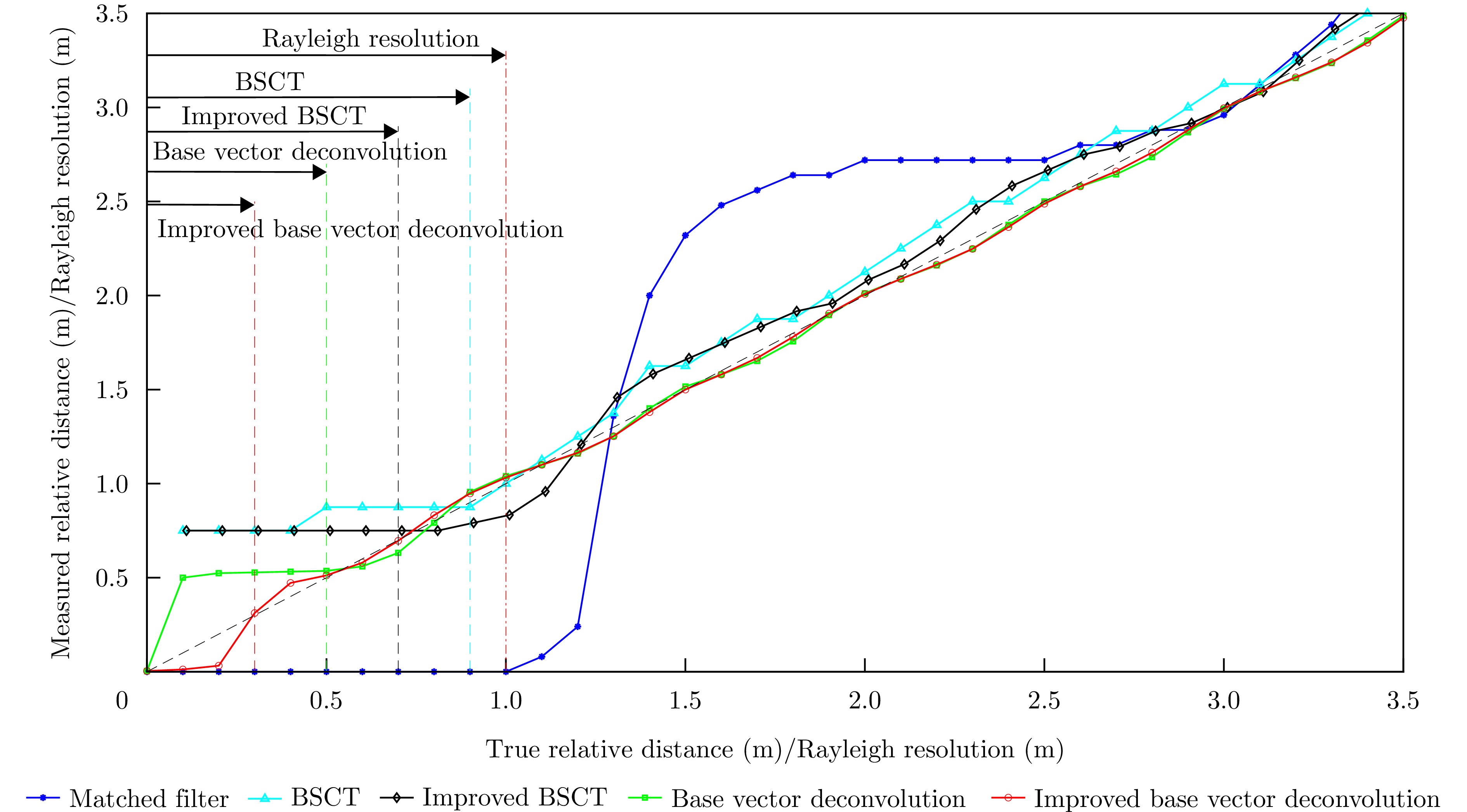
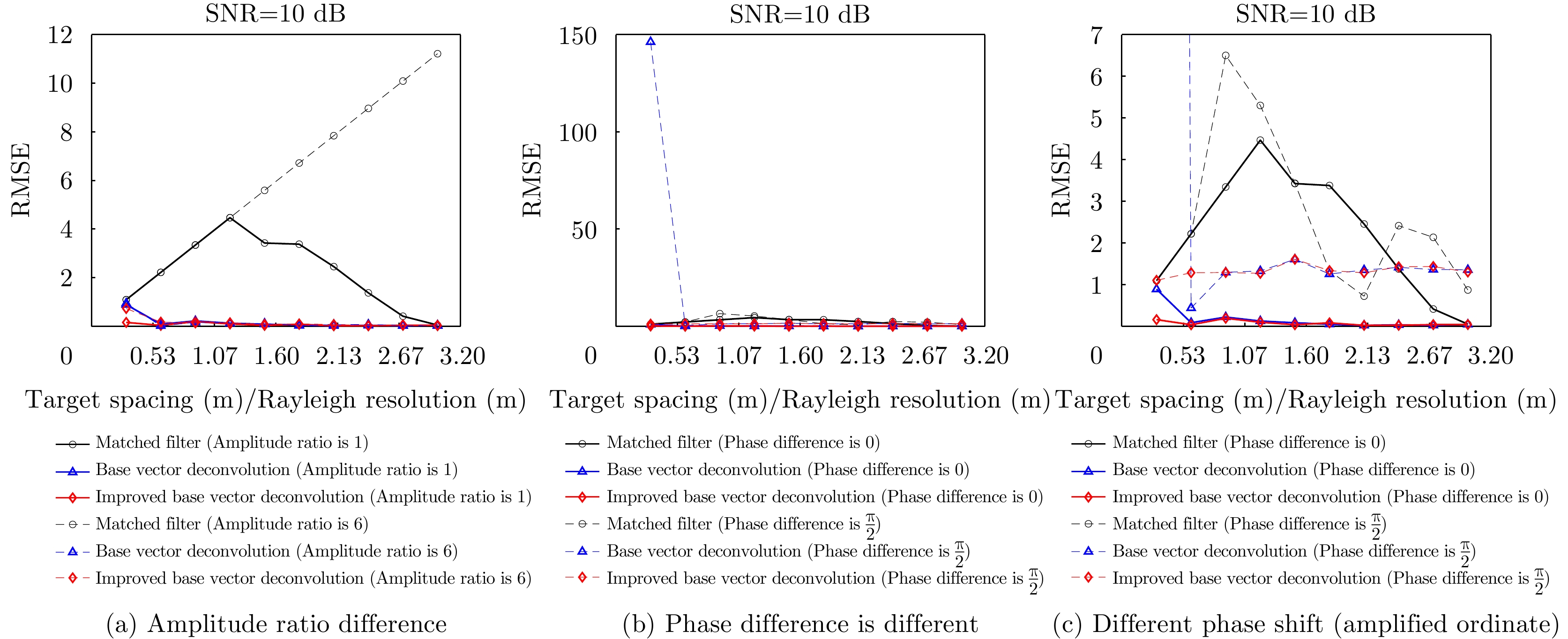
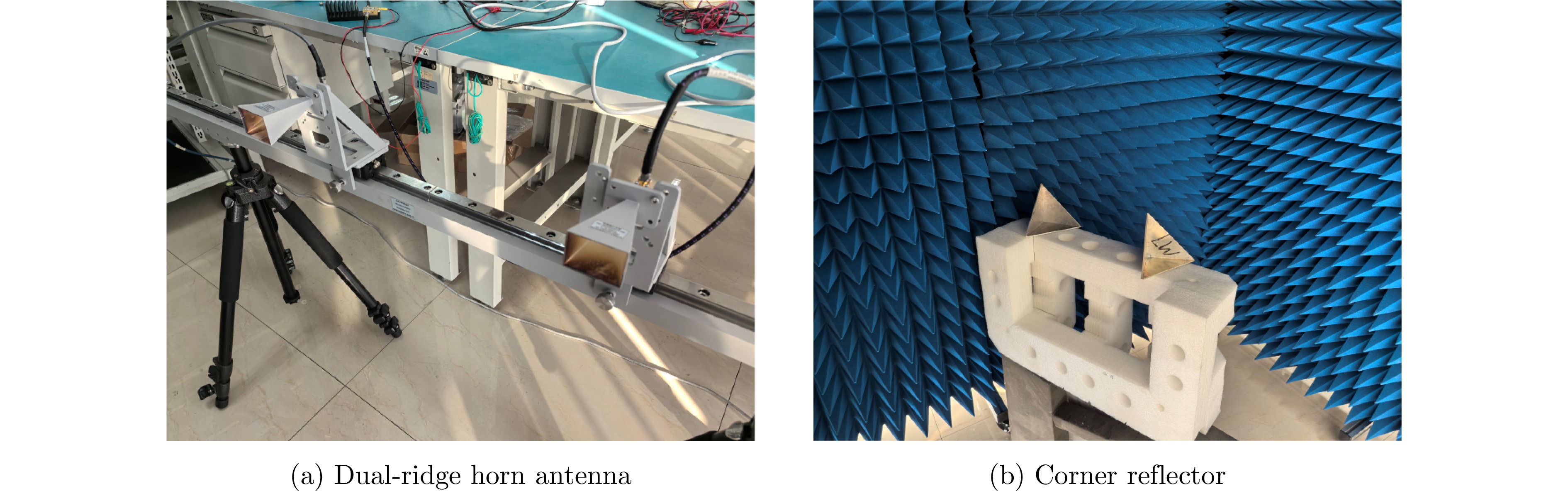
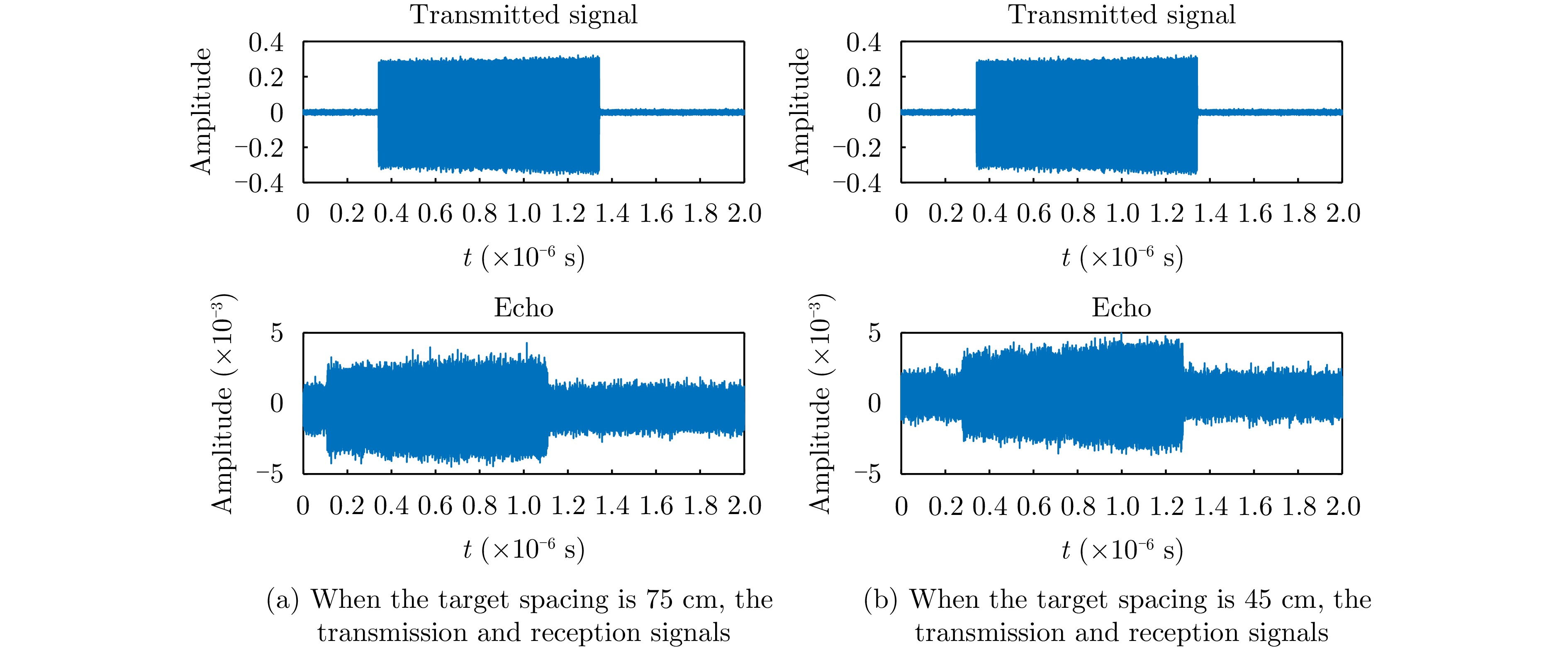
| [1] |
CHEN Suixin. Study on super-resolution for radar detection of group targets[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022: 1–5. doi: 10.27005/d.cnki.gdzku.2022.001266. |
| [2] |
FENG Junjie, SUN Yinan, and JI Xiuxia. High-resolution ISAR imaging based on improved sparse signal recovery algorithm[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021, 2021: 5541116. doi: 10.1155/2021/5541116. |
| [3] |
NI Jinlin, CHU Xiaobin, and LIN Youquan. The principle and limitation of the range super-resolution algorithms based on deconvolution[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2000, 22(3): 62–64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.03.019. |
| [4] |
王永良. 空间谱估计理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004: 18–52, 306–336.
WANG Yongliang. Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithms[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004: 18–52, 306–336.
|
| [5] |
DING Shanshan, TONG Ningning, ZHANG Yongshun, et al. Super-resolution 3D imaging in MIMO radar using spectrum estimation theory[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(2): 304–312. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0233. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, WANG Mou, et al. 3DRIED: A high-resolution 3-D millimeter-wave radar dataset dedicated to imaging and evaluation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3366. doi: 10.3390/rs13173366. |
| [9] |
KANG Le, ZHANG Qun, LI Taoyong, et al. Imaging method of downward-looking three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar based on bayesian learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0611003. |
| [10] |
SIMMONS J A, FERRAGAMO M, MOSS C F, et al. Discrimination of jittered sonar echoes by the echolocating bat, Eptesicus fuscus: The shape of target images in echolocation[J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 1990, 167(5): 589–616. doi: 10.1007/BF00192654. |
| [11] |
SIMMONS J A, SAILLANT P A, WOTTON J M, et al. Composition of biosonar images for target recognition by echolocating bats[J]. Neural Networks, 1995, 8(7/8): 1239–1261. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(95)00059-3. |
| [12] |
SCHMIDT S. Perception of structured phantom targets in the echolocating bat, Megaderma lyra[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1992, 91(4): 2203–2223. doi: 10.1121/1.403654. |
| [13] |
YANG Lin. Modeling and biomechanical analysis of the stapes, cochlea and organ of Corti[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Fudan University, 2009: 17–34. doi: 10.7666/d.y1970550. |
| [14] |
CHI T, RU Powen, and SHAMMA S A. Multiresolution spectrotemporal analysis of complex sounds[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 118(2): 887–906. doi: 10.1121/1.1945807. |
| [15] |
秦晓瑜. 基于听觉仿生的听觉谱生成方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 东北师范大学, 2013: 1–18.
QIN Xiaoyu. Study on the generation method of auditory spectrum based on auditory bionics[D]. [Master dissertation], Northeast Normal University, 2013: 1–18.
|
| [16] |
SAILLANT P A, SIMMONS J A, DEAR S P, et al. A computational model of echo processing and acoustic imaging in frequency-modulated echolocating bats: The spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1993, 94(5): 2691–2712. doi: 10.1121/1.407353. |
| [17] |
MATSUO I, KUNUGIYAMA K, and YANO M. An echolocation model for range discrimination of multiple closely spaced objects: Transformation of spectrogram into the reflected intensity distribution[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 115(2): 920–928. doi: 10.1121/1.1642626. |
| [18] |
MATSUO I and YANO M. An echolocation model for the restoration of an acoustic image from a single-emission echo[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 116(6): 3782–3788. doi: 10.1121/1.1811411. |
| [19] |
WIEGREBE L. An autocorrelation model of bat sonar[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 2008, 98(6): 587–595. doi: 10.1007/s00422-008-0216-2. |
| [20] |
PEREMANS H and HALLAM J. The spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver, revisited[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 104(2): 1101–1110. doi: 10.1121/1.423326. |
| [21] |
SIMON R, KNÖRNSCHILD M, TSCHAPKA M, et al. Biosonar resolving power: Echo-acoustic perception of surface structures in the submillimeter range[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2014, 5: 64. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00064. |
| [22] |
PARK M and ALLEN R. Pattern-matching analysis of fine echo delays by the spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010, 128(3): 1490–1500. doi: 10.1121/1.3466844. |
| [23] |
SIMMONS J A, SAILLANT P A, FERRAGAMO M J, et al. Auditory Computations for Biosonar Target Imaging in Bats[M]. HAWKINS H L, MCMULLEN T A, POPPER A N, et al. Auditory Computation. New York: Springer, 1996: 401–468. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-4070-9_9. |
| [24] |
GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Baseband version of the bat-inspired spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485152. |
| [25] |
GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Bio-inspired two target resolution at radio frequencies[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 2017: 436–440. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944242. |
| [26] |
GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Bio-inspired processing of radar target echoes[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(12): 1402–1409. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5241. |
| [27] |
成彬彬. 自适应雷达波形的仿生处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 清华大学, 2009.
CHENG Binbin. Research on bionic processing for auto-adaptive radar waveform[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Tsinghua University, 2009.
|
| [28] |
SU Mengna, LIANG Hong, and YANG Changsheng. Bionic imaging of underwater multiple targets with high resolution based on SCAT model[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(2): 189–193. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-1509.2019.02.010. |
| [29] |
CHEN Ming, BATES M E, and SIMMONS J A. How frequency hopping suppresses pulse-echo ambiguity in bat biosonar[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(29): 17288–17295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001105117. |
| [30] |
CHEN Ming, HARO S, SIMMONS A M, et al. A comprehensive computational model of animal biosonar signal processing[J]. PLOS Computational Biology, 2021, 17(2): e1008677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008677. |
| [31] |
BALLERI A, GRIFFITHS H, and BAKER C. Biologically-Inspired Radar and Sonar: Lessons from Nature[M]. Edison: SciTech Publishing, 2017: 1–81.
|
| [32] |
丁鹭飞, 耿富禄, 陈建春. 雷达原理[M]. 6版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2020: 210–211, 348–360.
DING Lufei, GENG Fulu, and CHEN Jianchun. Radar Principles[M]. 6th ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2020: 210–211, 348–360.
|
| [33] |
WANG Luoshengbin, WANG Xuesong, and XU Zhenhai. Principle and approach to polarization modulation for radar super-resolution[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141. |
| [34] |
WANG Luoshengbin, XU Zhenhai, DONG Wei, et al. A scheme of polarimetric superresolution for multitarget detection and localization[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 439–443. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3058007. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: