| [1] |
盖旭刚, 陈晋汶, 韩俊, 等. 合成孔径雷达的现状与发展趋势[J]. 飞航导弹, 2011(3): 82–86, 95.
GAI Xugang, CHEN Jinwen, HAN Jun, et al. Development status and trend of synthetic aperture radar[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2011(3): 82–86, 95.
|
| [2] |
张红, 王超, 张波, 等. 高分辨率SAR图像目标识别[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
ZHANG Hong, WANG Chao, ZHANG Bo, et al. Target Recognition in High Resolution SAR Images[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
|
| [3] |
MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 |
| [4] |
WANG Ruixia, LIN Wei, and MAO Jun. Speckle suppression for SAR image based on wavelet transform and PCA[J]. Computer Engineering, 2008, 34(20): 235–237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2008.20.086 |
| [5] |
CHEN Sizhe and WANG Haipeng. SAR target recognition based on deep learning[C]. 2014 International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics, Shanghai, China, 2015.
|
| [6] |
田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037TIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHAN Ronghui, HU Jiemin, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037 |
| [7] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720 |
| [8] |
FURUKAWA H. Deep learning for target classification from SAR imagery: Data augmentation and translation invariance[R]. SANE2017-30, 2017.
|
| [9] |
YUAN Yuan, YUAN Hao, LEI Ling, et al. An imaging method of GEO Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2007, 5(2): 128–132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2007.02.011 |
| [10] |
史洪印, 周荫清, 陈杰. 同步轨道星机双基地三通道SAR地面运动目标指示算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(8): 1881–1885.
SHI Hongyin, ZHOU Yinqing, and CHEN Jie. An algorithm of GEO spaceborne-airborne bistatic three-channel SAR ground moving target indication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(8): 1881–1885.
|
| [11] |
LI Zhuo, LI Chunsheng, YU Ze, et al. Back projection algorithm for high resolution GEO-SAR image formation[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 336–339.
|
| [12] |
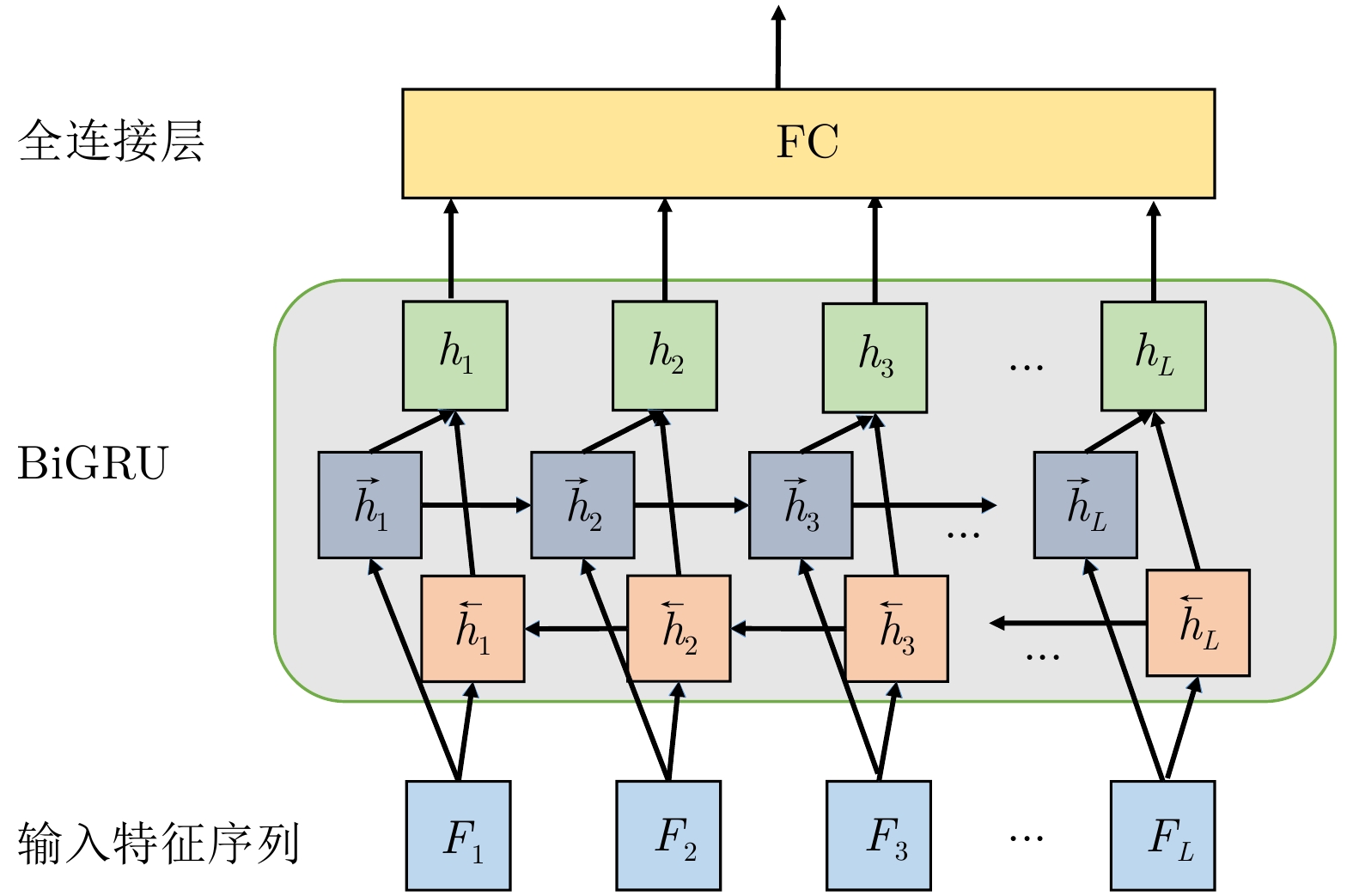
ZHANG Fan, HU Chen, YIN Qiang, et al. Multi-aspect-aware bidirectional LSTM networks for synthetic aperture radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 26880–26891. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2773363 |
| [13] |
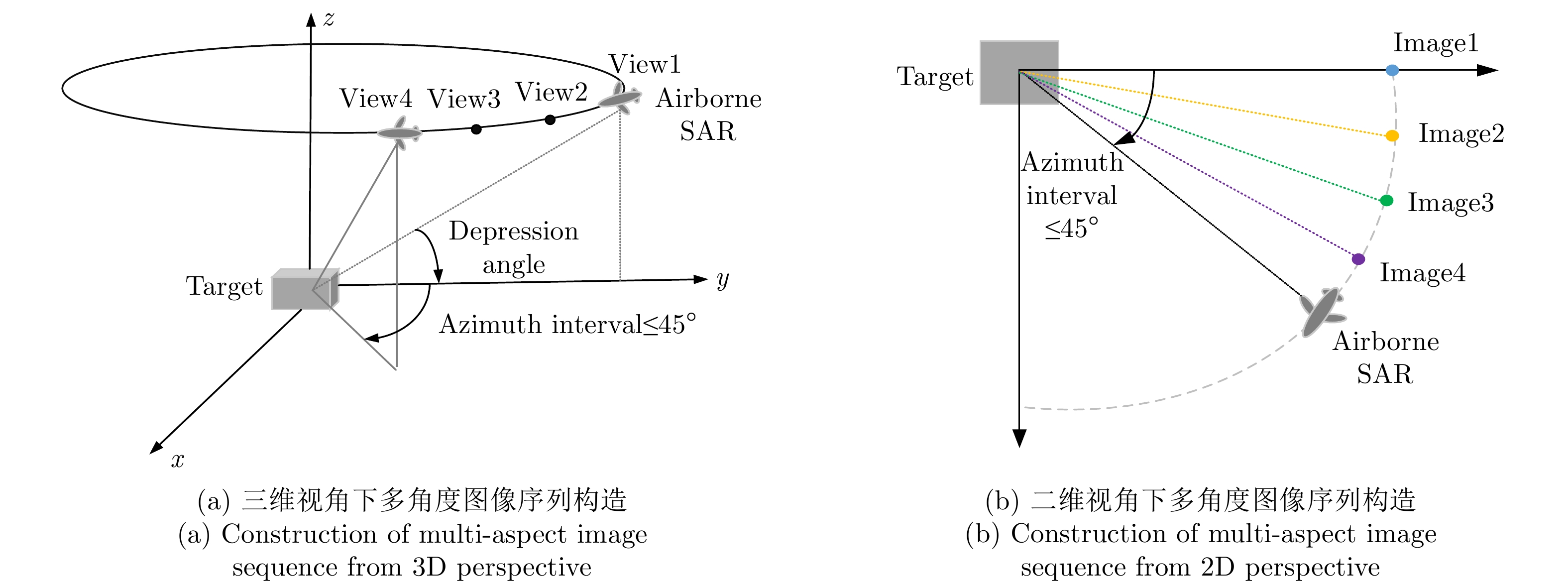
PEI Jifang, HUANG Yulin, HUO Weibo, et al. SAR automatic target recognition based on Multiview deep learning framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2196–2210. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2776357 |
| [14] |
ZOU Hao, LIN Yun, and HONG Wen. Research on multi-aspect SAR images target recognition using deep learning[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(5): 513–522. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.05.002 |
| [15] |
ZHAO Pengfei, LIU Kai, ZOU Hao, et al. Multi-stream convolutional neural network for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(9): 1473. doi: 10.3390/rs10091473 |
| [16] |
ZHANG Fan, FU Zhenzhen, ZHOU Yongsheng, et al. Multi-aspect SAR target recognition based on space-fixed and space-varying scattering feature joint learning[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 10(10): 998–1007. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2019.1635287 |
| [17] |
TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[J]. arXiv: 1905.11946, 2019.
|
| [18] |
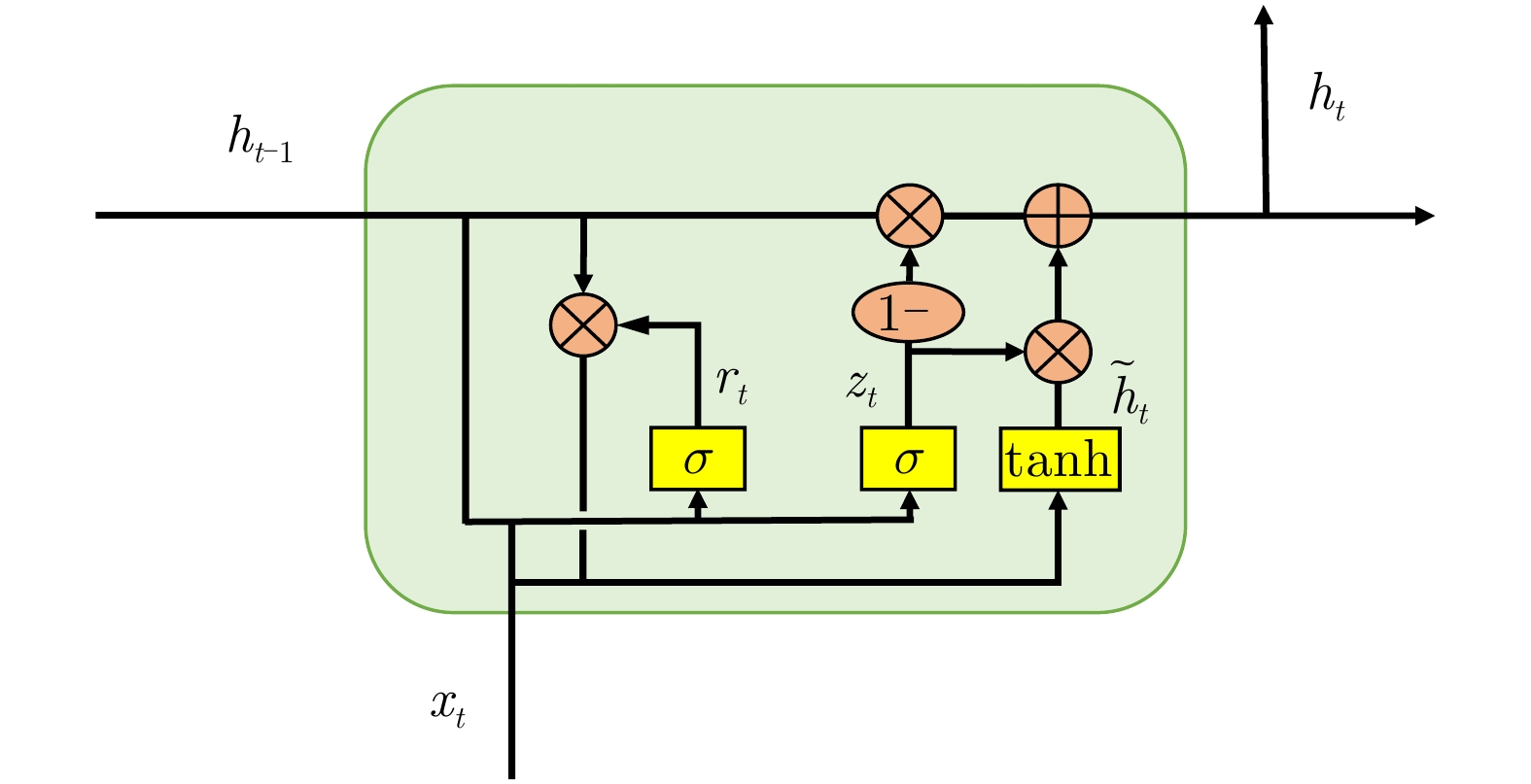
CHO K, VAN MERRIENBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[J]. arXiv: 1406.1078, 2014.
|
| [19] |
CAI Jie, MENG Zibo, KHAN A S, et al. Island loss for learning discriminative features in facial expression recognition[C]. The 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 2018: 302–309.
|
| [20] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016.
|
| [21] |
HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 |
| [22] |
WEN Yandong, ZHANG Kaipeng, LI Zhifeng, et al. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: