging based on approximated observation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(1): 352–363. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2263309. |
| [15] |
JIANG Chenglong, ZHANG Bingchen, FANG Jian, et al. Efficient ℓ q regularisation algorithm with range–azimuth decoupled for SAR imaging[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(3): 204–205. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.1989. |
| [16] |
GREGOR K and LECUN Y. Learning fast approximations of sparse coding[C]. The 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 2010: 399–406.
|
| [17] |
PU Wei. SAE-Net: A deep neural network for SAR autofocus[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5220714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3139914. |
| [18] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHI Jun, et al. CSR-Net: A novel complex-valued network for fast and precise 3-D microwave sparse reconstruction[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4476–4492. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3014696. |
| [19] |
HU Xiaowei, XU Feng, GUO Yiduo, et al. MDLI-Net: Model-driven learning imaging network for high-resolution microwave imaging with large rotating angle and sparse sampling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5212617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3110579. |
| [20] |
WEI Yangkai, LI Yinchuan, DING Zegang, et al. SAR parametric super-resolution image reconstruction methods based on ADMM and deep neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(12): 10197–10212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3052793. |
| [21] |
WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, WANG Mou, et al. AF-AMPNet: A deep learning approach for sparse aperture ISAR imaging and autofocusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5206514. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3073123. |
| [22] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, et al. Efficient ADMM framework based on functional measurement model for mmW 3-D SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5226417. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3165541. |
| [23] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. TPSSI-Net: Fast and enhanced two-path iterative network for 3D SAR sparse imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7317–7332. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3104168. |
| [24] |
PU Wei. Deep SAR imaging and motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2232–2247. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3051484. |
| [25] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. Lightweight FISTA-inspired sparse reconstruction network for mmW 3-D holography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5211620. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3093307. |
| [26] |
WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, LIANG Jiadian, et al. RMIST-Net: Joint range migration and sparse reconstruction network for 3-D mmW imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5205117. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068405. |
| [27] |
ZHANG Jian and GHANEM B. ISTA-Net: Interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1828–1837.
|
| [28] |
ZHOU Yulong, ZHONG Yu, WEI Zhun, et al. An improved deep learning scheme for solving 2-D and 3-D inverse scattering problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(5): 2853–2863. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3027898. |
| [29] |
LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M and FORTUNY-GUASCH J. 3-D radar imaging using range migration techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2000, 48(5): 728–737. doi: 10.1109/8.855491. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: