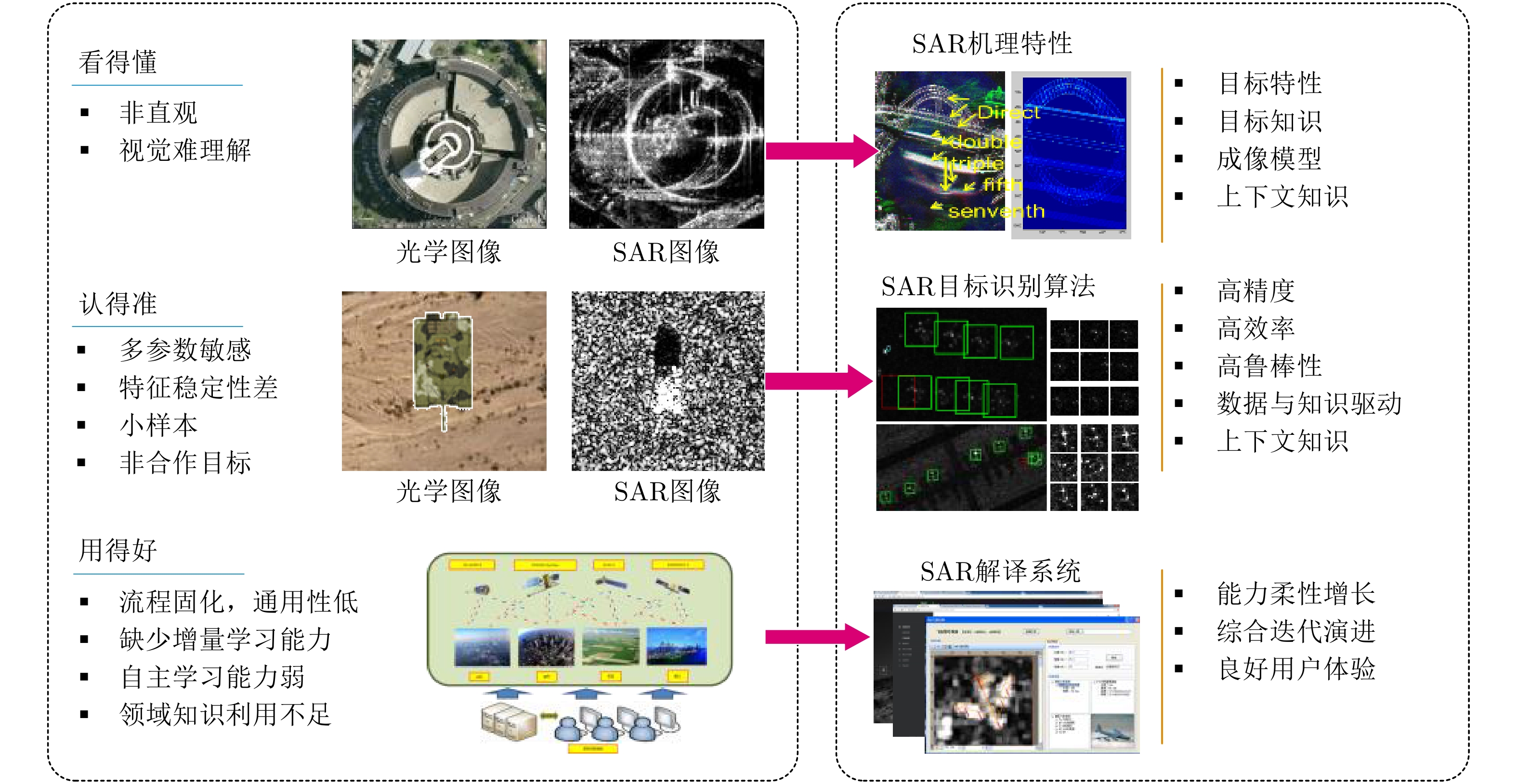
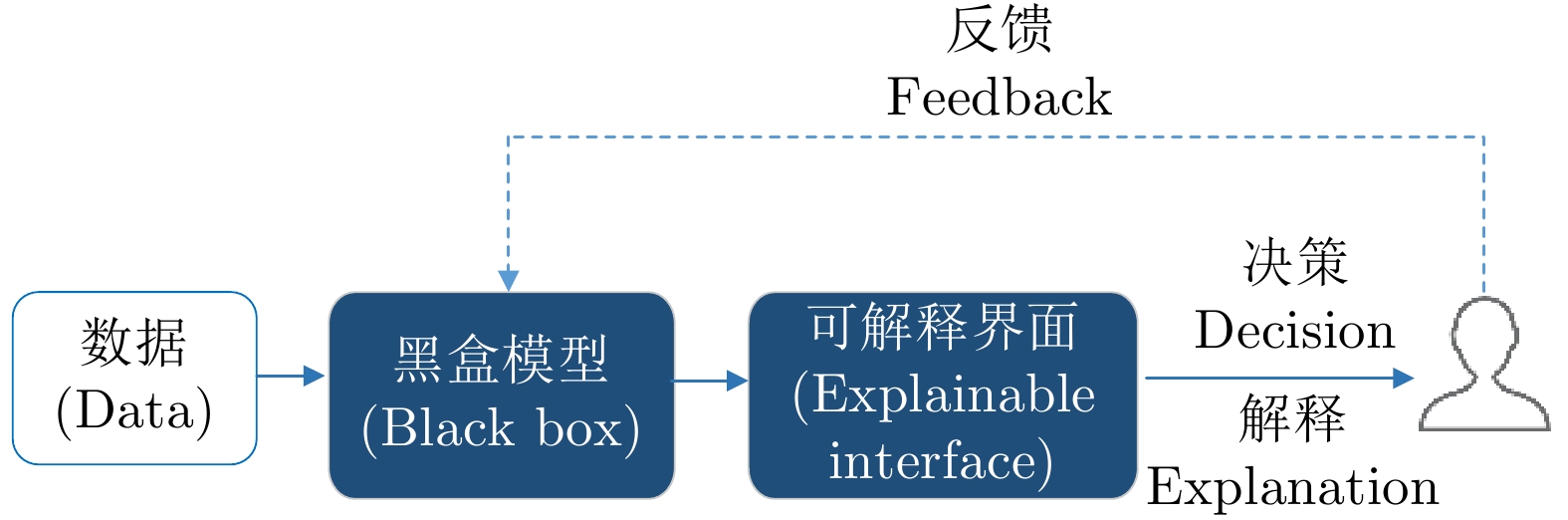
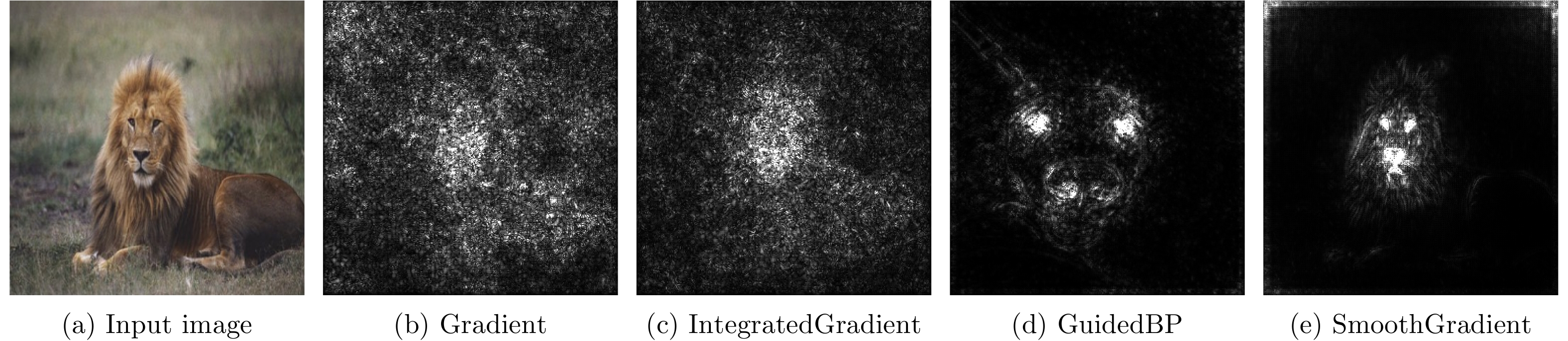
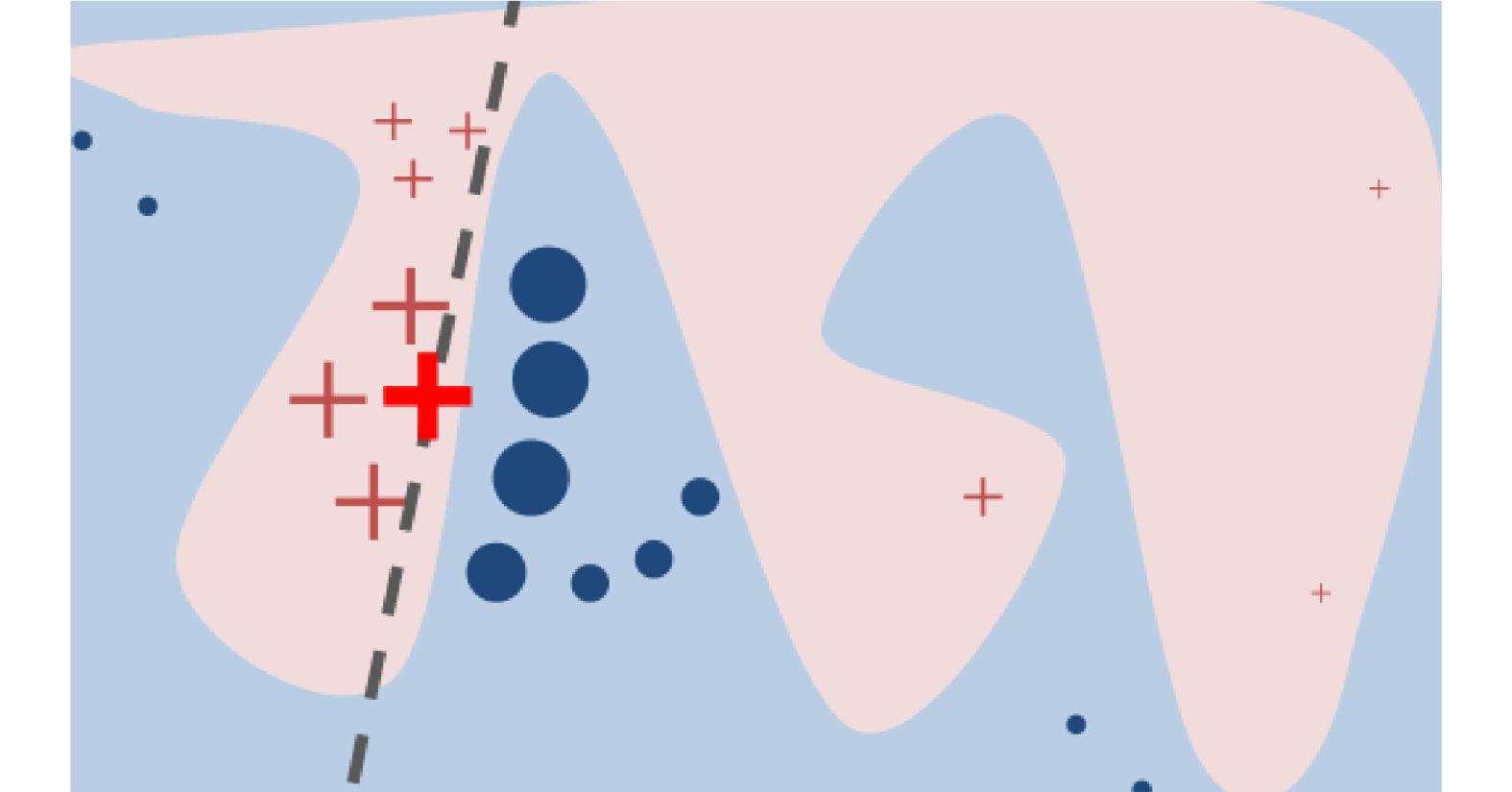
| [1] |
金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083 |
| [2] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE Volume 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996. doi: 10.1117/12.242059. |
| [3] |
ZHAO Juanping, GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, et al. A coupled convolutional neural network for small and densely clustered ship detection in SAR images[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(4): 42301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9405-6 |
| [4] |
杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104 |
| [5] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 |
| [6] |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336–359. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01228-7 |
| [7] |
GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, and SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[C]. 2015 International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015.
|
| [8] |
JI Shouling, LI Jinfeng, DU Tianyu, et al. Survey on techniques, applications and security of machine learning interpretability[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(10): 2071–2096. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190540 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
GUIDOTTI R, MONREALE A, RUGGIERI S, et al. A survey of methods for explaining black box models[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2018, 51(5): 93. doi: 10.1145/3236009 |
| [11] |
NOVAK L M, OWIRKA G J, and NETISHEN C M. Performance of a high-resolution polarimetric SAR automatic target recognition system[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1993, 6(1): 11–23.
|
| [12] |
GAO Gui. Statistical modeling of SAR images: A survey[J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(1): 775–795. doi: 10.3390/s100100775 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
郭炜炜. SAR图像目标分割与特征提取[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2007: 28–35.
GUO Weiwei. SAR image target segmentation and feature extraction[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2007: 28–35.
|
| [15] |
HUAN Ruohong and YANG Ruliang. SAR target recognition based on MRF and gabor wavelet feature extraction[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: II-907–II-910. doi: 10.1109/igarss.2008.4779142. |
| [16] |
PAPSON S and NARAYANAN R M. Classification via the shadow region in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 969–980. doi: 10.1109/taes.2012.6178042 |
| [17] |
CASASENT D and CHANG W T. Correlation synthetic discriminant functions[J]. Applied Optics, 1986, 25(14): 2343–2350. doi: 10.1364/ao.25.002343 |
| [18] |
ZHAO Q and PRINCIPE J C. Support vector machines for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(2): 643–654. doi: 10.1109/7.937475 |
| [19] |
SUN Yijun, LIU Zhipeng, TODOROVIC S, et al. Adaptive boosting for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(1): 112–125. doi: 10.1109/taes.2007.357120 |
| [20] |
SUN Yongguang, DU Lan, WANG Yan, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on dictionary learning and joint dynamic sparse representation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1777–1781. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2016.2608578 |
| [21] |
POTTER L C and MOSES R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(1): 79–91. doi: 10.1109/83.552098 |
| [22] |
JI Kefeng, KUANG Gangyao, SU Yi, et al. Research on the extracting method of the scattering center feature from SAR imagery[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2003, 25(1): 45–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2003.01.010 |
| [23] |
丁柏圆, 文贡坚, 余连生, 等. 属性散射中心匹配及其在SAR目标识别中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 157–166. doi: 10.12000/JR16104DING Baiyuan, WEN Gongjian, YU Liansheng, et al. Matching of attributed scattering center and its application to synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 157–166. doi: 10.12000/JR16104 |
| [24] |
JONES III G and BHANU B. Recognizing articulated objects in SAR images[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2001, 34(2): 469–485. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3203(99)00218-6 |
| [25] |
MAO Xiaojiao, SHEN Chunhua, and YANG Yubin. Image restoration using very deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks with symmetric skip connections[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 2810–2818.
|
| [26] |
DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295–307. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2015.2439281 |
| [27] |
LIU Li, OUYANG Wanli, WANG Xiaogang, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261–318. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 |
| [28] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778.
|
| [29] |
CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2017.2699184 |
| [30] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for sar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2551720 |
| [31] |
PAN Zongxu, AN Quanzhi, and ZHANG Bingchen. Progress of deep learning-based target recognition in radar images[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(12): 1626–1639. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0093 |
| [32] |
贺丰收, 何友, 刘准钆, 等. 卷积神经网络在雷达自动目标识别中的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899HE Fengshou, HE You, LIU Zhunga, et al. Research and development on applications of convolutional neural networks of radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899 |
| [33] |
ZHAO Juanping, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. A cascade coupled convolutional neural network guided visual attention method for ship detection from SAR images[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 50693–50708. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2869289 |
| [34] |
陈慧元, 刘泽宇, 郭炜炜, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的大场景遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041CHEN Huiyuan, LIU Zeyu, GUO Weiwei, et al. Fast detection of ship targets for large-scale remote sensing image based on a cascade convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041 |
| [35] |
WAGNER S. Combination of convolutional feature extraction and support vector machines for radar ATR[C]. The 17th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Salamanca, Spain, 2014: 1–6.
|
| [36] |
WAGNER S A. SAR ATR by a combination of convolutional neural network and support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(6): 2861–2872. doi: 10.1109/taes.2016.160061 |
| [37] |
HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2019.2947634 |
| [38] |
赵娟萍, 郭炜炜, 柳彬, 等. 基于概率转移卷积神经网络的含噪标记SAR图像分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 514–523. doi: 10.12000/JR16140ZHAO Juanping, GUO Weiwei, LIU Bin, et al. Convolutional neural network-based sar image classification with noisy labels[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 514–523. doi: 10.12000/JR16140 |
| [39] |
GUNNING D. EXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)[R]. DARPA/I2O, 2017.
|
| [40] |
ADADI A and BERRADA M. Peeking inside the black-box: A survey on EXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 52138–52160. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2870052 |
| [41] |
LIPTON Z C. The mythos of model interpretability[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2018, 61(10): 36–43. doi: 10.1145/3233231 |
| [42] |
ZHANG Quanshi and ZHU Songchun. Visual interpretability for deep learning: A survey[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2018, 19(1): 27–39. doi: 10.1631/fitee.1700808 |
| [43] |
MAHENDRAN A and VEDALDI A. Visualizing deep convolutional neural networks using natural pre-images[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 120(3): 233–255. doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0911-8 |
| [44] |
NGUYEN A, CLUNE J, BENGIO Y, et al. Plug & play generative networks: Conditional iterative generation of images in latent space[J]. arXiv: 1612.00005, 2016.
|
| [45] |
KIM B, WATTENBERG M, GILMER J, et al. Interpretability beyond feature attribution: Quantitative Testing with Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV)[J]. arXiv: 1711.11279, 2017.
|
| [46] |
FROSST N and HINTON G. Distilling a neural network into a soft decision tree[J]. arXiv: 1711.09784, 2017.
|
| [47] |
ALTMANN A, TOLOŞI L, SANDER O, et al. Permutation importance: A corrected feature importance measure[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(10): 1340–1347. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq134 |
| [48] |
SIMONYAN K, VEDALDI A, and ZISSERMAN A. Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising image classification models and saliency maps[J]. arXiv: 1312.6034, 2013.
|
| [49] |
SPRINGENBERG J T, DOSOVITSKIY A, BROX T, et al. Striving for simplicity: The all convolutional net[J]. arXiv: 1412.6806, 2014.
|
| [50] |
SUNDARARAJAN M, TALY A, and YAN Qiqi. Gradients of counterfactuals[J]. arXiv: 1611.02639, 2016.
|
| [51] |
SMILKOV D, THORAT N, KIM B, et al. SmoothGrad: Removing noise by adding noise[J]. arXiv: 1706.03825, 2017.
|
| [52] |
FONG R, PATRICK M, and VEDALDI A. Understanding deep networks via extremal perturbations and smooth masks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 2950–2958. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2019.00304. |
| [53] |
BACH S, BINDER A, MONTAVON G, et al. On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0130140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130140 |
| [54] |
ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921–2929. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2016.319. |
| [55] |
RIBEIRO M, SINGH S, and GUESTRIN C.“Why should I trust you?”: Explaining the predictions of any classifier[C]. 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Demonstrations, San Diego, USA, 2016: 97–101. doi: 10.18653/v1/n16-3020. |
| [56] |
KOH P W and LIANG P. Understanding black-box predictions via influence functions[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1885–1894.
|
| [57] |
KIM B, KHANNA R, and KOYEJO O. Examples are not enough, learn to criticize! Criticism for Interpretability[C]. The 30th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 2280–2288.
|
| [58] |
LUNDBERG S M and LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4768–4777.
|
| [59] |
ZHANG Quanshi, YANG Yu, MA Haotian, et al. Interpreting CNNs via decision trees[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6254–6263. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2019.00642. |
| [60] |
DU Mengnan, LIU Ninghao, SONG Qingquan, et al. Towards explanation of DNN-based prediction with guided feature inversion[C]. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 2018: 1358–1367.
|
| [61] |
ZEILER M D and FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 818–833.
|
| [62] |
SAMEK W, BINDER A, MONTAVON G, et al. Evaluating the visualization of what a deep neural network has learned[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(11): 2660–2673. doi: 10.1109/tnnls.2016.2599820 |
| [63] |
NAM W J, GUR S, CHOI J, et al. Relative attributing propagation: Interpreting the comparative contributions of individual units in deep neural networks[C]. The 34th Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, USA, 2020: 2501–2508.
|
| [64] |
RUDIN C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2019, 1(5): 206–215. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0048-x |
| [65] |
XU K, BA J L, KIROS R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning(ICML), Lille, France, 2015: 2048–2057.
|
| [66] |
GREGOR K and LECUN Y. Learning fast approximations of sparse coding[C]. The 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 2010: 399–406.
|
| [67] |
ZHENG Shuai, JAYASUMANA S, ROMERA-PAREDES B, et al. Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1529–1537. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2015.179. |
| [68] |
PENG Xi, TSANG I W, ZHOU J T, et al. K-meansNet: When k-means meets differentiable programming[J]. arxiv: 1808.07292, 2018.
|
| [69] |
ZHU Hongyuan, PENG Xi, Chandrasekhar V, et al. DehazeGAN: When image dehazing meets differential programming[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1234–1240.
|
| [70] |
KARPATNE A, WATKINS W, READ J, et al. Physics-guided Neural Networks (PGNN): An application in lake temperature modeling[J]. arxiv: 1710.11431, 2017.
|
| [71] |
CHEN Tianshui, XU Muxin, HUI Xiaolu, et al. Learning semantic- specific graph representation for multi-label image recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 522–531.
|
| [72] |
CHU Lingyang, HU Xia, HU Juhua, et al. Exact and consistent interpretation for piecewise linear neural networks: A closed form solution[C]. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 2018: 1244–1253.
|
| [73] |
BAU D, ZHOU Bolei, KHOSL A, et al. Network dissection: Quantifying interpretability of deep visual representations[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 3319–3327. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2017.354. |
| [74] |
DATCU M, ANDREI V, DUMITRU C O, et al. Explainable deep learning for SAR data[C]. Φ-week, Frascati, Italy, 2019.
|
| [75] |
HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. Deep SAR-Net: Learning objects from signals[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 161: 179–193. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.016 |
| [76] |
ZHAO Juanping, DATCU M, ZHANG Zenghui, et al. Contrastive-regulated CNN in the complex domain: A method to learn physical scattering signatures from flexible PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10116–10135. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2019.2931620 |
| [77] |
CHEN Lifu, TAN Siyu, PAN Zhouhao, et al. A new framework for automatic airports extraction from SAR images using multi-level dual attention mechanism[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3): 560. doi: 10.3390/rs12030560 |
| [78] |
LI Chen, DU Lan, DENG Sheng, et al. Point-wise discriminative auto-encoder with application on robust radar automatic target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 169: 107385. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107385 |
| [79] |
CETIN M, KARL W C, and CASTANON D A. Feature enhancement and ATR performance using nonquadratic optimization-based SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1375–1395. doi: 10.1109/taes.2003.1261134 |
| [80] |
KHANNA R, KIM B, GHOSH J, et al. Interpreting black box predictions using fisher kernels[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), Okinawa, Japan, 2019: 3382–3390.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: