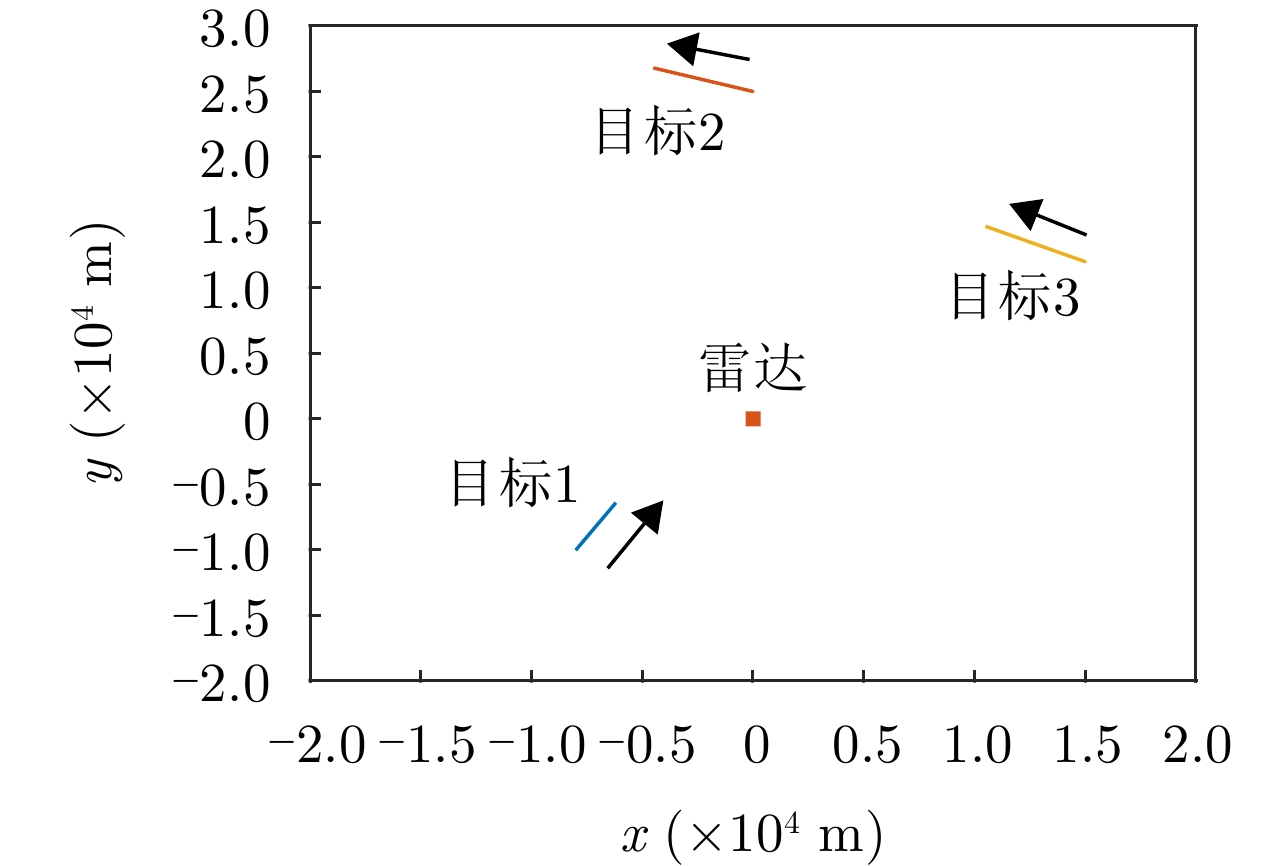
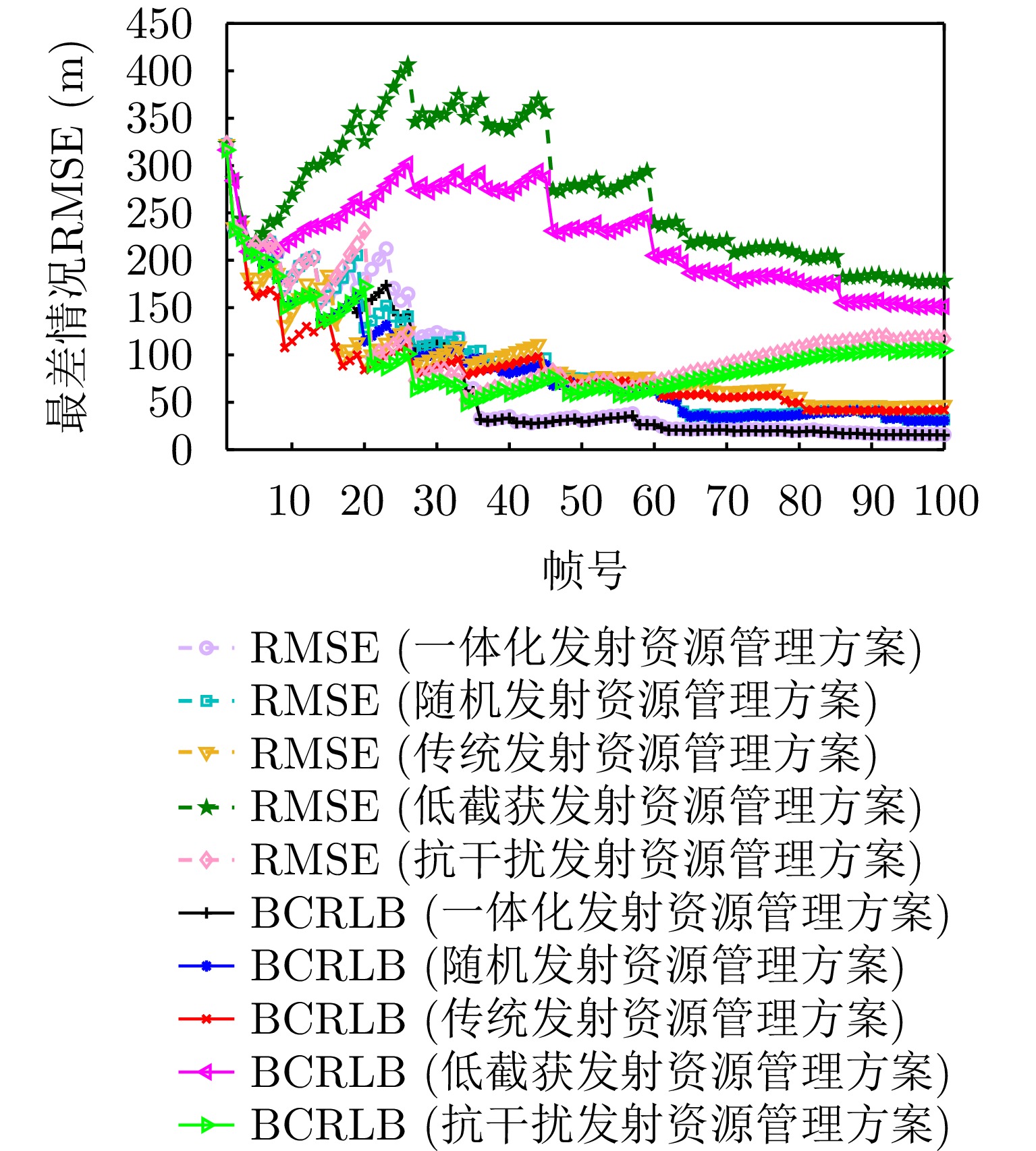
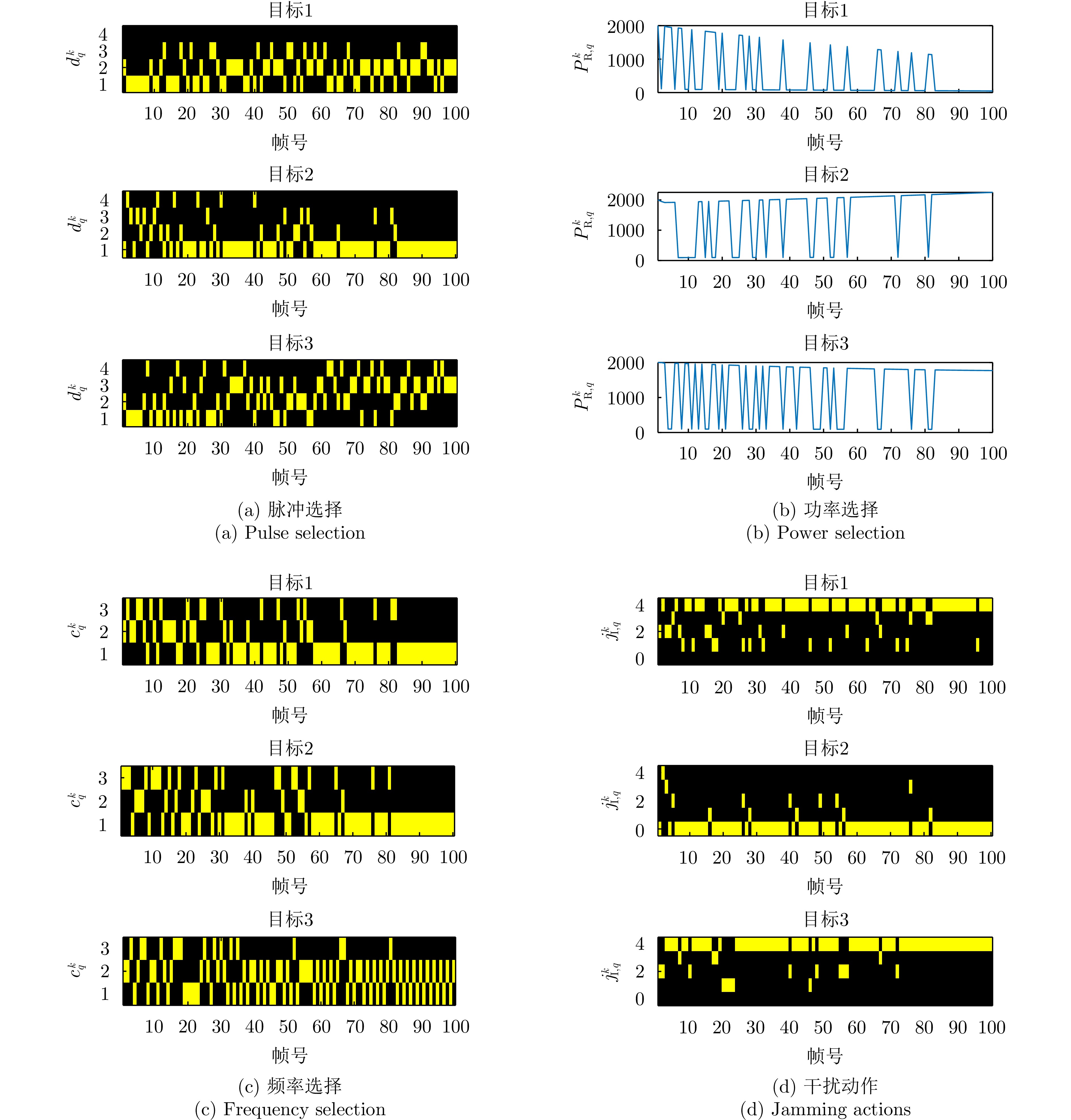
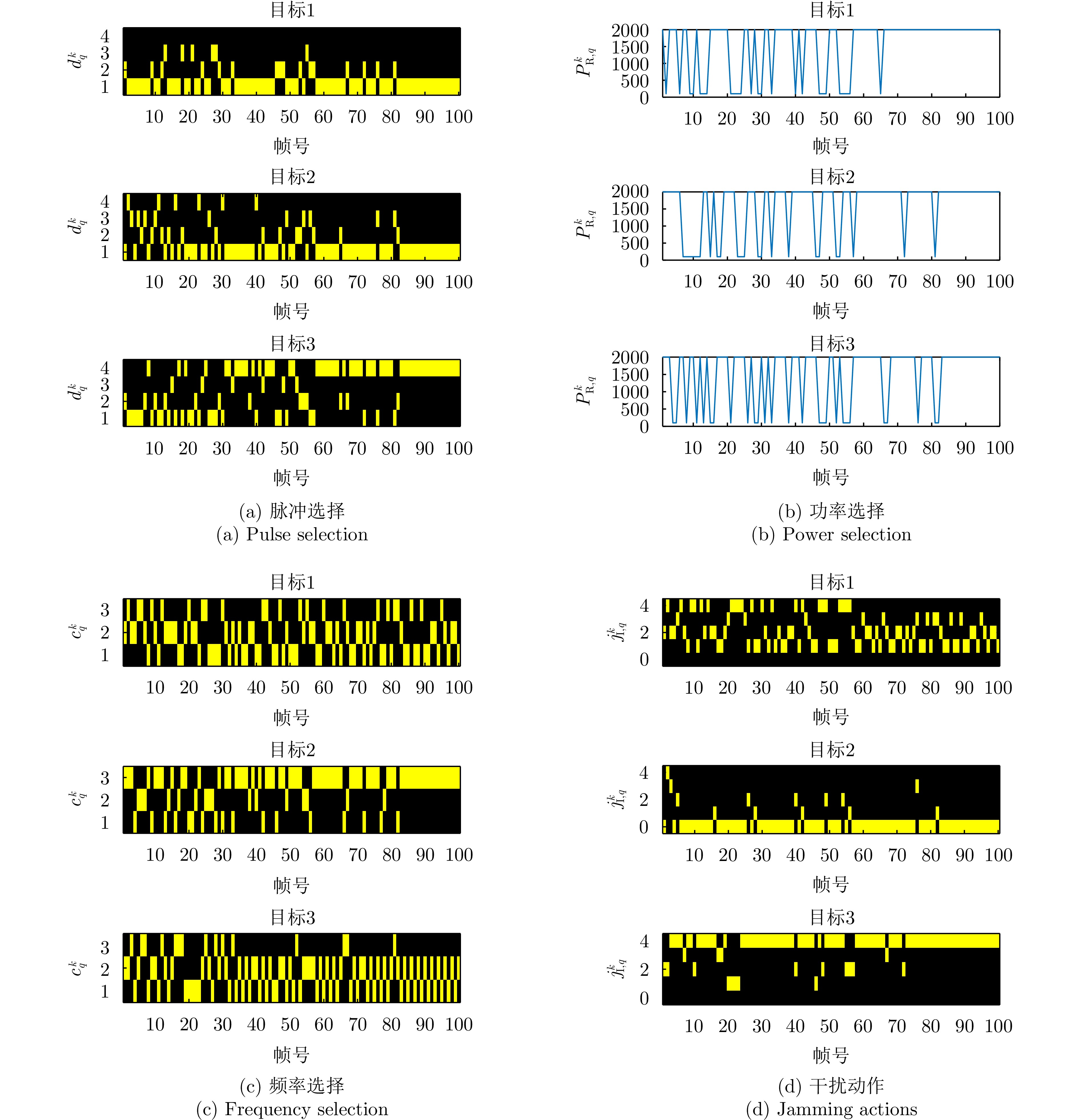
| [1] |
MORELANDE M R, KREUCHER C M, and KASTELLA K. A Bayesian approach to multiple target detection and tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(5): 1589–1604. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.889470. |
| [2] |
BLACKMAN S S. Multiple-Target Tracking with Radar Applications[M]. Dedham: Artech House, 1986: 1–449.
|
| [3] |
STONE L D, STREIT R L, CORWIN T L, et al. Bayesian Multiple Target Tracking[M]. 2nd ed. Boston: Artech House, 2014: 107–160.
|
| [4] |
HUE C, LE CADRE J P, and PÉREZ P. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multiple target tracking and data fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 309–325. doi: 10.1109/78.978386. |
| [5] |
WANG Xiangli, YI Wei, XIE Mingchi, et al. A joint beam and dwell time allocation strategy for multiple target tracking based on phase array radar system[C]. 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.23919/ICIF.2017.8009856. |
| [6] |
戴金辉, 严俊坤, 王鹏辉, 等. 基于目标容量的网络化雷达功率分配方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2688–2694. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200873. DAI Jinhui, YAN Junkun, WANG Penghui, et al. Target capacity based power allocation scheme in radar network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2688–2694. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200873. |
| [7] |
YUAN Ye, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Joint tracking sequence and dwell time allocation for multi-target tracking with phased array radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 192: 108374. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108374. |
| [8] |
NARYKOV A S, KRASNOV O A, and YAROVOY A. Algorithm for resource management of multiple phased array radars for target tracking[C]. 2013 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, Istanbul, Turkey, 2013: 1258–1264.
|
| [9] |
YUAN Ye, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Robust power allocation for resource-aware multi-target tracking with colocated MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 443–458. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047519. |
| [10] |
SCHLEHER D C. Electronic Warfare in the Information Age[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1999: 1–60.
|
| [11] |
SHI Chenguang, WANG Yijie, SALOUS S, et al. Joint transmit resource management and waveform selection strategy for target tracking in distributed phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2762–2778. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3138869. |
| [12] |
ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, ZHANG Qiliang, et al. Joint resource optimization for a distributed MIMO radar when tracking multiple targets in the presence of deception jamming[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 200: 108641. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2022.108641. |
| [13] |
AILIYA, YI Wei, and VARSHNEY P K. Adaptation of frequency hopping interval for radar anti-jamming based on reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(12): 12434–12449. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3197425. |
| [14] |
LI Kang, JIU Bo, WANG Penghui, et al. Radar active antagonism through deep reinforcement learning: A way to address the challenge of mainlobe jamming[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 186: 108130. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108130. |
| [15] |
ZHANG Peng, YAN Junkun, PU Wenqiang, et al. Multi-dimensional resource management scheme for multiple target tracking under dynamic electromagnetic environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 2377–2393. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3390119. |
| [16] |
YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, JIU Bo, et al. Simultaneous multibeam resource allocation scheme for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3110–3122. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2417504. |
| [17] |
YAN Junkun, LIU Hongwei, PU Wenqiang, et al. Joint beam selection and power allocation for multiple target tracking in netted colocated MIMO radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(24): 6417–6427. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2607147. |
| [18] |
LI Nengjing and ZHANG Yiting. A survey of radar ECM and ECCM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(3): 1110–1120. doi: 10.1109/7.395232. |
| [19] |
VAN TREES H L. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory, Part III: Radar-Sonar Signal Processing and Gaussian Signals in Noise[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2001: 294–307.
|
| [20] |
SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008: 313–370.
|
| [21] |
SUKHAREVSKY O I, VASILETS V A, and ZALEVSKY G S. Electromagnetic wave scattering by aerial and ground radar objects[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, USA, 2015: 162–167. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7130989. |
| [22] |
BERTSEKAS D P. Reinforcement Learning and Optimal Control[M]. Nashua: Athena Scientific, 2019: 1–40.
|
| [23] |
SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018: 37–58.
|
| [24] |
NERI F. Introduction to Electronic Defense Systems[M]. 2nd ed. Henderson: SciTech Publishing, 2006: 259–368.
|
| [25] |
STINCO P, GRECO M, GINI F, et al. Cognitive radars in spectrally dense environments[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(10): 20–27. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150193. |
| [26] |
SELVI E, BUEHRER R M, MARTONE A, et al. Reinforcement learning for adaptable bandwidth tracking radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(5): 3904–3921. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2987443. |
| [27] |
KOCHENDERFER M J, WHEELER T A, and WRAY K H. Algorithms for Decision Making[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2022: 311–326.
|
| [28] |
YAN Junkun, JIU Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Joint cluster and power allocation algorithm for multiple targets tracking in multistatic radar systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(8): 1875–1881. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01470. |
| [29] |
LISI F, FORTUNATI S, GRECO M S, et al. Enhancement of a state-of-the-art RL-based detection algorithm for massive MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(6): 5925–5931. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3168033. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: