- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | ZHANG Xiaoling, ZHANG Tianwen, SHI Jun, et al. High-speed and High-accurate SAR ship detection based on a depthwise separable convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111 |
High-speed and High-accurate SAR Ship Detection Based on a Depthwise Separable Convolution Neural Network
DOI: 10.12000/JR19111 CSTR: 32380.14.JR19111
More Information-
Abstract
With the development of artificial intelligence, Synthetic-Aperture Radar (SAR) ship detection using deep learning technology can effectively avoid traditionally complex feature design and thereby greatly improve detection accuracy. However, most existing detection models often improve detection accuracy at the expense of detection speed that limits some real-time applications of SAR such as emergency military deployment, rapid maritime rescue, and real-time marine environmental monitoring. To solve this problem, a high-speed and high-accuracy SAR ship detection method called SARShipNet-20 based on a Depthwise Separable Convolution Neural Network (DS-CNN) has been proposed in this paper, that replaces the Traditional Convolution Neural Network (T-CNN) and combines Channel Attention (CA) and Spatial Attention (SA). As a result, high-speed and high-accuracy SAR ship detection can be simultaneously achieved. This method has certain practical significance in the field of real-time SAR application, and its lightweight model is helpful for future FPGA or DSP hardware transplantation.
-

-
References
[1] ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. High-speed ship detection in SAR images based on a grid convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(10): 1206. doi: 10.3390/rs11101206[2] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Depthwise separable convolution neural network for high-speed SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(21): 2483. doi: 10.3390/rs11212483[3] GAO Gui. A parzen-window-kernel-based CFAR algorithm for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 557–561. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2090492[4] AN Wentao, XIE Chunhua, and YUAN Xinzhe. An improved iterative censoring scheme for CFAR ship detection with SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4585–4595. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282820[5] HOU Biao, CHEN Xingzhong, and JIAO Licheng. Multilayer CFAR detection of ship targets in very high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 811–815. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2362955[6] YIN Kuiying, JIN Lin, ZHANG Changchun, et al. A method for automatic target recognition using shadow contour of SAR image[J]. IETE Technical Review, 2013, 30(4): 313–323. doi: 10.4103/0256-4602.116721[7] JIANG Shaofeng, WANG Chao, ZHANG Bo, et al. Ship detection based on feature confidence for high resolution SAR images[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 6844–6847. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352591.[8] WANG Shigang, WANG Min, YANG Shuyuan, et al. New hierarchical saliency filtering for fast ship detection in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 351–362. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2606481[9] WANG Chonglei, BI Funkun, CHEN Liang, et al. A novel threshold template algorithm for ship detection in high-resolution SAR images[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 100–103. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7729016.[10] ZHU Jiwei, QIU Xiaolan, PAN Zongxu, et al. Projection shape template-based ship target recognition in TerraSAR-X images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(2): 222–226. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2635699[11] LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124934.[12] 李健伟, 曲长文, 彭书娟. 基于级联CNN的SAR图像舰船目标检测算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(10): 2191–2197.LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and PENG Shujuan. A ship detection method based on cascade CNN in SAR images[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(10): 2191–2197.[13] CHENG Mingming, LIU Yun, LIN Wenyan, et al. BING: Binarized normed gradients for objectness estimation at 300fps[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(1): 3–20. doi: 10.1007/s41095-018-0120-1[14] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556v1, 2014.[15] 李健伟, 曲长文, 彭书娟, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像舰船目标检测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(9): 1953–1959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.09LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, PENG Shujuan, et al. Ship detection in SAR images based on convolutional neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1953–1959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.09.09[16] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031[17] 杨龙, 苏娟, 李响. 基于深度卷积神经网络的SAR舰船目标检测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 1990–1997. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.11YANG Long, SU Juan, LI Xiang. Ship detection in SAR images based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 1990–1997. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.11[18] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.[19] 胡昌华, 陈辰, 何川, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的SAR图像舰船小目标检测[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2019, 27(3): 397–405, 414. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2019.03.018HU Changhua, CHEN Chen, HE Chuan, et al. Ship small target detection based on deep convolution neural network in SAR image[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2019, 27(3): 397–405, 414. doi: 10.13695/j.cnki.12-1222/o3.2019.03.018[20] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J]. arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018.[21] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106.[22] SIFRE L. Rigid-motion scattering for image classification[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Ecole Polytechnique, CMAP, 2014.[23] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.[24] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745.[25] HUBEL D H and WIESEL T N. Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat’s striate cortex[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1959, 148(3): 574–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006308[26] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386[27] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1800–1807. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.195.[28] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91.[29] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6517–6525. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.690.[30] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, French, 2015: 448–456.[31] MANASWI N K. Understanding and Working with Keras[M]. MANASWI N K. Deep Learning with Applications Using Python. Apress, Berkeley, CA: Springer, 2018: 31–43.[32] ABADI M, AGARWAL A, BARHAM P, et al. TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems. Software available from tensorflow.org[EB/OL]. https://www.bibsonomy.org/bibtex/2ba528cb1d5505ae48100cfc940c5fc3, 2015.[33] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J]. arXiv: 1706.05587, 2017.[34] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.324.[35] DAI Jifeng, HE Kaiming, and SUN Jian. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[J]. arXiv: 1605.06409v2, 2016.[36] HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, and DOLLÁR P. Rethinking ImageNet pre-training[J]. arXiv: 1811.08883, 2018.[37] CUI Zongyong, LI Qi, CAO Zongjie, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983–8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988[38] 孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097 -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Diagrammatic sketch of T-CNN and DS-CNN
- Figure 2. Network structure (SARShipNet-20)
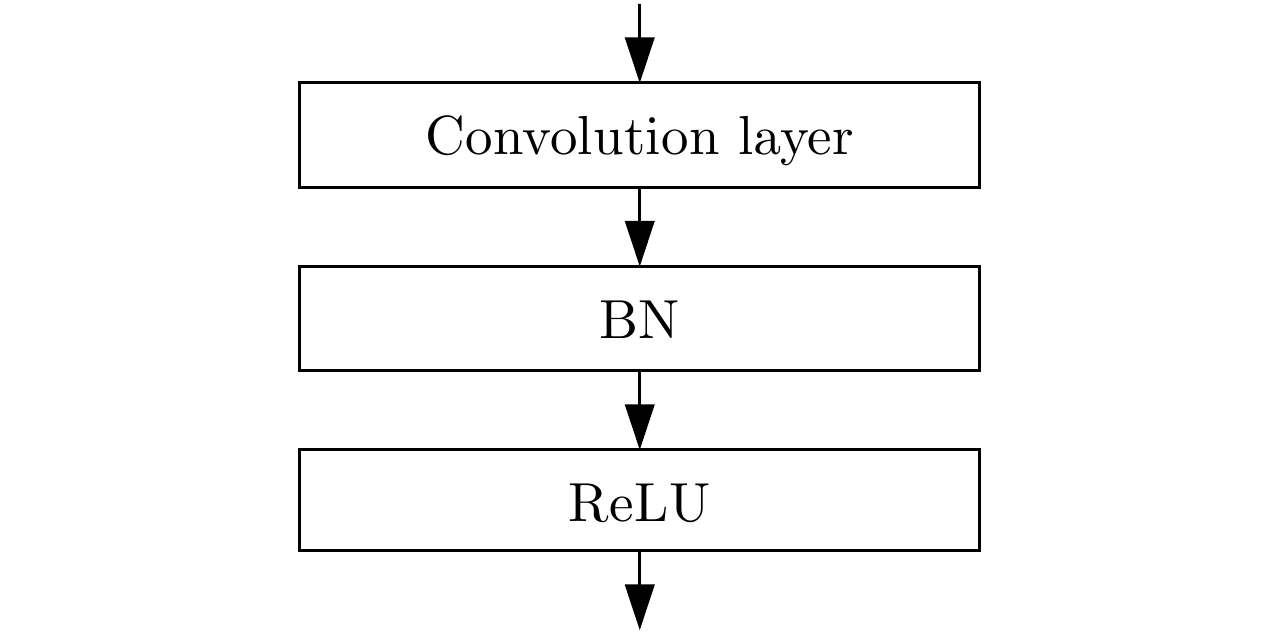
- Figure 3. Internal operation flow in convolution layers
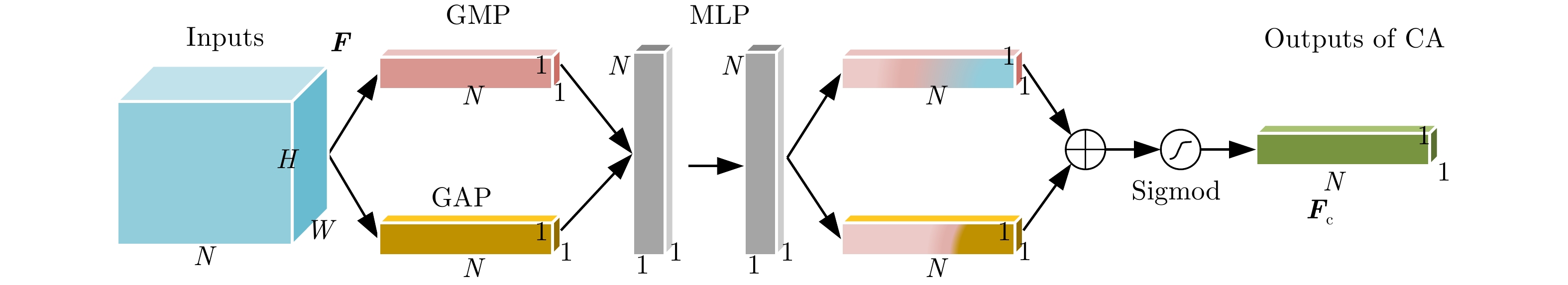
- Figure 4. Channel Attention (CA)
- Figure 5. Spatial Attention (SA)
- Figure 6. SAR ship detection results of SARShipNet-20
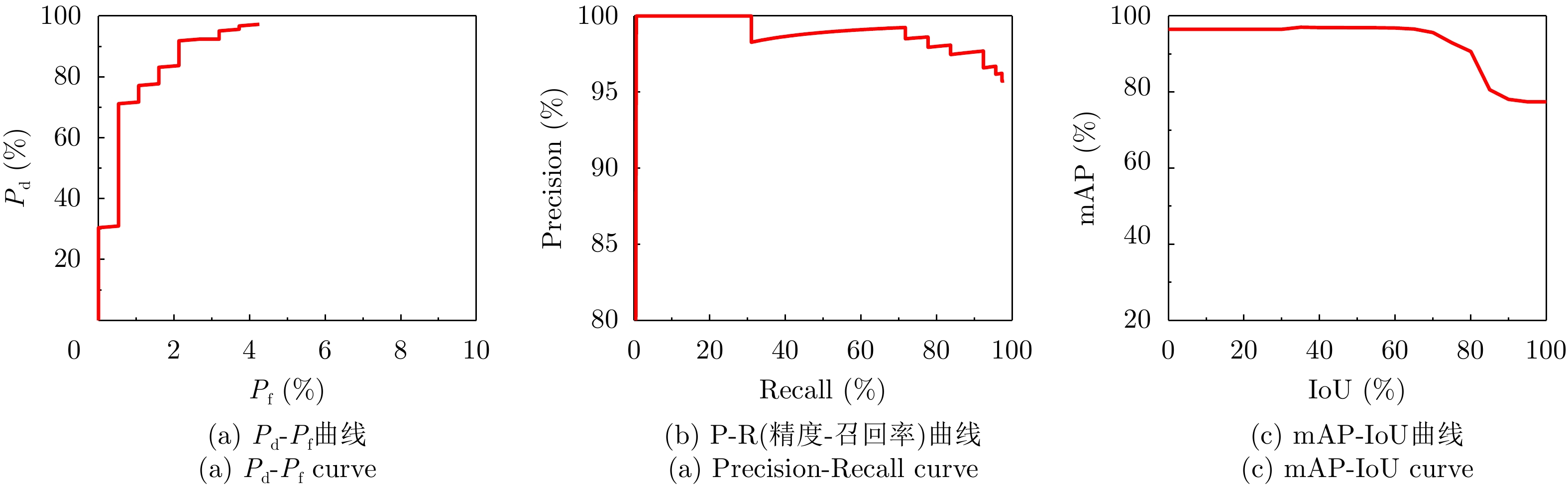
- Figure 7. Performance evaluation curve of SARShipNet-20


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: