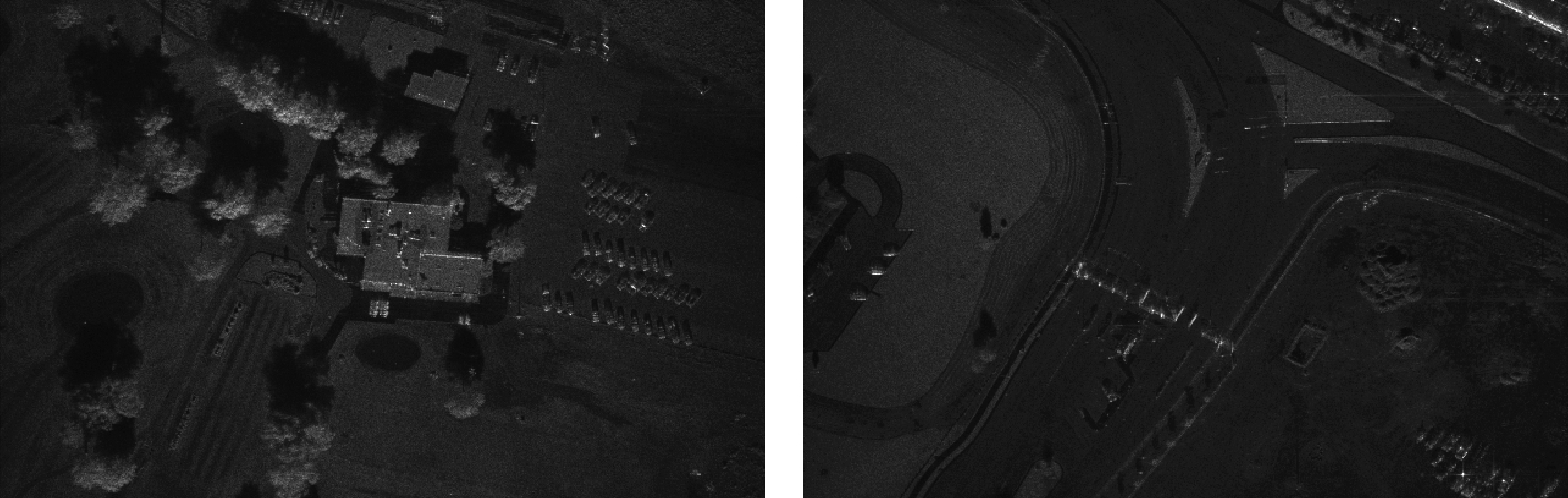
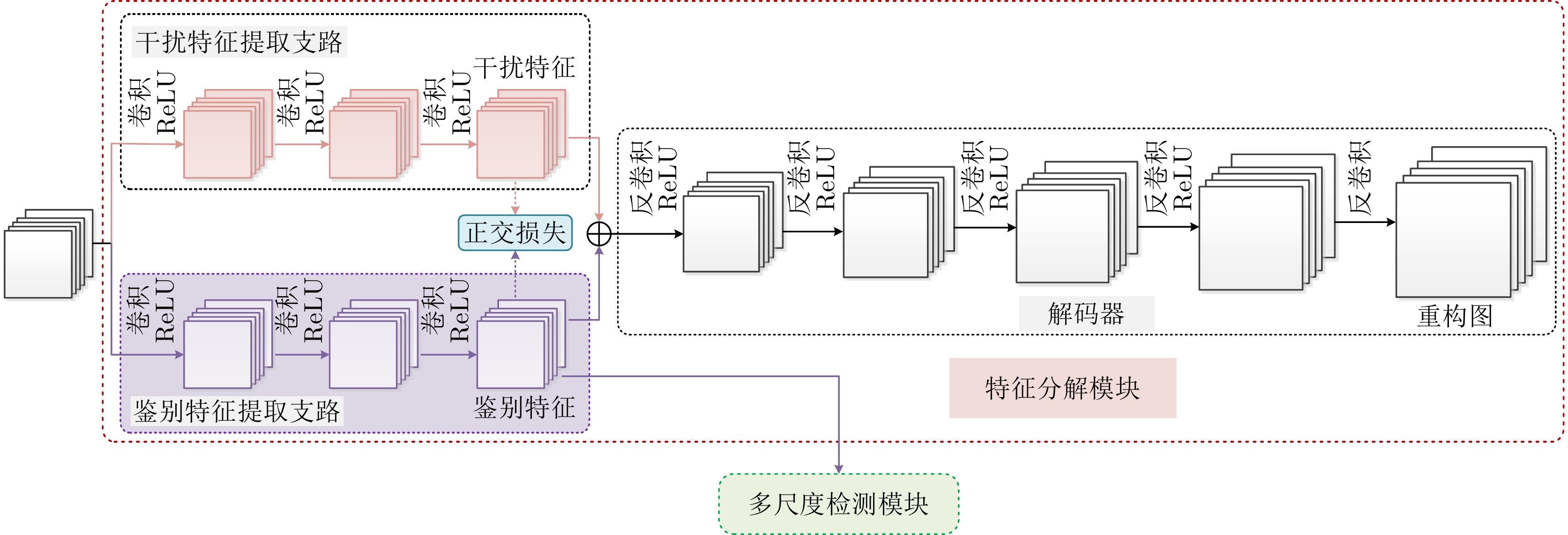
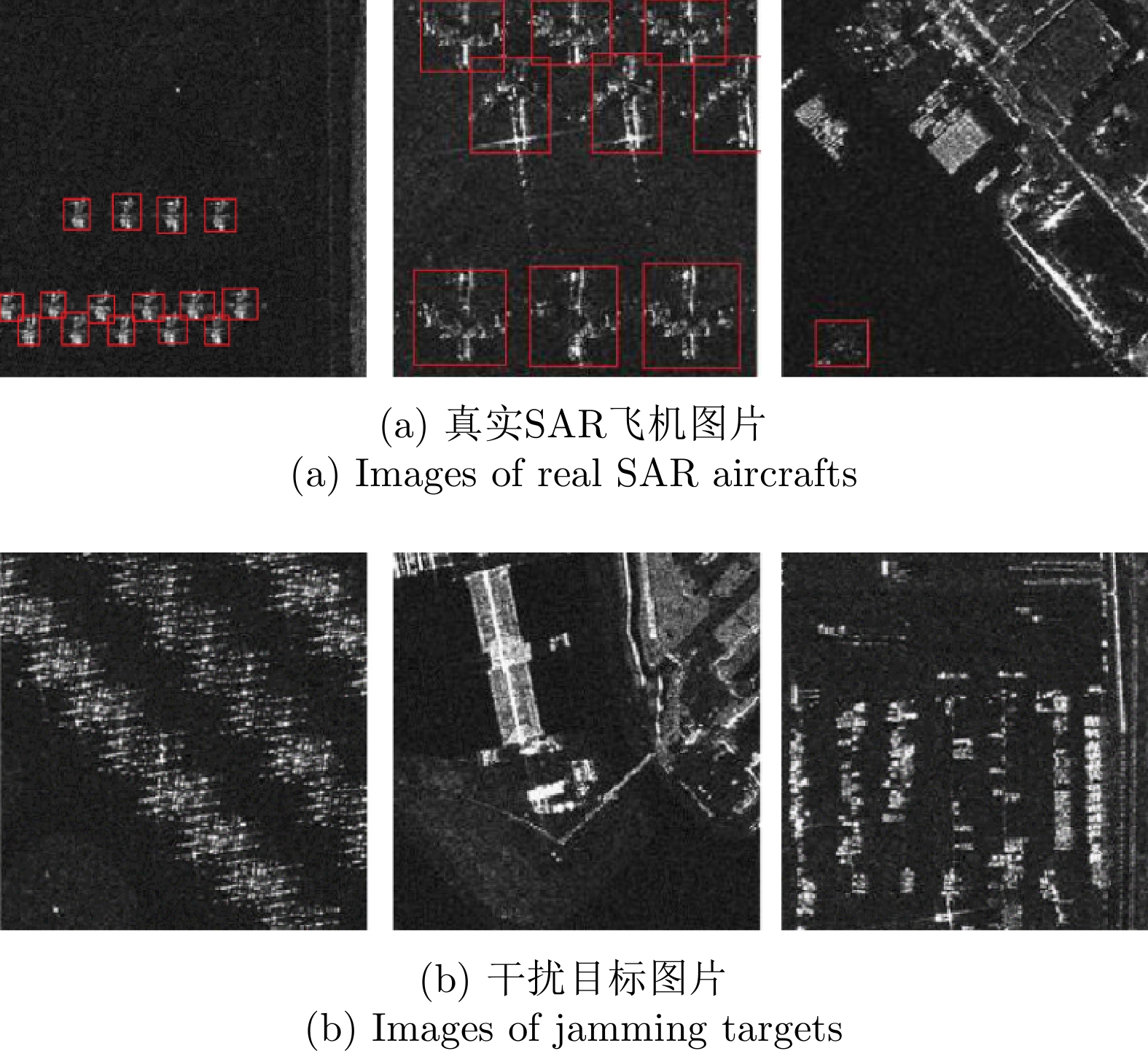
| [1] |
NOVAK L M, BURL M C, and IRVING W W. Optimal polarimetric processing for enhanced target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1993, 29(1): 234–244. doi: 10.1109/7.249129 |
| [2] |
XING Xiangwei, CHEN Zhenlin, ZOU Huanxin, et al. A fast algorithm based on two-stage CFAR for detecting ships in SAR images[C]. The 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xi’an, China, 2009: 506–509.
|
| [3] |
LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, YANG Kai, et al. A bilateral CFAR algorithm for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1536–1540. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2412174 |
| [4] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 |
| [5] |
HINTON G E and SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504–507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 |
| [6] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105.
|
| [7] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015.
|
| [8] |
SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9.
|
| [9] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778.
|
| [10] |
GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448.
|
| [11] |
REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2015: 91–99.
|
| [12] |
LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37.
|
| [13] |
NEUBECK A and VAN GOOL L. Efficient non-maximum suppression[C]. The 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 2006: 850–855.
|
| [14] |
王思雨, 高鑫, 孙皓, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的高分辨率SAR图像飞机目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR17009WANG Siyu, GAO Xin, SUN Hao, et al. An aircraft detection method based on convolutional neural networks in high-resolution SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 195–203. doi: 10.12000/JR17009 |
| [15] |
WANG Zhaocheng, DU Lan, MAO Jiashun, et al. SAR target detection based on SSD with data augmentation and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(1): 150–154. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2867242 |
| [16] |
LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, PENG Shujuan, et al. Ship detection in SAR images based on convolutional neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1953–1959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.09 |
| [17] |
ZHANG Shaoming, WU Ruize, XU Kunyuan, et al. R-CNN-based ship detection from high resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(6): 631. doi: 10.3390/rs11060631 |
| [18] |
陈慧元, 刘泽宇, 郭炜炜, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的大场景遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041CHEN Huiyuan, LIU Zeyu, GUO Weiwei, et al. Fast detection of ship targets for large-scale remote sensing image based on a cascade convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041 |
| [19] |
WEI Di, DU Yuang, DU Lan, et al. Target detection network for SAR images based on semi-supervised learning and attention mechanism[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(14): 2686. doi: 10.3390/RS13142686 |
| [20] |
GLOROT X, BORDES A, and BENGIO Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[C]. The 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2011: 315–323.
|
| [21] |
LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
ZHANG Peng, XU Hao, TIAN Tian, et al. SEFEPNet: Scale expansion and feature enhancement pyramid network for SAR aircraft detection with small sample dataset[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 3365–3375. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3169339 |
| [24] |
LIN Tsungyi, DOLLÁR Piotr, GIRSHICK Ross, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944.
|
| [25] |
LI Lu, DU Yuang, and DU Lan. Vehicle target detection network in SAR images based on rectangle-invariant rotatable convolution[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(13): 3086. doi: 10.3390/rs14133086 |
| [26] |
杜兰, 王梓霖, 郭昱辰, 等. 结合强化学习自适应候选框挑选的SAR目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 884–896. doi: 10.12000/JR22121DU Lan, WANG Zilin, GUO Yuchen, et al. Adaptive region proposal selection for SAR target detection using reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 884–896. doi: 10.12000/JR22121 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: