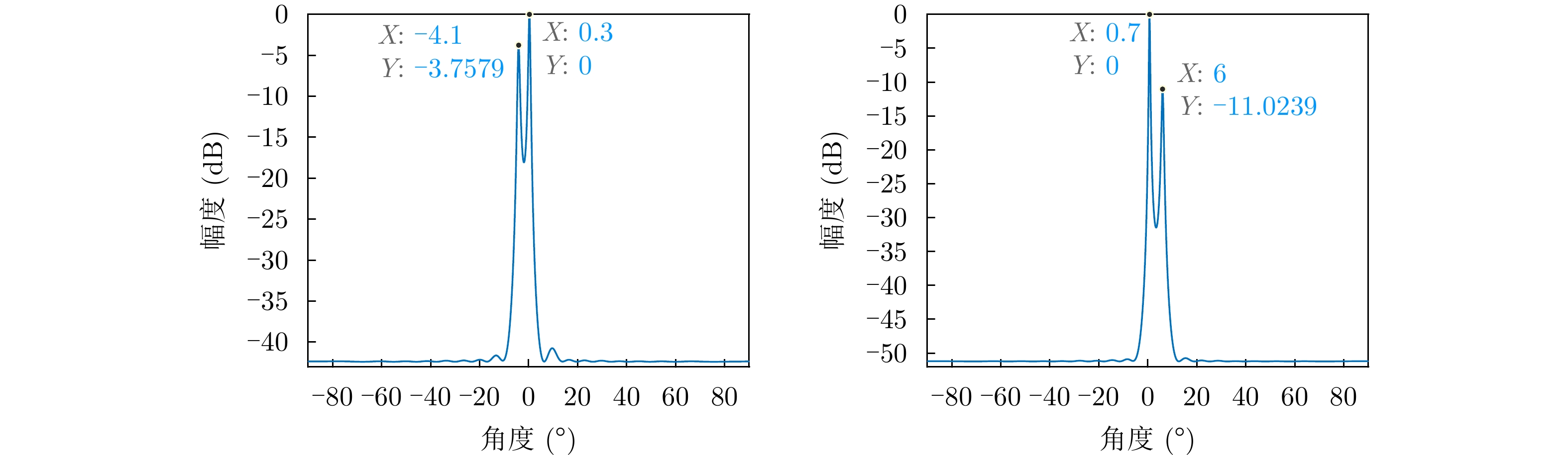
| [1] |
ENGELS F, HEIDENREICH P, ZOUBIR A M, et al. Advances in automotive radar: A framework on computationally efficient high-resolution frequency estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(2): 36–46. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2637700 |
| [2] |
GAMBA J. Fundamentals of Radar Systems[M]. GAMBA J. Radar Signal Processing for Autonomous Driving. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 1–14.
|
| [3] |
LI Xinrong, WANG Xiaodong, YANG Qing, et al. Signal processing for TDM MIMO FMCW millimeter-wave radar sensors[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 167959–167971. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3137387 |
| [4] |
王永良, 丁前军, 李荣锋. 自适应阵列处理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2009.
WANG Yongliang, DING Qianjun, and LI Rongfeng. Adaptive Array Processing[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2009.
|
| [5] |
YARDIBI T, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Source localization and sensing: A nonparametric iterative adaptive approach based on weighted least squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(1): 425–443. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5417172 |
| [6] |
王永良, 陈辉, 彭应宁, 等. 空间谱估计理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004.
WANG Yongliang, CHEN Hui, PENG Yingning, et al. Spatial Spectrum Estimation Theory and Algorithm[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004.
|
| [7] |
YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. A discretization-free sparse and parametric approach for linear array signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(19): 4959–4973. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2339792 |
| [8] |
WU Xiaohuan, ZHU Weiping, and YAN Jun. A toeplitz covariance matrix reconstruction approach for direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(9): 8223–8237. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2695226 |
| [9] |
ZHANG Zhe, WANG Yue, and TIAN Zhi. Efficient two-dimensional line spectrum estimation based on decoupled atomic norm minimization[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 163: 95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.04.024 |
| [10] |
LÜ Mingjiu, MA Jianchao, WEI Xu, et al. Two-dimensional Range-Doppler estimation method for high frequency radar based on matrix atomic norm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(5): 1150–1158. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210479 |
| [11] |
CHANDRASEKARAN V, RECHT B, PARRILO P A, et al. The convex geometry of linear inverse problems[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2012, 12(6): 805–849. doi: 10.1007/s10208-012-9135-7 |
| [12] |
CHEN Xushan, ZHANG Xiongwei, YANG Jibin, et al. How to overcome basis mismatch: From atomic norm to gridless compressive sensing[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(3): 335–346. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150539 |
| [13] |
TANG Gongguo, BHASKAR N B, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465–7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451 |
| [14] |
BHASKAR B N, TANG Gongguo, and RECHT B. Atomic norm denoising with applications to line spectral estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(23): 5987–5999. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2273443 |
| [15] |
YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. On gridless sparse methods for line spectral estimation from complete and incomplete data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3139–3153. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2420541 |
| [16] |
YANG Zai, LI Jian, STOICA P, et al. Sparse Methods for Direction-of-arrival Estimation[M]. CHELLAPPA R and THEODORIDIS S. Academic Press Library in Signal Processing, Volume 7: Array, Radar and Communications Engineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2018: 509–581. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-811887-0.00011-0. |
| [17] |
HUANG Yan, ZHANG Hui, GUO Kunpeng, et al. Density-based vehicle detection approach for automotive millimeter-wave radar[C]. The IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology (ICEICT), Shenzhen, China, 2020: 534–537.
|
| [18] |
BARAL A B and TORLAK M. Joint Doppler frequency and direction of arrival estimation for TDM MIMO automotive radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(4): 980–995. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3073572 |
| [19] |
HALPERN D, WILSON H B, and TURCOTTE L H. Chapter 6: Fourier Series and the Fast Fourier Transform[M]. WILSON H B, TURCOTTE L H, and HALPERN D. Advanced Mathematics and Mechanics Applications Using MATLAB. 3rd ed. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2002.
|
| [20] |
XU Zhihuo, BAKER C J, and POONI S. Range and Doppler cell migration in wideband automotive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5527–5536. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2912852 |
| [21] |
ZHAO Chunlei, WANG Yaliang, MAO Xingpeng, et al. Compressive sensing based two-dimensional DOA estimation for high frequency surface wave radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(4): 733–741. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.04.07 |
| [22] |
YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and STOICA P. Vandermonde decomposition of multilevel toeplitz matrices with application to multidimensional super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(6): 3685–3701. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2553041 |
| [23] |
RODRÍGUEZ A F, DE SANTIAGO RODRIGO L, GUILLÉN E L, et al. Coding Prony’s method in MATLAB and applying it to biomedical signal filtering[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2018, 19(1): 451. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2473-y |
| [24] |
吕明久, 陈文峰, 徐芳, 等. 基于原子范数最小化的步进频率ISAR一维高分辨距离成像方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2267–2275. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200501LÜ Mingjiu, CHEN Wenfeng, XU Fang, et al. One dimensional high resolution range imaging method of stepped frequency ISAR based on atomic norm minimization[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2267–2275. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200501 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

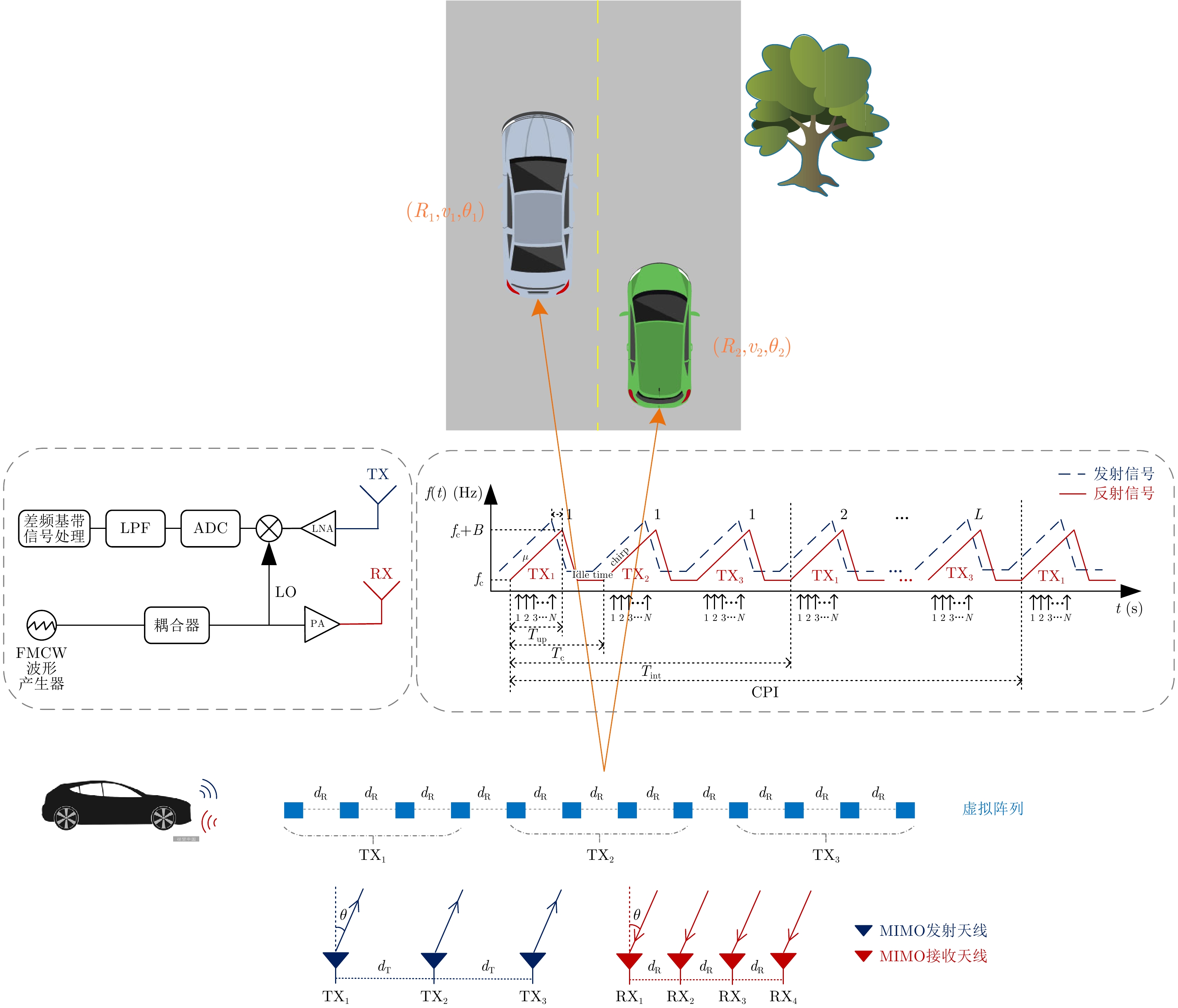



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: