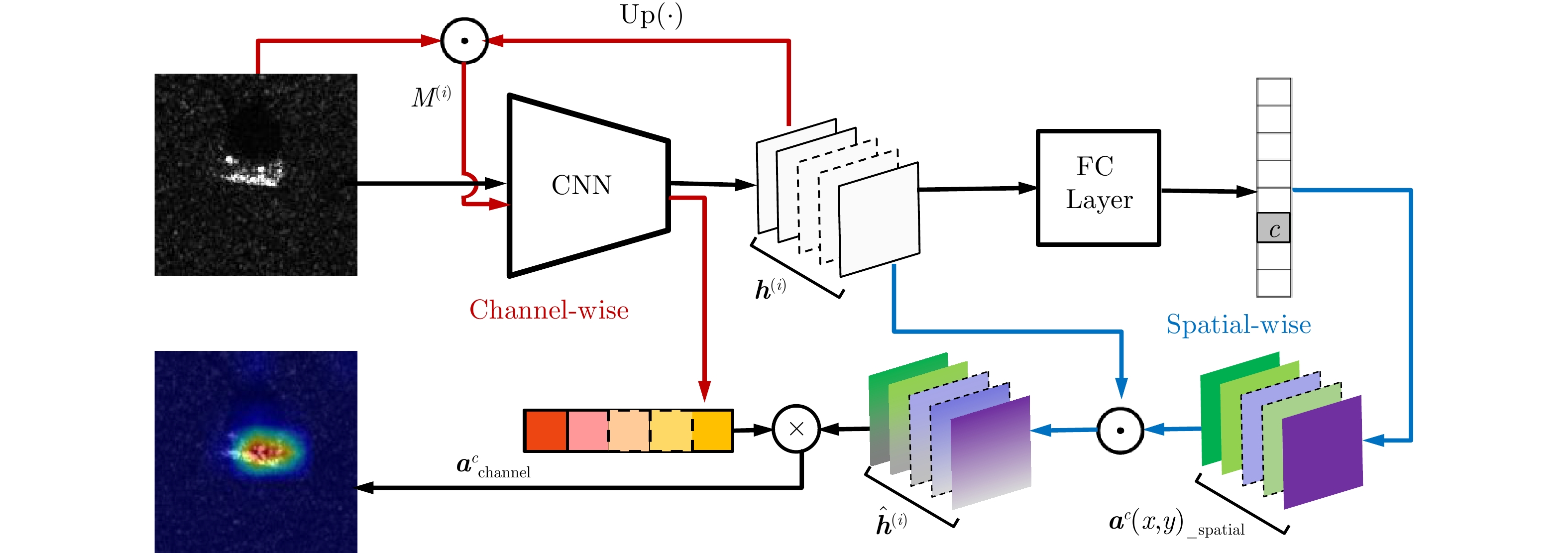
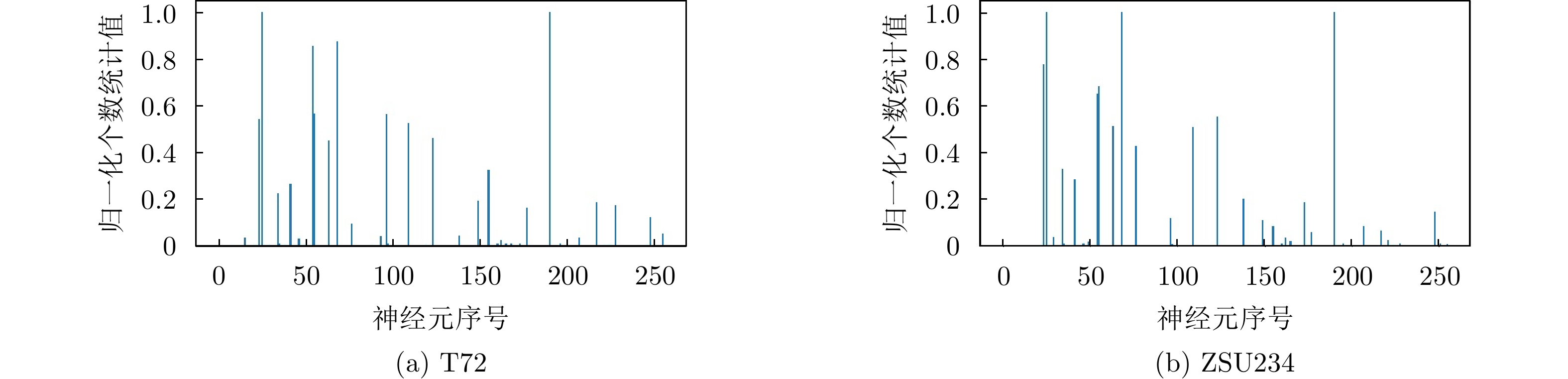
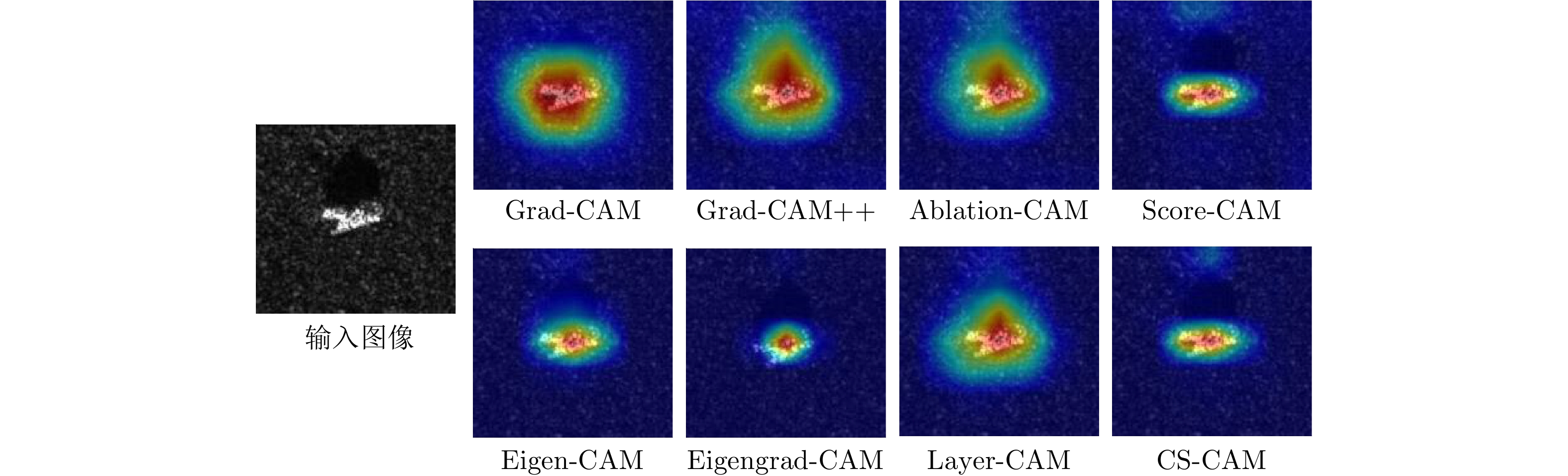
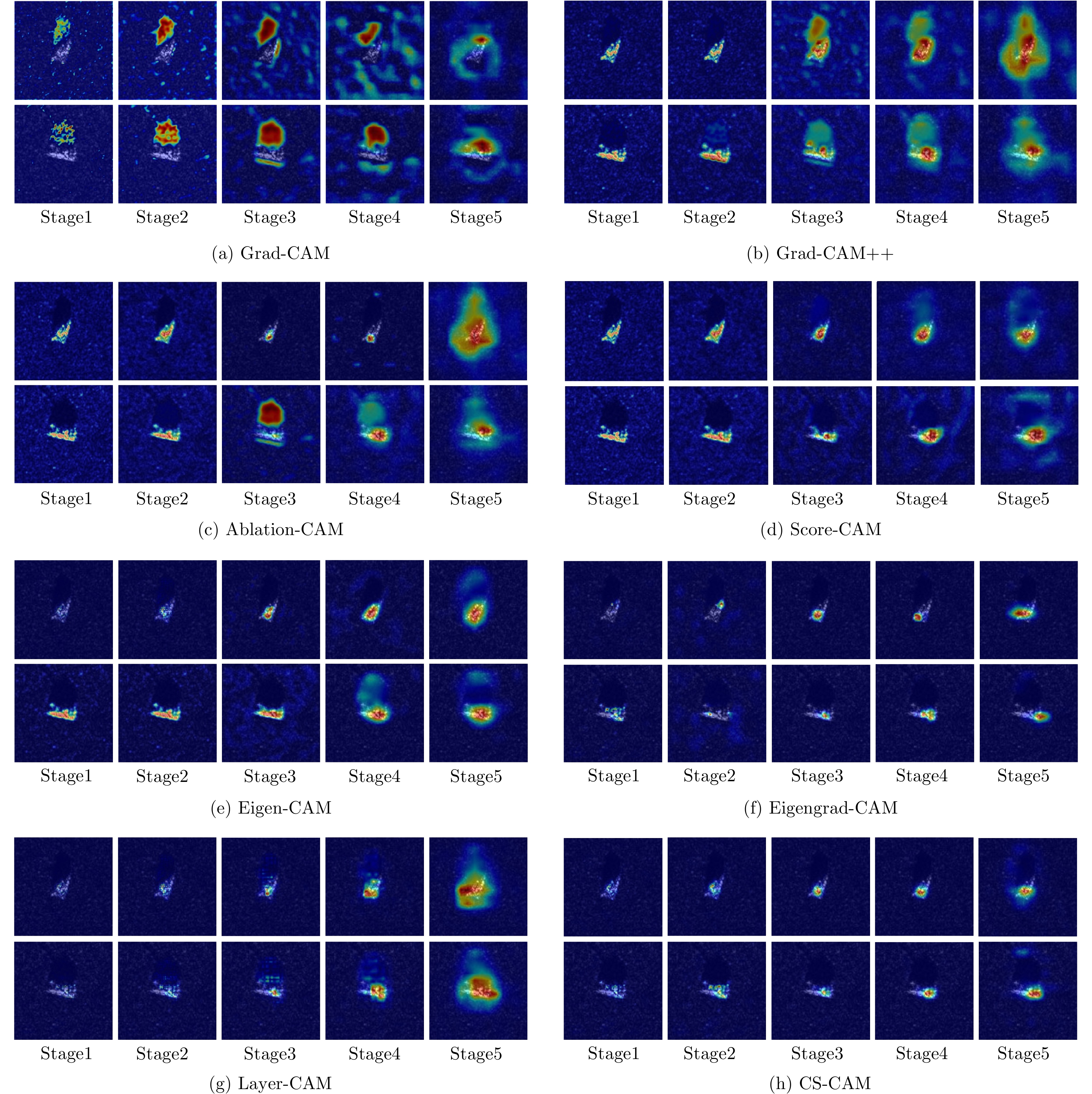
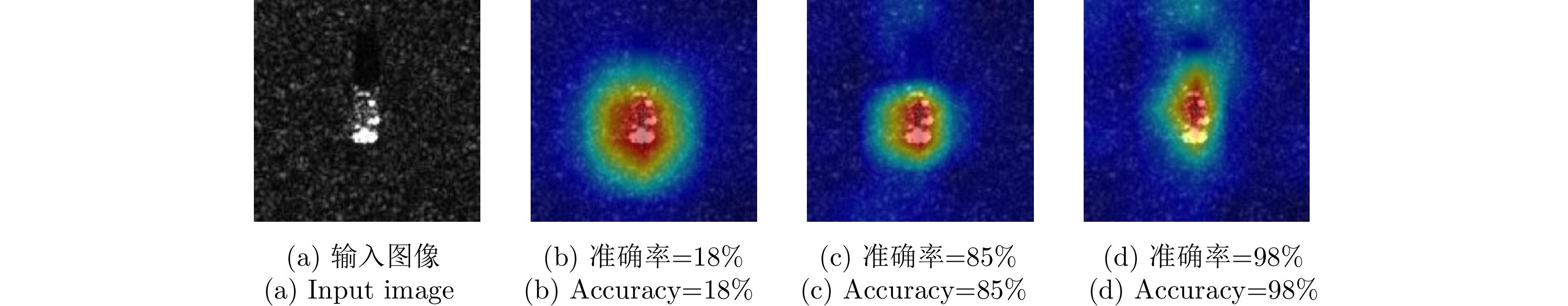
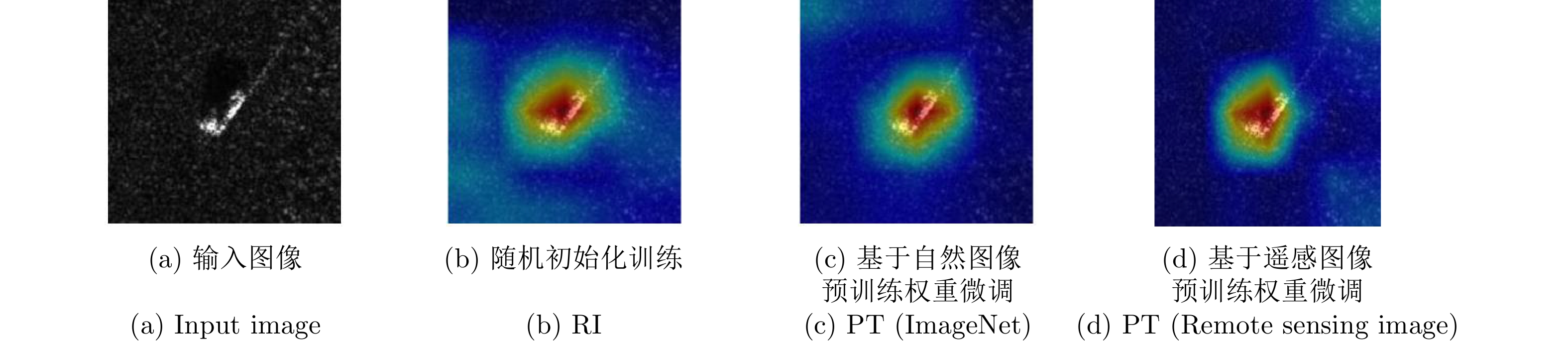
| [1] |
PALLOTTA L, CLEMENTE C, DE MAIO A D, et al. Detecting covariance symmetries in polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 80–95. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2595626. |
| [2] |
WANG Zhen, WANG Shuang, XU Caijin, et al. SAR images super-resolution via cartoon-texture image decomposition and jointly optimized regressors[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 1668–1671.
|
| [3] |
LI Weike, ZOU Bin, and ZHANG Lamei. Ship detection in a large scene SAR image using image uniformity description factor[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–5.
|
| [4] |
YUAN Ye, WU Yanxia, FU Yan, et al. An advanced SAR image despeckling method by bernoulli-sampling-based self-supervised deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3636. doi: 10.3390/rs13183636. |
| [5] |
SHU Yuanjun, LI Wei, YANG Menglong, et al. Patch-based change detection method for SAR images with label updating strategy[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(7): 1236. doi: 10.3390/rs13071236. |
| [6] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720. |
| [7] |
PAN Zongxu, AN Quanzhi, and ZHANG Bingchen. Progress of deep learning-based target recognition in radar images[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2019, 49(12): 1626–1639. doi: 10.1360/ssi-2019-0093. |
| [8] |
贺丰收, 何友, 刘准钆, 等. 卷积神经网络在雷达自动目标识别中的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899. HE Fengshou, HE You, LIU Zhunga, et al. Research and development on applications of convolutional neural networks of radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899. |
| [9] |
ZHAO Juanping, GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, et al. A coupled convolutional neural network for small and densely clustered ship detection in SAR images[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(4): 42301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9405-6. |
| [10] |
杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104. DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104. |
| [11] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. |
| [12] |
黄钟泠, 姚西文, 韩军伟. 面向SAR图像解译的物理可解释深度学习技术进展与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, and HAN Junwei. Progress and perspective on physically explainable deep learning for synthetic aperture radar image interpretation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. |
| [13] |
DATCU M, HUANG Zhongling, ANGHEL A, et al. Explainable, physics-aware, trustworthy artificial intelligence: A paradigm shift for synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2023, 11(1): 8–25. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2023.3237465. |
| [14] |
LI Yi and DU Lan. Design of the physically interpretable sar target recognition network combined with electromagnetic scattering characteristics[C]. 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 4988–4991.
|
| [15] |
李玮杰, 杨威, 刘永祥, 等. 雷达图像深度学习模型的可解释性研究与探索[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2022, 52(6): 1114–1134. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0102. LI Weijie, YANG Wei, LIU Yongxiang, et al. Research and exploration on the interpretability of deep learning model in radar image[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2022, 52(6): 1114–1134. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0102. |
| [16] |
FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, WANG Fulai, et al. Electromagnetic scattering feature (ESF) module embedded network based on ASC model for robust and interpretable SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5235415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3208333. |
| [17] |
LI Chen, DU Lan, LI Yi, et al. A novel SAR target recognition method combining electromagnetic scattering information and GCN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4508705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3178234. |
| [18] |
LIU Zhunga, WANG Longfei, WEN Zaidao, et al. Multilevel scattering center and deep feature fusion learning framework for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5227914. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3174703. |
| [19] |
ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264. |
| [20] |
FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, ZHANG Linbin, et al. SAR target classification based on integration of ASC parts model and deep learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 10213–10225. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3116979. |
| [21] |
LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137. |
| [22] |
FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, WANG Fulai, et al. PAN: Part attention network integrating electromagnetic characteristics for interpretable SAR vehicle target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3256399. |
| [23] |
DATCH M, ANDREI V, DUMITRU C O, et al. Explainable deep learning for SAR data[C]. Φ-Week, Frascati, Italy, 2019.
|
| [24] |
SU Shenghan, CUI Ziteng, GUO Weiwei, et al. Explainable analysis of deep learning methods for SAR image classification[C]. 2022 – 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022, 2570–2573.
|
| [25] |
郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. |
| [26] |
BELLONI C, BALLERI A, AOUF N, et al. Explainability of deep SAR ATR through feature analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 659–673. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3031435. |
| [27] |
PANATI C, WAGNER S, and BRÜGGENWIRTH S. Feature relevance evaluation using grad-CAM, LIME and SHAP for deep learning SAR data classification[C]. 2022 23rd International Radar Symposium, Gdansk, Poland, 2022: 457–462.
|
| [28] |
SUNDARARAJAN M, TALY A, and YAN Qiqi. Axiomatic attribution for deep networks[C]. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017.
|
| [29] |
LUO Wenjie, LI Yujia, URTASUN R, et al. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks[C]. 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 4898–4906.
|
| [30] |
ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921–2929.
|
| [31] |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626.
|
| [32] |
CHATTOPADHAY A, SARKAR A, HOWLADER P, et al. Grad-CAM++: Generalized gradient-based visual explanations for deep convolutional networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 839–847.
|
| [33] |
DESAI S and RAMASWAMY H G. Ablation-CAM: Visual explanations for deep convolutional network via gradient-free localization[C]. 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass, USA, 2020: 972–980.
|
| [34] |
WANG Haofan, WANG Zifan, DU Mengnan, et al. Score-CAM: Score-weighted visual explanations for convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 111–119.
|
| [35] |
MUHAMMAD M B and YEASIN M. Eigen-CAM: Class activation map using principal components[C]. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 1–7.
|
| [36] |
JIANG Pengtao, ZHANG Changbin, HOU Qibin, et al. LayerCAM: Exploring hierarchical class activation maps for localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 5875–5888. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3089943. |
| [37] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996.
|
| [38] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego, USA, 2015.
|
| [39] |
YEH C K, HSIEH C Y, SUGGALA A S, et al. On the (in)fidelity and sensitivity of explanations[C]. 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019.
|
| [40] |
ADEBAYO J, GILMER J, MUELLY M, et al. Sanity checks for saliency maps[C]. 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 9525–9536.
|
| [41] |
HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2947634. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: