- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 |
SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic Aperture Radar Microwave Vision 3D Imaging Dataset(in English)
DOI: 10.12000/JR21112 CSTR: 32380.14.JR21112
More Information-
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) imaging is one of the leading trends in the development of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technology. The current SAR 3D imaging system mainly includes tomography and array interferometry, both with drawbacks of either long acquisition cycle or too much system complexity. Therefore, a novel framework of SAR microwave vision 3D imaging is proposed, which is to effectively combine the SAR imaging model with various 3D cues contained in SAR microwave scattering mechanism and the perceptual semantics in SAR images, so as to significantly reduce the system complexity, and achieve high-efficiency and low-cost SAR 3D imaging. In order to promote the development of SAR microwave vision 3D imaging theory and technology, a comprehensive SAR microwave vision 3D imaging dataset is planned to be constructed with the support of NSFC major projects. This paper outlines the composition and construction plan of the dataset, and gives detailed composition and information description of the first version of published data and the method of making the dataset, so as to provide some helpful support for SAR community.
-

-
References
[1] MAGGIORI E, TARABALKA Y, CHARPIAT G, et al. Can semantic labeling methods generalize to any city? The Inria aerial image labeling benchmark[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 3226–3229.[2] 季顺平, 魏世清. 遥感影像建筑物提取的卷积神经元网络与开源数据集方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(4): 448–459. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20180206.JI Shunping and WEI Shiqing. Building extraction via convolutional neural networks from an open remote sensing building dataset[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(4): 448–459. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20180206.[3] [4] LE S B, YOKOYA N, HAENSCH R, et al. 2019 IEEE GRSS data fusion contest: Large-scale semantic 3D reconstruction [technical committees][J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2019, 7(4): 33–36. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2949679.[5] ZHANG Guo, QIANG Qiang, LUO Ying, et al. Application of RPC model in orthorectification of spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. The Photogrammetric Record, 2012, 27(137): 94–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-9730.2011.00667.x.[6] ZHANG Guo, FEI Wenbo, LI Zhen, et al. Evaluation of the RPC model for spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering &Remote Sensing, 2010, 76(6): 727–733.[7] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755.[8] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988.[9] WANG Xinlong, ZHANG Rufeng, KONG Tao, et al. SOLOv2: Dynamic, faster and stronger[OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10152v2. 2020.[10] BOLYA D, ZHOU Chong, XIAO Fanyi, et al. YOLACT: Real-time instance segmentation[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 9156–9165.[11] [12] Everingham M, Gool L V, Williams C K I, et al. The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338.[13] ERTIN E, AUSTIN C D, SHARMA S, et al. GOTCHA experience report: Three-dimensional SAR imaging with complete circular apertures[C]. Proceedings of SPIE, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIV, Orlando, USA, 2007: 656802.[14] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090.[15] 卜运成. 阵列干涉SAR定标技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2018: 71–95.BU Yuncheng. Research on calibration technology of array synthetic aperture radar interferometry[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018: 71–95.[16] 崔磊, 仇晓兰, 郭嘉逸, 等. 一种基于误差反向传播优化的多通道SAR相位误差估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 878–885. doi: 10.12000/JR20096.CUI Lei, QIU Xiaolan, GUO Jiayi, et al. Multi-channel phase error estimation method based on an error backpropagation algorithm for a multichannel SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 878–885. doi: 10.12000/JR20096.[17] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Composition of SARMV3D dataset
- Figure 2. Composition of SARMV3D-BIS dataset
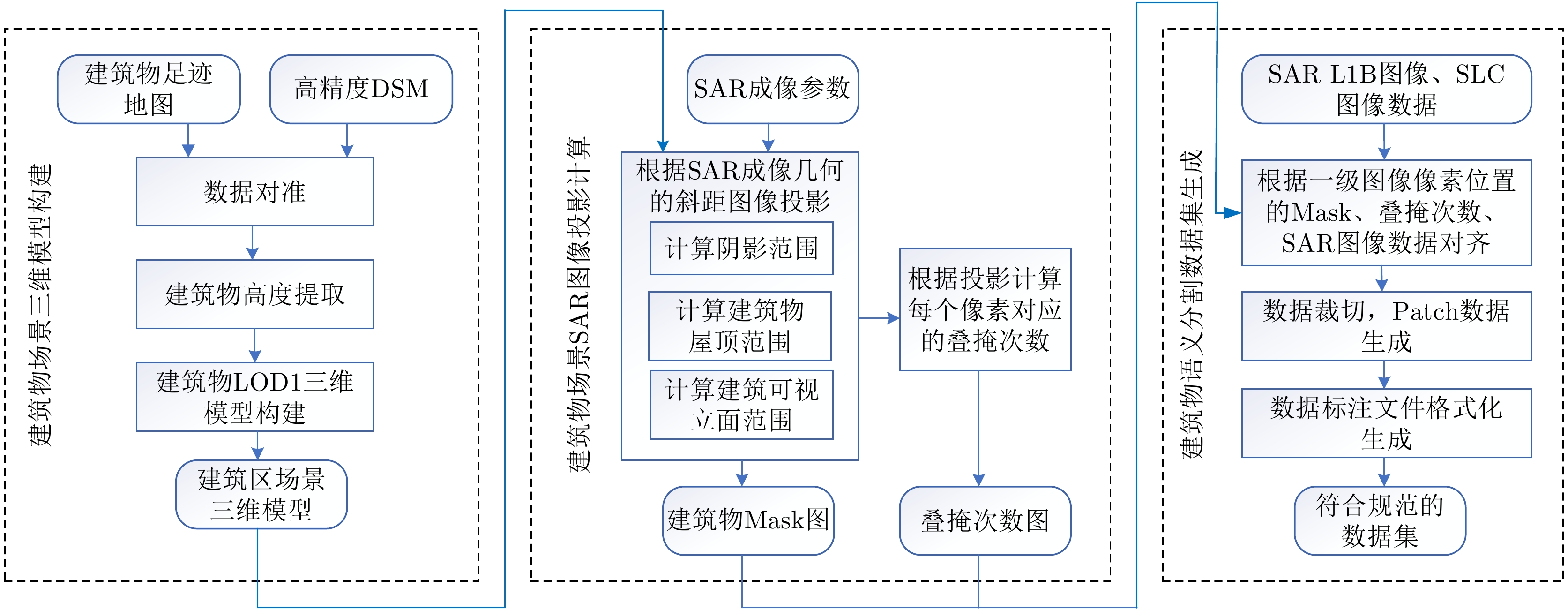
- Figure 3. Flow chart of construction of SARMV3D-BIS dataset
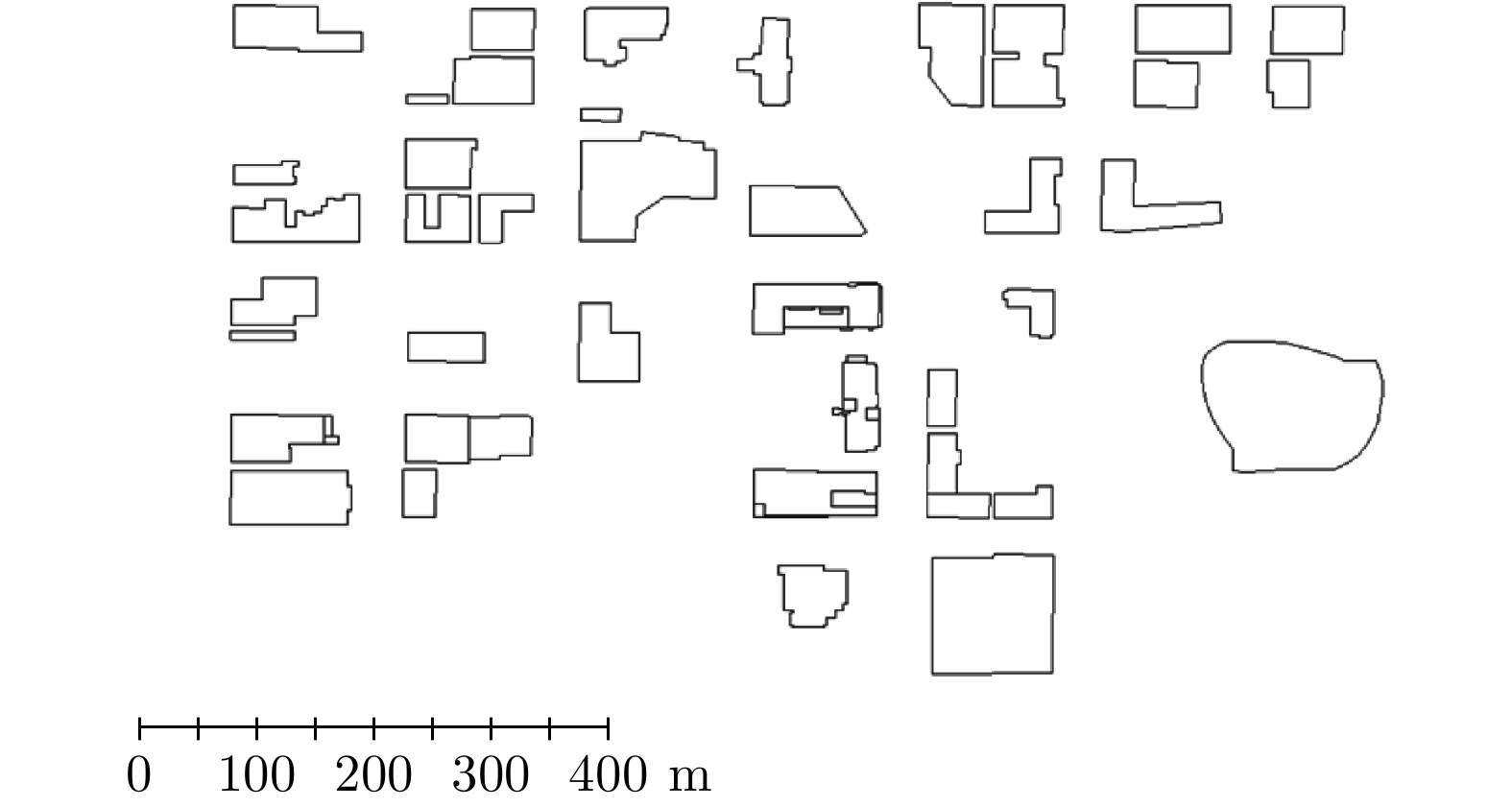
- Figure 4. Extraction of building footprint
- Figure 5. Schematic diagram of building roof
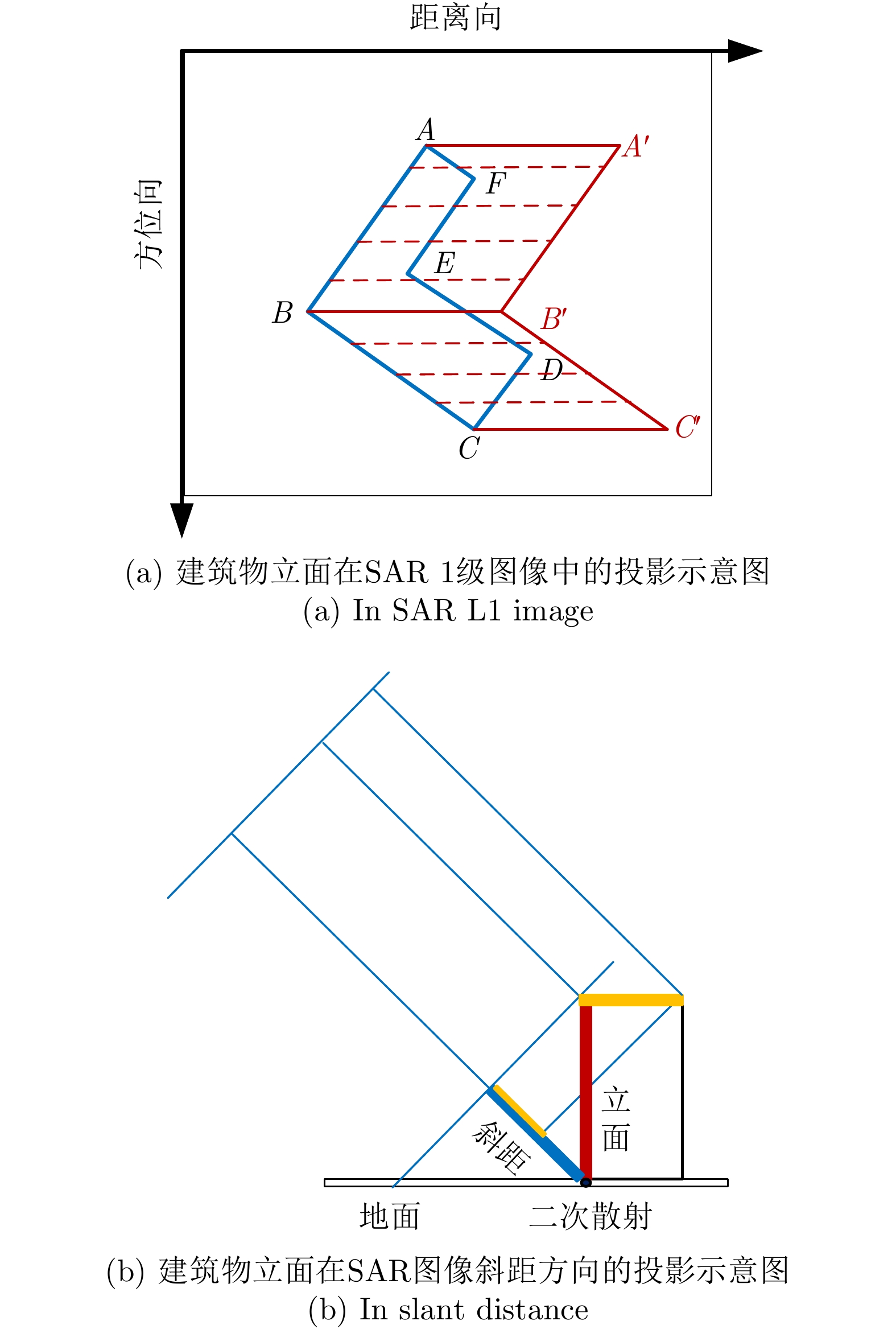
- Figure 6. Projection of building elevation
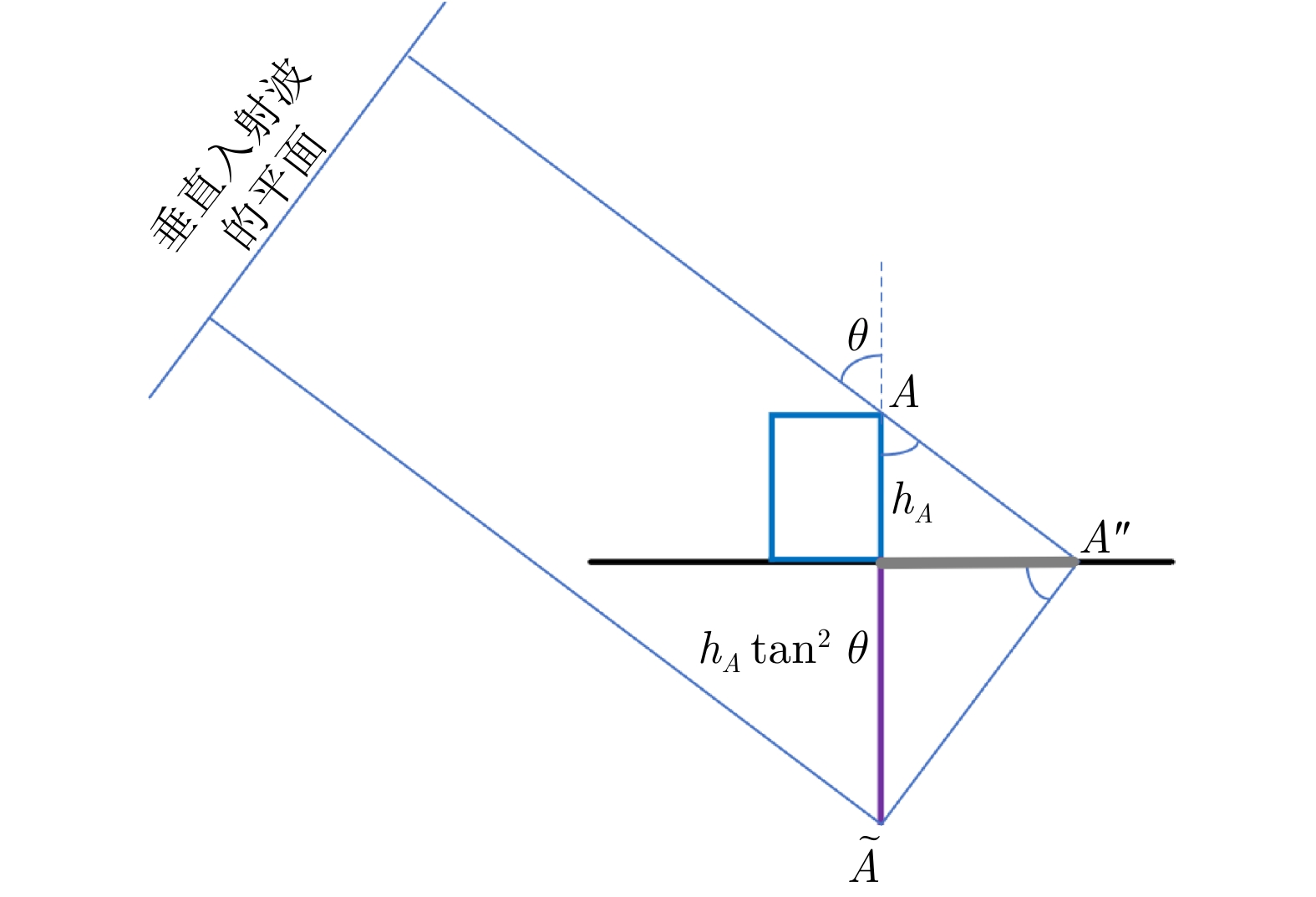
- Figure 7. Schematic diagram of equivalent mirror point
- Figure 8. Projection of building shadow in SAR image
- Figure 9. Projection of multiple buildings in SAR image
- Figure 10. Loss curve in the train process on the SARMV3D-BIS 1.0(S) validation set by using Mask RCNN
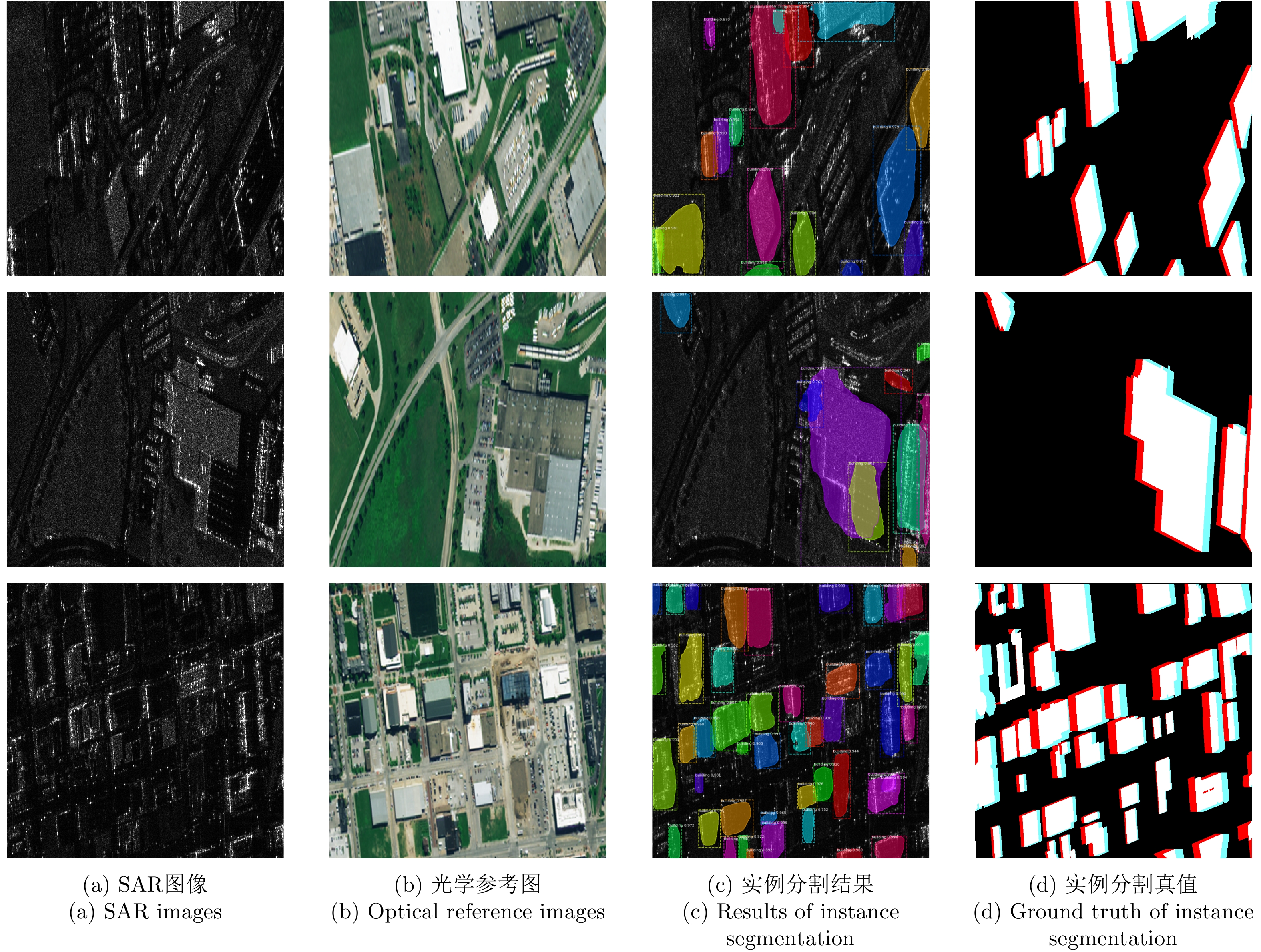
- Figure 11. Results of instance segmentation on the SARMV3D-BIS 1.0(S) validation set by using Mask RCNN
- Figure 12. Amplitude image of GOTCHA dataset
- Figure 13. Array InSAR
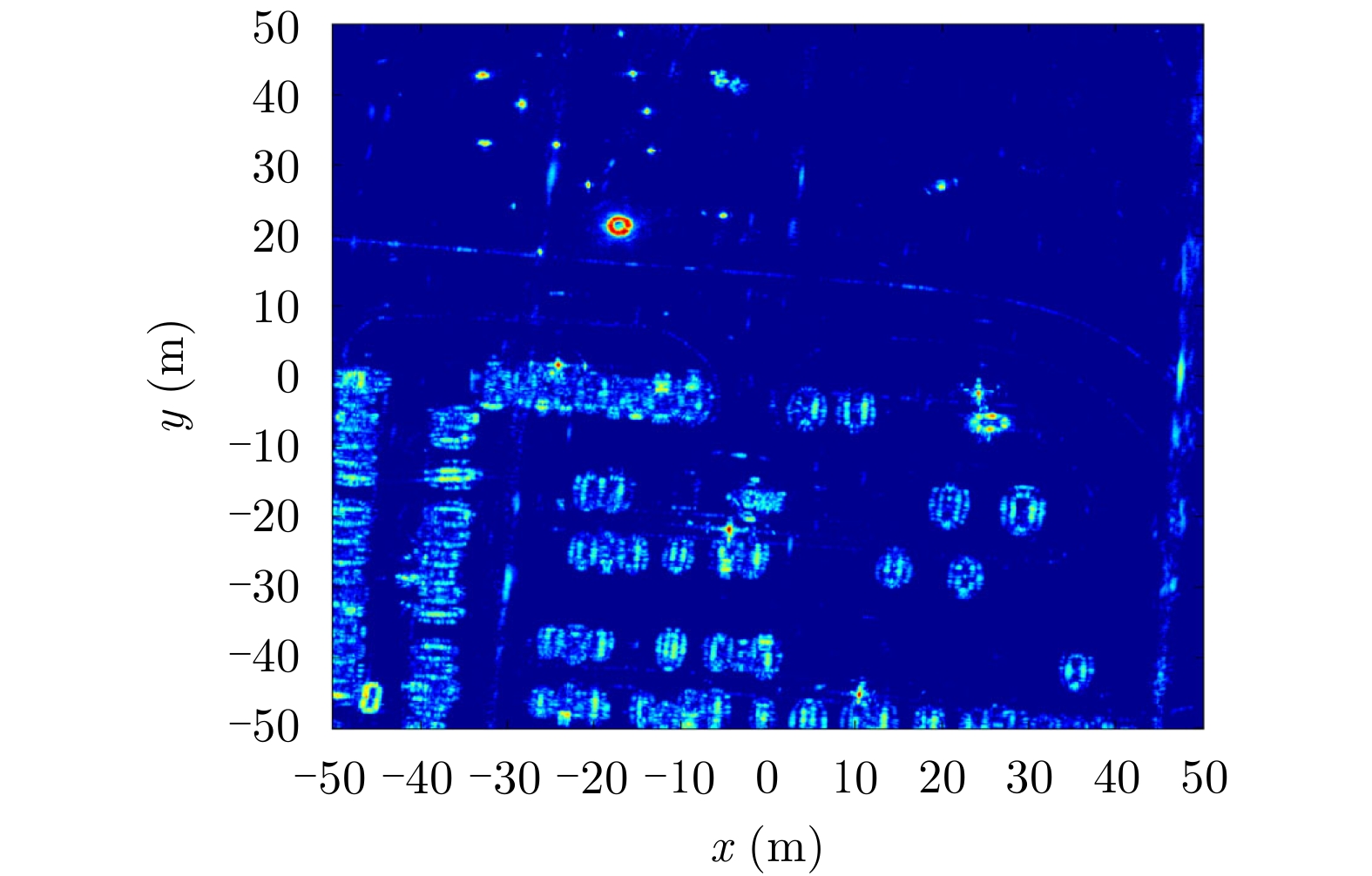
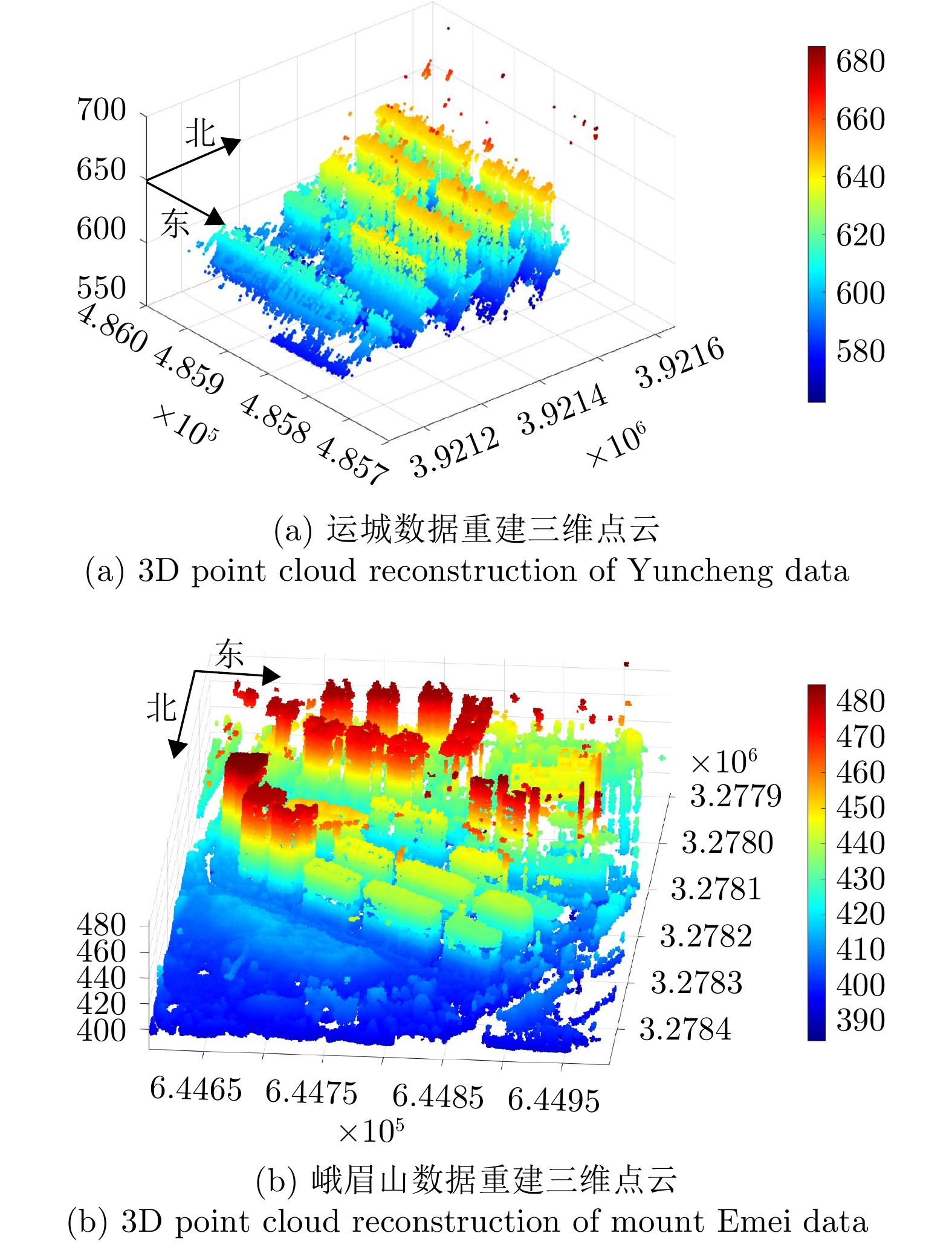
- Figure 14. Data of Yuncheng area
- Figure 15. Data of mount Emei area
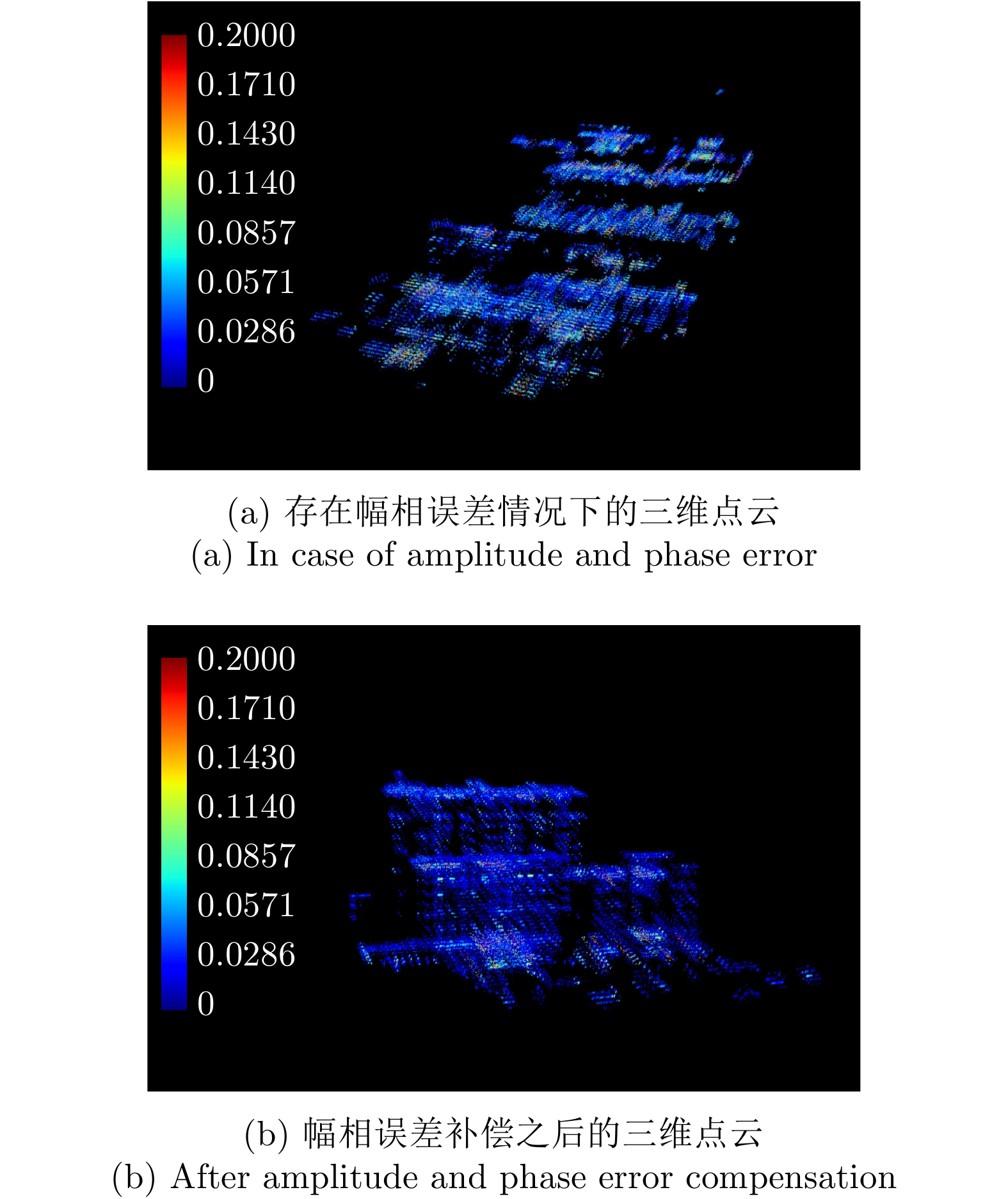
- Figure 16. Comparison of 3D point cloud results
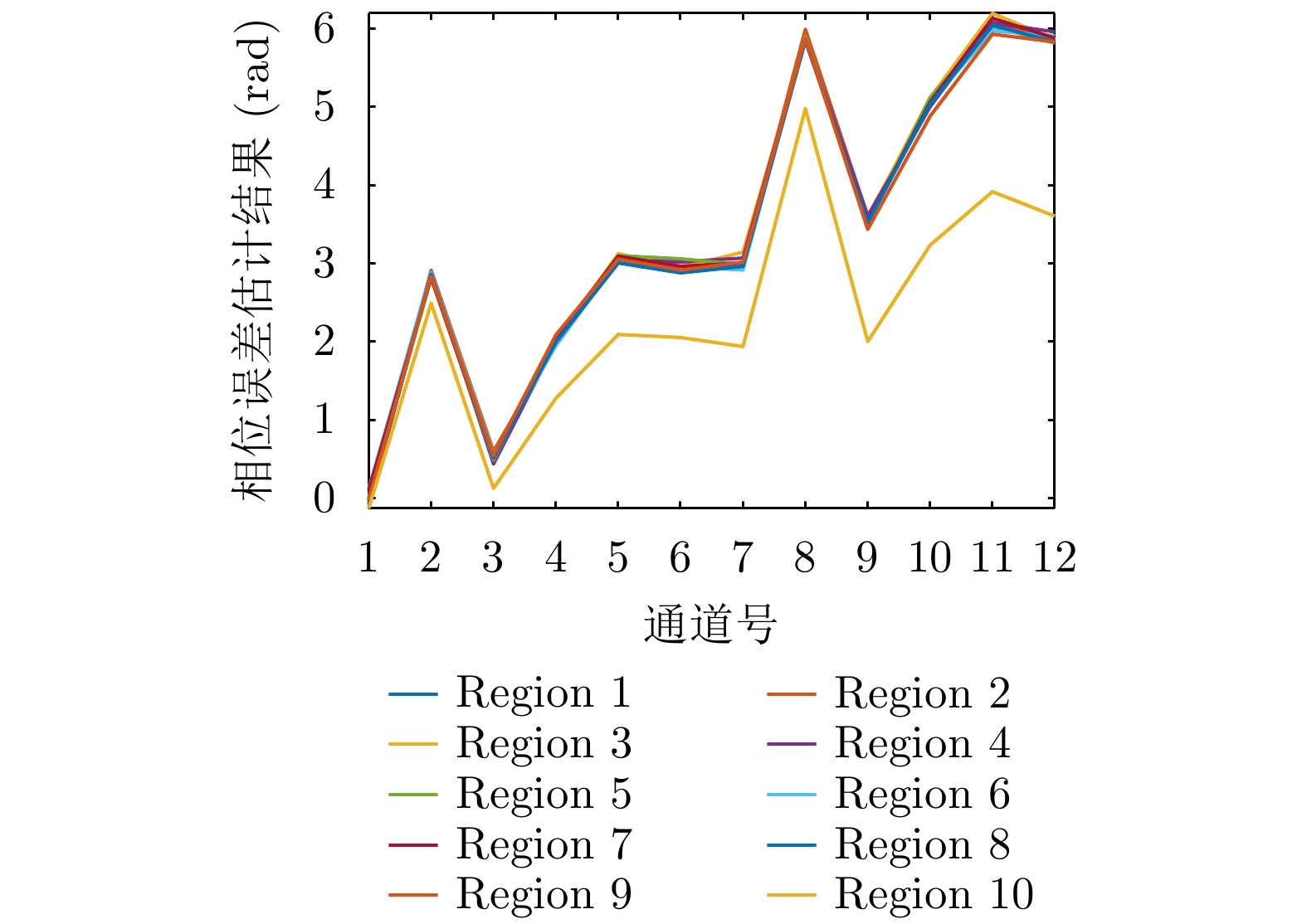
- Figure 17. Results of phase error estimation between channels
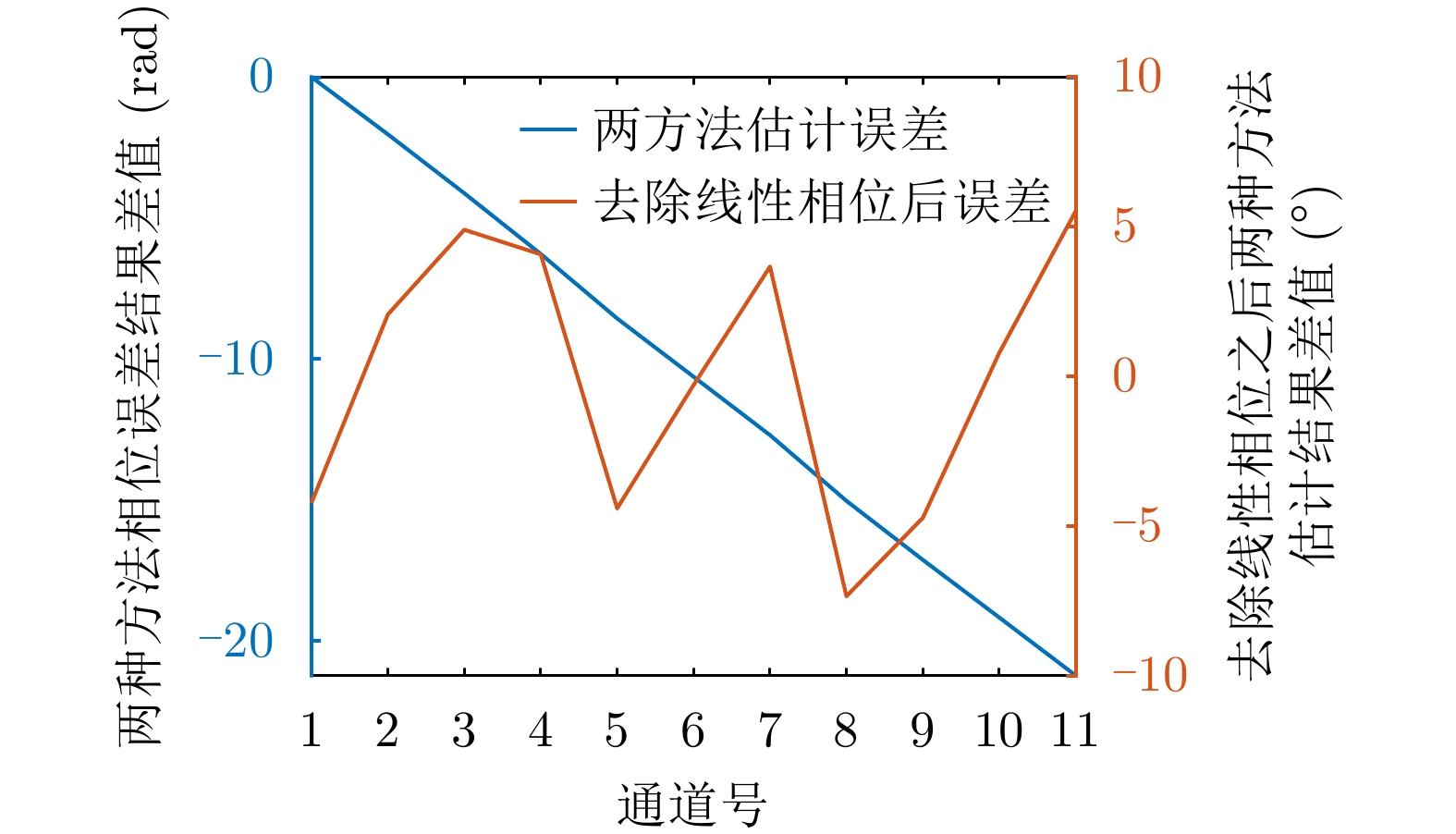
- Figure 18. Comparison results of two phase estimation methods
- Figure 19. 3D imaging results of SARMV3D Imaging dataset
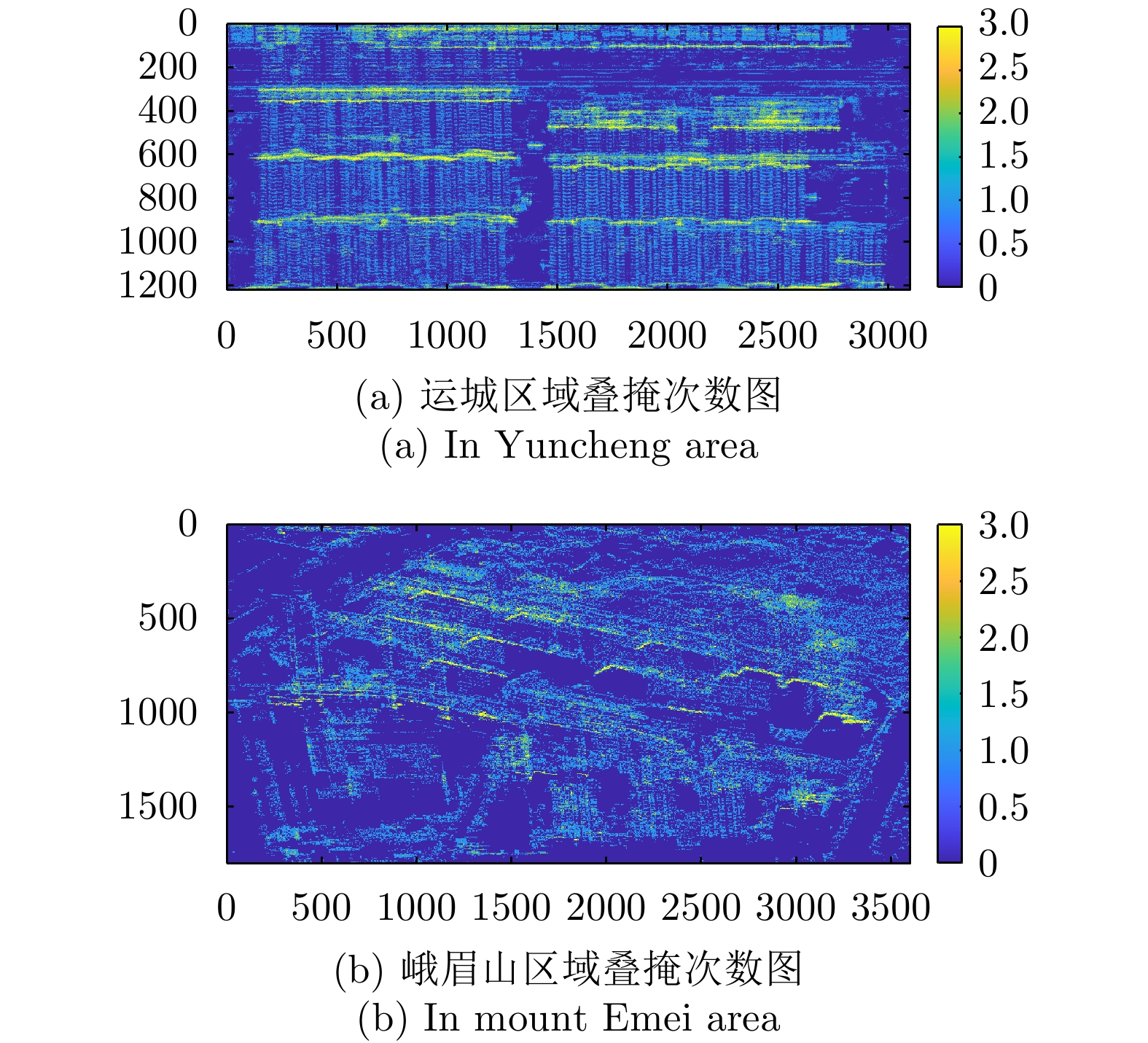
- Figure 20. Overlay times map of SARMV3D Imaging dataset
- Figure 1. Release webpage of Synthetic Aperture Radar Microwave Vision 3D Imaging Dataset


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: