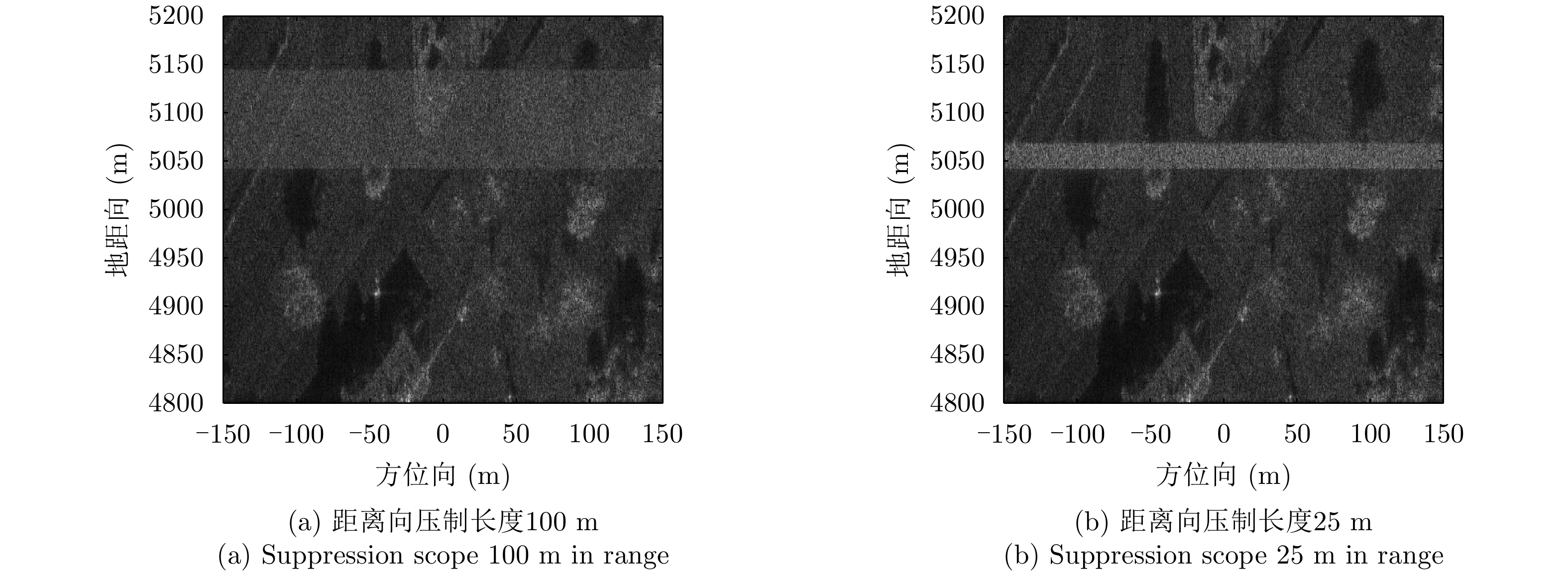
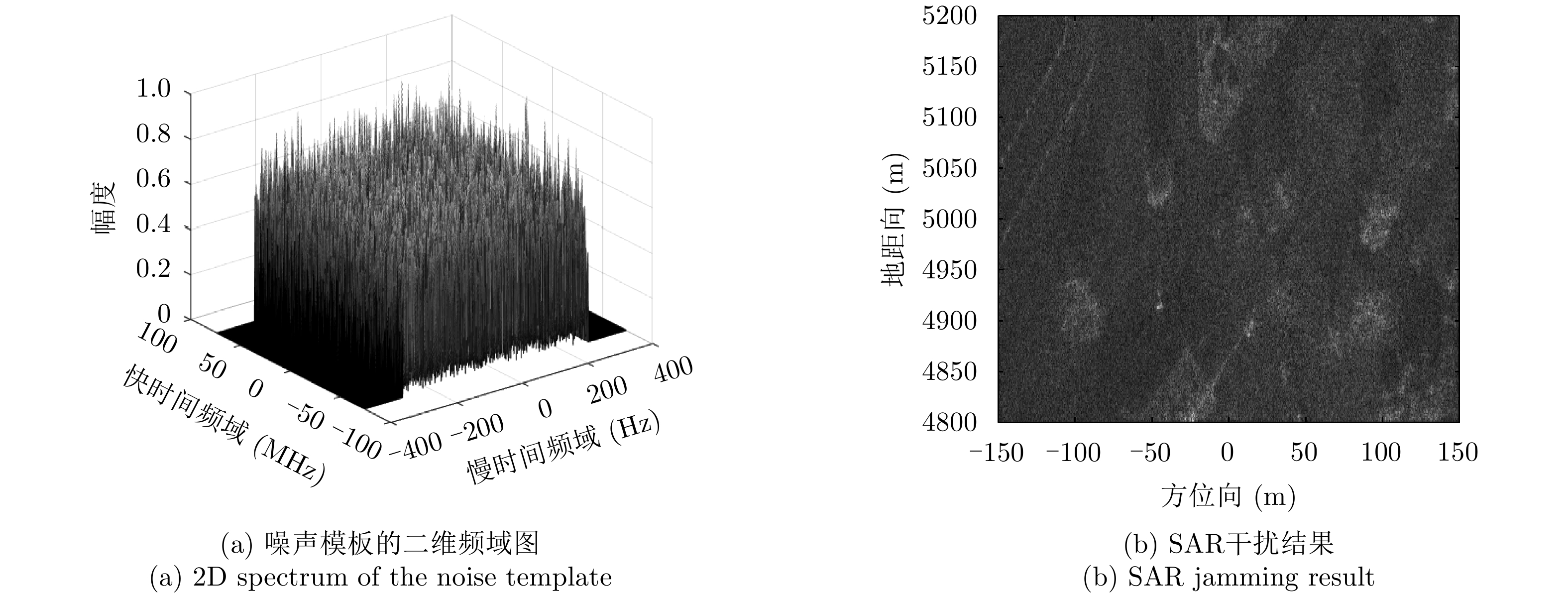
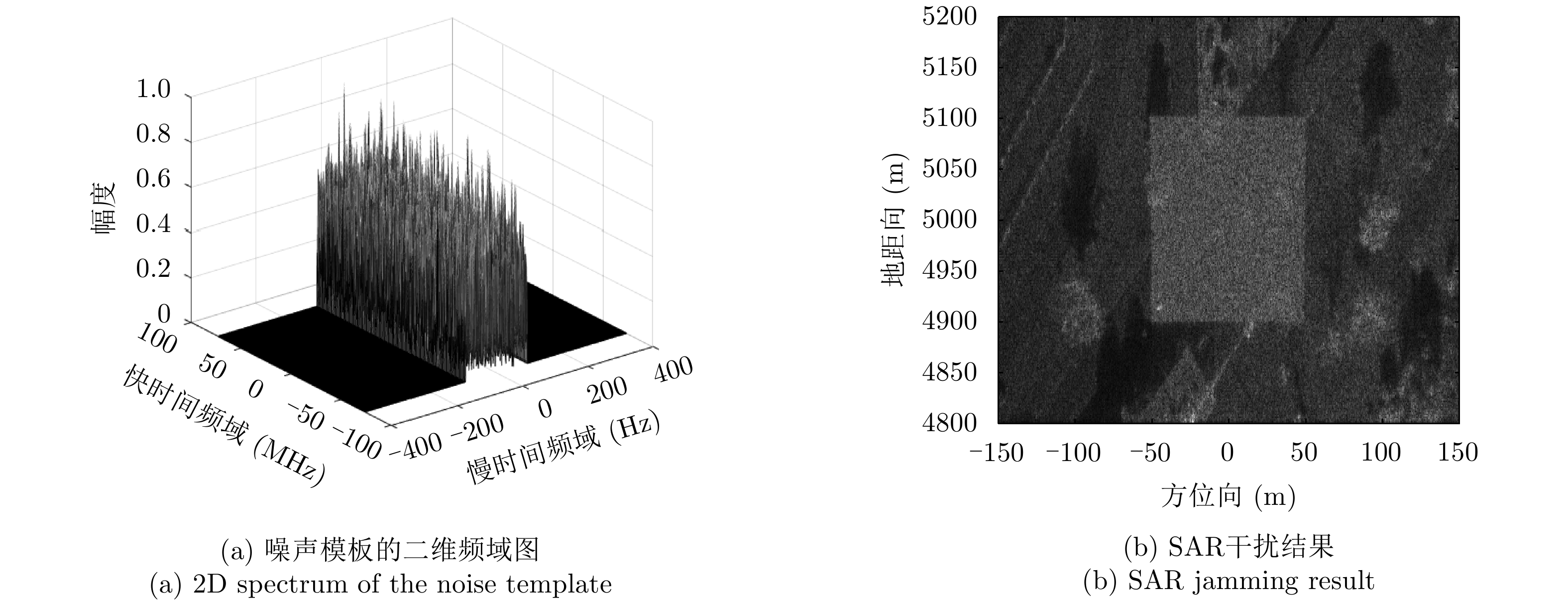
| [1] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005.
|
| [2] |
纪朋徽, 代大海, 吴昊, 等. SAR成像电子对抗技术综述[J]. 无线电工程, 2019, 49(6): 508–513.
JI Penghui, DAI Dahai, WU Hao, et al. Review of SAR imaging electronic countermeasures[J]. Radio Engineering, 2019, 49(6): 508–513.
|
| [3] |
SUN Hongbo, SHIMADA M, and XU Feng. Recent advances in synthetic aperture radar remote sensing-systems, data processing, and applications[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(11): 2013–2016. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2747602 |
| [4] |
CHANG Xin and DONG Chunxi. A barrage noise jamming method based on double jammers against three channel SAR GMTI[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 18755–18763. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2897043 |
| [5] |
刘玉玲. SAR有源假目标精确位置欺骗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012.
LIU Yuling. Research on SAR precisely position deception jamming[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012.
|
| [6] |
SCHLEHER D C. Electronic Warfare in the Information Age[M]. Boston, MA: Artech House, 2000.
|
| [7] |
李欣, 王春阳, 原慧, 等. 雷达灵巧干扰样式建模及仿真研究[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2015, 31(5): 38–41, 59.
LI Xin, WANG Chunyang, YUAN Hui, et al. The modeling and simulation of radar smart jamming types[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2015, 31(5): 38–41, 59.
|
| [8] |
ABOUELFADL A, SAMIR A M, AHMED F M, et al. Performance analysis of LFM pulse compression radar under effect of convolution noise jamming[C]. The 2016 33rd National Radio Science Conference, Aswan, Egypt, 2016: 282–289.
|
| [9] |
GONG Shixian, WEI Xizhang, LI Xiang, et al. Mathematic principle of active jamming against wideband LFM radar[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 26(1): 50–60. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2015.00008 |
| [10] |
HAO Honglian, ZENG Dazhi, GE Ping, et al. Research on the method of smart noise jamming on pulse radar[C]. The 2015 5th International Conference on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Qinhuangdao, China, 2015: 1339–1342.
|
| [11] |
邱杰. 灵巧噪声干扰本质含义探讨[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2011, 26(5): 481–484.
QIU Jie. Research on essential signification of smart noise jamming[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2011, 26(5): 481–484.
|
| [12] |
曾云健, 陶建锋, 孙青. 灵巧噪声在SAR中的干扰应用研究[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2009, 25(2): 39–41.
ZENG Yunjian, TAO Jianfeng, and SUN Qing. Application and research of smart noise in jamming SAR[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2009, 25(2): 39–41.
|
| [13] |
吕波, 冯起, 张晓发, 等. 对SAR的随机脉冲卷积干扰研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2008, 3(3): 276–279.
LV Bo, FENG Qi, ZHANG Xiaofa, et al. Study of random pulse convolution jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2008, 3(3): 276–279.
|
| [14] |
降佳伟, 吴彦鸿, 王宏艳, 等. 一种对SAR-GMTI的密集假目标干扰技术[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2016, 39(1): 9–14, 88.
JIANG Jiawei, WU Yanhong, WANG Hongyan, et al. A dense false target jamming technique against SAR-GMTI[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2016, 39(1): 9–14, 88.
|
| [15] |
周传晟. 合成孔径雷达卷积干扰技术的研究[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2013, 36(2): 6–10.
ZHOU Chuansheng. Study of convolution jamming technology of synthetic aperture radar[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2013, 36(2): 6–10.
|
| [16] |
沈爱国, 姜秋喜. 脉冲卷积干扰技术在超宽带SAR中的应用分析[J]. 电光与控制, 2010, 17(2): 39–42.
SHEN Aiguo and JIANG Qiuxi. Analysis of pulse convolution jamming technique applied to counter UWB SAR[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2010, 17(2): 39–42.
|
| [17] |
黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 周一宇. 对合成孔径雷达的移频干扰研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2006, 27(3): 463–468.
HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. A study on the shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2006, 27(3): 463–468.
|
| [18] |
黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 周一宇. 对合成孔径雷达的随机移频干扰[J]. 信号处理, 2007, 23(1): 41–45.
HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. Randomly-shift-frequency jamming style to SAR[J]. Signal Processing, 2007, 23(1): 41–45.
|
| [19] |
黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 吴京, 等. 对合成孔径雷达的步进移频干扰[J]. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(4): 898–902.
HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, Wu Jing, et al. Stepped-shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(4): 898–902.
|
| [20] |
YANG Kaizhi, YE Wei, MA Fangfang, et al. A large-scene deceptive jamming method for space-borne SAR based on time-delay and frequency-shift with template segmentation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(1): 53. doi: 10.3390/rs12010053 |
| [21] |
和小冬. 弹载合成孔径雷达干扰技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015.
HE Xiaodong. Research on the jamming technologies of missile-borne synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015.
|
| [22] |
YE Wei, RUAN Hang, ZHANG Shuxian, et al. Study of noise jamming based on convolution modulation to SAR[C]. 2010 International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering, Changchun, China, 2010: 169–172.
|
| [23] |
FANG Mingxing, WANG Jiegui, and LEI Lei. Study on 2D noise convolution modulation jamming to SAR[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2014, 42(2): 139–144, 160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.02.025 |
| [24] |
ZHANG Yanbin. Technology of smart noise jamming based on multiplication modulation[C]. 2011 International Conference on Electric Information and Control Engineering, Wuhan, China, 2011: 4557–4559.
|
| [25] |
ZHU Ninglong and LIU Hailiang. Research into the influence of frequency shift on smart noise jamming with convolution modulation[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2016, 39(2): 17–20. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2016.02.005 |
| [26] |
林欢, 甘德云, 李宏, 等. 基于移频卷积的合成孔径雷达干扰技术研究[J]. 军械工程学院学报, 2014, 26(4): 47–50.
LIN Huan, GAN Deyun, LI Hong, et al. Interference technology research of synthetic aperture radar based on frequency-shift convolution[J]. Journal of Ordnance Engineering College, 2014, 26(4): 47–50.
|
| [27] |
吴晓芳, 邢世其, 王雪松, 等. 对合成孔径雷达的脉间分段移频干扰[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2010, 26(1): 53–57.
WU Xiaofang, XING Shiqi, WANG Xuesong, et al. Interpulse subsection-shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2010, 26(1): 53–57.
|
| [28] |
栾琳. 灵巧噪声干扰的建模仿真研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2009.
LUAN Lin. Modeling, simulation and study of smart noise jamming[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2009.
|
| [29] |
LIU Yongcai, WANG Wei, DAI Shaoqi, et al. Transmitter power comparison between incoherent noise and coherent deceptive jamming against synthetic aperture radar[C]. 2017 IEEE Microwaves, Radar and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kiev, Ukraine, 2017: 279–284.
|
| [30] |
刘永才. 基于卷积调制的SAR有源欺骗干扰技术[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2013.
LIU Yongcai. Active deceptive jamming against SAR based on convolutional modulation[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2013.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: