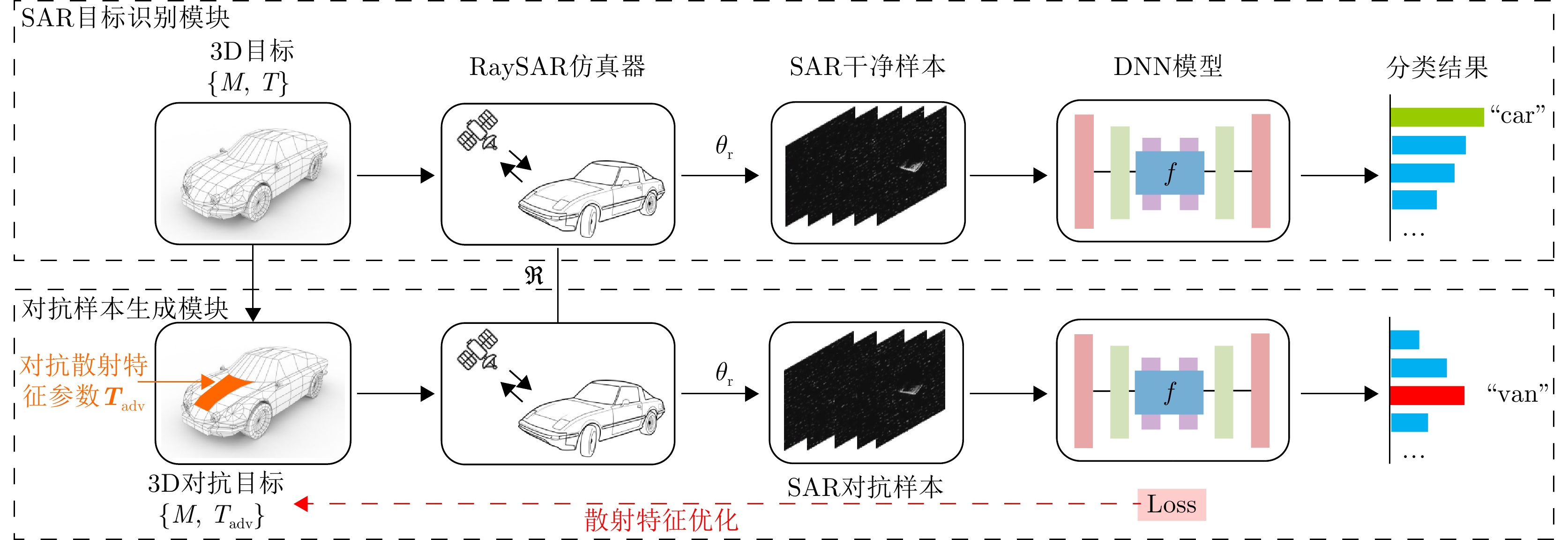
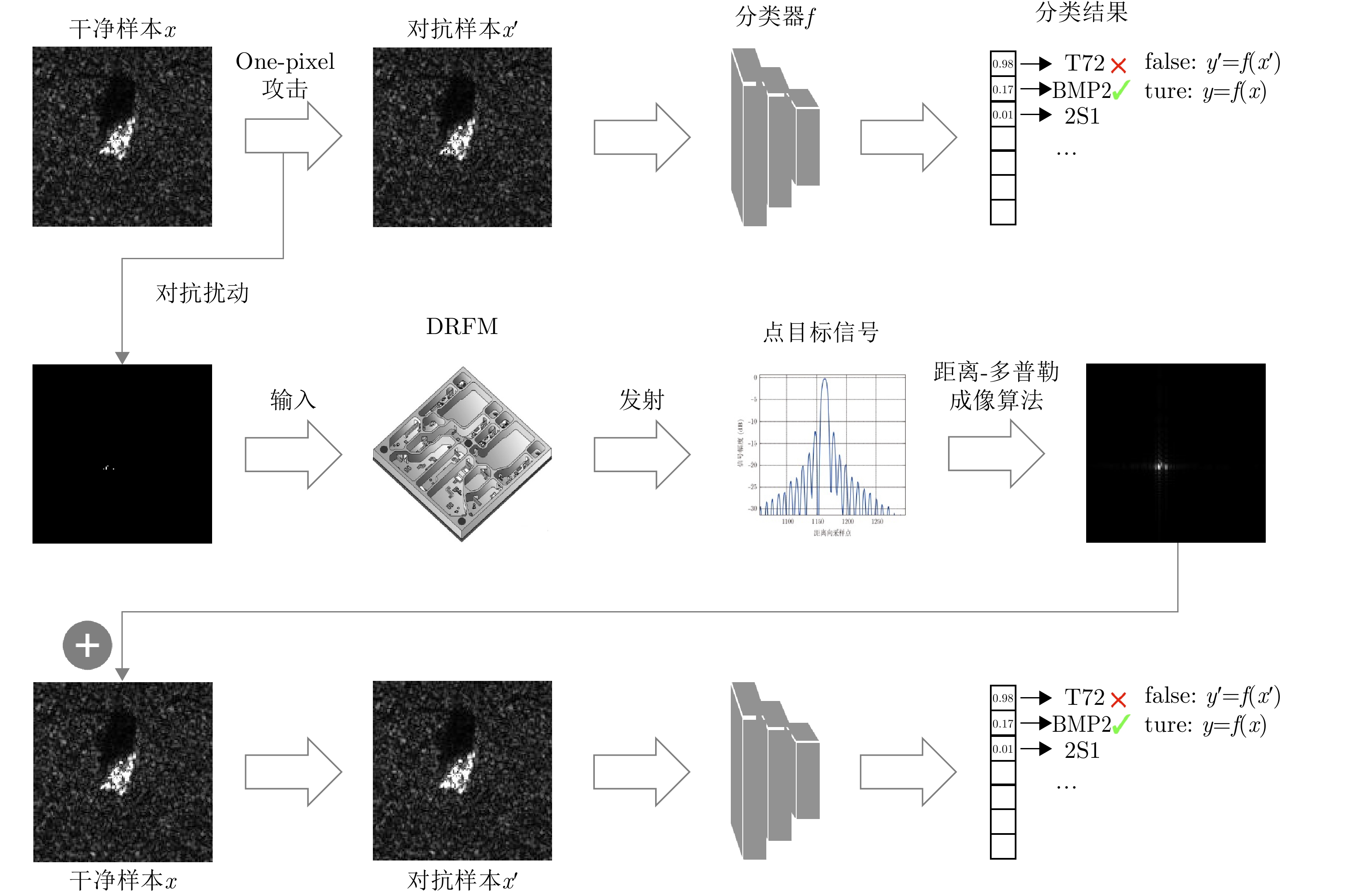
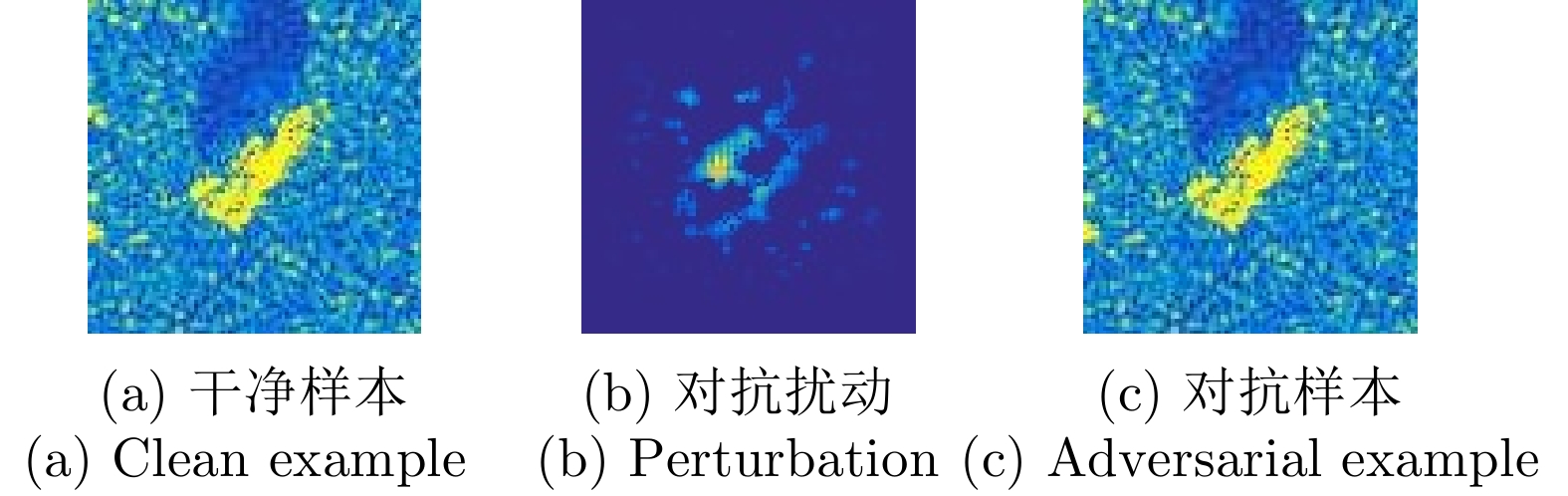
| [1] |
CHEN Sizhe and WANG Haipeng. SAR target recognition based on deep learning[C]. 2014 International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics, Shanghai, China, 2014: 541–547. doi: 10.1109/DSAA.2014.7058124. |
| [2] |
SCHEHER D C. Electronic Warfare in the Information Age[M]. Boston, MA: Artech House, 2000.
|
| [3] |
ZHOU Feng, ZHAO Bo, TAO Mingliang, et al. A large scene deceptive jamming method for space-borne SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4486–4495. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2259178. |
| [4] |
SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[C]. 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014: 6199.
|
| [5] |
LI Haifeng, HUANG Haikuo, CHEN Li, et al. Adversarial examples for CNN-based SAR image classification: An experience study[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 1333–1347. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3038683. |
| [6] |
ZHOU Jie, PENG Bo, and PENG Bowen. Adversarial attacks on radar target recognition based on deep learning[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 2646–2649. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883914. |
| [7] |
SUN Hao, XU Yanjie, KUANG Gangyao, et al. Adversarial robustness evaluation of deep convolutional neural network based SAR ATR algorithm[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 5263–5266. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9554783. |
| [8] |
DU Chuan, HUO Chaoying, ZHANG Lei, et al. Fast C&W: A fast adversarial attack algorithm to fool SAR target recognition with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4010005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3058011. |
| [9] |
HUANG Teng, ZHANG Qixiang, LIU Jiabao, et al. Adversarial attacks on deep-learning-based SAR image target recognition[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 162: 102632. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102632. |
| [10] |
WANG Mian, WANG Hongqiao, and WANG Ling. Adversarial examples generation and attack on SAR image classification[C]. 2021 5th International Conference on Innovation in Artificial Intelligence, Xiamen, China, 2021: 87–91. doi: 10.1145/3461353.3461375. |
| [11] |
DU Chuan and ZHANG Lei. Adversarial attack for SAR target recognition based on UNet-generative adversarial network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(21): 4358. doi: 10.3390/rs13214358. |
| [12] |
DANG Xunwang, YAN Hua, HU Liping, et al. SAR image adversarial samples generation based on parametric model[C]. 2021 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT52847.2021.9618140. |
| [13] |
PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, ZHOU Jie, et al. Scattering model guided adversarial examples for SAR target recognition: Attack and defense[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5236217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213305. |
| [14] |
DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9185–9193. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00957. |
| [15] |
CARLINI N and WAGNER D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2017: 39–57. doi: 10.1109/SP.2017.49. |
| [16] |
MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, and FROSSARD P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2574–2582. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.282. |
| [17] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 108–110.
|
| [18] |
JACKSON J A and MOSES R L. Feature extraction algorithm for 3D scene modeling and visualization using monostatic SAR[C]. SPIE 6237, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIII, Florida, USA, 2006: 55–66. doi: 10.1117/12.666558. |
| [19] |
SHARIF M, BHAGAVATULA S, BAUER L, et al. Accessorize to a crime: Real and stealthy attacks on state-of-the-art face recognition[C]. 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 2016: 1528–1540. doi: 10.1145/2976749.2978392. |
| [20] |
ZHENG Junhao, LIN Chenhao, SUN Jiahao, et al. Physical 3D adversarial attacks against monocular depth estimation in autonomous driving[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 24452–24461. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.02308. |
| [21] |
WEI Xingxing, HUANG Yao, SUN Yitong, et al. Unified adversarial patch for visible-infrared cross-modal attacks in the physical world[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(4): 2348–2363. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3330769. |
| [22] |
XU Kaidi, ZHANG Gaoyuan, LIU Sijia, et al. Adversarial T-shirt! Evading person detectors in a physical world[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 665–681. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_39. |
| [23] |
HU Zhanhao, HUANG Siyuan, ZHU Xiaopei, et al. Adversarial texture for fooling person detectors in the physical world[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 13297–13306. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01295. |
| [24] |
JAN S T K, MESSOU J, LIN Y C, et al. Connecting the digital and physical world: Improving the robustness of adversarial attacks[C]. 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 962–969. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.3301962. |
| [25] |
FENG Weiwei, XU Nanqing, ZHANG Tianzhu, et al. Robust and generalized physical adversarial attacks via meta-GAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 1112–1125. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3288426. |
| [26] |
ZHONG Yiqi, LIU Xianming, ZHAI Deming, et al. Shadows can be dangerous: Stealthy and effective physical-world adversarial attack by natural phenomenon[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 15324–15333. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01491. |
| [27] |
WANG Donghua, YAO Wen, JIANG Tingsong, et al. RFLA: A stealthy reflected light adversarial attack in the physical world[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 4432–4442. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00411. |
| [28] |
TANG Guijian, YAO Wen, JIANG Tingsong, et al. Natural weather-style black-box adversarial attacks against optical aerial detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5620911. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3315053. |
| [29] |
SCHMALFUSS J, MEHL L, and BRUHN A. Distracting downpour: Adversarial weather attacks for motion estimation[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 10072–10082. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00927. |
| [30] |
WANG Yihan, BA Yunhao, ZHANG H C, et al. Evaluating worst case adversarial weather perturbations robustness[C]. 2022, NeurIPS ML Safety Workshop.
|
| [31] |
SAYLES A, HOODA A, GUPTA M, et al. Invisible perturbations: Physical adversarial examples exploiting the rolling shutter effect[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 14661–14670. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01443. |
| [32] |
PHAN B, MANNAN F, and HEIDE F. Adversarial imaging pipelines[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 16046–16056. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01579. |
| [33] |
YIN Bangjie, WANG Wenxuan, YAO Taiping, et al. Adv-makeup: A new imperceptible and transferable attack on face recognition[C]. Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1252–1258.
|
| [34] |
ATHALYE A, ENGSTROM L, ILYAS A, et al. Synthesizing robust adversarial examples[C]. 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 284–293.
|
| [35] |
HUANG Yao, DONG Yinpeng, RUAN Shouwei, et al. Towards transferable targeted 3D adversarial attack in the physical world[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 24512–24522. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.02314. |
| [36] |
ZHU Xiaopei, LI Xiao, LI Jianmin, et al. Fooling thermal infrared pedestrian detectors in real world using small bulbs[C]. 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021: 3616–3624. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i4.16477. |
| [37] |
WEI Hui, WANG Zhixiang, JIA Xuemei, et al. HOTCOLD block: Fooling thermal infrared detectors with a novel wearable design[C]. 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 15233–15241. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i12.26777. |
| [38] |
WEI Xingxing, YU Jie, and HUANG Yao. Physically adversarial infrared patches with learnable shapes and locations[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 12334–12342. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01187. |
| [39] |
LANDY N I, SAJUYIGBE S, MOCK J J, et al. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(20): 207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402. |
| [40] |
宋一川. 人工电磁材料及其在电磁隐身方面的应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 西北工业大学, 2016.
SONG Yichuan. Artificial electromagnetic material and its applications in electromagnetic stealth technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2016.
|
| [41] |
ZHANG Guowen, GAO Jun, CAO Xiangyu, et al. An ultra-thin low-frequency tunable metamaterial absorber based on lumped element[J]. Radioengineering, 2019, 28(3): 579–584. doi: 10.13164/re.2019.0579. |
| [42] |
LI You, LI Huangyan, WANG Yunwen, et al. A novel switchable absorber/linear converter based on active metasurface and its application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(11): 7688–7693. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2980301. |
| [43] |
WANG Junjie, FENG Dejun, XU Letao, et al. Synthetic aperture radar target feature modulation using active frequency selective surface[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(6): 2113–2125. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2886013. |
| [44] |
OMAR A A, HUANG Hao, and SHEN Zhongxiang. Absorptive frequency-selective reflection/transmission structures: A review and future perspectives[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2020, 62(4): 62–74. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2019.2943302. |
| [45] |
高勋章, 张志伟, 刘梅, 等. 雷达像智能识别对抗研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098. GAO Xunzhang, ZHANG Zhiwei, LIU Mei, et al. Intelligent radar image recognition countermeasures: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098. |
| [46] |
孙浩, 陈进, 雷琳, 等. 深度卷积神经网络图像识别模型对抗鲁棒性技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 571–594. doi: 10.12000/JR21048. SUN Hao, CHEN Jin, LEI Lin, et al. Adversarial robustness of deep convolutional neural network-based image recognition models: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 571–594. doi: 10.12000/JR21048. |
| [47] |
GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, and SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[J]. arXiv: 1412.6572, 2015.
|
| [48] |
CZAJA W, FENDLEY N, PEKALA M, et al. Adversarial examples in remote sensing[C]. 26th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Washington, USA, 2018: 408–411. doi: 10.1145/3274895.3274904. |
| [49] |
CHEN Li, XU Zewei, LI Qi, et al. An empirical study of adversarial examples on remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7419–7433. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3051641. |
| [50] |
XU Yanjie, SUN Hao, LEI Lin, et al. The research for the robustness of SAR ship identification based on adversarial example[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1965–1978. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.002. |
| [51] |
YE Tian, KANNAN R, PRASANNA V, et al. Adversarial attack on GNN-based SAR image classifier[C]. SPIE 12538, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Multi-Domain Operations Applications V, Orlando, USA, 2023: 291–295. doi: 10.1117/12.2666030. |
| [52] |
ZHOU Peng, XIAO Shunping, LI Mingdian, et al. Impact investigation of adversarial samples on CNN-based SAR image target detectors[C]. 2023 IEEE 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, Haikou, China, 2023: 777–781. doi: 10.1109/PRAI59366.2023.10332037. |
| [53] |
REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018.
|
| [54] |
REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. |
| [55] |
KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I, and BENGIO S. Adversarial machine learning at scale[J]. arXiv: 1611.01236, 2017.
|
| [56] |
PANG Ling, WANG Lulu, ZHANG Yi, et al. Adversarial examples of SAR images for deep learning based automatic target recognition[C]. 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Nanjing, China, 2021: 24–27. doi: 10.1109/ICSIP52628.2021.9688913. |
| [57] |
HUANG Teng, CHEN Yongfeng, YAO Bingjian, et al. Adversarial attacks on deep-learning-based radar range profile target recognition[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 531: 159–176. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.066. |
| [58] |
ZHANG Hanmeng and JIANG Xue. Benchmarking adversarial attacks and defenses in remote sensing images[C]. IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 899–902. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10283102. |
| [59] |
XU Yue, LIU Xin, HE Kun, et al. Image mixing and gradient smoothing to enhance the SAR image attack transferability[C]. ICASSP 2024–2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Seoul, Korea, 2024: 5380–5384. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10448395. |
| [60] |
GAO Wei, LIU Yunqing, ZENG Yi, et al. SAR image ship target detection adversarial attack and defence generalization research[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 2266. doi: 10.3390/s23042266. |
| [61] |
MĄDRY A, MAKELOV A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks[EB/OL]. arXiv: 1706.06083. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.06083v4, 2019.
|
| [62] |
INKAWHICH N, DAVIS E, MAJUMDER U, et al. Advanced techniques for robust SAR ATR: Mitigating noise and phase errors[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference, Washington, USA, 2020: 844–849. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114784. |
| [63] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings[C]. 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Saarbruecken, Germany, 2016: 372–387. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP.2016.36. |
| [64] |
SIMONYAN K, VEDALDI A, and ZISSERMAN A. Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising image classification models and saliency maps[C]. 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014.
|
| [65] |
CHEN Pinyu, SHARMA Y, ZHANG Huan, et al. EAD: Elastic-net attacks to deep neural networks via adversarial examples[C]. 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 10–17. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11302. |
| [66] |
ZOU Hui and HASTIE T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology, 2005, 67(2): 301–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00503.x. |
| [67] |
SU Jiawei, VARGAS D V, and SAKURAI K. One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(5): 828–841. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2890858. |
| [68] |
ZHOU Jie, PENG Bo, XIE Jianyue, et al. Conditional random field-based adversarial attack against SAR target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4004505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3365788. |
| [69] |
CHEN Kai, ZHU Haoqi, YAN Leiming, et al. A survey on adversarial examples in deep learning[J]. Journal on Big Data, 2020, 2(2): 71–84. doi: 10.32604/jbd.2020.012294. |
| [70] |
CHEN Jianbo, JORDAN M I, and WAINWRIGHT M J. HopSkipJumpAttack: A query-efficient decision-based attack[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 1277–1294. doi: 10.1109/SP40000.2020.00045. |
| [71] |
MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FAWZI O, et al. Universal adversarial perturbations[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 86–94. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.17. |
| [72] |
WANG Lulu, WANG Xiaolei, MA Shixin, et al. Universal adversarial perturbation of SAR images for deep learning based target classification[C]. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology, Chengdu, China, 2021: 1272–1276. doi: 10.1109/ICET51757.2021.9450944. |
| [73] |
LIU Zhe, XIA Weijie, and LEI Yongzhen. SAR image adversarial sample generation method based on Targeted-UAP algorithm[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2023, 42(8): 131–134. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2023)08-0131-04. |
| [74] |
XIE Chulin, HUANG Keli, CHEN Pinyu, et al. DBA: Distributed backdoor attacks against federated learning[C]. 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020.
|
| [75] |
QIN Weibo and WANG Feng. A universal adversarial attack on CNN-SAR image classification by feature dictionary modeling[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 1027–1030. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883668. |
| [76] |
MAO Cong, HUANG Lizhen, XIAO Yongsheng, et al. Target recognition of SAR image based on CN-GAN and CNN in complex environment[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 39608–39617. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064362. |
| [77] |
AO Dongyang, DUMITRU C O, SCHWARZ G, et al. Dialectical GAN for SAR image translation: From Sentinel-1 to TerraSAR-X[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(10): 1597. doi: 10.3390/rs10101597. |
| [78] |
DU Shaoyan, HONG Jun, WANG Yu, et al. A high-quality multicategory SAR images generation method with multiconstraint GAN for ATR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4011005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3065682. |
| [79] |
LEY A, DHONDT O, VALADE S, et al. Exploiting GAN-based SAR to optical image transcoding for improved classification via deep learning[C]. 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–6.
|
| [80] |
XIAO Chaowei, LI Bo, ZHU Junyan, et al. Generating adversarial examples with adversarial networks[C]. Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3905–3911.
|
| [81] |
RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. |
| [82] |
DU Meng, SUN Yuxin, SUN Bing, et al. TAN: A transferable adversarial network for DNN-based UAV SAR automatic target recognition models[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(3): 205. doi: 10.3390/drones7030205. |
| [83] |
WAN Xuanshen, LIU Wei, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Black-box universal adversarial attack for DNN-based models of SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 8673–8696. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3384188. |
| [84] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, and GOODFELLOW I. Transferability in machine learning: From phenomena to black-box attacks using adversarial samples[J]. arXiv: 1605.07277, 2016.
|
| [85] |
LIN Gengyou, PAN Zhisong, ZHOU Xingyu, et al. Boosting adversarial transferability with shallow-feature attack on SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(10): 2699. doi: 10.3390/rs15102699. |
| [86] |
CHEN Yuzhou, DU Jiawei, YANG Yang, et al. Positive weighted feature attack: Toward transferable adversarial attack to SAR target recognition[C]. 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Technology, Communication and Information, Changchun, China, 2023: 93–98. doi: 10.1109/ICETCI57876.2023.10176719. |
| [87] |
PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, YONG Shaowei, et al. An empirical study of fully black-box and universal adversarial attack for SAR target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(16): 4017. doi: 10.3390/rs14164017. |
| [88] |
PENG Bo, PENG Bowen, ZHOU Jie, et al. Low-frequency features optimization for transferability enhancement in radar target adversarial attack[C]. 32nd International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Heraklion, Crete, 2023: 115–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44192-9_10. |
| [89] |
PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, XIA Jingyuan, et al. Towards assessing the synthetic-to-measured adversarial vulnerability of SAR ATR[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2024, 214: 119–134. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.06.004. |
| [90] |
万烜申, 刘伟, 牛朝阳, 等. 基于动量迭代快速梯度符号的SAR-ATR深度神经网络黑盒攻击算法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 714–729. doi: 10.12000/JR23220. WAN Xuanshen, LIU Wei, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Black-box attack algorithm for SAR-ATR deep neural networks based on MI-FGSM[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 714–729. doi: 10.12000/JR23220. |
| [91] |
HUANG Xichen, LU Zhengzhi, and PENG Bo. Enhancing transferability with intra-class transformations and inter-class nonlinear fusion on SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(14): 2539. doi: 10.3390/rs16142539. |
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
CROCE F, ANDRIUSHCHENKO M, SINGH N D, et al. Sparse-RS: A versatile framework for query-efficient sparse black-box adversarial attacks[C]. 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 6437–6445. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i6.20595. |
| [94] |
MODAS A, MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, and FROSSARD P. Sparsefool: A few pixels make a big difference[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9079–9088. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00930. |
| [95] |
CROCE F and HEIN M. Sparse and imperceivable adversarial attacks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 4723–4731. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00482. |
| [96] |
JIN Xiaying, LI Yang, and PAN Quan. DE-JSMA: A sparse adversarial attack algorithm for SAR-ATR models[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2023, 41(6): 1170–1178. doi: 10.1051/jnwpu/20234161170. |
| [97] |
MENG Tianying, ZHANG Fan, and MA Fei. A target-region-based SAR ATR adversarial deception method[C]. 2022 7th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Suzhou, China, 2022: 142–146. doi: 10.1109/ICSIP55141.2022.9887044. |
| [98] |
王璐, 张帆, 李伟, 等. 基于Gabor滤波器和局部纹理特征提取的SAR目标识别算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(6): 658–665. doi: 10.12000/JR15076. WANG Lu, ZHANG Fan, LI Wei, et al. A method of SAR target recognition based on Gabor filter and local texture feature extraction[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(6): 658–665. doi: 10.12000/JR15076. |
| [99] |
ZHANG Fan, MENG Tianying, XIANG Deliang, et al. Adversarial deception against SAR target recognition network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 4507–4520. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3179171. |
| [100] |
DU Meng, BI Daping, DU Mingyang, et al. ULAN: A universal local adversarial network for SAR target recognition based on layer-wise relevance propagation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(1): 21. doi: 10.3390/rs15010021. |
| [101] |
PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, ZHOU Jie, et al. Speckle-variant attack: Toward transferable adversarial attack to SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4509805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3184311. |
| [102] |
BROWN T B, MANÉ D, ROY A, et al. Adversarial patch[C]. 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017.
|
| [103] |
YU Yameng, ZOU Haiyan, and ZHANG Fan. SAR sticker: An adversarial image patch that can deceive SAR ATR deep model[C]. IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 7050–7053. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282390. |
| [104] |
MA Yanjing, XU Langjun, PEI Jifang, et al. Target partial-occlusion: An adversarial examples generation approach against SAR target recognition networks[C]. IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 7054–7057. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10281447. |
| [105] |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74. |
| [106] |
DUAN Jiale, QIU Linyao, HE Guangjun, et al. A region-adaptive local perturbation-based method for generating adversarial examples in synthetic aperture radar object detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(6): 997. doi: 10.3390/rs16060997. |
| [107] |
DONG Yingbo, ZHANG Hong, WANG Chao, et al. Fine-grained ship classification based on deep residual learning for high-resolution SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 10(11): 1095–1104. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2019.1650982. |
| [108] |
CHIERCHIA G, COZZOLINO D, POGGI G, et al. SAR image despeckling through convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 5438–5441. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8128234. |
| [109] |
HENRY C, AZIMI S M, and MERKLE N. Road segmentation in SAR satellite images with deep fully convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(12): 1867–1871. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2864342. |
| [110] |
ZHANG Qixiang. Research on adversarial example attack method for SAR target recognition based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Guangzhou University, 2021. doi: 10.27040/d.cnki.ggzdu.2021.000643. |
| [111] |
XIAO Chaowei, ZHU Junyan, LI Bo, et al. Spatially transformed adversarial examples[C]. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018.
|
| [112] |
ZHANG Lei, JIANG Tianpeng, GAO Songyi, et al. Generating adversarial examples on SAR images by optimizing flow field directly in frequency domain[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 2979–2982. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883169. |
| [113] |
GERRY M J, POTTER L C, GUPTA I J, et al. A parametric model for synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(7): 1179–1188. doi: 10.1109/8.785750. |
| [114] |
YE T, KANNAN R, PRASANNA V, et al. Realistic scatterer based adversarial attacks on SAR image classifiers[C]. 2023 IEEE International Radar Conference, Sydney, Australia, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR54928.2023.10371090. |
| [115] |
ZHOU Junfan, FENG Sijia, SUN Hao, et al. Attributed scattering center guided adversarial attack for DCNN SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4001805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3235051. |
| [116] |
QIN Weibo, LONG Bo, and WANG Feng. SCMA: A scattering center model attack on CNN-SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4003305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3253189. |
| [117] |
WEI Hui, TANG Hao, JIA Xuemei, et al. Physical adversarial attack meets computer vision: A decade survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3430860. |
| [118] |
KELLER J B. Geometrical Theory of Diffraction[M]. KLEM-MUSATOV K, HOEBER H C, JAN T, et al. Classical and Modern Diffraction Theory. Tulsa: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2016. doi: 10.1190/1.9781560803232. |
| [119] |
KOUYOUMJIAN R G and PATHAK P H. A uniform geometrical theory of diffraction for an edge in a perfectly conducting surface[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1974, 62(11): 1448–1461. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9651. |
| [120] |
KOUYOUMJIAN R G. The Geometrical Theory of Diffraction and its Application[M]. MITTRA R. Numerical and Asymptotic Techniques in Electromagnetics. Berlin: Springer, 2005: 165–215. doi: 10.1007/3540070729_27. |
| [121] |
李郝亮, 陈思伟. 海面角反射体电磁散射特性与雷达鉴别研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 738–761. doi: 10.12000/JR23100. LI Haoliang and CHEN Siwei. Electromagnetic scattering characteristics and radar identification of sea corner reflectors: Advances and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 738–761. doi: 10.12000/JR23100. |
| [122] |
ZHANG Lin, HU Shengliang, and HU Hai. Research on current equipment situation and tactical application of ship-born inflatable corner reflector[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2018, 39(6): 48–51. doi: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2018.06.010. |
| [123] |
LI Xiaonan, LI Tianpeng, and GAO Xinbao. Advances in passive jamming material countering of precision guide weapon[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2021, 41(7): 1–8, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.07.001. |
| [124] |
许恒, 许红, 全英汇, 等. 基于时域编码超表面脉内-脉间编码优化的雷达干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(1): 215–226. doi: 10.12000/JR23186. XU Heng, XU Hong, QUAN Yinghui, et al. A radar jamming method based on time domain coding metasurface intrapulse and interpulse coding optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 215–226. doi: 10.12000/JR23186. |
| [125] |
蒋卫祥, 田翰闱, 宋超, 等. 数字编码超表面: 迈向电磁功能的可编程与智能调控[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2022, 11(6): 1003–1019. doi: 10.12000/JR22167. JIANG Weixiang, TIAN Hanwei, SONG Chao, et al. Digital coding metasurfaces: Toward programmable and smart manipulations of electromagnetic functions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1003–1019. doi: 10.12000/JR22167. |
| [126] |
王俊杰, 冯德军, 王志凇, 等. 电控时变电磁材料的SAR成像特性研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 865–873. doi: 10.12000/JR21104. WANG Junjie, FENG Dejun, WANG Zhisong, et al. Synthetic aperture rader imaging characteristics of electronically controlled time-varying electromagnetic materials[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 865–873. doi: 10.12000/JR21104. |
| [127] |
YANG Yang and JING Lei. Impact of the metal permittivity on radar target scattering cross section[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2013, 43(2): 155–158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2013.02.008. |
| [128] |
CUI Jiahao, GUO Wang, SHAO Rui, et al. Physics-oriented adversarial attacks on SAR image target recognition[C]. 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, USA, 2023.
|
| [129] |
李永祯, 黄大通, 邢世其, 等. 合成孔径雷达干扰技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087. LI Yongzhen, HUANG Datong, XING Shiqi, et al. A review of synthetic aperture radar jamming technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087. |
| [130] |
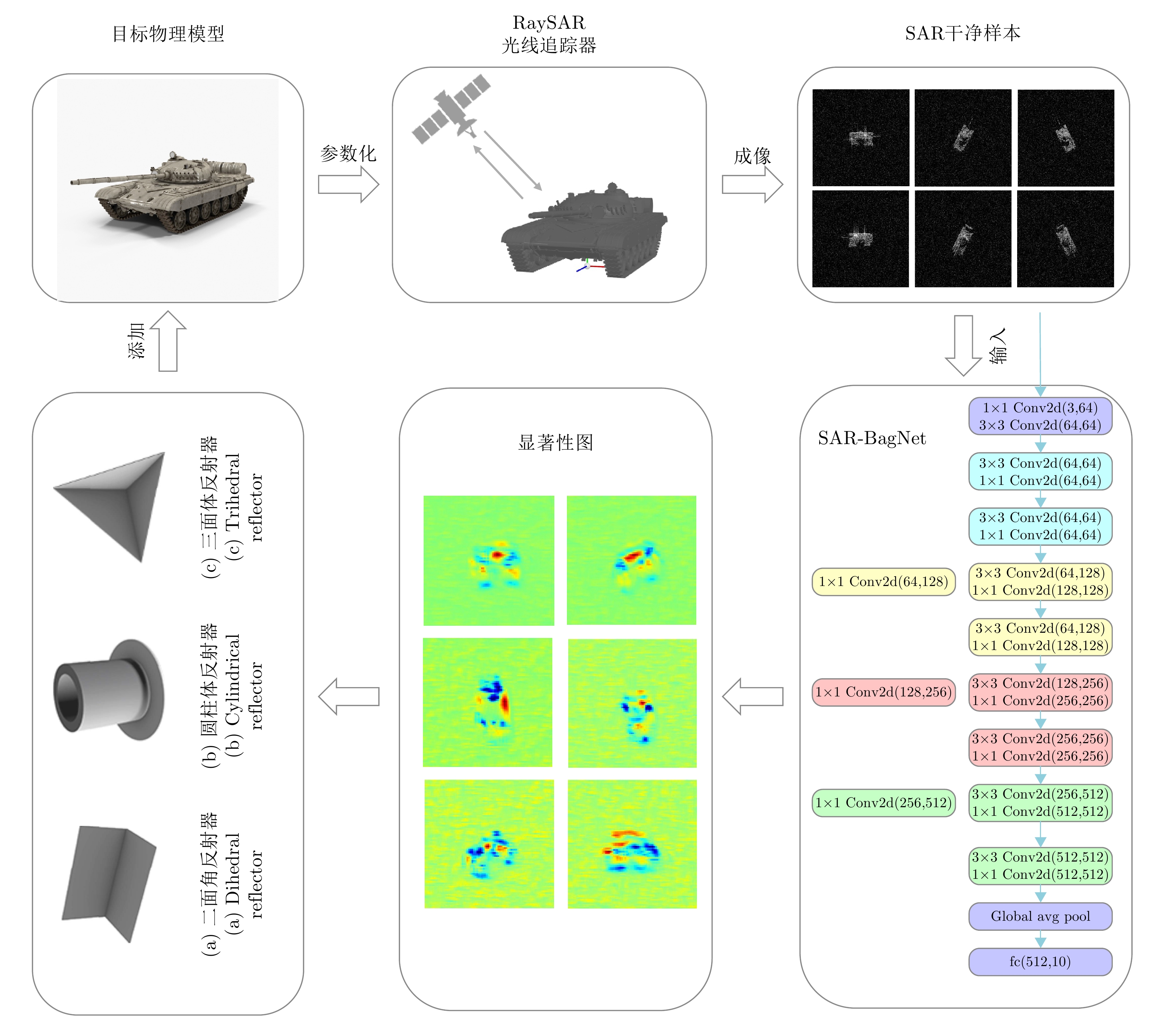
LI Peng, FENG Cunqian, HU Xiaowei, et al. SAR-BagNet: An ante-hoc interpretable recognition model based on deep network for SAR image[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2150. doi: 10.3390/rs14092150. |
| [131] |
杨欢欢, 曹祥玉, 高军, 等. 可重构电磁超表面及其应用研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(2): 206–219. doi: 10.12000/JR20137. YANG Huanhuan, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. Recent advances in reconfigurable metasurfaces and their applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(2): 206–219. doi: 10.12000/JR20137. |
| [132] |
OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076. |
| [133] |
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: