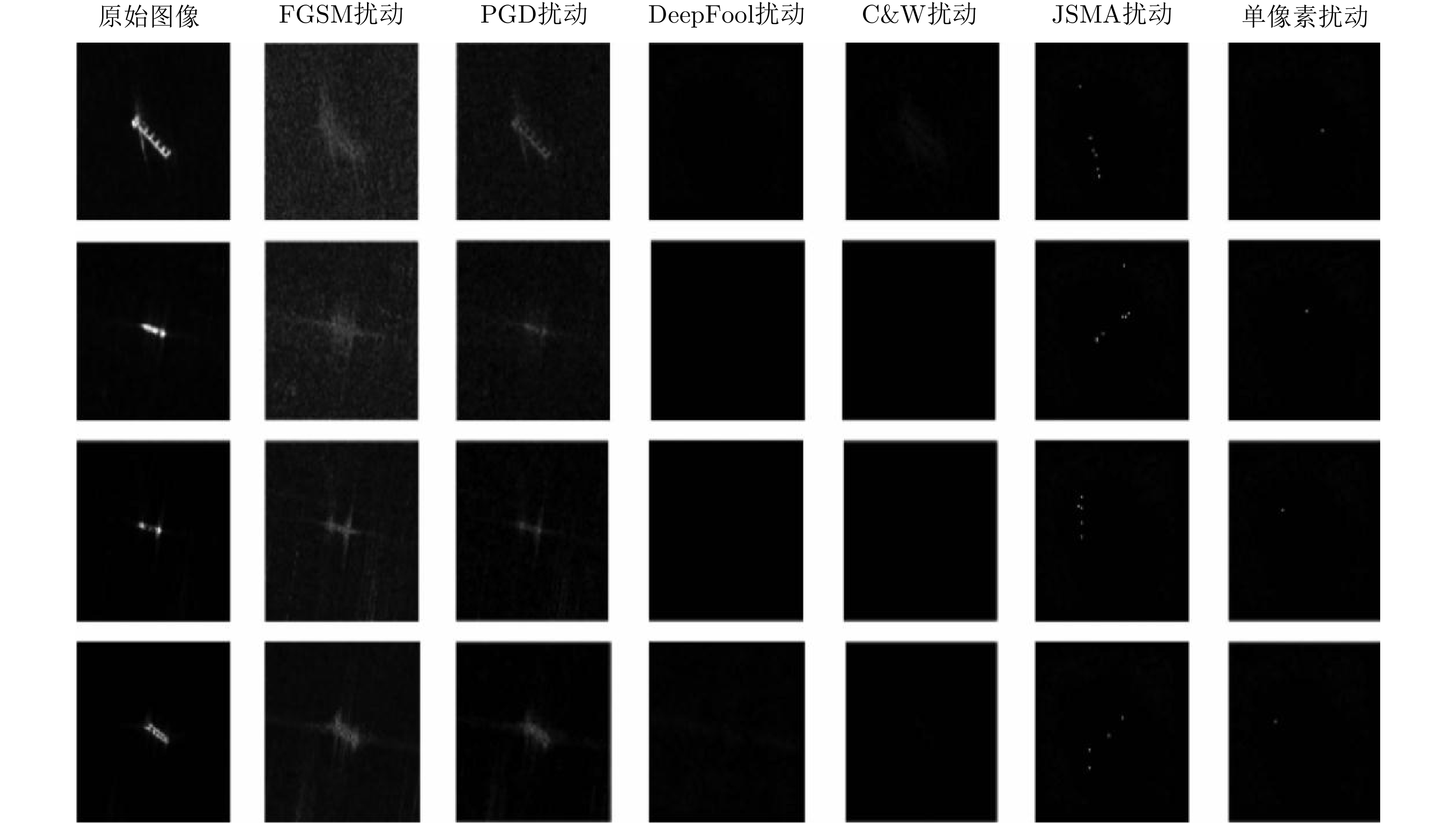
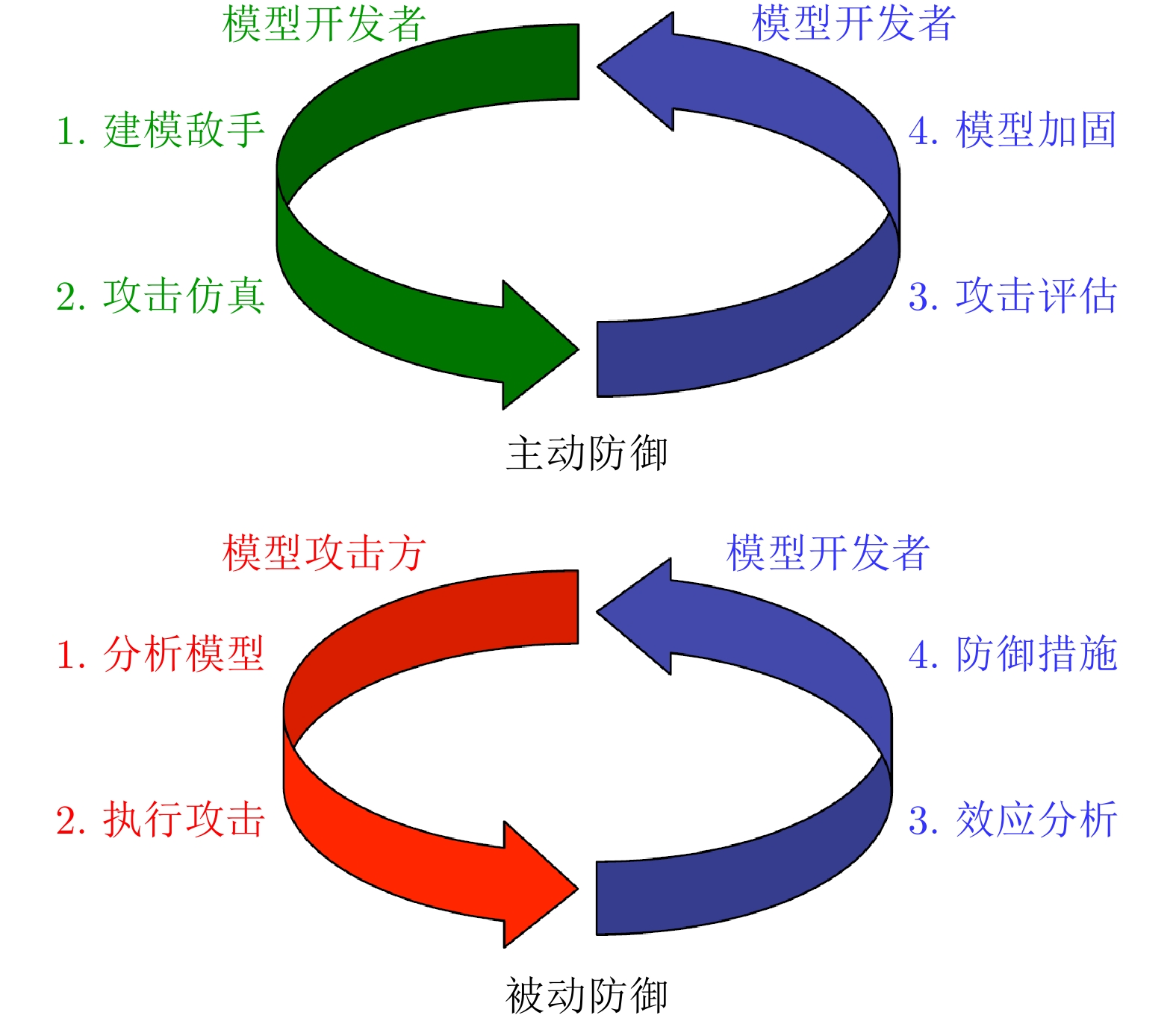
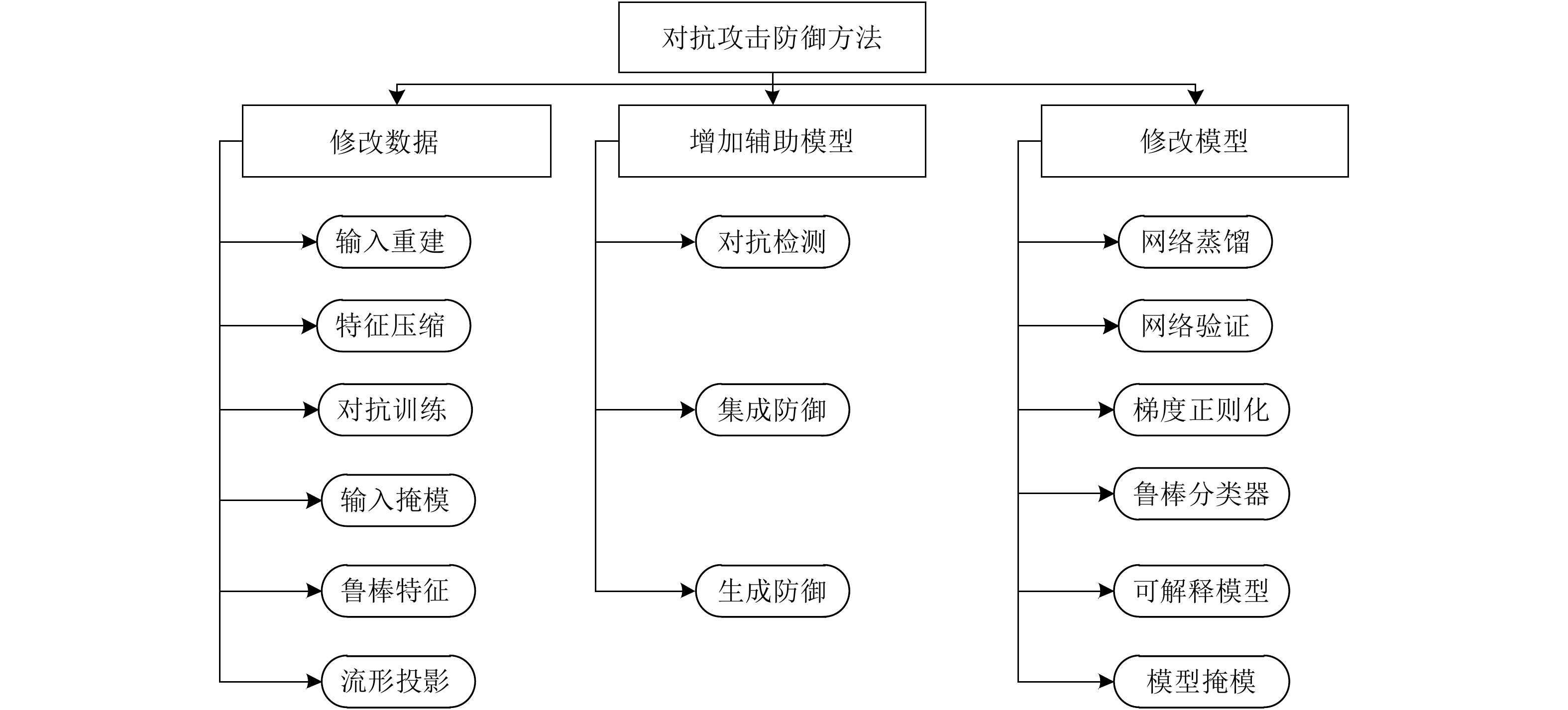
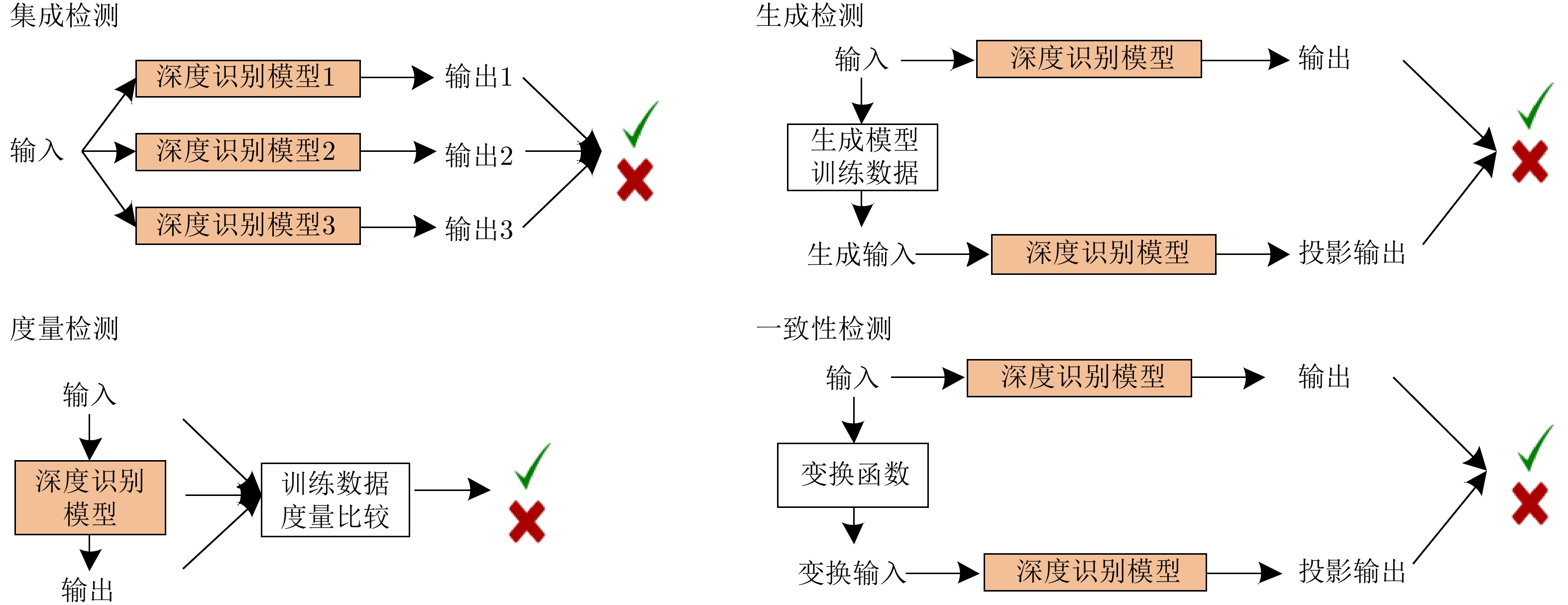
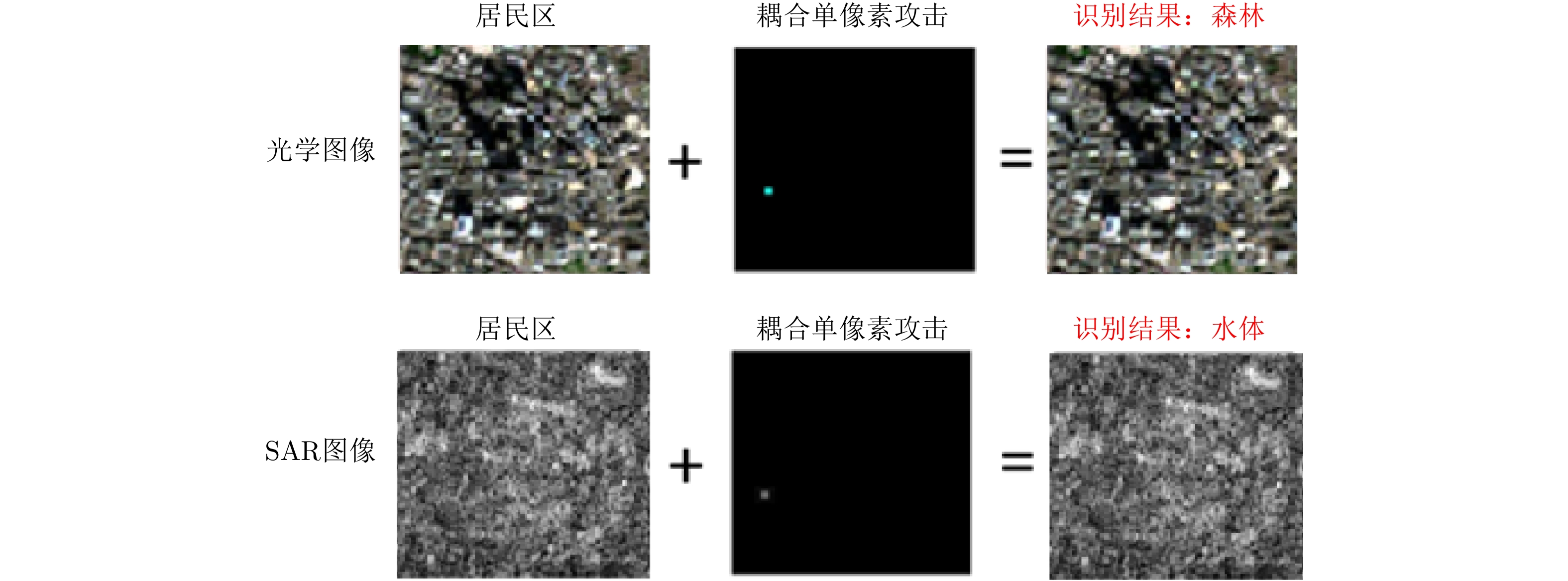
| [1] |
BERGHOFF C, NEU M, and VON TWICKEL A. Vulnerabilities of connectionist AI applications: Evaluation and defense[J]. Frontiers in Big Data, 2020, 3: 23. doi: 10.3389/fdata.2020.00023 |
| [2] |
PAN Zongxu, AN Quanzhi, and ZHANG Bingchen. Progress of deep learning-based target recognition in radar images[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(12): 1626–1639. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0093 |
| [3] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 |
| [4] |
CHENG Gong, XIE Xingxing, HAN Junwei, et al. Remote sensing image scene classification meets deep learning: Challenges, methods, benchmarks, and opportunities[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 3735–3756. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3005403 |
| [5] |
BLASCH E, MAJUMDER U, ZELNIO E, et al. Review of recent advances in AI/ML using the MSTAR data[C]. SPIE 11393, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXVII, Online Only, 2020.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
MACHADO G R, SILVA E, and GOLDSCHMIDT R R. Adversarial machine learning in image classification: A survey towards the defender’s perspective[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.03728v1, 2020. |
| [10] |
SERBAN A, POLL E, and VISSER J. Adversarial examples on object recognition: A comprehensive survey[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2020, 53(3): 66. doi: 10.1145/3398394 |
| [11] |
OSENI A, MOUSTAFA N, JANICKE H, et al. Security and privacy for artificial intelligence: Opportunities and challenges[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.04661, 2021. |
| [12] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, United States, 1996: 228–242.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
WANG Bolun, YAO Yuanshun, SHAN S, et al. Neural cleanse: Identifying and mitigating backdoor attacks in neural networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 707–723. doi: 10.1109/SP.2019.00031. |
| [15] |
SHEN Juncheng, ZHU Xiaolei, and MA De. TensorClog: An imperceptible poisoning attack on deep neural network applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 41498–41506. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905915 |
| [16] |
QUIRING E and RIECK K. Backdooring and poisoning neural networks with image-scaling attacks[C]. 2020 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 41–47. doi: 10.1109/SPW50608.2020.00024. |
| [17] |
SINGH J and SHARMILA V C. Detecting Trojan attacks on deep neural networks[C]. The 4th International Conference on Computer, Communication and Signal Processing, Chennai, India, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCCSP49186.2020.9315256. |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
DELDJOO Y, NOIA T D, and MERRA F A. Adversarial machine learning in recommender systems: State of the art and challenges[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.10322v1, 2020. |
| [20] |
BIGGIO B and ROLI F. Wild patterns: Ten years after the rise of adversarial machine learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 84: 317–331. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.07.023 |
| [21] |
ROSS T D, BRADLEY J J, HUDSON L J, et al. SAR ATR: So what’s the problem? An MSTAR perspective[C]. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 606–610.
|
| [22] |
CHENG Keyang, WANG Ning, SHI Wenxi, et al. Research advances in the interpretability of deep learning[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(6): 1208–1217. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190485 |
| [23] |
HUA Yingying, ZHANG Daichi, and GE Shiming. Research progress in the interpretability of deep learning models[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2020, 5(3): 1–12. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2020.05.01 |
| [24] |
郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059 |
| [25] |
ORTIZ-JIMENEZ G, MODAS A, MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, et al. Optimism in the face of adversity: Understanding and improving deep learning through adversarial robustness[EB/OL]. HYPERLINK "https: //arxiv. org/abs/2010.09624v2" https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.09624v2, 2021. |
| [26] |
QAYYUM A, USAMA M, QADIR J, et al. Securing connected & autonomous vehicles: Challenges posed by adversarial machine learning and the way forward[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(2): 998–1026. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2975048 |
| [27] |
YUAN Xiaoyong, HE Pan, ZHU Qile, et al. Adversarial examples: Attacks and defenses for deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(9): 2805–2824. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2886017 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings[C]. 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, Saarbruecken, Germany, 2016: 372–387.
|
| [30] |
MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, and FROSSARD P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2574–2582.
|
| [31] |
KARMON D, ZORAN D, and GOLDBERG Y. LaVAN: Localized and visible adversarial noise[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018.
|
| [32] |
HAYES J and DANEZIS G. Learning universal adversarial perturbations with generative models[C]. 2018 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 43–49.
|
| [33] |
ATHALYE A, ENGSTROM L, ILYAS A, et al. Synthesizing robust adversarial examples[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018.
|
| [34] |
CARLINI N and WAGNER D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2017: 39–57.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
CHEN Pinyu, SHARMA Y, ZHANG Huan, et al. EAD: Elastic-net attacks to deep neural networks via adversarial examples[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.04114, 2018. |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
HE W, LI Bo, and SONG D. Decision boundary analysis of adversarial examples[C]. 2018 International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9185–9193.
|
| [43] |
CHEN Jinyin, SU Mengmeng, SHEN Shijing, et al. POBA-GA: Perturbation optimized black-box adversarial attacks via genetic algorithm[J]. Computers & Security, 2019, 85: 89–106. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2019.04.014 |
| [44] |
TU Chunchen, TING Paishun, CHEN Pinyu, et al. AutoZOOM: Autoencoder-based zeroth order optimization method for attacking black-box neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.11770v5, 2020. |
| [45] |
NARODYTSKA N and KASIVISWANATHAN S. Simple black-box adversarial attacks on deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1310–1318.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
BRENDEL W, RAUBER J, and BETHGE M. Decision-based adversarial attacks: Reliable attacks against black-box machine learning models[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.04248, 2018. |
| [48] |
ALZANTOT M, SHARMA Y, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. GenAttack: Practical black-box attacks with gradient-free optimization[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.11090, 2019. |
| [49] |
CHEN Pinyu, ZHANG Huan, SHARMA Y, et al. ZOO: Zeroth order optimization based black-box attacks to deep neural networks without training substitute models[C]. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 15–26.
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
CHEN Jianbo, JORDAN M I, and WAINWRIGHT M J. HopSkipJumpAttack: A query-efficient decision-based attack[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 1277–1294.
|
| [52] |
SU Jiawei, VARGAS D V, and SAKURAI K. One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(5): 828–841. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2890858 |
| [53] |
ATHALYE A, CARLINI N, and WAGNER D. Obfuscated gradients give a false sense of security: Circumventing defenses to adversarial examples[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.00420, 2018. |
| [54] |
UESATO J, O’DONOGHUE B, VAN DEN OORD A, et al. Adversarial risk and the dangers of evaluating against weak attacks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.05666, 2018. |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74. |
| [58] |
HOU Xiyue, AO Wei, SONG Qian, et al. FUSAR-Ship: Building a high-resolution SAR-AIS matchup dataset of Gaofen-3 for ship detection and recognition[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(4): 140303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2772-5 |
| [59] |
XU Yanjie, SUN Hao, LEI Lin, et al. The research for the robustness of SAR ship identification based on adversarial example[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1965–1978. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.002 |
| [60] |
BIGGIO B, FUMERA G, and ROLI F. Security evaluation of pattern classifiers under attack[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 26(4): 984–996. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2013.57 |
| [61] |
LI Pan, ZHAO Wentao, LIU Qiang, et al. Security issues and their countermeasuring techniques of machine learning: A survey[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2018, 12(2): 171–184. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.1708038 |
| [62] |
BUCKMAN J, ROY A, RAFFEL C, et al. Thermometer encoding: One hot way to resist adversarial examples[C]. The ICLR 2018, Vancouver, Canada, 2018.
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
MUSTAFA A, KHAN S H, HAYAT M, et al. Image super-resolution as a defense against adversarial attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 1711–1724. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2940533 |
| [65] |
PRAKASH A, MORAN N, GARBER S, et al. Deflecting adversarial attacks with pixel deflection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8571–8580.
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
BHAGOJI A N, CULLINA D, SITAWARIN C, et al. Enhancing robustness of machine learning systems via data transformations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.02654, 2017. |
| [69] |
LI Changjiang, WENG Haiqin, JI Shouling, et al. DeT: Defending against adversarial examples via decreasing transferability[C]. The 11th International Symposium on Cyberspace Safety and Security, Guangzhou, China, 2019: 307–322.
|
| [70] |
LIU Zihao, LIU Qi, LIU Tao, et al. Feature distillation: DNN-oriented JPEG compression against adversarial examples[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.05787, 2019. |
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
DAS N, SHANBHOGUE M, CHEN S T, et al. Keeping the bad guys out: Protecting and vaccinating deep learning with jpeg compression[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.02900, 2017. |
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
YAN Ziang, GUO Yiwen, and ZHANG Changshui. Deep defense: Training DNNs with improved adversarial robustness[C]. 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 419–428.
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
CAO Xiaoyu and GONG Zhenqiang. Mitigating evasion attacks to deep neural networks via region-based classification[C]. The 33rd Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Orlando, USA, 2017: 278–287.
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
WANG Jianyu and ZHANG Haichao. Bilateral adversarial training: Towards fast training of more robust models against adversarial attacks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 6629–6638.
|
| [81] |
ZHANG Hongyang, YU Yaodong, JIAO Jiantao, et al. Theoretically principled trade-off between robustness and accuracy[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, California, 2019: 7472–7482.
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
RANJAN R, SANKARANARAYANAN S, CASTILLO C D, et al. Improving network robustness against adversarial attacks with compact convolution[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.00699, 2018. |
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
DUBEY A, VAN DER MAATEN L, YALNIZ Z, et al. Defense against adversarial images using web-scale nearest-neighbor search[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 8767–8776.
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, WU Xi, et al. Distillation as a defense to adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2016: 582–597.
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
STRAUSS T, HANSELMANN M, JUNGINGER A, et al. Ensemble methods as a defense to adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.03423, 2018. |
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
SENGUPTA S, CHAKRABORTI T, and KAMBHAMPATI S. MTDeep: Boosting the security of deep neural nets against adversarial attacks with moving target defense[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07213, 2019. |
| [92] |
SAMANGOUEI P, KABKAB M, and CHELLAPPA R. Defense-GAN: Protecting classifiers against adversarial attacks using generative models[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1805.06605, 2018. |
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
ZANTEDESCHI V, NICOLAE M I, and RAWAT A. Efficient defenses against adversarial attacks[C]. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 39–49.
|
| [95] |
CISSE M, BOJANOWSKI P, GRAVE E, et al. Parseval networks: Improving robustness to adversarial examples[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 854–863.
|
| [96] |
LIAO Fangzhou, LIANG Ming, DONG Yinpeng, et al. Defense against adversarial attacks using high-level representation guided denoiser[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1778–1787.
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
SINHA A, NAMKOONG H, VOLPI R, et al. Certifying some distributional robustness with principled adversarial training[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10571, 2020. |
| [99] |
LAMB A, BINAS J, GOYAL A, et al. Fortified networks: Improving the robustness of deep networks by modeling the manifold of hidden representations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02485, 2018. |
| [100] |
GAO Ji, WANG Beilun, LIN Zeming, et al. DeepCloak: Masking deep neural network models for robustness against adversarial samples[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1702.06763, 2017. |
| [101] |
BAKHTI Y, FEZZA S A, HAMIDOUCHE W, et al. DDSA: A defense against adversarial attacks using deep denoising sparse autoencoder[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 160397–160407. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2951526 |
| [102] |
LIU Xuanqing, LI Yao, WU Chongruo, et al. Adv-BNN: Improved adversarial defense through robust Bayesian neural network[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.01279, 2019. |
| [103] |
SONG Yang, KIM T, NOWOZIN S, et al. PixelDefend: Leveraging generative models to understand and defend against adversarial examples[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10766, 2018. |
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
CARRARA F, FALCHI F, CALDELLI R, et al. Adversarial image detection in deep neural networks[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(3): 2815–2835. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-5853-4 |
| [106] |
LI Xin and LI Fuxin. Adversarial examples detection in deep networks with convolutional filter statistics[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5775–5783.
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
ZHENG Zhihao and HONG Pengyu. Robust detection of adversarial attacks by modeling the intrinsic properties of deep neural networks[C]. The 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 7913–7922.
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
MA Shiqing, LIU Yingqi, TAO Guanhong, et al. NIC: Detecting adversarial samples with neural network invariant checking[C]. 2019 Network and Distributed Systems Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2019: 1–15.
|
| [111] |
MA Xingjun, LI Bo, WANG Yisen, et al. Characterizing adversarial subspaces using local intrinsic dimension-ality[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1801.02613, 2018. |
| [112] |
COHEN G, SAPIRO G, and GIRYES R. Detecting adversarial samples using influence functions and nearest neighbors[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1909.06872, 2020. |
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
MENG Dongyu and CHEN Hao. MagNet: A two-pronged defense against adversarial examples[C]. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 135–147.
|
| [116] |
MACHADO G R, GOLDSCHMIDT R R, and SILVA E. MultiMagNet: A non-deterministic approach based on the formation of ensembles for defending against adversarial images[C]. The 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, Heraklion, Greece, 2019: 307–318.
|
| [117] |
LU Jiajun, ISSARANON T, and FORSYTH D. SafetyNet: Detecting and rejecting adversarial examples robustly[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 446–454.
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
RUAN Yibin and DAI Jiazhu. TwinNet: A double sub-network framework for detecting universal adversarial perturbations[J]. Future Internet, 2018, 10(3): 26. doi: 10.3390/fi10030026 |
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
LIANG Bin, LI Hongcheng, SU Miaoqiang, et al. Detecting adversarial image examples in deep networks with adaptive noise reduction[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1705.08378, 2019. |
| [122] |
LUST J and CONDURACHE A P. A survey on assessing the generalization envelope of deep neural networks at inference time for image classification[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2008.09381v2, 2020. |
| [123] |
MA Lei, JUEFEI-XU F, ZHANG Fuyuan, et al. DeepGauge: Multi-granularity testing criteria for deep learning systems[C]. The 33rd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, Montpellier, France, 2018: 120–131.
|
| [124] |
LING Xiang, JI Shouling, ZOU Jiaxu, et al. DEEPSEC: A uniform platform for security analysis of deep learning model[C]. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 673–690.
|
| [125] |
WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 |
| [126] |
LUO Bo, LIU Yannan, WEI Lingxiao, et al. Towards imperceptible and robust adversarial example attacks against neural networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04693, 2018. |
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
ZHANG Chongzhi, LIU Aishan, LIU Xianglong, et al. Interpreting and improving adversarial robustness of deep neural networks with neuron sensitivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 30: 1291–1304. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3042083 |
| [129] |
VARGAS D V and KOTYAN S. Robustness assessment for adversarial machine learning: Problems, solutions and a survey of current neural networks and defenses[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.06026v2, 2020. |
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
DONG Yinpeng, FU Qi’an, YANG Xiao, et al. Benchmarking adversarial robustness on image classification[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 318–328.
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
ZHANG Xuyao, LIU Chenglin, and SUEN C Y. Towards robust pattern recognition: A review[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2020, 108(6): 894–922. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.2989782 |
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
TRAMÈR F, BEHRMANN J, CARLINI N, et al. Fundamental tradeoffs between invariance and sensitivity to adversarial perturbations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.04599, 2020. |
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
CARMON Y, RAGHUNATHAN A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Unlabeled data improves adversarial robustness[C]. The 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 1–12.
|
| [141] |
HENDRYCKS D, MAZEIKA M, KADAVATH S, et al. Using self-supervised learning can improve model robustness and uncertainty[C]. The 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019.
|
| [142] |
CHEN Tianlong, LIU Sijia, CHANG Shiyu, et al. Adversarial robustness: From self-supervised pre-training to fine-tuning[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 696–705.
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
KIM M, TACK J, and HWANG S J. Adversarial self-supervised contrastive learning[C]. The 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1–12.
|
| [145] |
CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998 |
| [146] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. |
| [147] |
GRILL J B, STRUB F, ALTCHÉ F, et al. Bootstrap your own latent a new approach to self-supervised learning[C]. The 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1–14.
|
| [148] |
XU Yanjie, SUN Hao, CHEN Jin, et al. Robust remote sensing scene classification by adversarial self-supervised learning[C]. 2021 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 1–4.
|
| [149] |
LI Haifeng, HUANG Haikuo, CHEN Li, et al. Adversarial examples for CNN-based SAR image classification: An experience study[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 1333–1347. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3038683 |
| [150] |
XU Yonghao, DU Bo, and ZHANG Liangpei. Assessing the threat of adversarial examples on deep neural networks for remote sensing scene classification: Attacks and defenses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1604–1617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2999962 |
| [151] |
TU J, LI Huichen, YAN Xinchen, et al. Exploring adversarial robustness of multi-sensor perception systems in self driving[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.06784v1, 2021. |
| [152] |
MODAS A, SANCHEZ-MATILLA R, FROSSARD P, et al. Toward robust sensing for autonomous vehicles: An adversarial perspective[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2020, 37(4): 14–23. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2020.2985363 |
| [153] |
SUN Hao, XU Yanjie, KUANG Gangyao, et al. Adversarial robustness evaluation of deep convolutional neural network based SAR ATR algorithm[C]. 2021 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 1–4.
|
| [154] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang, HU Jingliang, QIU Chunping, et al. So2Sat LCZ42: A benchmark data set for the classification of global local climate zones [Software and Data Sets][J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(3): 76–89. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2020.2964708 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

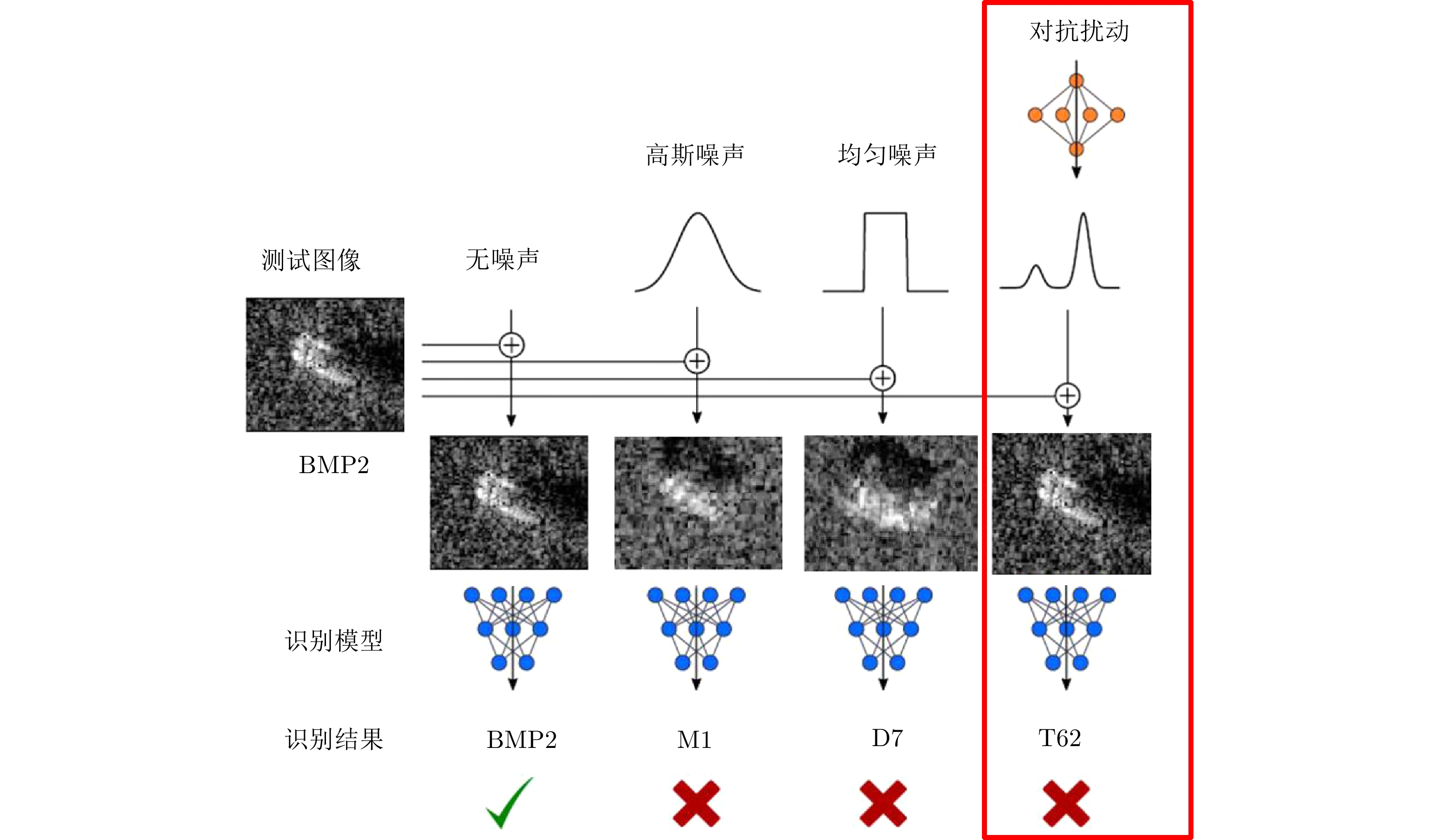



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: