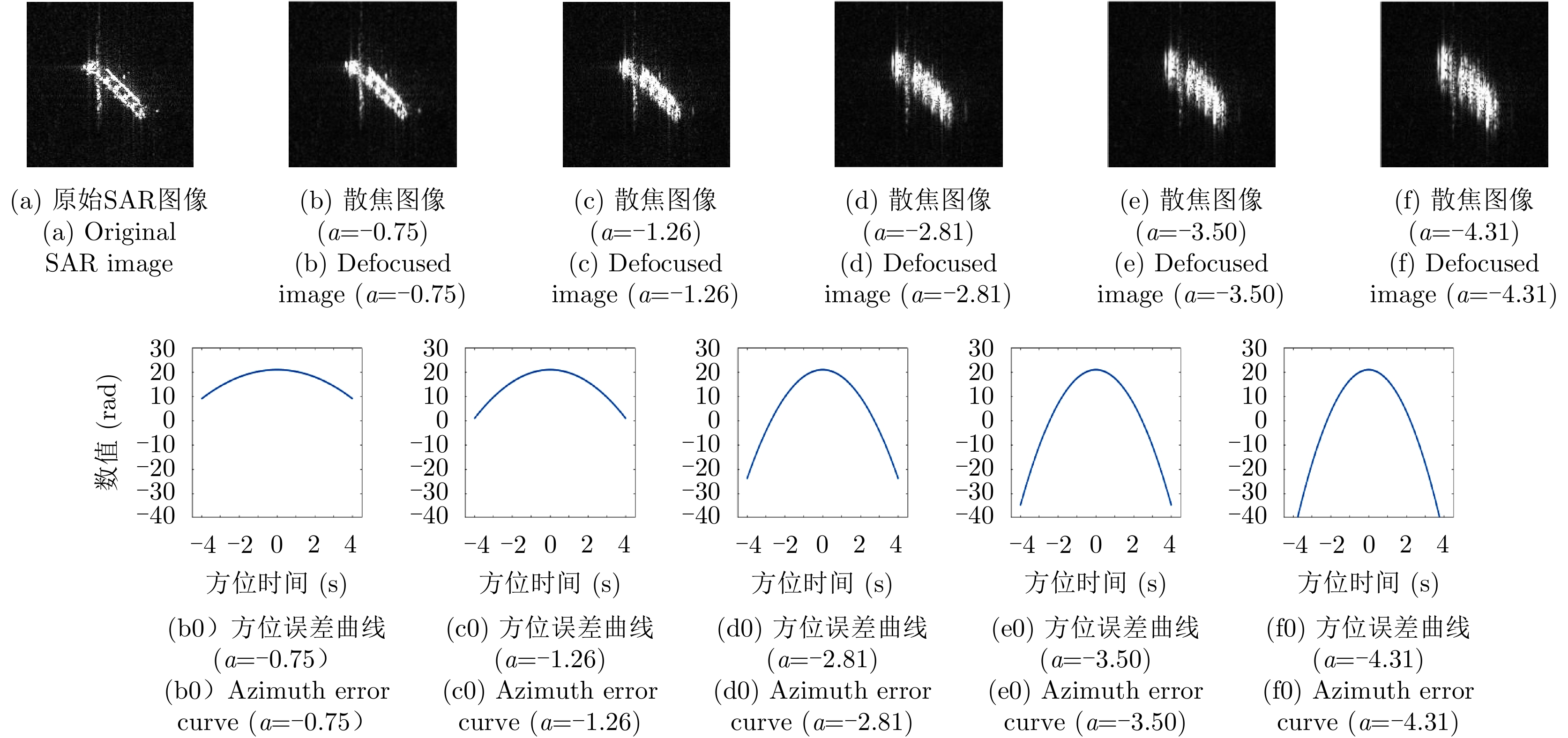
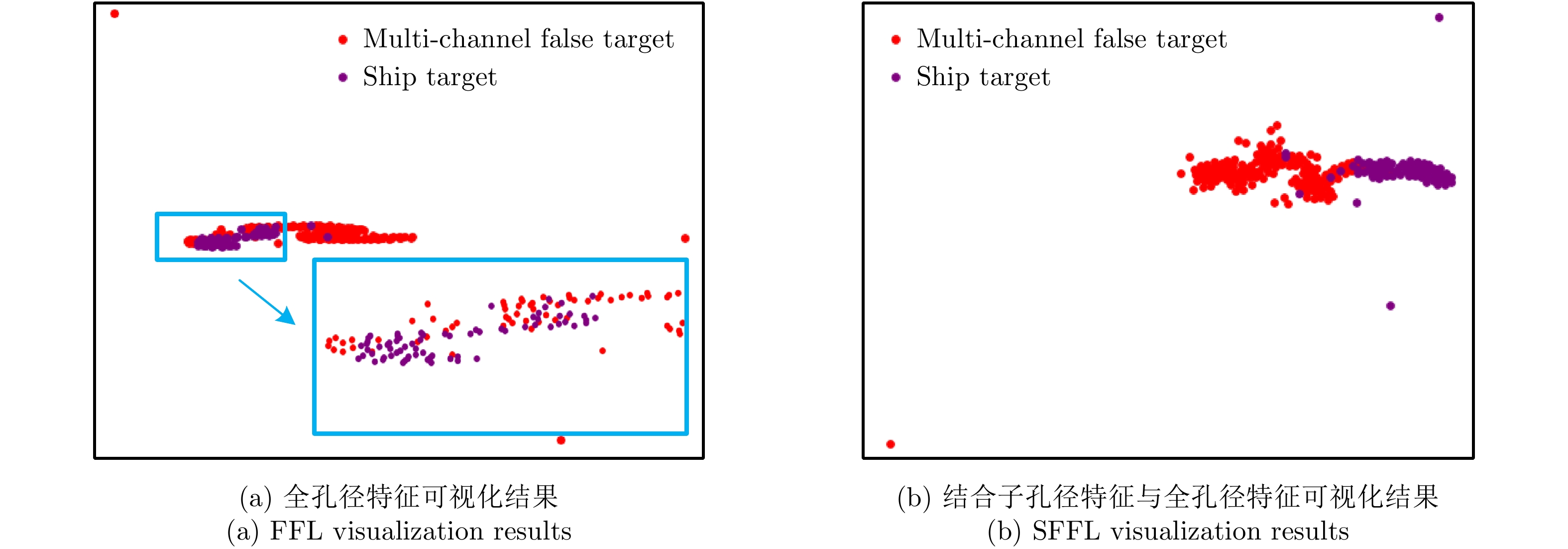
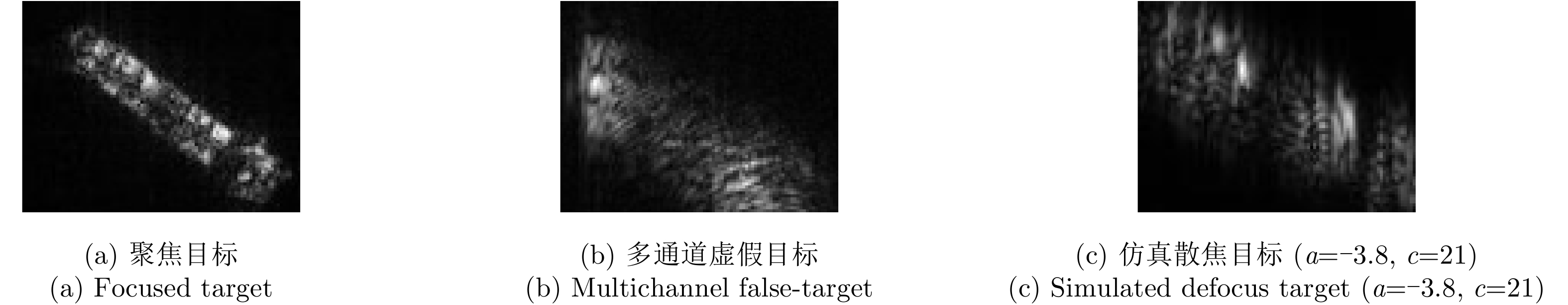
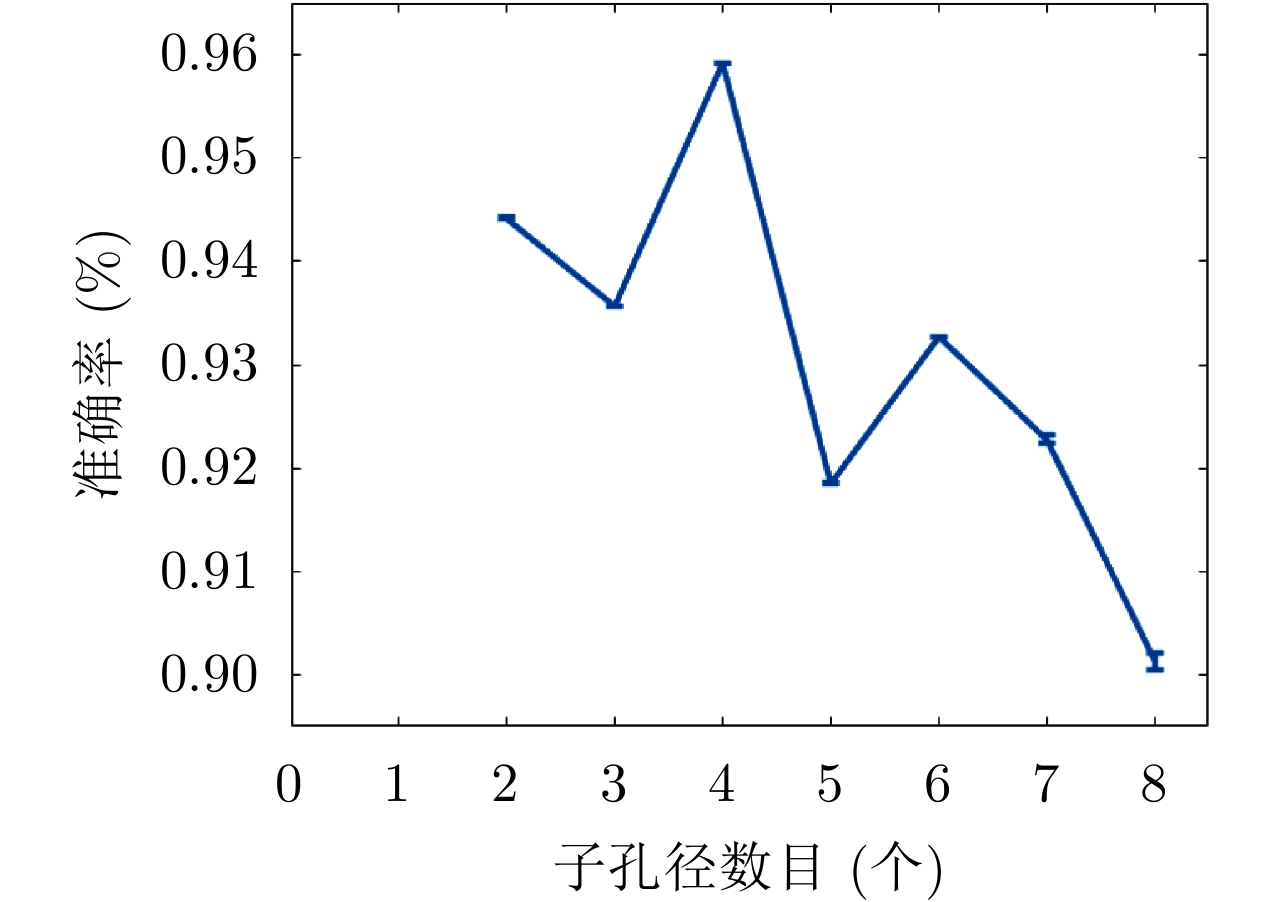
| [1] |
杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104 |
| [2] |
WU Liang, LEI Bin, HAN Bing, et al. The impact of satellite attitude error on multi-channel SAR image quality[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2015, (1): 124–130. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2015.0026 |
| [3] |
张双喜, 乔宁, 邢孟道, 等. 多普勒频谱模糊情况下的星载方位向多通道高分宽幅SAR-GMTI杂波抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 295–303. doi: 10.12000/JR20005ZHANG Shuangxi, QIAO Ning, XING Mengdao, et al. A novel clutter suppression approach for the space-borne multiple channel in the azimuth high-resolution and wide-swath SAR-GMTI system with an ambiguous Doppler spectrum[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 295–303. doi: 10.12000/JR20005 |
| [4] |
ZHANG Shuangxi, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Multichannel HRWS SAR imaging based on range-variant channel calibration and multi-Doppler-direction restriction ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4306–4327. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281329 |
| [5] |
PAN Zongxu, LIU Lei, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Fast vessel detection in Gaofen-3 SAR images with ultrafine strip-map mode[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(7): 1578. doi: 10.3390/s17071578 |
| [6] |
DI MARTINO G, IODICE A, RICCIO D, et al. Filtering of azimuth ambiguity in stripmap synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(9): 3967–3978. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2320155 |
| [7] |
温雪娇, 仇晓兰, 尤红建, 等. 高分辨率星载SAR起伏运动目标精细聚焦与参数估计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 213–220. doi: 10.12000/JR17005WEN Xuejiao, QIU Xiaolan, YOU Hongjian, et al. Focusing and parameter estimation of fluctuating targets in high resolution spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 213–220. doi: 10.12000/JR17005 |
| [8] |
WEN Xuejiao, QIU Xiaolan, and YOU Hongjian. Focusing and parameter estimating of fluctuating target in high resolution spaceborne SAR[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059537. |
| [9] |
REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 |
| [10] |
LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Holland, 2016. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. |
| [11] |
LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124934. |
| [12] |
KANG Miao, LENG Xiangguang, LIN Zhao, et al. A modified faster R-CNN based on CFAR algorithm for SAR ship detection[C]. 2017 International Workshop on Remote Sensing with Intelligent Processing, Shanghai, China, 2017: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RSIP.2017.7958815. |
| [13] |
LIU Lei, CHEN Guowei, PAN Zongxu, et al. Inshore ship detection in SAR images based on deep neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 25–28. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8519555. |
| [14] |
ZHANG Fan, WANG Yunchong, NI Jun, et al. SAR target small sample recognition based on CNN cascaded features and AdaBoost rotation forest[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(6): 1008–1012. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2939156 |
| [15] |
LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Ship detection based on complex signal kurtosis in single-channel SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6447–6461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906054 |
| [16] |
LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Discriminating ship from radio frequency interference based on noncircularity and non-gaussianity in sentinel-1 SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(1): 352–363. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2854661 |
| [17] |
ZHANG Zhimian, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 |
| [18] |
HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. Deep SAR-Net: Learning objects from signals[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 161: 179–193. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.016 |
| [19] |
TANG Jiaxin, ZHANG Fan, ZHOU Yongsheng, et al. A fast inference networks for SAR target few-shot learning based on improved siamese networks[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1212–1215. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898180. |
| [20] |
OUCHI K, TAMAKI S, YAGUCHI H, et al. Ship detection based on coherence images derived from cross correlation of multilook SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(3): 184–187. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.827462 |
| [21] |
MARINO A, SANJUAN-FERRER M J, HAJNSEK I, et al. Ship detection with spectral analysis of synthetic aperture radar: A comparison of new and well-known algorithms[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(5): 5416–5439. doi: 10.3390/rs70505416 |
| [22] |
RENGA A, GRAZIANO M D, and MOCCIA A. Segmentation of marine SAR images by sublook analysis and application to sea traffic monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(3): 1463–1477. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2866934 |
| [23] |
BREKKE C, ANFINSEN S N, and LARSEN Y. Subband extraction strategies in ship detection with the subaperture cross-correlation magnitude[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 786–790. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2223656 |
| [24] |
SOUYRIS J C, HENRY C, and ADRAGNA F. On the use of complex SAR image spectral analysis for target detection: Assessment of polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(12): 2725–2734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817809 |
| [25] |
FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, POTTIER E, et al. Scene characterization using subaperture polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(10): 2264–2276. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817188 |
| [26] |
DUMITRU C O, SCHWARZ G, and DATCU M. Land cover semantic annotation derived from high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2215–2232. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2549557 |
| [27] |
HUANG Zhongling, DUMITRU C O, PAN Zongxu, et al. Classification of large-scale high-resolution SAR images with deep transfer learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(1): 107–111. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2965558 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2947634 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

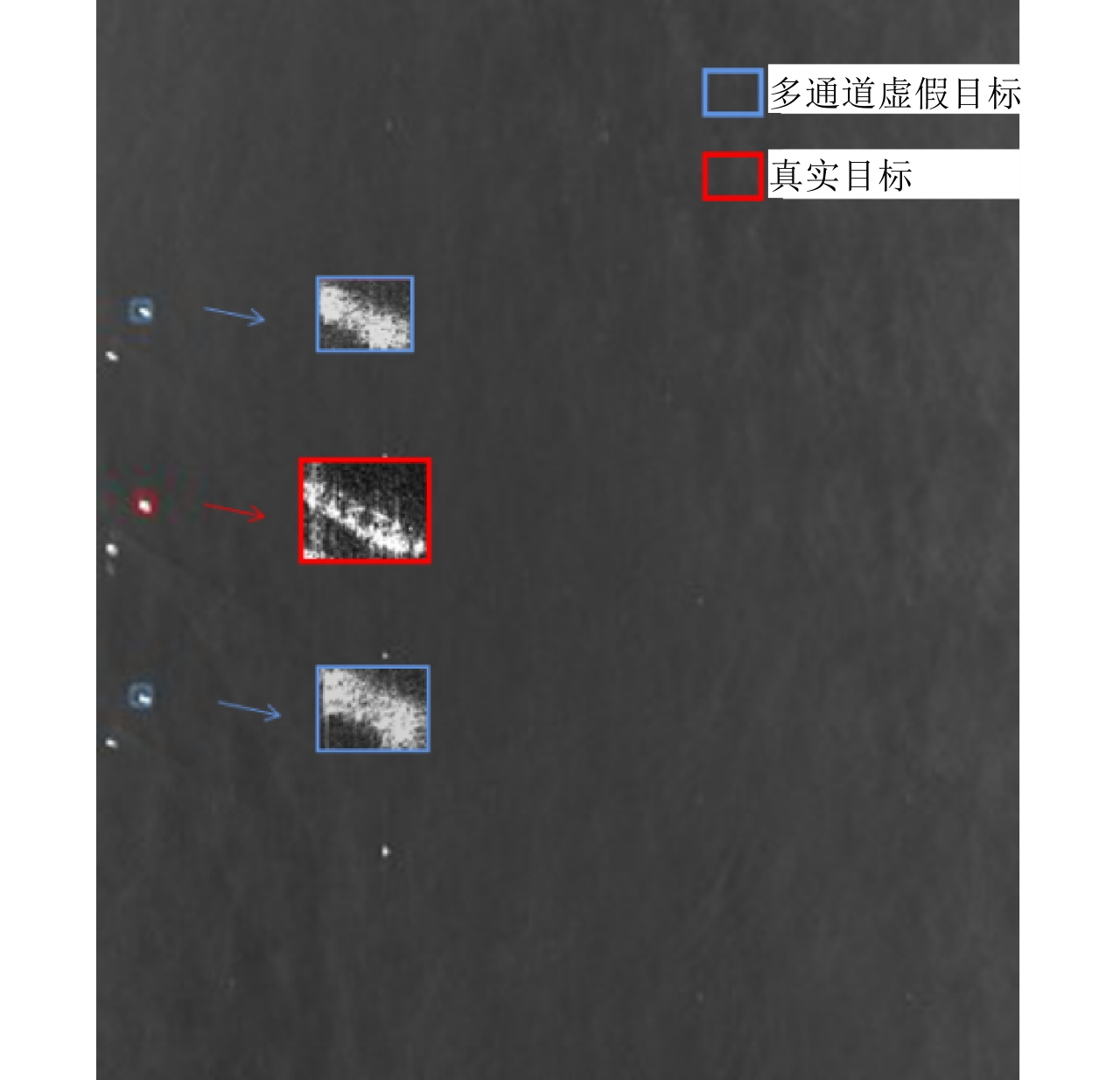



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: