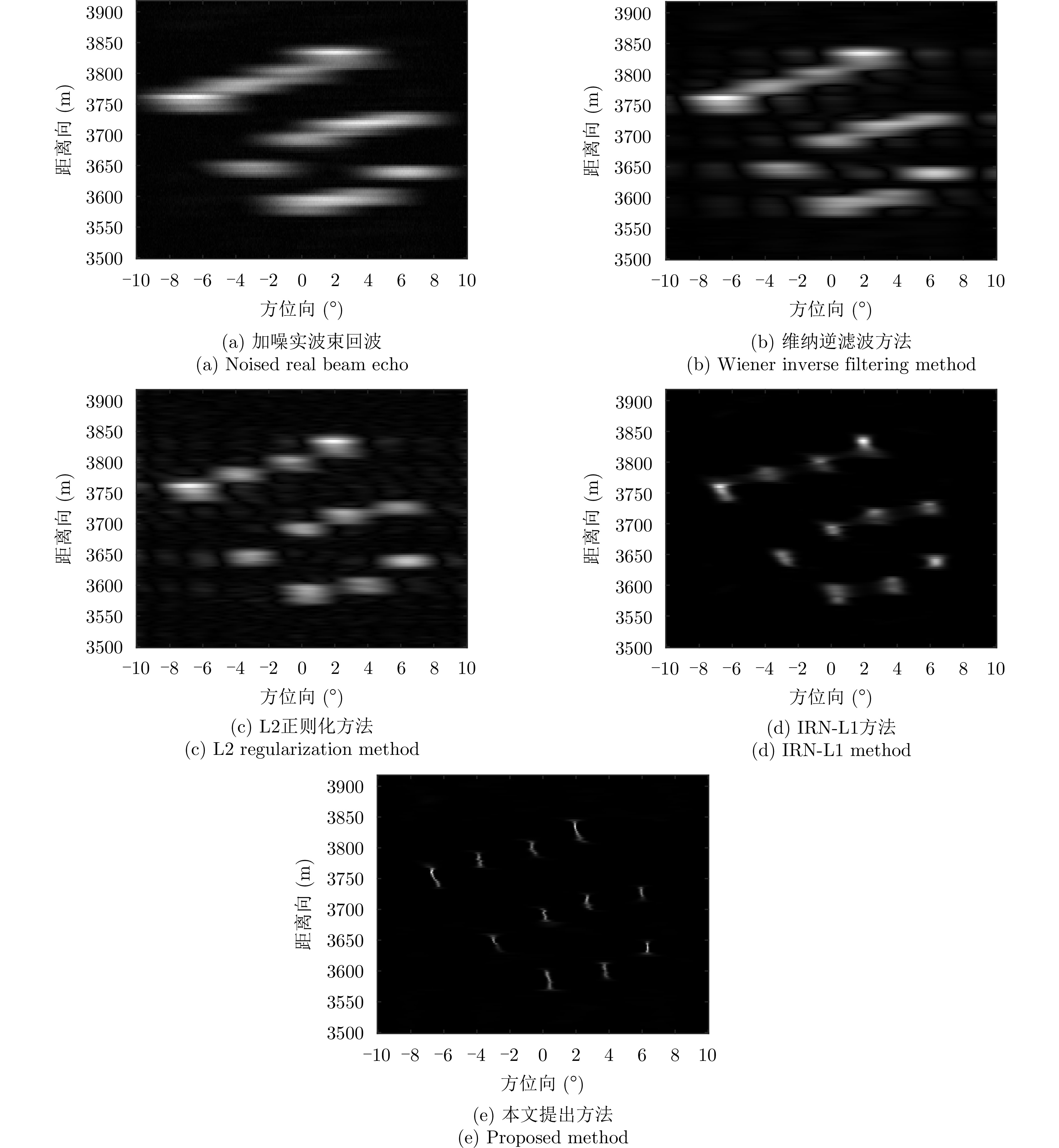
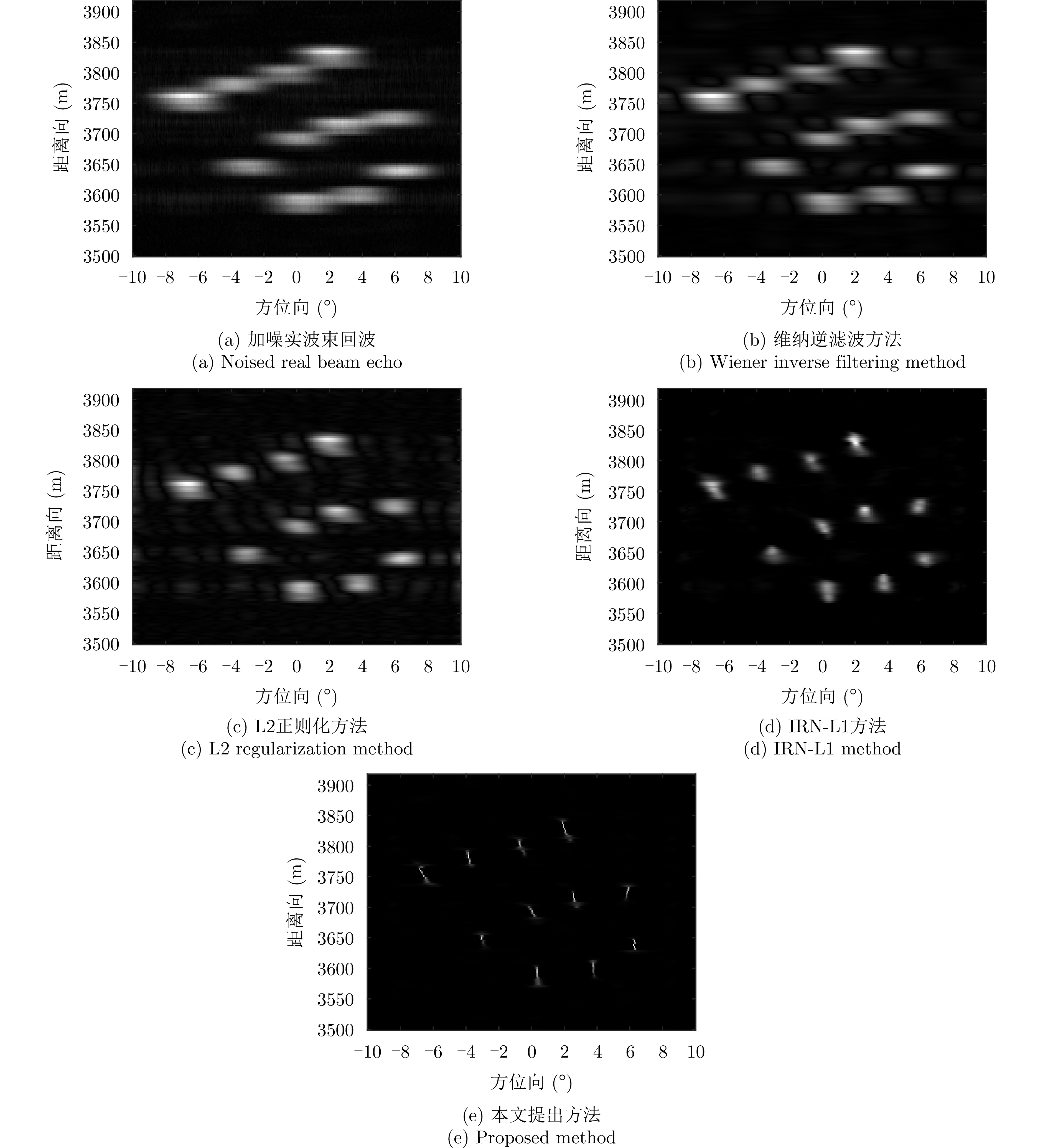
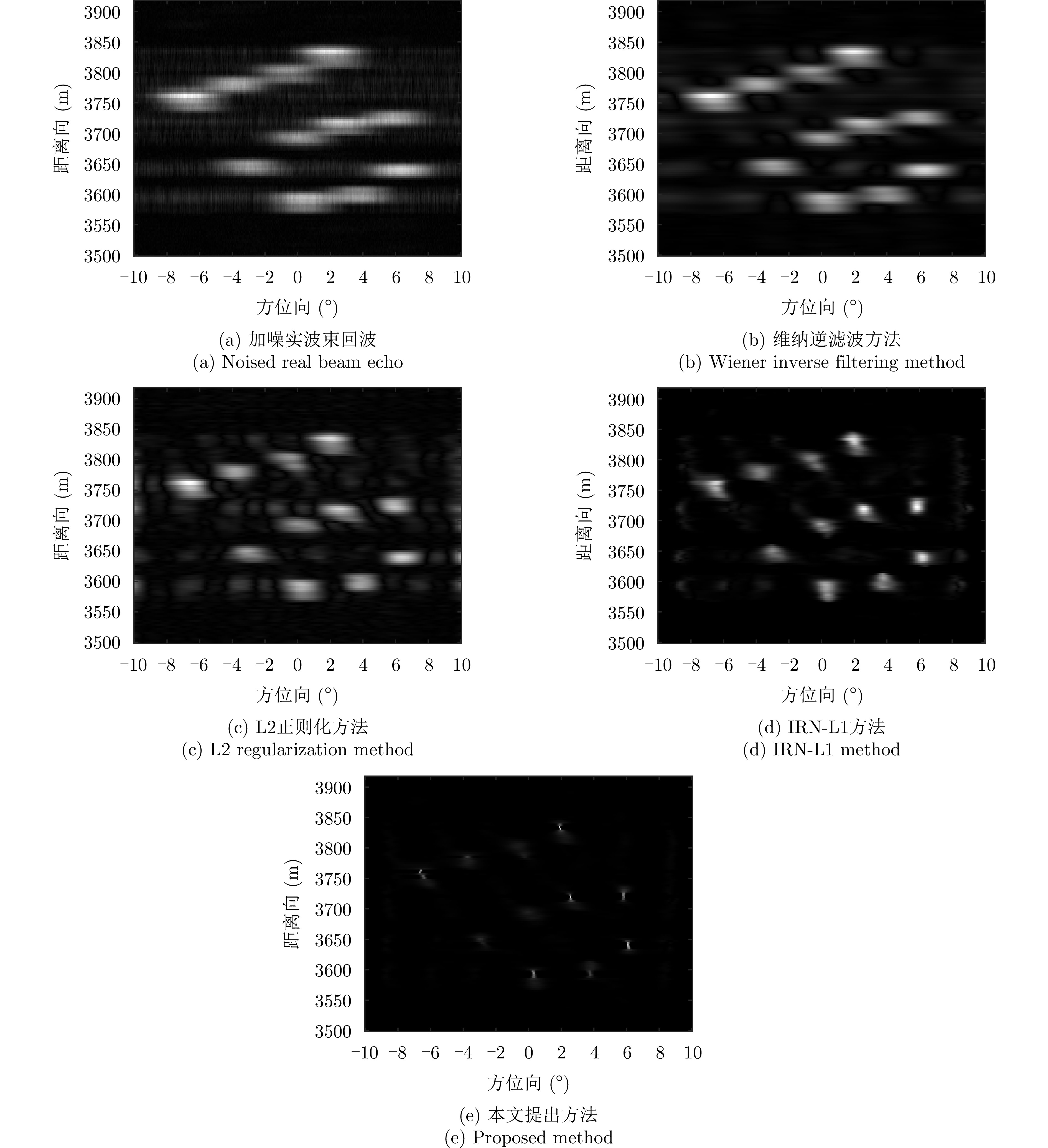
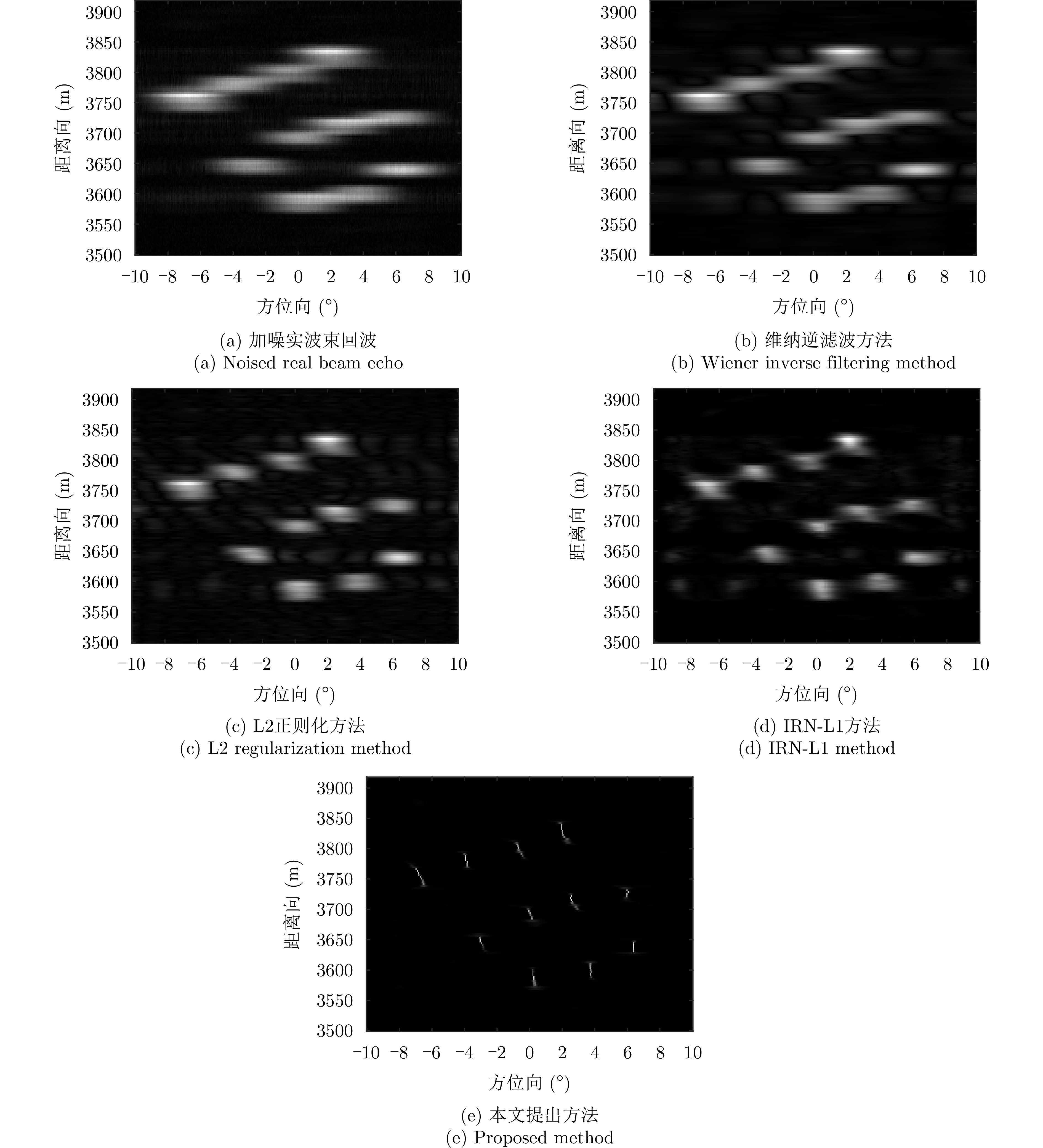
| [1] |
Rigelsford J. Introduction to airborne radar[J]. Sensor Review, 2002, 22(3): 265–266.
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Liang, ZHU Huan, and WU Tao. A study on the evolution way of the system architecture of AEW radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2015, 37(12): 11–18. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2015.12.003. |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Qiping, ZHANG Yin, HUANG Yulin, et al. TV-sparse super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6534–6549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2977719. |
| [5] |
LING Hao. Novel radar techniques and applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2018, 60(1): 132–134. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2017.2776153. |
| [6] |
BEKKADAL F. Novel radar technology and applications[C]. 17th International Conference on Applied Electromagnetics and Communications, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2003: 6–12. doi: 10.1109/ICECOM.2003.1290942. |
| [7] |
ZHANG Yongchao, ZHANG Yin, LI Wenchao, et al. Super-resolution surface mapping for scanning radar: Inverse filtering based on the fast iterative adaptive approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 127–144. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743263. |
| [8] |
ZHANG Yongchao, JAKOBSSON A, ZHANG Yin, et al. Wideband sparse reconstruction for scanning radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6055–6068. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2830100. |
| [9] |
CHEN Rui, LI Wenchao, LI Kefeng, et al. A super-resolution scheme for multichannel radar forward-looking imaging considering failure channels and motion error[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3501305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3234264. |
| [10] |
KANG Yao, ZHANG Yin, MAO Deqing, et al. Bayesian azimuth super-resolution of sea-surface target in forward-looking imaging[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266692. |
| [11] |
CHEN Hongmeng, WANG Zeyu, ZHANG Yingjie, et al. Data-driven airborne Bayesian forward-looking superresolution imaging based on generalized Gaussian distribution[J]. Frontiers in Signal Processing, 2023, 3: 1093203. doi: 10.3389/frsip.2023.1093203. |
| [12] |
MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yin, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Super-resolution Doppler beam sharpening method using fast iterative adaptive approach-based spectral estimation[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(1): 015020. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.12.015020. |
| [13] |
LIU Sijia and PAN Minghai. Research on a forward-looking scanning imaging algorithm for a high-speed radar platform[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2023, 17(6): e12221. doi: 10.1049/sil2.12221. |
| [14] |
MAO Deqing, YANG Jianyu, TUO Xingyu, et al. Angular superresolution of real aperture radar for target scale measurement using a generalized hybrid regularization approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5109314. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3315310. |
| [15] |
TUO Xingyu, MAO Deqing, ZHANG Yin, et al. Radar forward-looking super-resolution imaging using a two-step regularization strategy[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 4218–4231. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3270309. |
| [16] |
YOUNG P. Alternative Recursive Approaches to Time-series Analysis[M]. YOUNG P. Recursive Estimation and Time-Series Analysis: An Introduction. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1984: 205–230.
|
| [17] |
RICHARDS M A. Iterative noncoherent angular superresolution (radar)[C]. 1988 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1988: 100–105. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1988.10940. |
| [18] |
LI Dongye, HUANG Yulin, and YANG Jianyu. Real beam radar imaging based on adaptive Lucy-Richardson algorithm[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 1437–1440. doi: 10.1109/CIE-Radar.2011.6159830. |
| [19] |
TAN Ke, LU Xingyu, YANG Jianchao, et al. A novel Bayesian super-resolution method for radar forward-looking imaging based on Markov random field model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(20): 4115. doi: 10.3390/rs13204115. |
| [20] |
CHEN Hongmeng, LI Yachao, GAO Wenquan, et al. Bayesian forward-looking super-resolution imaging using Doppler deconvolution in expanded beam space for high-speed platform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107717. |
| [21] |
LI Weixin, LI Ming, ZUO Lei et al. A computationally efficient airborne forward-looking super-resolution imaging method based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5102613. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3260094. |
| [22] |
CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278. |
| [23] |
ZHANG Yongchao, LI Wenchao, ZHANG Yin, et al. A fast iterative adaptive approach for scanning radar angular superresolution[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 5336–5345. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2449090. |
| [24] |
LI Yueli, LIU Jianguo, JIANG Xiaoqing, et al. Angular superresolution for signal model in coherent scanning radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3103–3116. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2900133. |
| [25] |
GAMBARDELLA A and MIGLIACCIO M. On the superresolution of microwave scanning radiometer measurements[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 796–800. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2006285. |
| [26] |
HUO Weibo, TUO Xingyu, ZHANG Yin, et al. Balanced tikhonov and total variation deconvolution approach for radar forward-looking super-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3505805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3072389. |
| [27] |
TANG Junkui, LIU Zheng, RAN Lei, et al. Enhancing forward-looking image resolution: Combining low-rank and sparsity priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5100812. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3237332. |
| [28] |
KOZAKOFF D J. Analysis of radome-enclosed antennas[J]. Artech House, 1997 (685): 217–227.
|
| [29] |
PERSSON K and GUSTAFSSON M. Reconstruction of equivalent currents using a near-field data transformation-with radome applications[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 2005, 54: 179–198. doi: 10.2528/PIER04111602. |
| [30] |
Fierro R D, Golub G H, Hansen P C, et al. Regularization by truncated total least squares[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 1997, 18(4): 1223–1241. doi: 10.1137/S106482759426383. |
| [31] |
GOLUB G H, HEATH M, and WAHBA G. Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter[J]. Technometrics, 1979, 21(2): 215–223. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1979.10489751. |
| [32] |
JOHNSTON P R and GULRAJANI R M. Selecting the corner in the L-curve approach to Tikhonov regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2000, 47(9): 1293–1296. doi: 10.1109/10.867966. |
| [33] |
ENGL H W. Discrepancy principles for Tikhonov regularization of ill-posed problems leading to optimal convergence rates[J]. Journal of optimization theory and applications, 1987, 52: 209–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00941281. |
| [34] |
RUDIN L I, OSHER S, and FATEMI E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 60(1/4): 259–268. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: