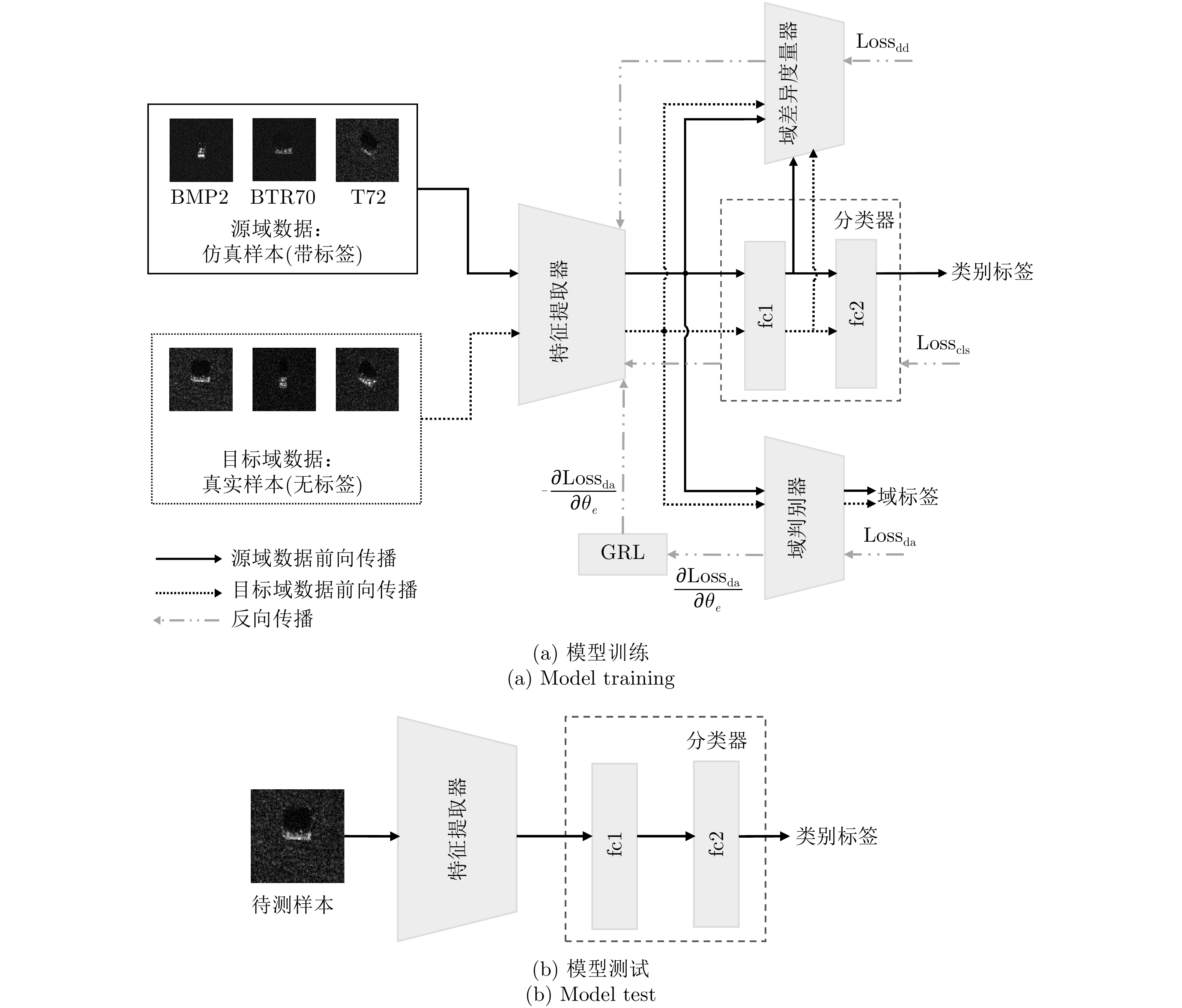
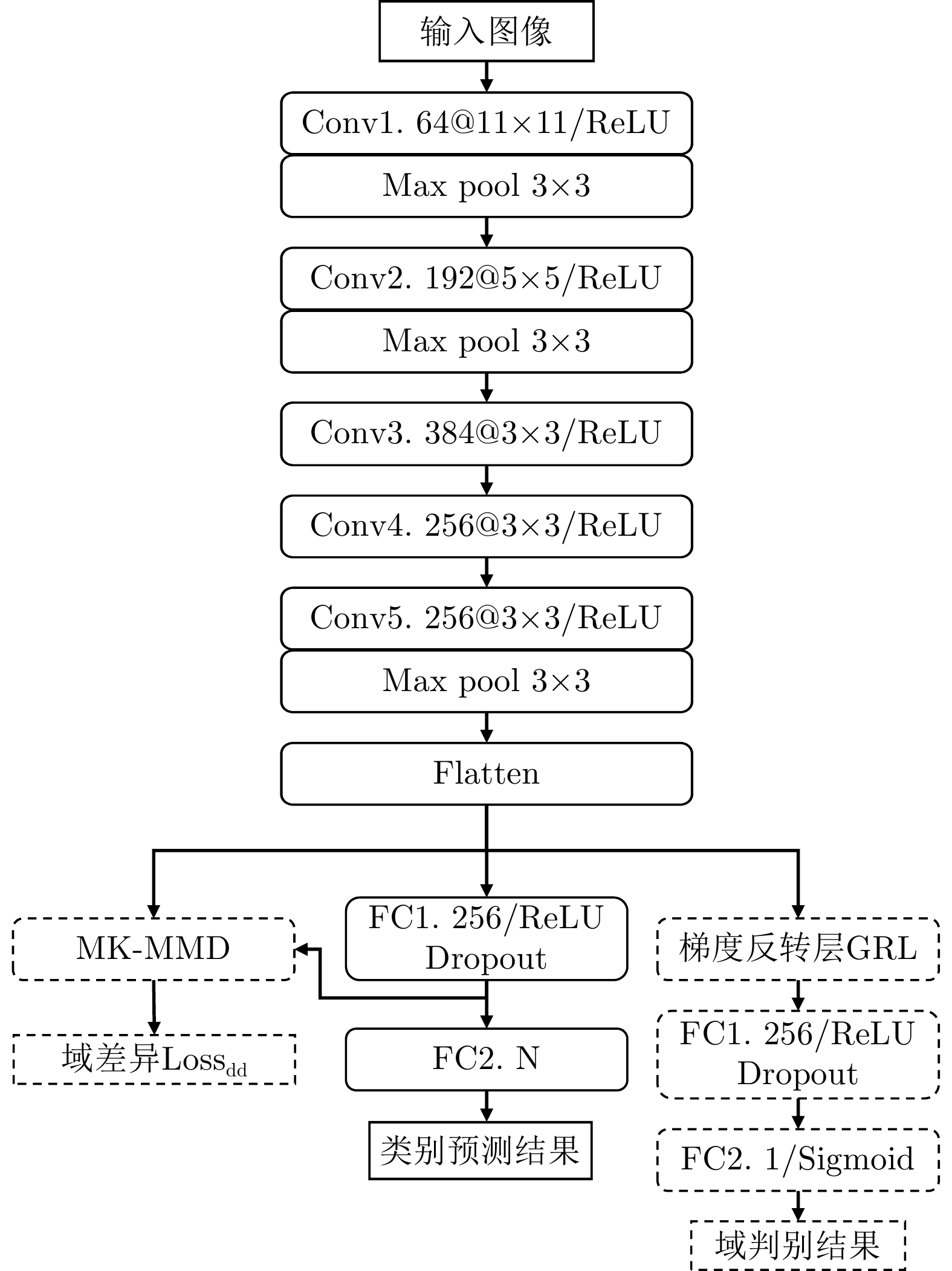
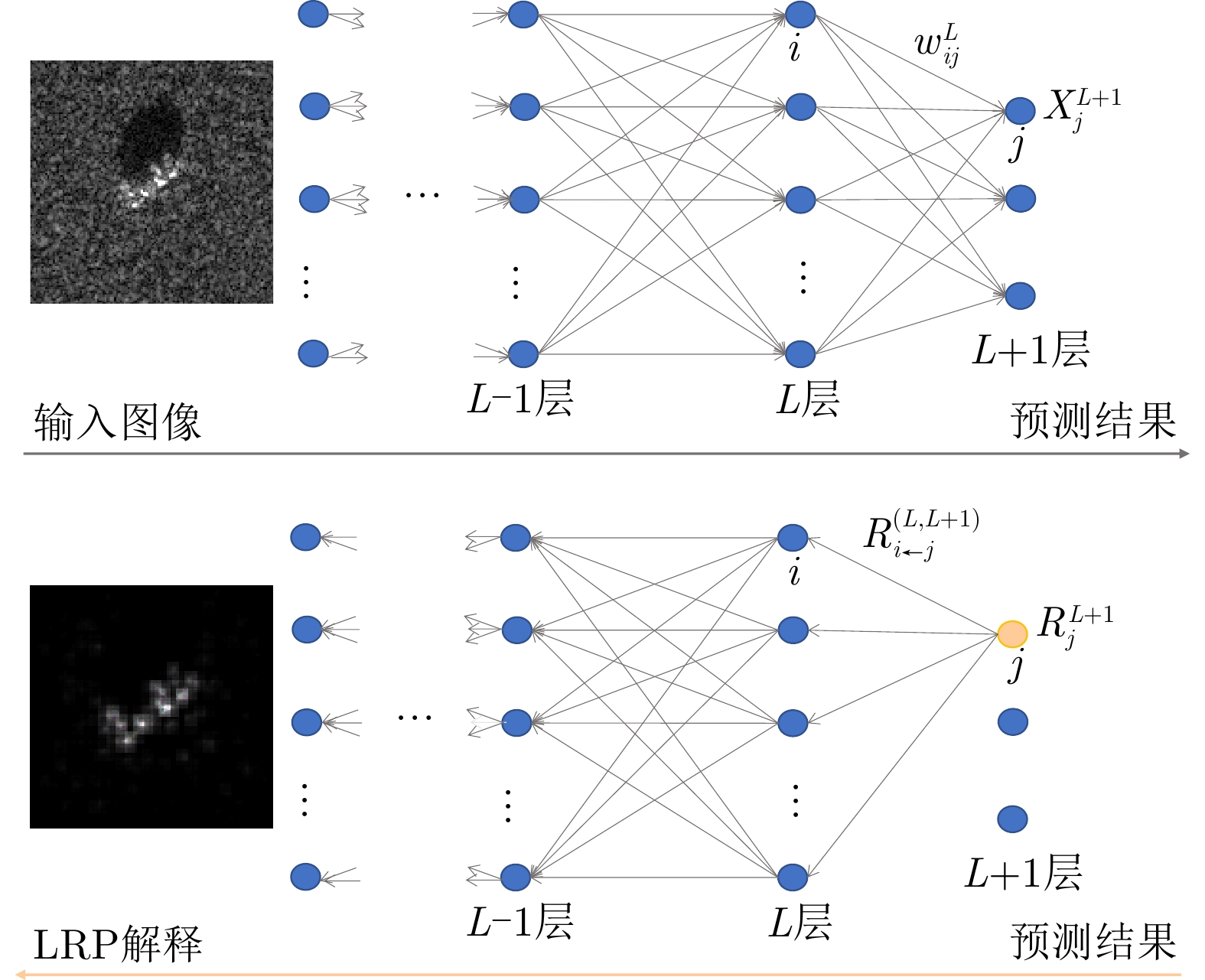
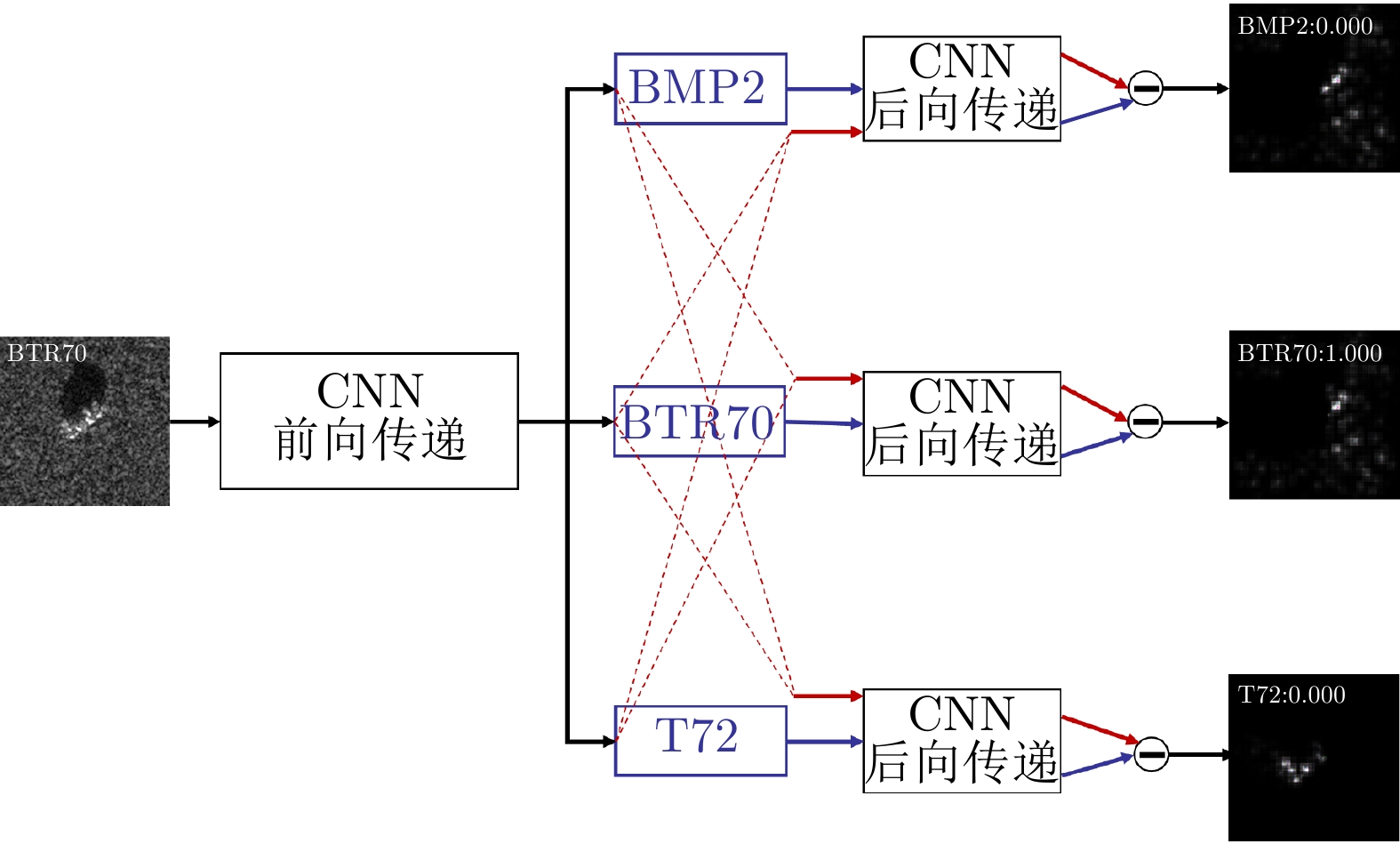
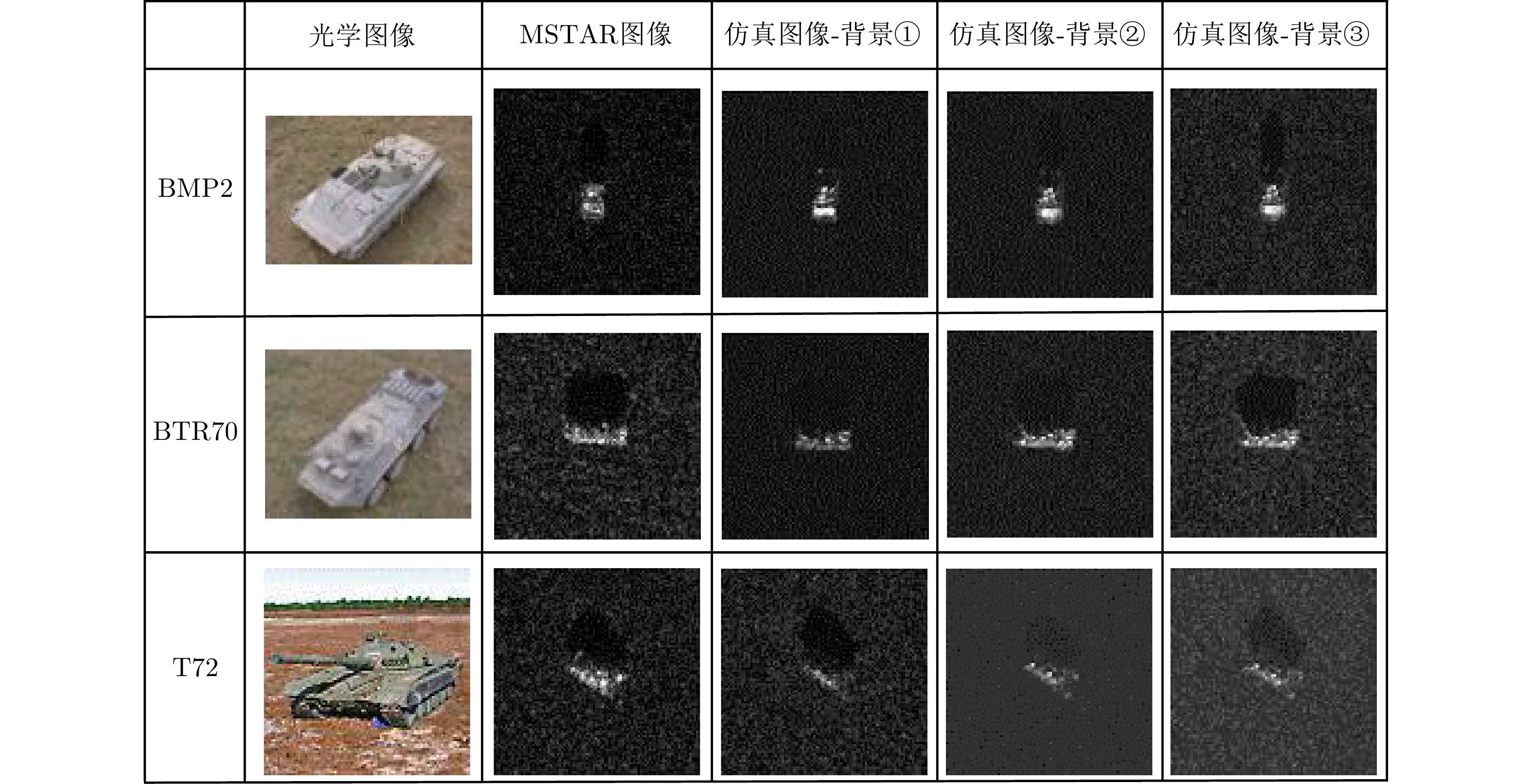
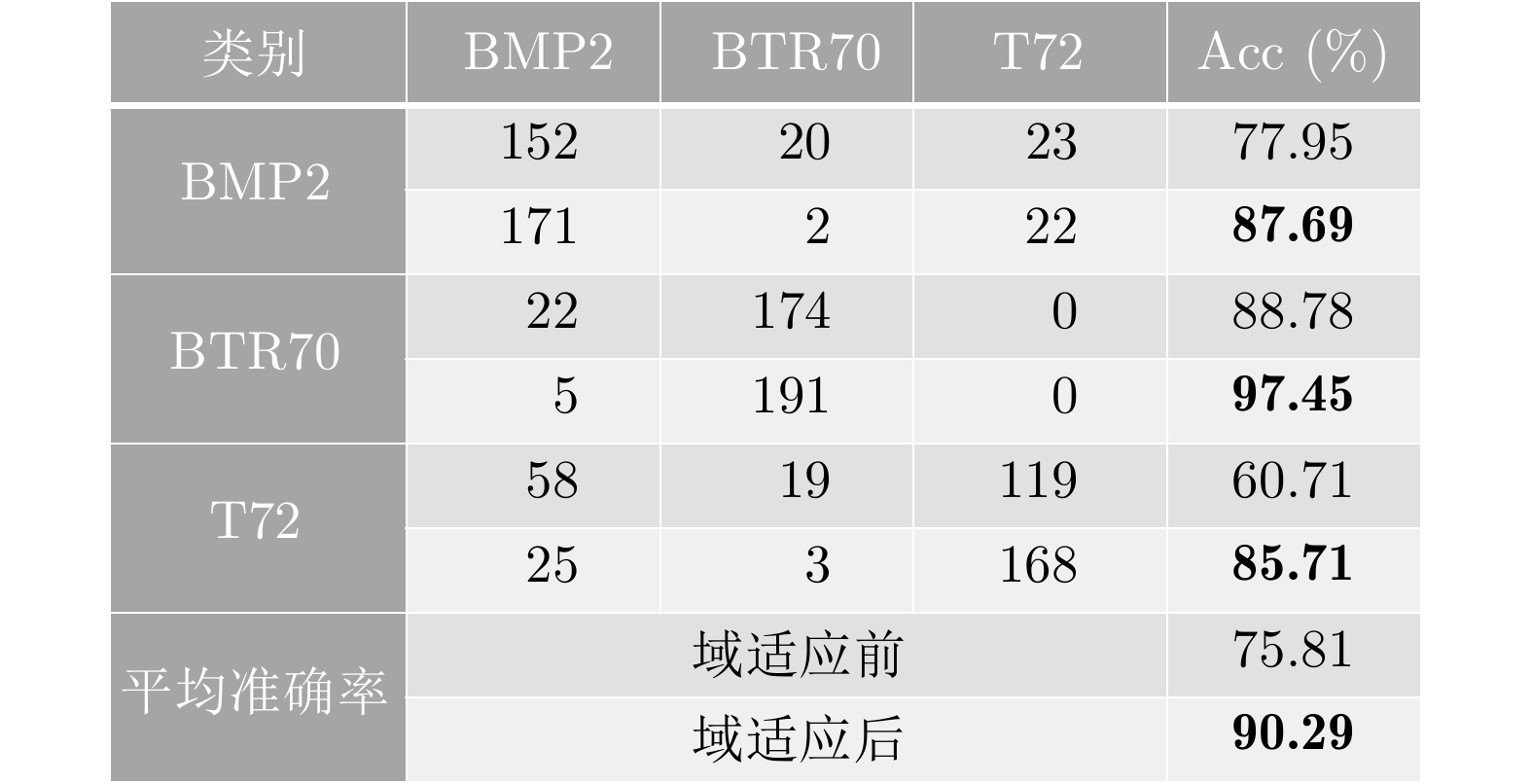
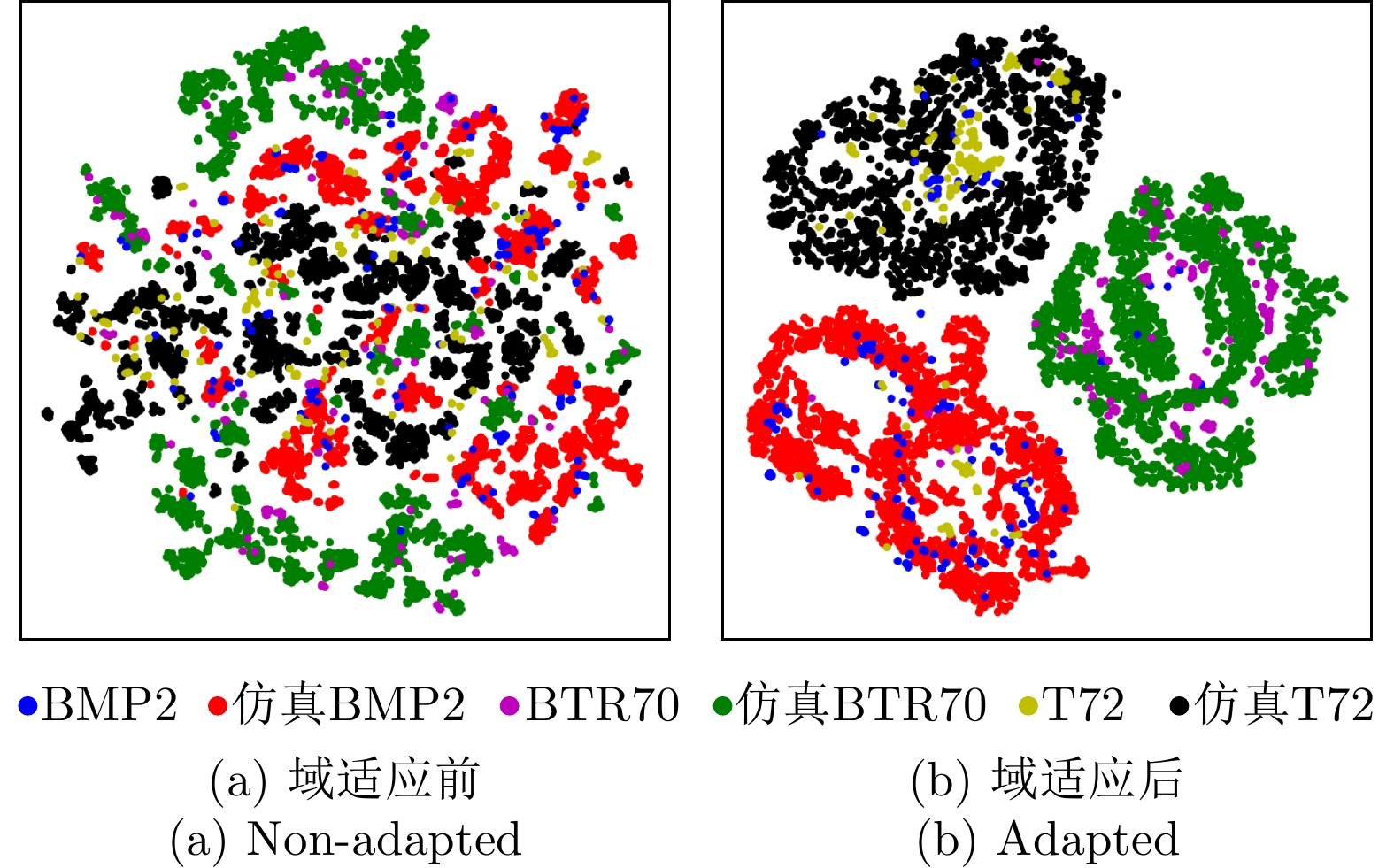
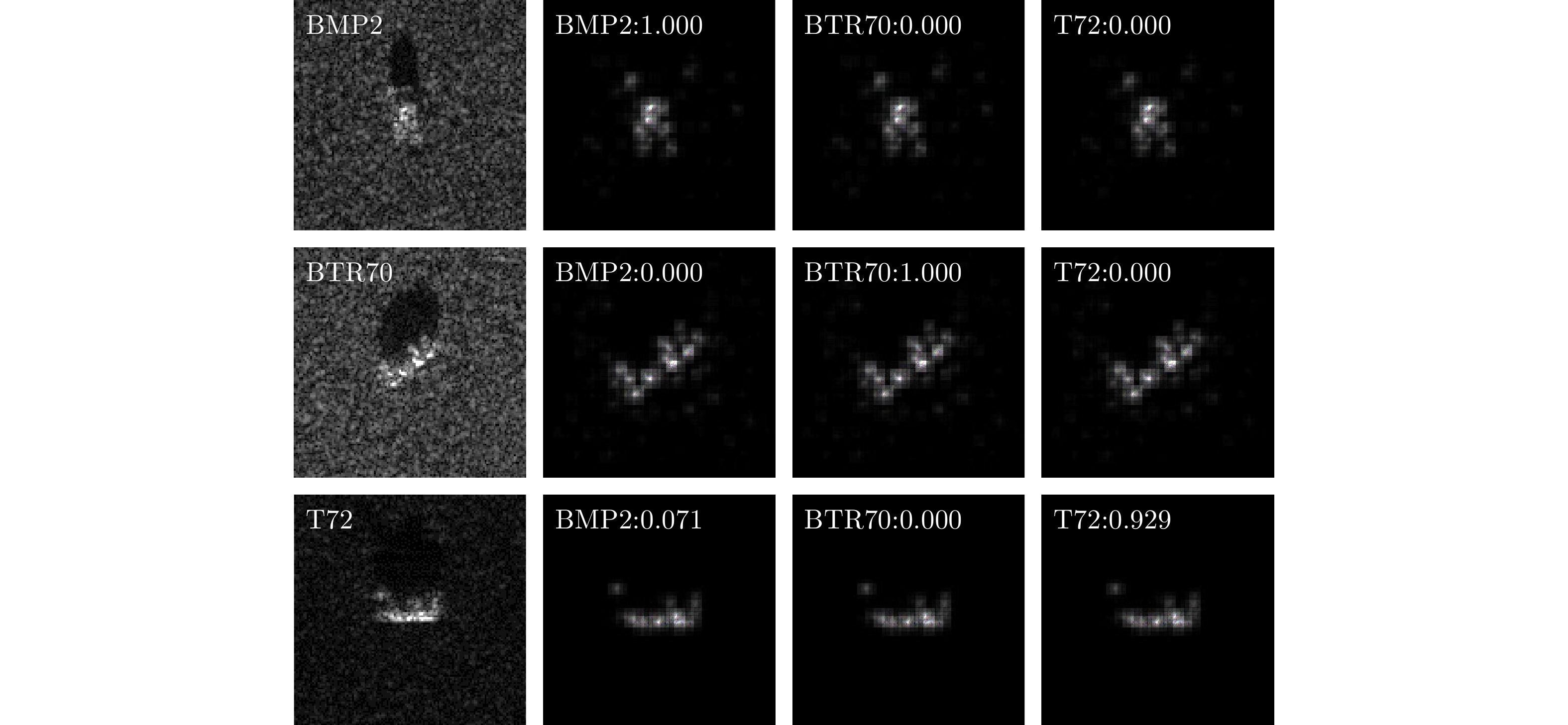
| [1] |
EL-DARYMLI K, MCGUIRE P, POWER D, et al. Target detection in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art survey[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2013, 7(1): 071598. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.7.071598 |
| [2] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 |
| [3] |
ZHANG Zhimian, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 |
| [4] |
PAN Zongxu, BAO Xianjie, ZHANG Yueting, et al. Siamese network based metric learning for SAR target classification[C]. IGARSS 2019 – 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1342–1345.
|
| [5] |
董纯柱, 胡利平, 朱国庆, 等. 地面车辆目标高质量SAR图像快速仿真方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(3): 351–360. doi: 10.12000/JR15057DONG Chunzhu, HU Liping, ZHU Guoqing, et al. Efficient simulation method for high quality SAR images of complex ground vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(3): 351–360. doi: 10.12000/JR15057 |
| [6] |
SONG Qian, CHEN Hui, XU Feng, et al. EM simulation-aided zero-shot learning for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(6): 1092–1096. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2936897 |
| [7] |
HU Liping, DONG Chunzhu, LIU Jinfan, et al. Non-homologous target recognition of ground vehicles based on SAR simulation image[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3518–3525. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.12.13 |
| [8] |
MALMGREN-HANSEN D, KUSK A, DALL J, et al. Improving SAR automatic target recognition models with transfer learning from simulated data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1484–1488. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2717486 |
| [9] |
ZHANG Linbin, LENG Xiangguang, FENG Sijia, et al. Domain knowledge powered two-stream deep network for few-shot SAR vehicle recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–15. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3116349 |
| [10] |
FAN Cangning, LIU Peng, XIAO Ting, et al. A review of deep domain adaptation: General situation and complex situation[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(3): 515–548. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200238 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
LONG Mingsheng, CAO Yue, WANG Jianmin, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 97–105.
|
| [13] |
LONG Mingsheng, ZHU Han, WANG Jianmin, et al. Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 2208–2217.
|
| [14] |
ZHU Yongchun, ZHUANG Fuzhen, WANG Jindong, et al. Deep subdomain adaptation network for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(4): 1713–1722. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2988928 |
| [15] |
GANIN Y, USTINOVA E, AJAKAN H, et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 2096–2030.
|
| [16] |
SAITO K, WATANABE K, USHIKU Y, et al. Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3723–3732.
|
| [17] |
PEI Zhongyi, CAO Zhangjie, LONG Mingsheng, et al. Multi-adversarial domain adaptation[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 3934–3941.
|
| [18] |
DU Zhekai, LI Jingjing, SU Hongzu, et al. Cross-domain gradient discrepancy minimization for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 3936–3945.
|
| [19] |
LONG Mingsheng, CAO Zhangjie, WANG Jianmin, et al. Conditional adversarial domain adaptation[C]. Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 1647–1657.
|
| [20] |
GHIFARY M, KLEIJN W B, ZHANG Mengjie, et al. Deep reconstruction-classification networks for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 597–613.
|
| [21] |
BOUSMALIS K, TRIGEORGIS G, SILBERMAN N, et al. Domain separation networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 343–351.
|
| [22] |
SANKARANARAYANAN S, BALAJI Y, CASTILLO C D, et al. Generate to adapt: Aligning domains using generative adversarial networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8503–8512.
|
| [23] |
HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2947634 |
| [24] |
WANG Ke, ZHANG Gong, and LEUNG H. SAR target recognition based on cross-domain and cross-task transfer learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 153391–153399. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2948618 |
| [25] |
ZHANG Wei, ZHU Yongfeng, and FU Qiang. Adversarial deep domain adaptation for multi-band SAR images classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 78571–78583. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2922844 |
| [26] |
XU Yongjie, LANG Haitao, NIU Lihui, et al. Discriminative adaptation regularization framework-based transfer learning for ship classification in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(11): 1786–1790. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2907139 |
| [27] |
BACH S, BINDER A, MONTAVON G, et al. On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0130140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130140 |
| [28] |
GU Jindong, YANG Yinchong, and TRESP V. Understanding individual decisions of CNNs via contrastive backpropagation[C]. The 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2018: 119–134.
|
| [29] |
GRETTON A, SRIPERUMBUDUR B, SEJDINOVIC D, et al. Optimal kernel choice for large-scale two-sample tests[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1205–1213.
|
| [30] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105.
|
| [31] |
GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680.
|
| [32] |
CHOI J, JEONG M, KIM T, et al. Pseudo-labeling curriculum for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. The 30th British Machine Vision Conference, Cardiff, UK, 2019: 67.
|
| [33] |
SHU Yang, CAO Zhangjie, LONG Mingsheng, et al. Transferable curriculum for weakly-supervised domain adaptation[C]. The 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hawaii, USA, 2019: 4951–4958.
|
| [34] |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626.
|
| [35] |
ZEILER M D and FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 818–833.
|
| [36] |
MONTAVON G, LAPUSCHKIN S, BINDER A, et al. Explaining nonlinear classification decisions with deep taylor decomposition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 65: 211–222. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.11.008 |
| [37] |
VAN DER MAATEN L and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(86): 2579–2605.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: