- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | Lu Yanxi, He Zishu, Cheng Ziyang, Liu Shuangli. Joint Selection of Transmitters and Receivers in Distributed Multi-input Multi-output Radar Network for Multiple Targets Tracking[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 73-80. doi: 10.12000/JR16106 |
Joint Selection of Transmitters and Receivers in Distributed Multi-input Multi-output Radar Network for Multiple Targets Tracking
DOI: 10.12000/JR16106 CSTR: 32380.14.JR16106
-
Abstract
Only a subset of transmitters and receivers in a distributed Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) radar network is allowed to actively track a target at a particular instance due to the limited time and energy resource of a MIMO radar network. It is therefore desirable to obtain an efficient method to overcome the resource constraints while optimizing the tracking performance. In this study, posterior Cramer-Rao lower bound is used as the performance metric and the selection problem is formulated as a Boolean programming problem aiming at optimizing the worst tracking performance of multiple targets. It is later relaxed to a semidefinite programming and solved by the block coordinate descend method. Numerical results show that proposed method superior to the fixed selection method. In addition, with less computation complexity, the proposed method obtains nearly equivalent performance compared with exhaustive search method. -

-
References
[1] Li J and Stoica P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.904812[2] Haimovich A M, Blum R S, and Cimini L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448[3] Joshi S and Boyd S. Sensor selection via convex optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 451–462. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007095[4] Shen X, Liu S, and Varshney P K. Sensor selection for nonlinear systems in large sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(4): 2664–2678. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014ITAES..50.2664S[5] Masazade E, Fardad M, and Varshney P K. Sparsity-Promoting extended Kalman filtering for target tracking in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 19(19): 845–848. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258655744_Sparsity-Promoting_Extended_Kalman_Filtering_for_Target_Tracking_in_Wireless_Sensor_Networks[6] Godrich H, Petropulu A P, and Poor H V. Sensor selection in distributed multiple-radar architectures for localization: A knapsack problem formulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(1): 247–260. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2170170[7] Ma Botao, Chen Haowen, Sun Bin, et al.. A joint scheme of antenna selection and power allocation for localization in MIMO radar sensor networks[C]. IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Hangzhou, China, 2014: 2226–2229. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7015390/[8] Glass J D and Smith L D. MIMO radar resource allocation using posterior Cramér-Rao lower bounds[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2011: 1–9. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2053918.2054178[9] Xie M, Yi W, Kirubajaran T, et al.. Receive-beam allocation for multiple target tracking with distributed MIMO radar systems[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. DOI: 10.1109/RADAR. 2016.7485153.[10] Godrich H, Tajer A, and Poor H.V. Distributed target tracking in multiple widely separated radar architectures[C]. IEEE 7th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM), Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012: 153–156. DOI: 10.1109/SAM. 2012.6250453.[11] Trees H L V. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory—Part I[M]. Publishing House of Electronics Industry, Beijing, China, 2003: 131–143.[12] Tichavsky P, Muravchik C H, and Nehorai A. Posterior Cramer-Rao bounds for discrete-time nonlinear filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1998, 46(5): 1386–1396. doi: 10.1109/78.668800[13] Boyd S and Vandenberghe L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2004: 55–60.[14] Arulampalam M S, Maskell S, Gordon N, et al.. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. doi: 10.1109/78.978374[15] Nemirovski A. Interior point polynomial time methods in convex programming[OL]. . 2012.[16] Razaviyayn M, Hong M, and Luo Z Q. A unified convergence analysis of block successive minimization methods for nonsmooth optimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2013, 23(2): 1126–1153. doi: 10.1137/120891009 -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Selection results of transmitters and receivers varied with time
- Figure 2. Performance of proposed method and fixed selection method
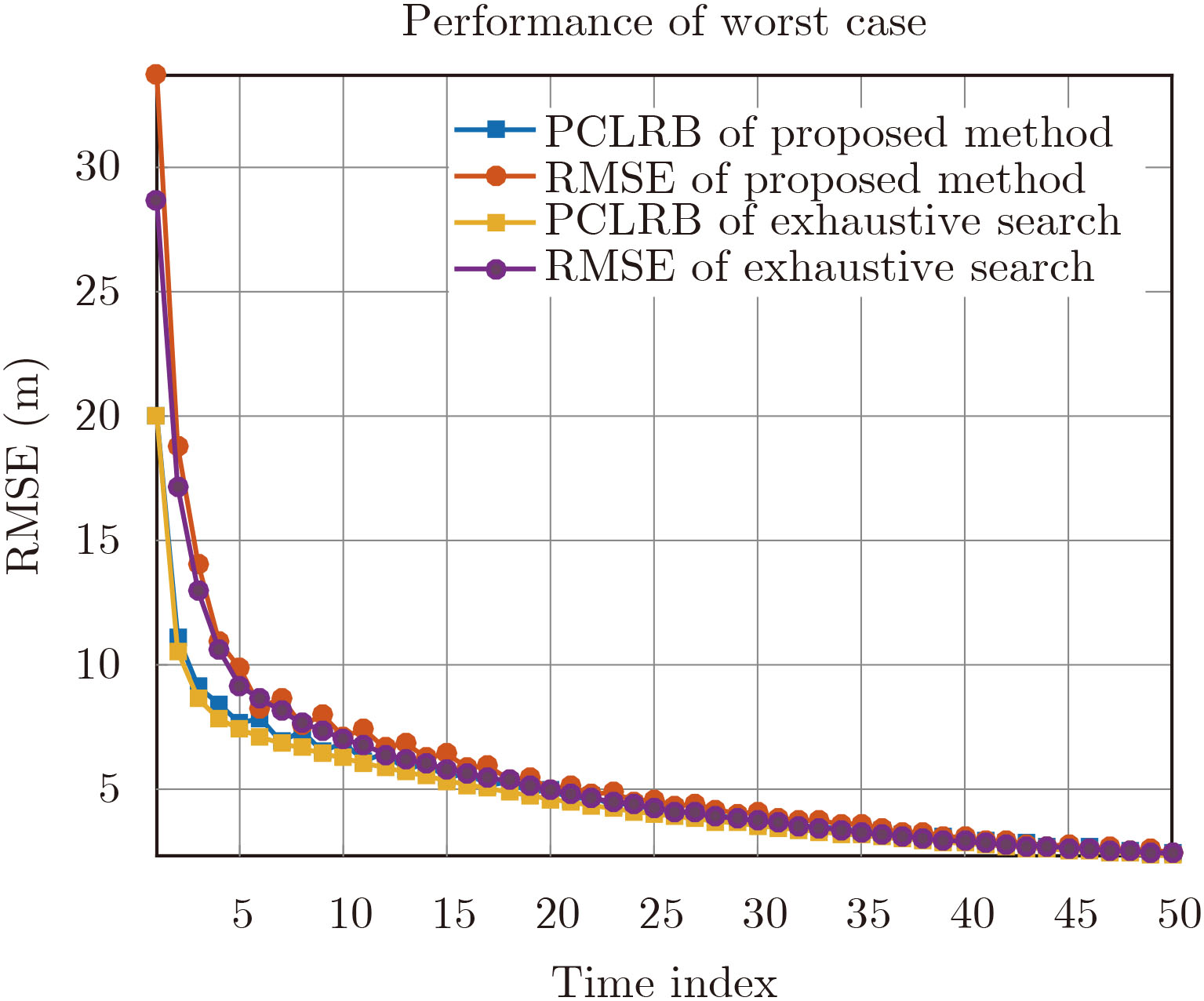
- Figure 3. Performance of proposed method and exhaustive search method
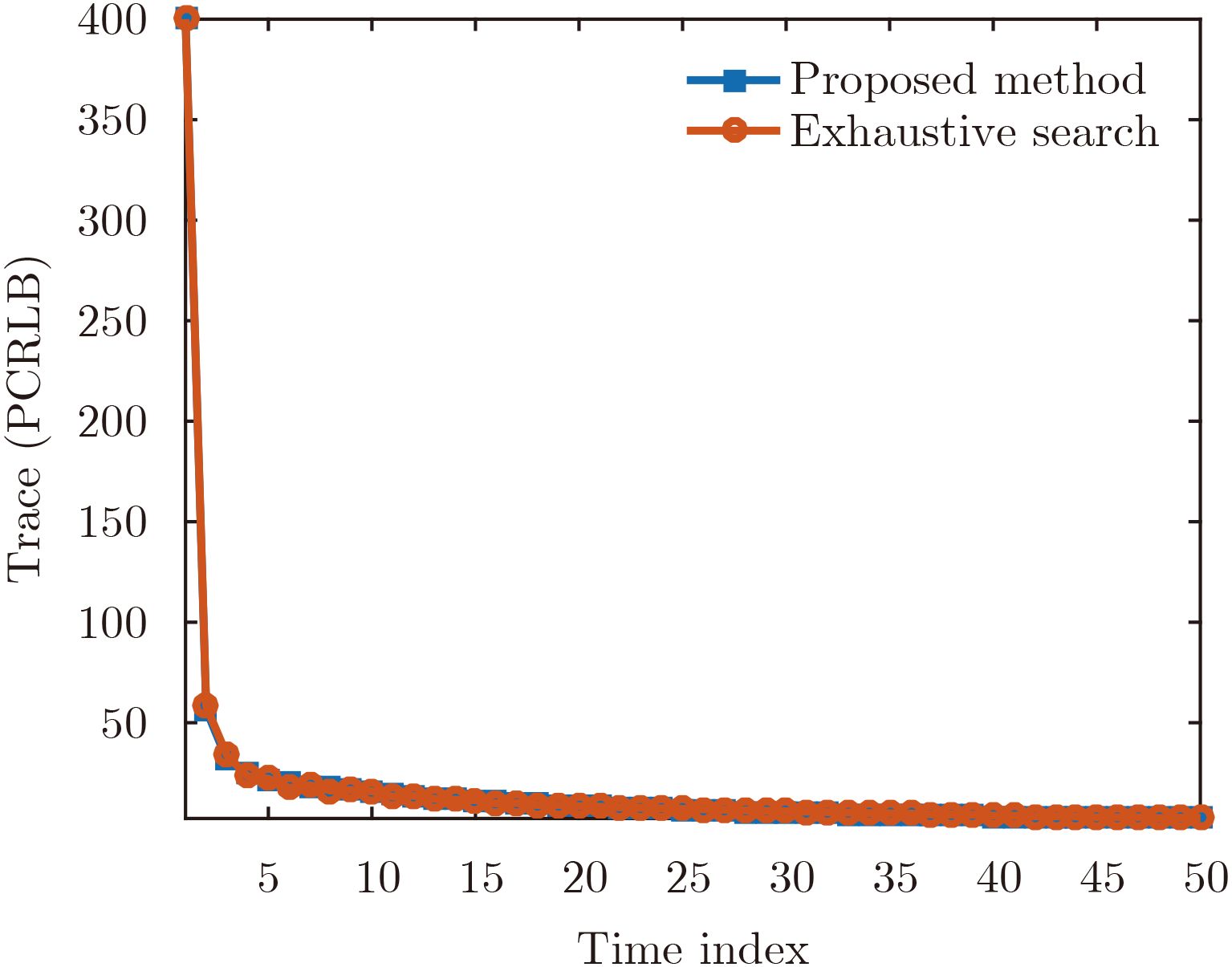
- Figure 4. Average performance of proposed method and exhaustive search method
- Figure 5. Execution time of proposed method and exhaustive search method


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: