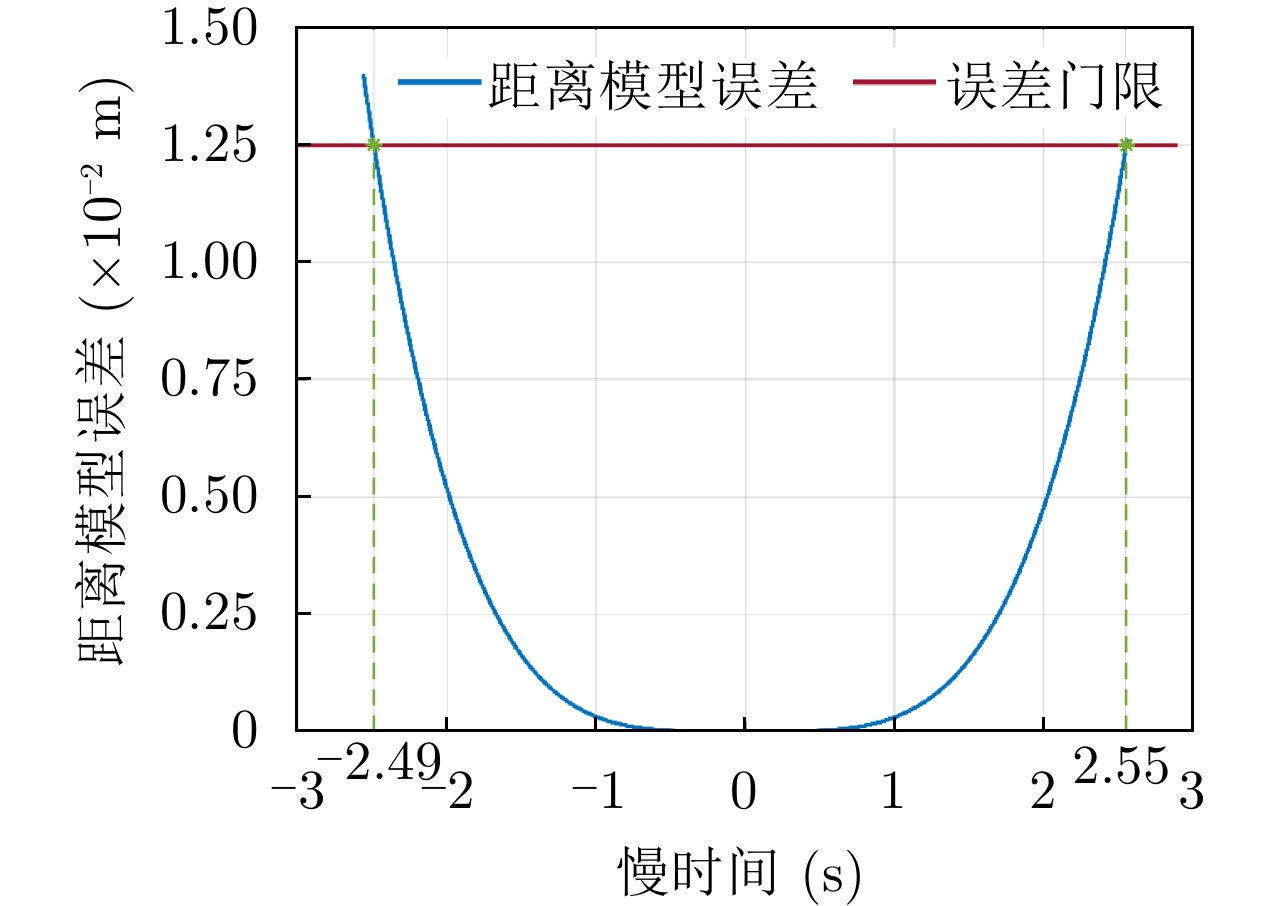
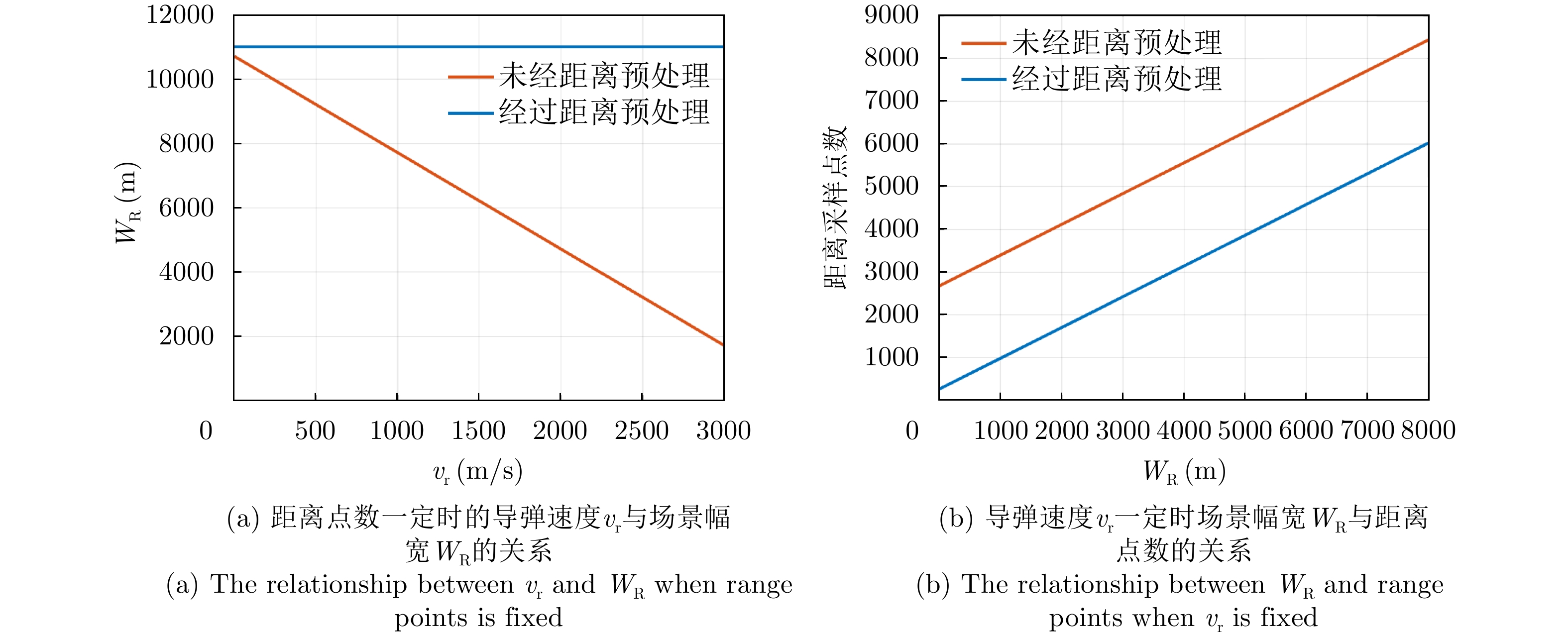
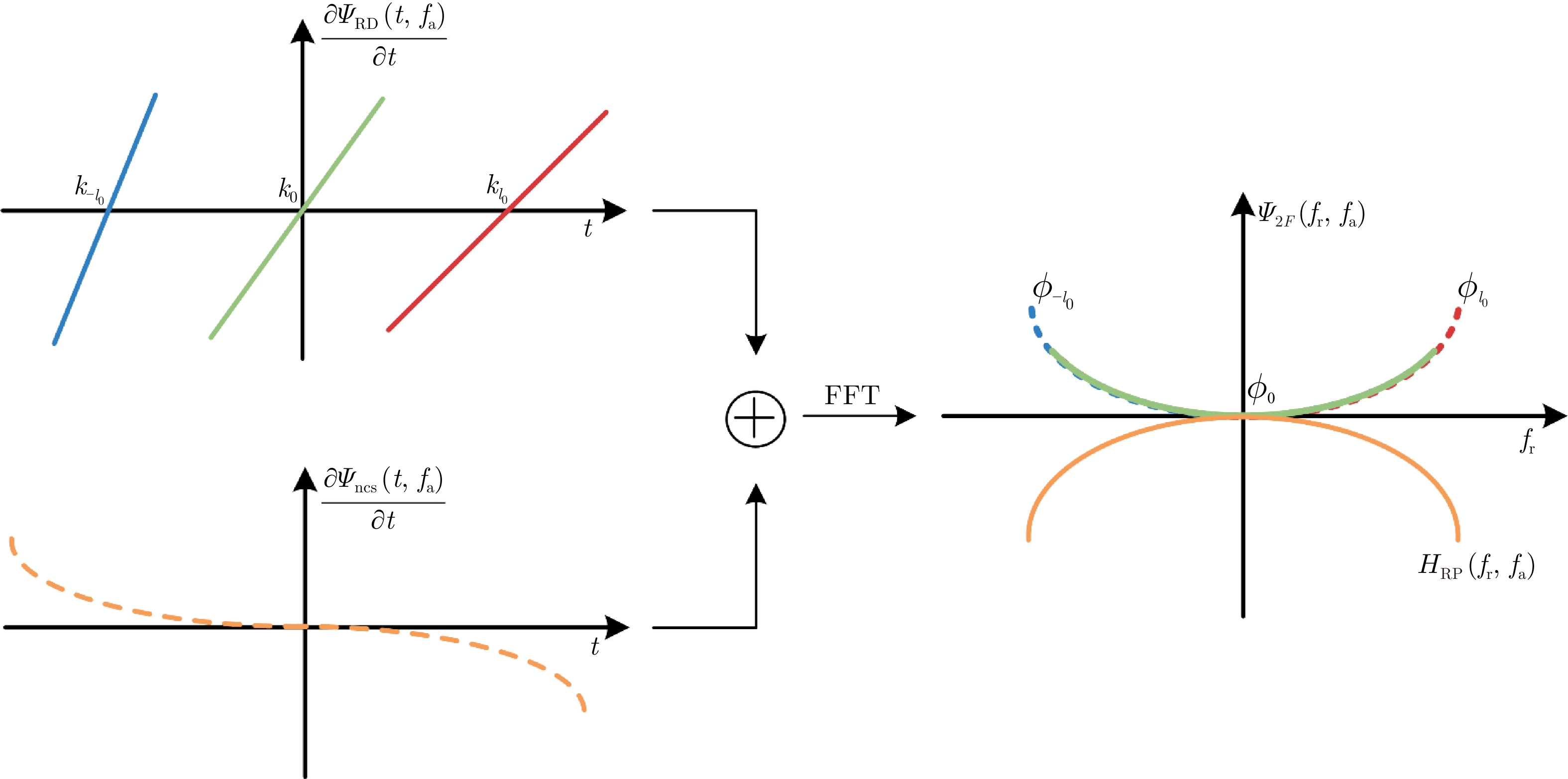
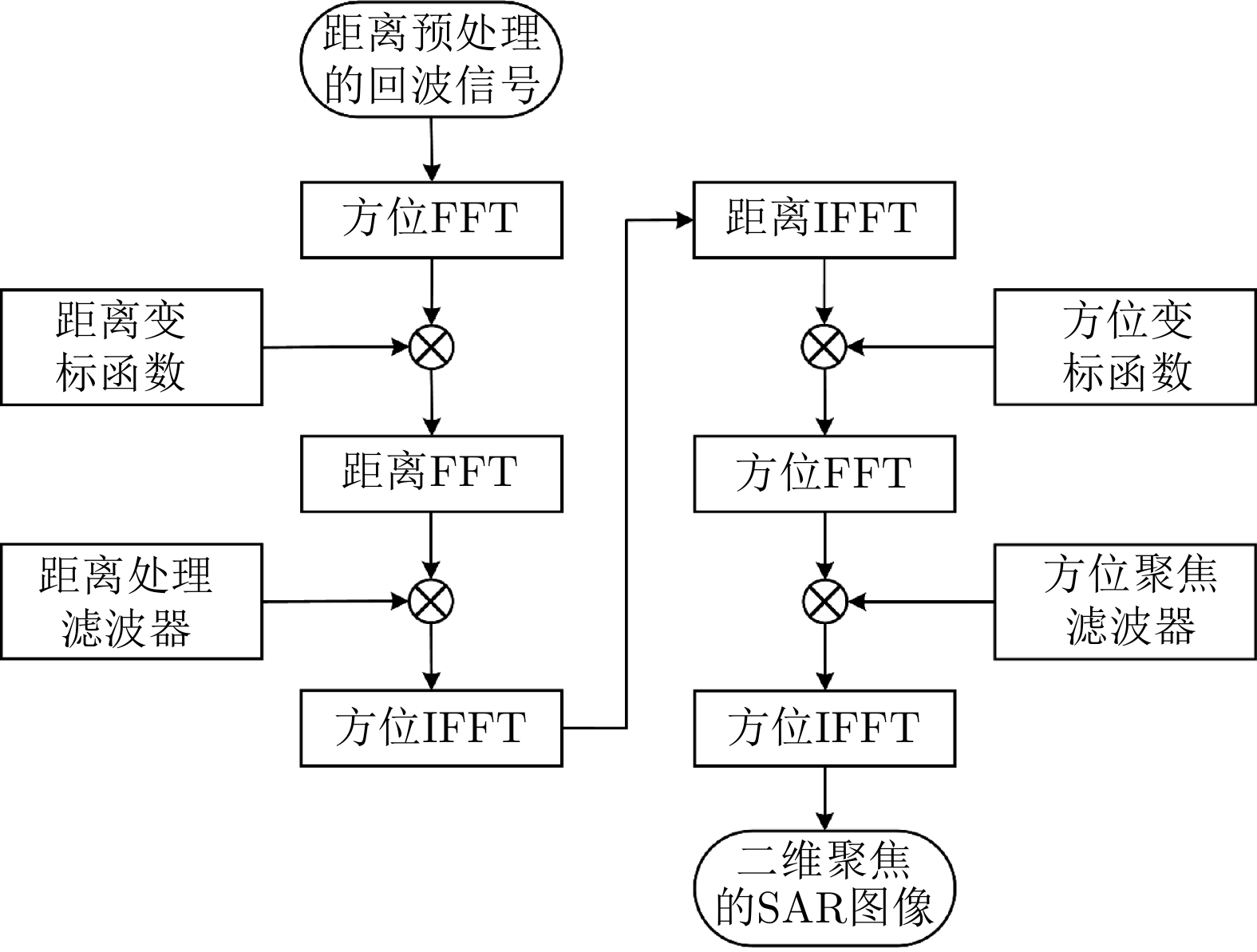
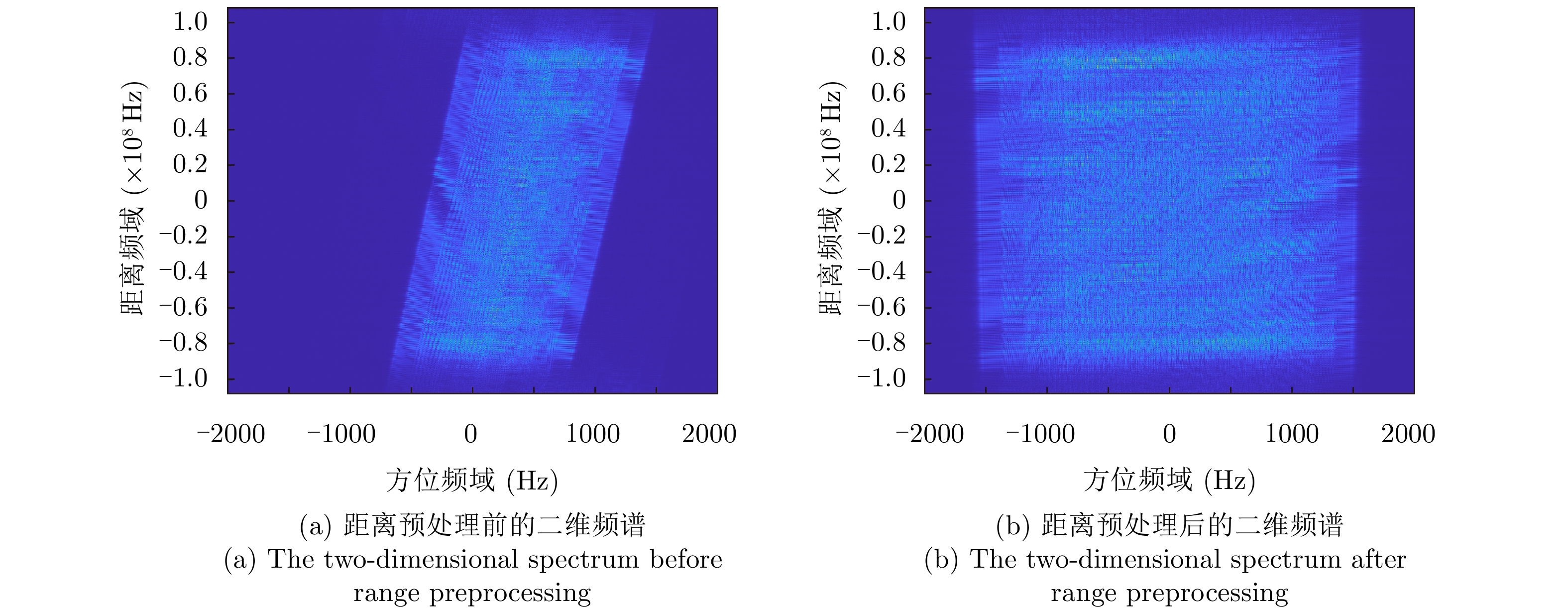
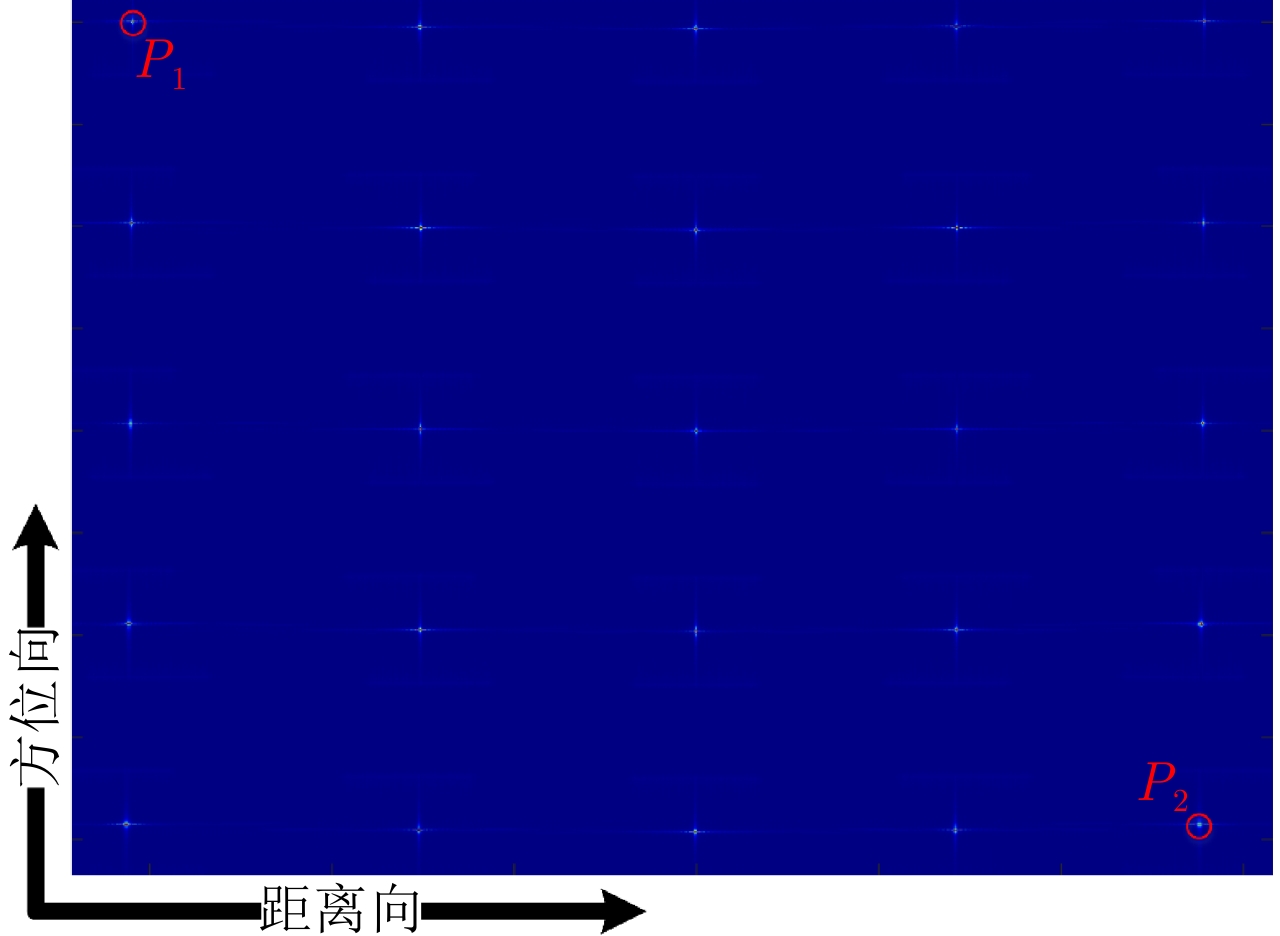
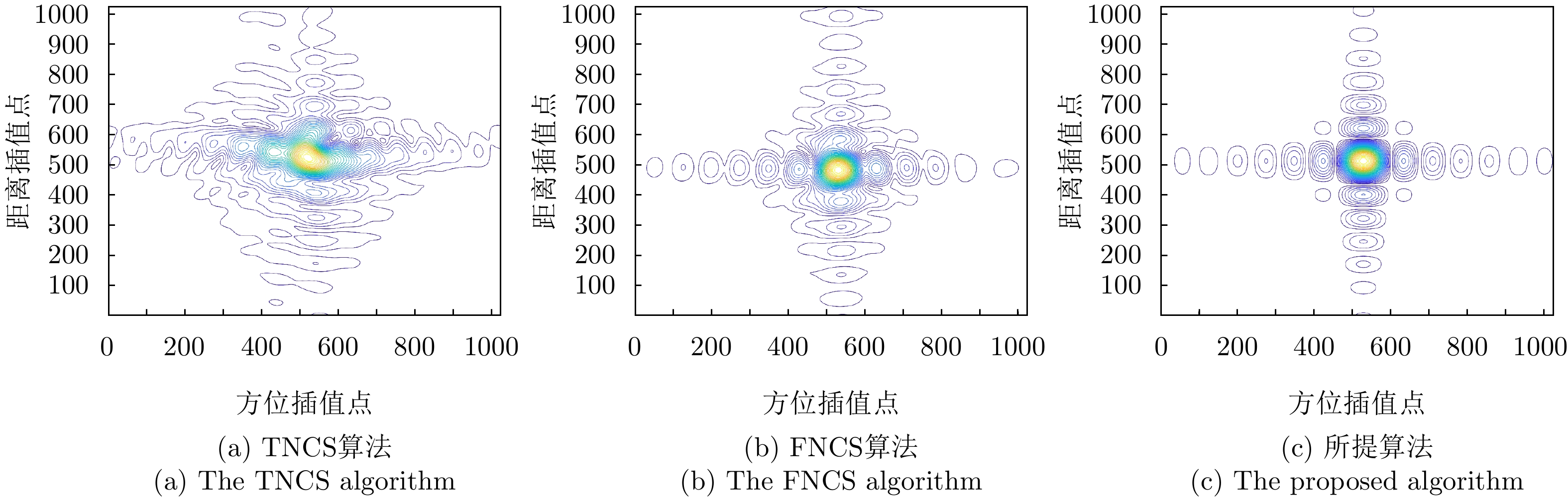
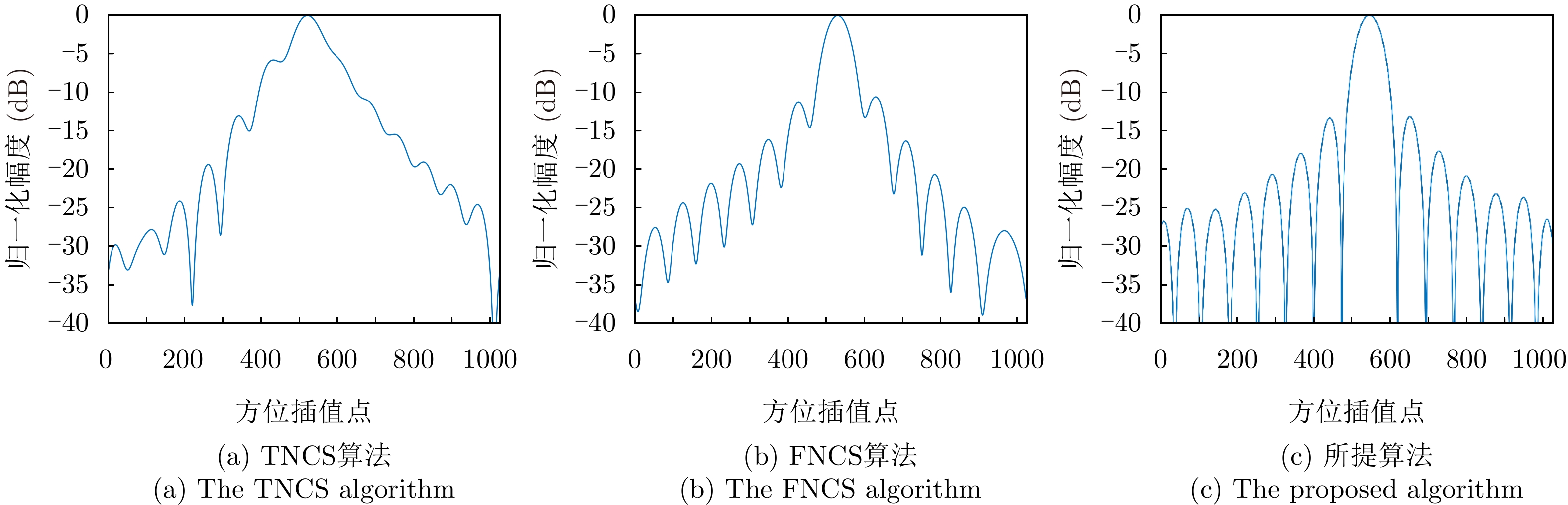
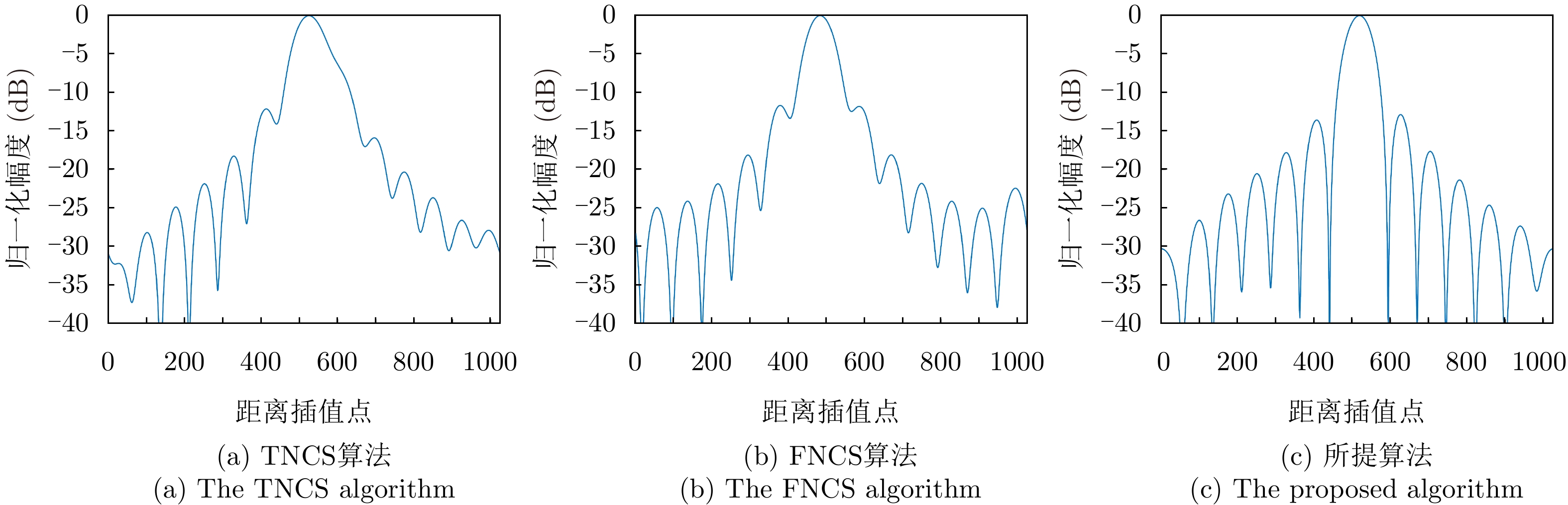
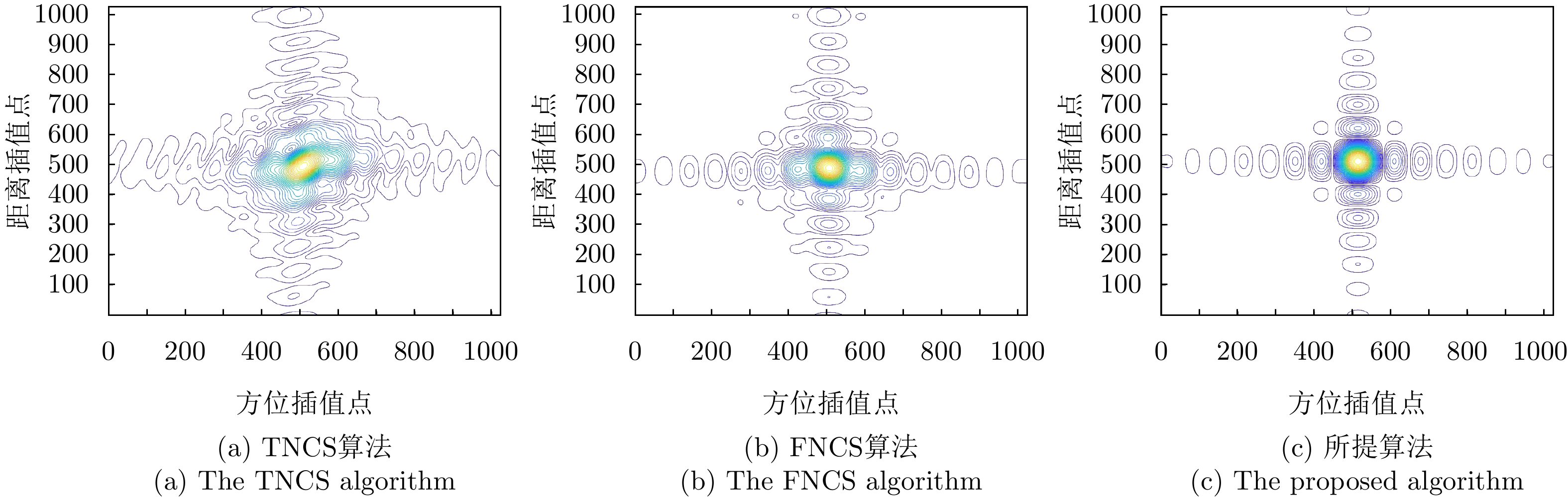
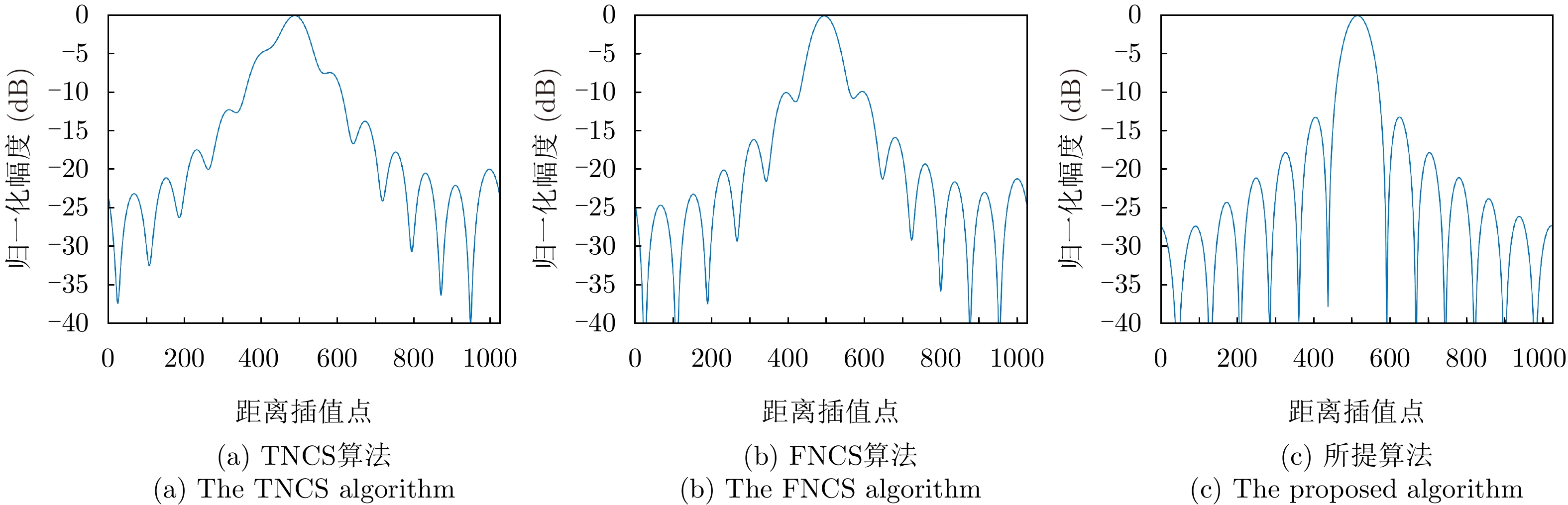
| [1] |
CHEN Hongmeng, LI Yachao, GAO Wenquan, et al. Bayesian forward-looking superresolution imaging using Doppler deconvolution in expanded beam space for high-speed platform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107717 |
| [2] |
李亚超, 王家东, 张廷豪, 等. 弹载雷达成像技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Present situation and prospect of missile-borne radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119 |
| [3] |
林春辉. 单基/双基SAR成像若干关键问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2019.
LIN Chunhui. Study on some imaging issues of monostatic and bistatic SAR[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2019.
|
| [4] |
NEO Y L, WONG F H, and CUMMING I G. Processing of azimuth-invariant bistatic SAR data using the range Doppler algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1): 14–21. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.909090 |
| [5] |
刘婵. 双基地前视SAR频域成像算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015.
LIU Chan. Study on frequency-domain imaging algorithms for bistatic forward-looking SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015.
|
| [6] |
CHEN Si, YUAN Yue, ZHANG Shuning, et al. A new imaging algorithm for forward-looking missile-borne bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(4): 1543–1552. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2507260 |
| [7] |
ZHANG Qianghui, WU Junjie, SONG Yue, et al. Bistatic-range-Doppler-aperture wavenumber algorithm for forward-looking spotlight SAR with stationary transmitter and maneuvering receiver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2080–2094. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3004726 |
| [8] |
PU Wei, LI Wenchao, LV Youxin, et al. An extended omega-K algorithm with integrated motion compensation for bistatic forward-looking SAR[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 1291–1295.
|
| [9] |
FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. An extended fast factorized back projection algorithm for missile-borne bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(6): 2724–2734. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2828238 |
| [10] |
LI Yachao, XU Gaotian, ZHOU Song, et al. A novel CFFBP algorithm with noninterpolation image merging for bistatic forward-looking SAR focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–16. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3162230 |
| [11] |
DESAI M D and JENKINS W K. Convolution backprojection image reconstruction for spotlight mode synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1992, 1(4): 505–517. doi: 10.1109/83.199920 |
| [12] |
XU Gaotian, ZHOU Song, YANG Lei, et al. Efficient fast time-domain processing framework for airborne bistatic SAR continuous imaging integrated with data-driven motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5208915. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3099204 |
| [13] |
AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, HE Zhiwei, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne multichannel bistatic SAR imaging using weighted fast factorized backprojection method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1590–1594. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2902036 |
| [14] |
蒲巍. 机载双基地前视SAR运动补偿方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2018.
PU Wei. Research on airborne bistatic forward-looking SAR motion compensation[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018.
|
| [15] |
QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, and DING Chibiao. Some reflections on bistatic SAR of forward-looking configuration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 735–739. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2004506 |
| [16] |
WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for translational invariant bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 2013, E96.B(2): 605–612. doi: 10.1587/transcom.E96.B.605 |
| [17] |
WU Junjie, YANG Jianyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. Focusing bistatic forward-looking SAR using Chirp Scaling algorithm[C]. 2011 IEEE RadarCon, Kansas City, USA, 2011: 1036–1039. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960693. |
| [18] |
QI C D, SHI X M, BIAN M M, et al. Focusing forward-looking bistatic SAR data with chirp scaling[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(3): 206–207. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.3978 |
| [19] |
WU Junjie, PU Wei, HUANG Yulin, et al. Bistatic forward-looking SAR focusing using ω-k based on spectrum modeling and optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(11): 4500–4512.
|
| [20] |
ZHANG Xiaohu, GU Hong, and SU Weimin. Focusing bistatic forward-looking SAR images use omega-k algorithm based on modified hyperbolic approximating[C]. 2019 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCAIS46528.2019.9074596. |
| [21] |
张强辉. 高速机动平台双基前视SAR成像方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019.
ZHANG Qianghui. Imaging method research for bistatic forward-looking SAR mounted on high-speed maneuvering platform[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019.
|
| [22] |
LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, MEI Haiwen, et al. Focusing translational-variant bistatic forward-looking SAR data using the modified omega-K algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5203916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3063780 |
| [23] |
ZENG Tao, WANG Rui, LI Feng, et al. A modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR based on series reversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3108–3118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219057 |
| [24] |
SONG Xuan, LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Focusing high-maneuverability bistatic forward-looking SAR using extended azimuth nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5240814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3228803 |
| [25] |
陈溅来, 熊毅, 徐刚, 等. 基于子图像变标的非线性轨迹SAR成像及其自聚焦方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1098–1109. doi: 10.12000/JR22171CHEN Jianlai, XIONG Yi, XU Gang, et al. Nonlinear trajectory synthetic aperture radar imaging and autofocus algorithm based on sub-image nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1098–1109. doi: 10.12000/JR22171 |
| [26] |
WONG F H, CUMMING I G, and LAM NEO Y. Focusing bistatic SAR data using the nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(9): 2493–2505. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.917599 |
| [27] |
QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, and DING Chibiao. An improved NLCS algorithm with capability analysis for one-stationary BiSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3179–3186. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.921569 |
| [28] |
WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LI Zhongyu, et al. Focusing translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR using keystone transform and extended nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(10): 840. doi: 10.3390/rs8100840 |
| [29] |
MEI Haiwen, LI Yachao, XING Mengdao, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2943743 |
| [30] |
LIANG Mu, SU Weimin, and GU Hong. Focusing high-resolution high forward-looking bistatic SAR with nonequal platform velocities based on keystone transform and modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(3): 901–908. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2877387 |
| [31] |
DING Jiabiao, LI Yachao, LI Ming, et al. Focusing high maneuvering bistatic forward-looking SAR with stationary transmitter using extended keystone transform and modified frequency nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 2476–2492. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3153824 |
| [32] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and ImpleMentation[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005: 225–362.
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and ImpleMentation[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005: 225–362.
|
| [33] |
LI Yanping, ZHANG Zhenhua, XING Mengdao, et al. A novel range migration algorithm for general bistatic SAR imaging based on series reversion and numerical computation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(12): 2800–2804. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00810 |
| [34] |
王谋, 韦顺军, 沈蓉, 等. 基于自学习稀疏先验的三维SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 36–52. doi: 10.12000/JR22101WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHEN Rong, et al. 3D SAR imaging method based on learned sparse prior[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 36–52. doi: 10.12000/JR22101 |
| [35] |
CARDILLO G P. On the use of the gradient to determine bistatic SAR resolution[C]. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation Society, Merging Technologies for the 90’s, Dallas, USA, 1990: 1032–1035.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: