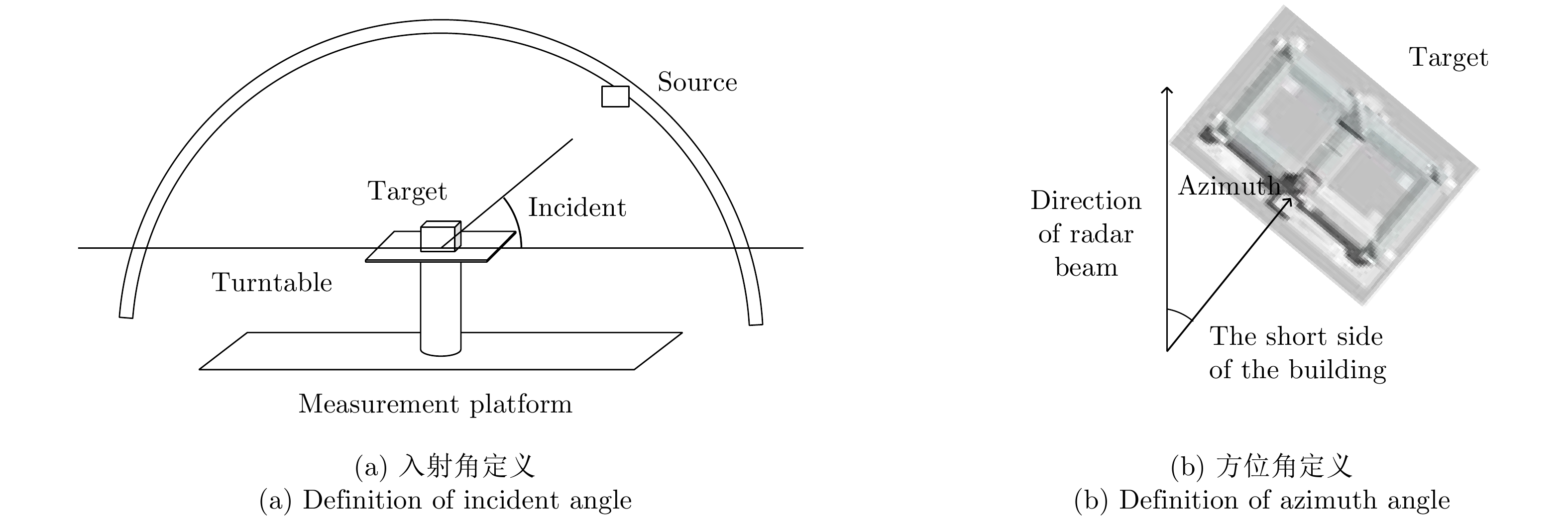
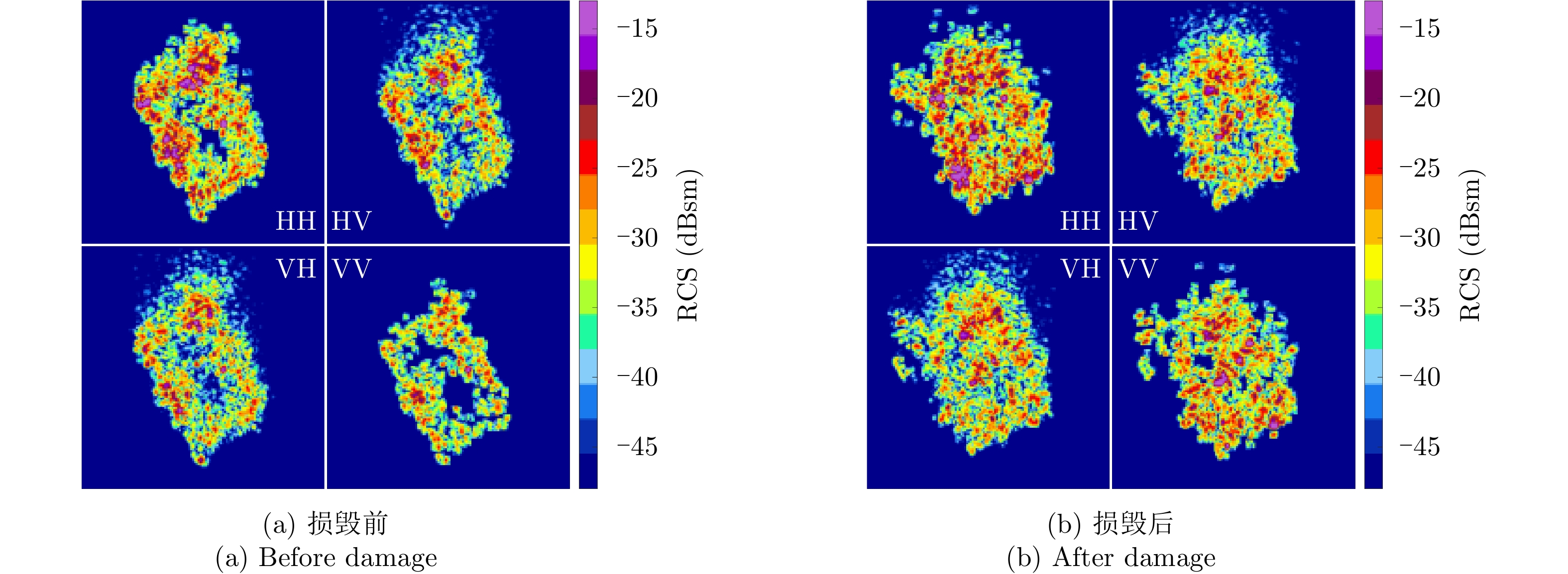
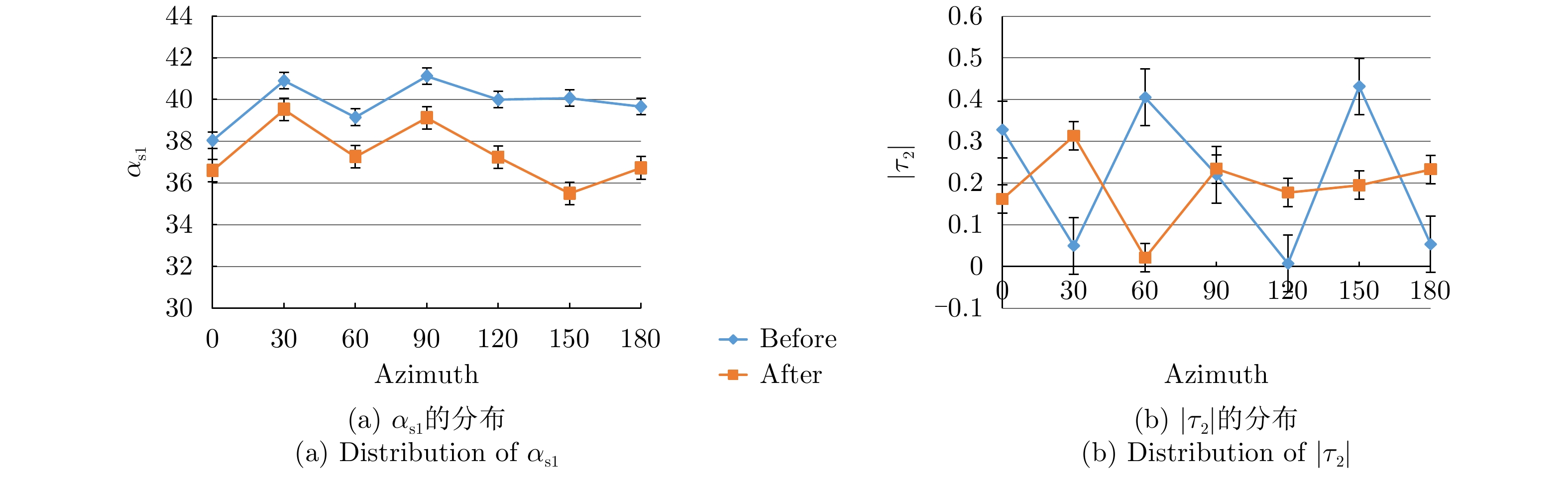
| [1] |
Tadono T, Ohki M, and Abe T. Summary of natural disaster responses by the Advanced Land Observing Satellite-2(ALOS-2)[C]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences, Kyoto, Japan, 2019: 69–72. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-3-W7-69-2019. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Fengli and SHAO Yun. Urban target monitoring using high resolution SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2010, 25(3): 415–422. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2010.3.415 |
| [3] |
CHEN Qihao, LI Linlin, JIANG Ping, et al. Building collapse extraction using modified freeman decomposition from post-disaster polarimetric SAR image[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience And Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 5769–5772. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730507. |
| [4] |
WANG Xiaoqing, DOU Aixia, JIN Dingjian, et al. Study on the comparation of building damage extracted from different RS images acquired after 2010 M = 7.1 Yushu, Qinghai, China earthquake[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 935–938. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351401. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Haizhen, WANG Qing, ZENG Qiming, et al. A novel approach to building collapse detection from post-seismic polarimetric SAR imagery by using optimization of polarimetric contrast enhancement[C]. 2015 IEEE International Geoscience And Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 2015: 3270–3273. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326516. |
| [6] |
PARK S E, YAMAGUCHI Y, and KIM D J. Polarimetric SAR remote sensing of the 2011 Tohoku earthquake using ALOS/PALSAR[J]. Remote sensing of Environment, 2013, 132: 212–220. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.01.018 |
| [7] |
ZHAI Wei, SHEN Huanfeng, HUANG Chunlin, et al. Building earthquake damage information extraction from a single post-earthquake PolSAR image[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(3): 171. doi: 10.3390/rs8030171 |
| [8] |
SATO M, CHEN Siwei, and SATAKE M. Polarimetric SAR analysis of tsunami damage following the March 11, 2011 East Japan earthquake[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(10): 2861–2875. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2200649 |
| [9] |
WATANABE M, MOTOHKA T, MIYAGI Y, et al. 2012. Analysis of urban areas affected by the 2011 off the pacific coast of Tohoku earthquake and tsunami with L-Band SAR full-polarimetric mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 472–476. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2182030 |
| [10] |
ZHAI Wei and HUANG Chunlin. Fast building damage mapping using a single post-earthquake PolSAR image: A case study of the 2010 Yushu earthquake[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2016, 68(1): 86. doi: 10.1186/s40623-016-0469-2 |
| [11] |
ZHAI Wei, HUANG Chunlin, and PEI Wansheng. Two new polarimetric feature parameters for the recognition of the different kinds of buildings in earthquake-stricken areas based on entropy and eigenvalues of PolSAR decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1613. doi: 10.3390/rs10101613 |
| [12] |
LI Xinwu, GUO Huadong, ZHANG Lu, et al. A new approach to collapsed building extraction using RADARSAT-2 polarimetric SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 677–681. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2178392 |
| [13] |
SUN Weidong, SHI Lei, YANG Jie, et al. Building collapse assessment in urban areas using texture information from postevent SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(8): 3792–3808. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2580610 |
| [14] |
ZHAO Lingli, YANG Jie, LI Pingxiang, et al. Damage assessment in urban areas using post-earthquake airborne PolSAR imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(24): 8952–8966. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.860566 |
| [15] |
GE Pinglan, GOKON H, and MEGURO K. A review on synthetic aperture radar-based building damage assessment in disasters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 240: 111693. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111693 |
| [16] |
CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. Urban damage level mapping based on scattering mechanism investigation using fully polarimetric SAR data for the 3.11 East Japan earthquake[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(12): 6919–6929. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2588325 |
| [17] |
王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 |
| [18] |
FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 |
| [19] |
YAMAGUCHI Y, SATO A, BOERNER W M, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with rotation of coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2251–2258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2099124 |
| [20] |
JI Kefeng and WU Yonghui. Scattering mechanism extraction by a modified cloude-pottier decomposition for dual polarization SAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(6): 7447–7470. doi: 10.3390/rs70607447 |
| [21] |
CHIEN L L C, EWE H T, and SAW S H. Understanding the correlation in scattering mechanisms between H-Alpha decomposition and theoretical modelling[C]. 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS-Toyama), Toyama, Japan, 2018: 1198–1203. doi: 10.23919/PIERS.2018.8597662. |
| [22] |
TOUZI R. Target scattering decomposition in terms of roll-invariant target parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(1): 73–84. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.886176 |
| [23] |
AN Wentao, XIE Chunhua, YUAN Xinzhe, et al. Four-component decomposition of polarimetric SAR images with deorientation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(6): 1090–1094. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2157078 |
| [24] |
孙翔, 宋红军, 王宇, 等. 基于高分辨率全极化SAR图像的取向角校正方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 465–474. doi: 10.12000/JR18026SUN Xiang, SONG Hongjun, WANG R, et al. POA correction method using high-resolution full-polarization SAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 465–474. doi: 10.12000/JR18026 |
| [25] |
LIU Shan, ZHANG Fengli, WEI Shiying, et al. Building damage mapping based on Touzi decomposition using quad-polarimetric ALOS PALSAR data[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2020: 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s11707-019-0779-3 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: