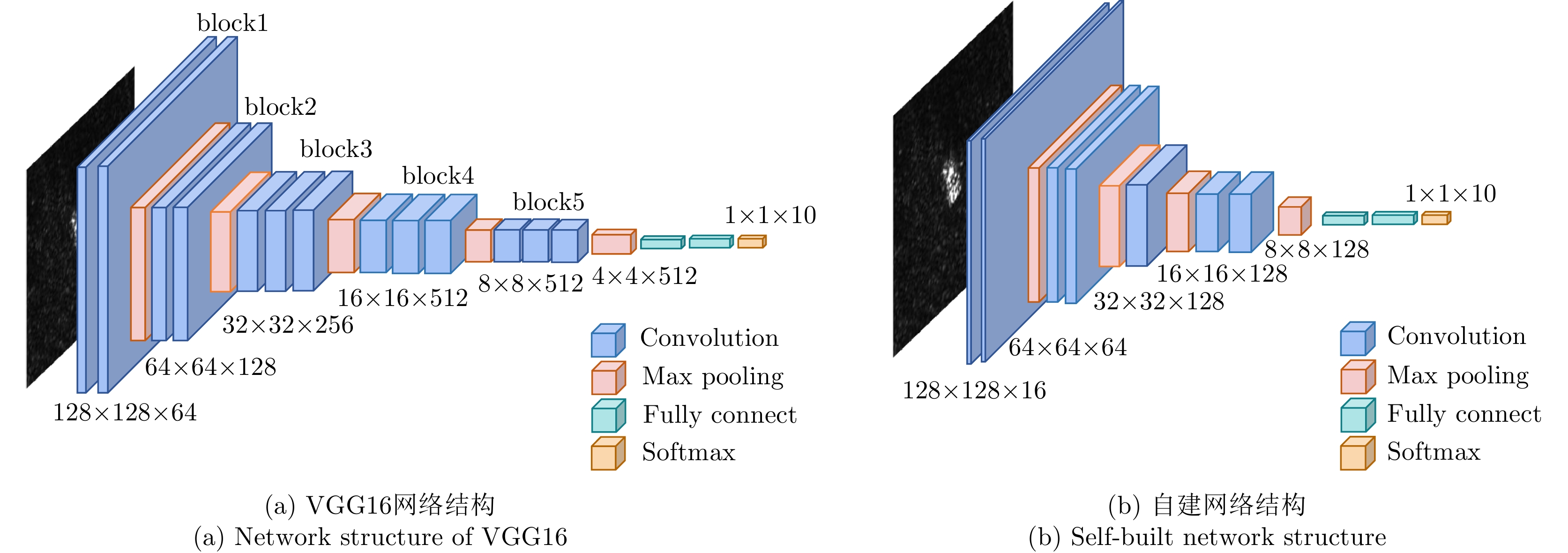
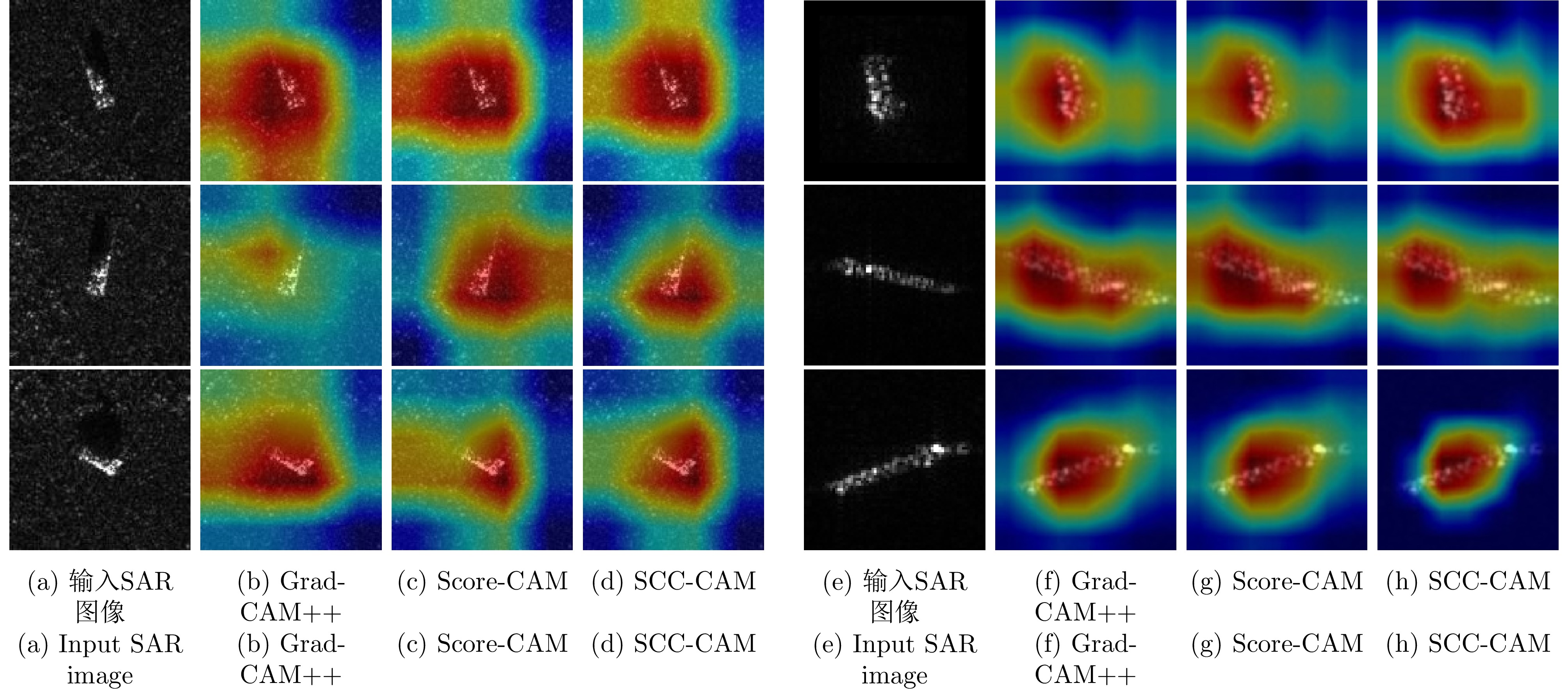
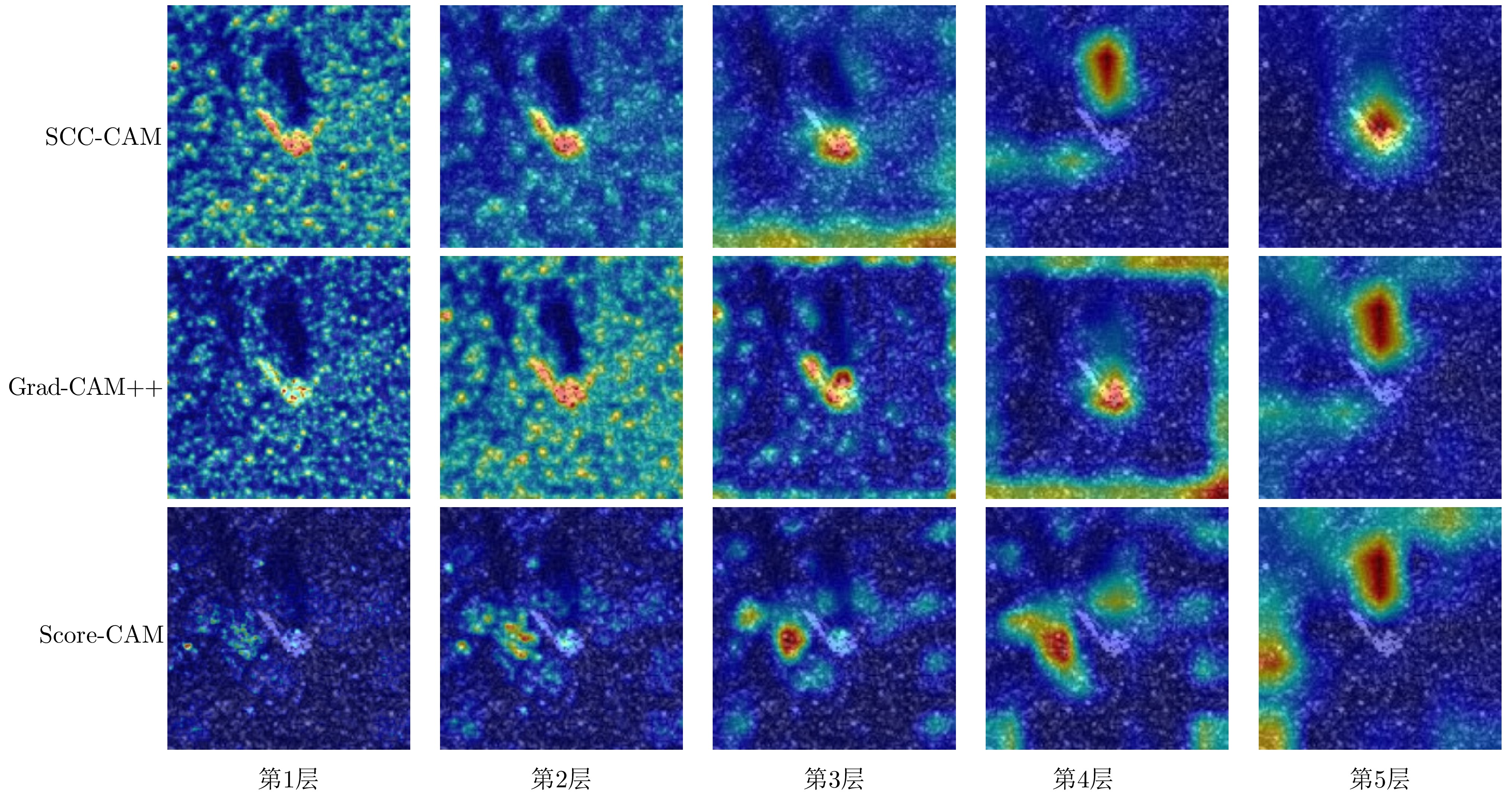
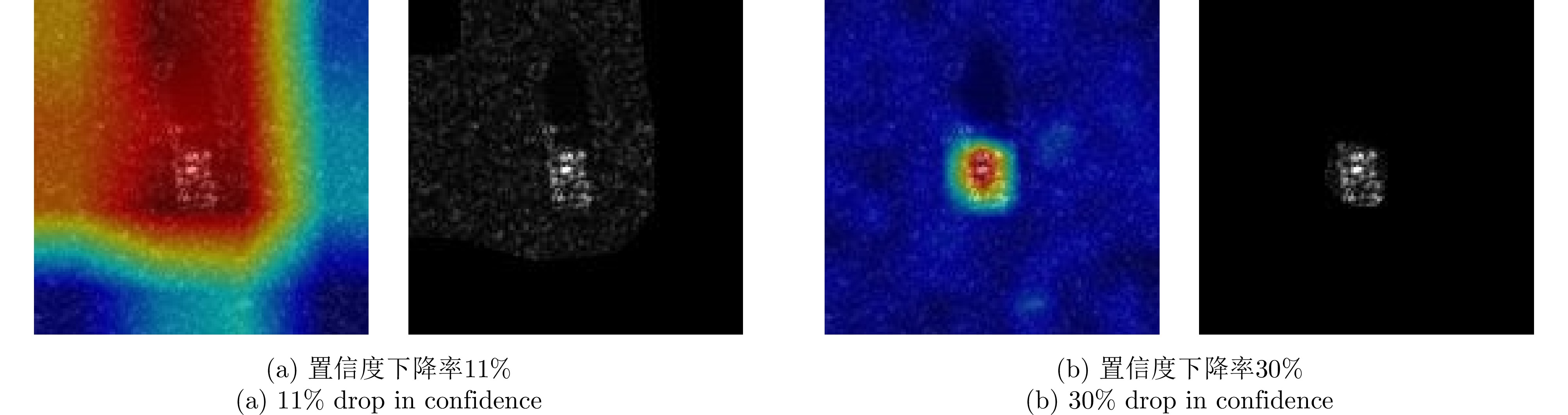
| [1] |
PANATI C, WAGNER S, and BRÜGGENWIRTH S. Feature relevance evaluation using grad-CAM, LIME and SHAP for deep learning SAR data classification[C]. 2022 23rd International Radar Symposium (IRS), Gdansk, Poland, 2022: 457–462. doi: 10.23919/irs54158.2022.9904989. |
| [2] |
SU Shenghan, CUI Ziteng, GUO Weiwei, et al. Explainable analysis of deep learning methods for SAR image classification[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 2570–2573. doi: 10.1109/igarss46834.2022.9883815. |
| [3] |
李玮杰, 杨威, 刘永祥, 等. 雷达图像深度学习模型的可解释性研究与探索[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2022, 52(6): 1114–1134. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0102. LI Weijie, YANG Wei, LIU Yongxiang, et al. Research and exploration on the interpretability of deep learning model in radar image[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2022, 52(6): 1114–1134. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0102. |
| [4] |
金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083. JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083. |
| [5] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 228–242. doi: 10.1117/12.242059. |
| [6] |
ZHAO Juanping, GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, et al. A coupled convolutional neural network for small and densely clustered ship detection in SAR images[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(4): 42301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9405-6. |
| [7] |
杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104. DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104. |
| [8] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. |
| [9] |
郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. |
| [10] |
FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, WANG Fulai, et al. Electromagnetic scattering feature (ESF) module embedded network based on ASC model for robust and interpretable SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5235415. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2022.3208333. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
JI Shouling, LI Jinfeng, DU Tianyu, et al. Survey on techniques, applications and security of machine learning interpretability[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(10): 2071–2096. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190540. |
| [13] |
DHURANDHAR A, CHEN Pinyu, LUSS R, et al. Explanations based on the missing: Towards contrastive explanations with pertinent negatives[C]. 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 590–601.
|
| [14] |
DATCU M, ANDREI V, DUMITRU C O, et al. Explainable deep learning for SAR data[C]. Φ-week, Frascati, Italy, 2019.
|
| [15] |
LI Yang, WANG Jiabao, XU Yulong, et al. DeepSAR-Net: Deep convolutional neural networks for SAR target recognition[C]. 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data Analysis (ICBDA), Beijing, China, 2017: 740–743. doi: 10.1109/icbda.2017.8078734. |
| [16] |
ZHAO Juanping, DATCU M, ZHANG Zenghui, et al. Contrastive-regulated CNN in the complex domain: A method to learn physical scattering signatures from flexible PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10116–10135. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2019.2931620. |
| [17] |
HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. Deep SAR-Net: Learning objects from signals[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 161: 179–193. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.016. |
| [18] |
HUANG Zhongling, DUMITRU C O, and REN Jun. Physics-aware feature learning of SAR images with deep neural networks: A case study[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 1264–1267. doi: 10.1109/igarss47720.2021.9554842. |
| [19] |
HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, LIU Ying, et al. Physically explainable CNN for SAR image classification[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 190: 25–37. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.05.008. |
| [20] |
LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2021.3100137. |
| [21] |
ZEILER M D and FERGUS R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 818–833. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53. |
| [22] |
ZHOU Bolei, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2921–2929. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2016.319. |
| [23] |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.74. |
| [24] |
CHATTOPADHAY A, SARKAR A, HOWLADER P, et al. Grad-CAM++: Generalized gradient-based visual explanations for deep convolutional networks[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 839–847. doi: 10.1109/wacv.2018.00097. |
| [25] |
WANG Haofan, WANG Zifan, DU Mengnan, et al. Score-CAM: Score-weighted visual explanations for convolutional neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, USA, 2020: 111–119. doi: 10.1109/cvprw50498.2020.00020. |
| [26] |
FENG Zhenpeng, ZHU Mingzhe, STANKOVIĆ L, et al. Self-matching CAM: A novel accurate visual explanation of CNNs for SAR image interpretation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(9): 1772. doi: 10.3390/rs13091772. |
| [27] |
SUNDARARAJAN M, TALY A, and YAN Qiqi. Axiomatic attribution for deep networks[C]. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 3319–3328.
|
| [28] |
MONTAVON G, SAMEK W, and MÜLLER K R. Methods for interpreting and understanding deep neural networks[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2018, 73: 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.10.011. |
| [29] |
匡纲要, 高贵, 蒋咏梅, 等. 合成孔径雷达: 目标检测理论、算法及应用[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 2007: 45–50.
KUANG Gangyao, GAO Gui, JIANG Yongmei, et al. Synthetic Aperture Radar Target: Detection Theory Algorithms and Applications[M]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology Press, 2007: 45–50.
|
| [30] |
ANASTASSOPOULOS, LAMPROPOULOS G A, DROSOPOULOS A, et al. High resolution radar clutter statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(1): 43–60. doi: 10.1109/7.745679. |
| [31] |
KURUOGLU E E and ZERUBIA J. Modeling SAR images with a generalization of the Rayleigh distribution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 527–533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.818017. |
| [32] |
BELLONI C, BALLERI A, AOUF N, et al. Explainability of deep SAR ATR through feature analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 659–673. doi: 10.1109/taes.2020.3031435. |
| [33] |
RICE J A. Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis[M]. 3rd ed. Belmont: Cengage Learning, 2006: 71–99.
|
| [34] |
BERTSEKAS D P and TSITSIKLIS J N. Introduction to Probability[M]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2000: 6–48.
|
| [35] |
SIMONYAN K, VEDALDI A, and ZISSERMAN A. Deep inside convolutional networks: Visualising image classification models and saliency maps[C]. 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014.
|
| [36] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2015.123. |
| [37] |
FONG R C and VEDALDI A. Interpretable explanations of black boxes by meaningful perturbation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3449–3457. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.371. |
| [38] |
ANCONA M, OZTIRELI C, and GROSS M. Explaining deep neural networks with a polynomial time algorithm for shapley value approximation[C]. In International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019: 272–281. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1903.10992. |
| [39] |
DIEMUNSCH J R and WISSINGER J. Moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) model-based automatic target recognition: Search technology for a robust ATR[C]. SPIE 3370, Algorithms for synthetic aperture radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 481–492. doi: 10.1117/12.321851. |
| [40] |
HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to Sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2017.2755672. |
| [41] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015.
|
| [42] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2016.90. |
| [43] |
HEILIGERS M and HUIZING A. On the importance of visual explanation and segmentation for SAR ATR using deep learning[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 394–399. doi: 10.1109/radar.2018.8378591. |
| [44] |
DEVRIES T and TAYLOR G W. Learning confidence for out-of-distribution detection in neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.04865, 2018.
|
| [45] |
LI Weijie, YANG Wei, LIU Li, et al. Discovering and explaining the noncausality of deep learning in SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4004605. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2023.3266493. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: