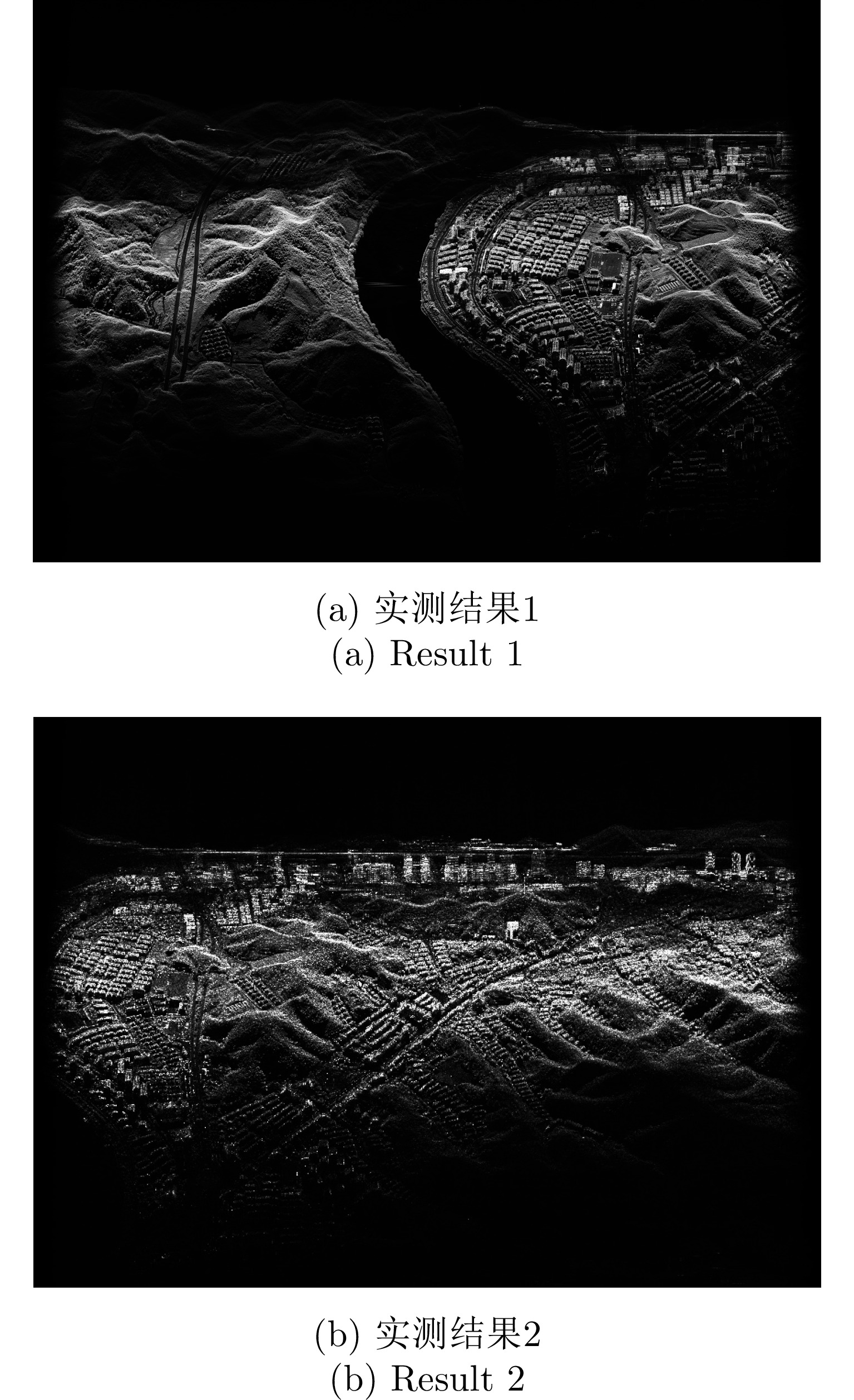
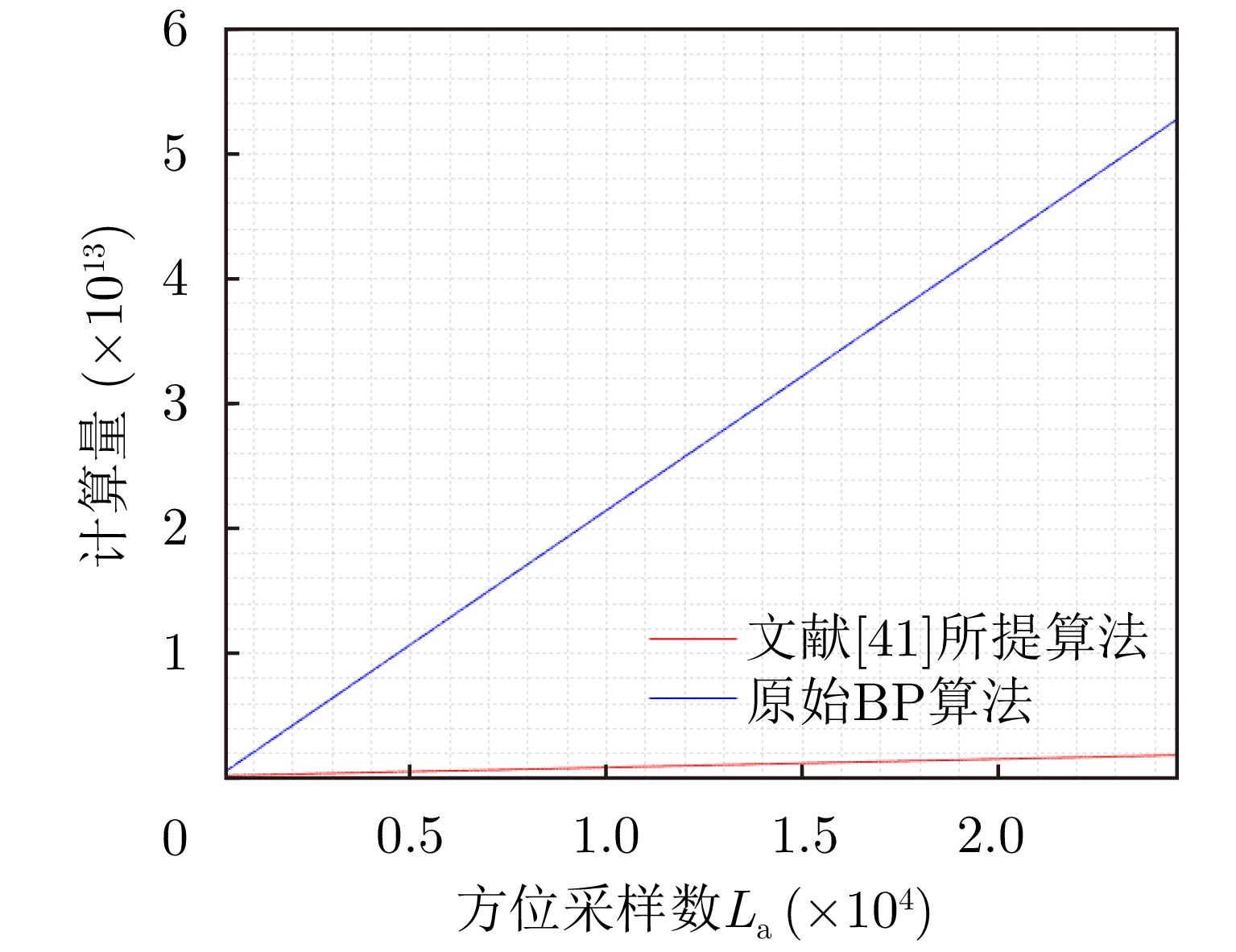
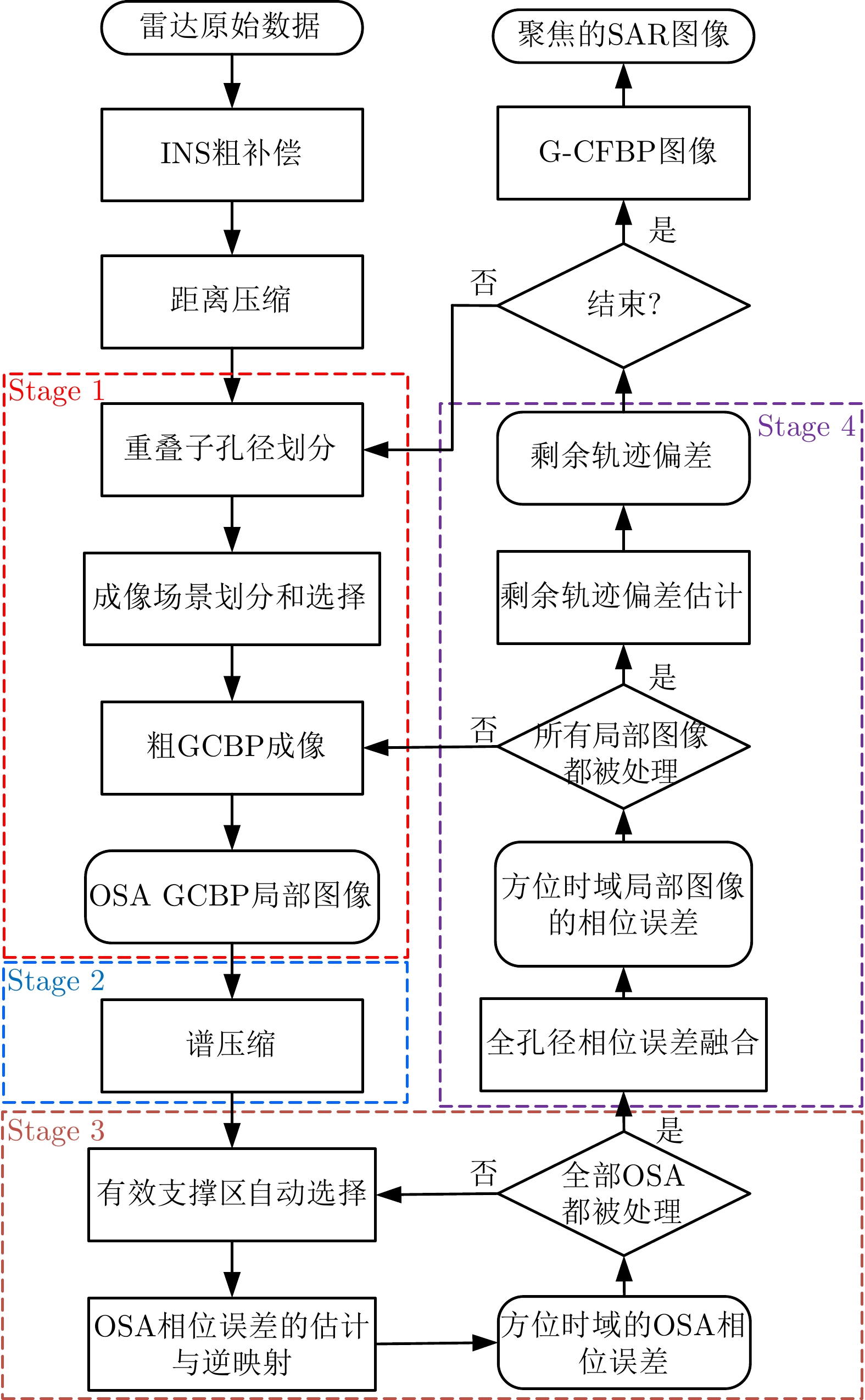
| [1] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005.
|
| [2] |
SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: Wiley, 1999.
|
| [3] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 108–110.
|
| [4] |
MOREIRA A and HUANG Yonghong. Airborne SAR processing of highly squinted data using a chirp scaling approach with integrated motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5): 1029–1040. doi: 10.1109/36.312891 |
| [5] |
RANEY R K, RUNGE H, BAMLER R, et al. Precision SAR processing using chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(4): 786–799. doi: 10.1109/36.298008 |
| [6] |
BAMLER R. A comparison of range-Doppler and wavenumber domain SAR focusing algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(4): 706–713. doi: 10.1109/36.158864 |
| [7] |
LIN Yun, HONG Wen, TAN Weixian, et al. Extension of range migration algorithm to squint circular SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 651–655. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098843 |
| [8] |
VU V T, SJÖGREN T K, and PETTERSSON M I. SAR imaging in ground plane using fast backprojection for mono- and bistatic cases[C]. 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012: 184–189.
|
| [9] |
杨泽民. 快速时域SAR成像与三维SAR运动补偿方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2016.
YANG Zemin. Study on fast time domain SAR imaging and three dimensional SAR motion compensation methods[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2016.
|
| [10] |
ANDERSSON L E. On the determination of a function from spherical averages[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 1988, 19(1): 214–232. doi: 10.1137/0519016 |
| [11] |
FAWCETT J A. Inversion of N-dimensional spherical averages[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1985, 45(2): 336–341. doi: 10.1137/0145018 |
| [12] |
ALBUQUERQUE M, PRATS P, and SCHEIBER R. Applications of time-domain back-projection SAR processing in the airborne case[C]. 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–4.
|
| [13] |
DURAND R, GINOLHAC G, THIRION-LEFEVRE L, et al. Back projection version of subspace detector SAR processors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1489–1497. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751274 |
| [14] |
MUNSON D C, O’BRIEN J D, and JENKINS W K. A tomographic formulation of spotlight-mode synthetic aperture radar[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1983, 71(8): 917–925. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1983.12698 |
| [15] |
YEGULALP A F. Fast backprojection algorithm for synthetic aperture radar[C]. The 1999 IEEE Radar Conference. Radar into the Next Millennium (Cat. No.99CH36249), Waltham, MA, USA, 1999: 60–65.
|
| [16] |
ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734 |
| [17] |
龙腾, 丁泽刚, 肖枫, 等. 星载高分辨频率步进SAR成像技术[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 782–792. doi: 10.12000/JR19076LONG Teng, DING Zegang, XIAO Feng, et al. Spaceborne high-resolution stepped-frequency SAR imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 782–792. doi: 10.12000/JR19076 |
| [18] |
丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 |
| [19] |
CHEN Jianlai, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. A two-dimensional beam-steering method to simultaneously consider doppler centroid and ground observation in GEOSAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(1): 161–167. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2544349 |
| [20] |
DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 |
| [21] |
李浩林. 机载SAR快速后向投影成像算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2015.
LI Haolin. Study on fast back-projection algorithms for airborne SAR image[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2015.
|
| [22] |
陈潇翔. 机载超高分辨SAR运动补偿成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2021.
CHEN Xiaoxiang. Study on motion compensation algorithm for ultra high resolution airborne SAR imaging[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2021.
|
| [23] |
YANG Zemin, SUN Guangcai, WU Yufeng, et al. A new fast back projection algorithm based on polar format algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2014, 36(3): 537–544. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00613 |
| [24] |
ZHANG Lei, LI Haolin, QIAO Zhijun, et al. A fast BP algorithm with wavenumber spectrum fusion for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(9): 1460–1464. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2295326 |
| [25] |
ZHANG Lei, LI Haolin, QIAO Zhijun, et al. Integrating autofocus techniques with fast factorized back-projection for high-resolution spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1394–1398. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2258886 |
| [26] |
LIANG Yi, LI Guofei, WEN Jun, et al. A fast time-domain SAR imaging and corresponding autofocus method based on hybrid coordinate system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8627–8640. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2921917 |
| [27] |
DONG Qi, YANG Zemin, SUN Guangcai, et al. Cartesian factorized backprojection algorithm for synthetic aperture radar[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 1074–1077.
|
| [28] |
FROLIND P O and ULANDER L M H. Evaluation of angular interpolation kernels in fast back-projection SAR processing[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar And Navigation, 2006, 153(3): 243–249. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045110 |
| [29] |
YANG Zemin, SUN Guangcai, and XING Mengdao. A new fast back-projection algorithm using polar format algorithm[C]. 2013 Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Tsukuba, Japan, 2013: 373–376.
|
| [30] |
YANG Zemin, DONG Qi, SUN Guangcai, et al. A fast implementation method for the FFBP algorithm[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 2015: 411–414.
|
| [31] |
YANG Lei, ZHOU Song, and BI Guoan. A modified fast factorized back-projection algorithm for squint UWB-SAR imaging[C]. 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Singapore, 2015: 413–416.
|
| [32] |
WANG Yue, WU Junjie, ZHANG Shaoqing, et al. An accelerate FFBP algorithm of bistatic forward-looking SAR based on azimuth equidistant coordinates[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–5.
|
| [33] |
邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 |
| [34] |
DONG Qi, YANG Zemin, SUN Guangcai, et al. Missile-borne forward squint SAR time-domain imaging algorithm based on sub-region processing[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1013–1018. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.10 |
| [35] |
FENG Dong, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. An extended fast factorized back projection algorithm for missile-borne bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(6): 2724–2734. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2828238 |
| [36] |
BIE Bowen, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A frequency domain backprojection algorithm based on local cartesian coordinate and subregion range migration correction for high-squint sar mounted on maneuvering platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(12): 7086–7101. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2848249 |
| [37] |
CHEN Xiaoxiang, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Ground cartesian back-projection algorithm for high squint diving TOPS SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(7): 5812–5827. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3011589 |
| [38] |
HU Cheng, LIU Feifeng, YANG Wenfu, et al. Modification of slant range model and imaging processing in GEO SAR[C]. 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2010: 4679–4682.
|
| [39] |
MONTI GUARNIERI A, LEANZA A, RECCHIA A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen in GEO-SAR: Estimation and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(3): 1668–1679. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2766084 |
| [40] |
ZENG Tao, LI Yinghe, DING Zegang, et al. Subaperture approach based on azimuth-dependent range cell migration correction and azimuth focusing parameter equalization for maneuvering high-squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6718–6734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2447393 |
| [41] |
CHEN Quan, LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, et al. A fast cartesian back-projection algorithm based on ground surface grid for GEO SAR focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5217114. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3125797 |
| [42] |
RAN Lei, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Lei, et al. An autofocus algorithm for estimating residual trajectory deviations in synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3408–3425. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2670785 |
| [43] |
WU Junjie, LI Yunli, PU Wei, et al. An effective autofocus method for fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 6145–6154. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2904608 |
| [44] |
ZHANG Tao, LIAO Guisheng, LI Yachao, et al. A two-stage time-domain autofocus method based on generalized sharpness metrics and AFBP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5205413. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068789 |
| [45] |
WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus—a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752 |
| [46] |
YE Wei, YEO T S, and BAO Zheng. Weighted least-squares estimation of phase errors for SAR/ISAR autofocus[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2487–2494. doi: 10.1109/36.789644 |
| [47] |
SAMCZYNSKI P, PIETRZYK G, and KULPA K. Simple method for estimating along track acceleration using autofocus map drift algorithm[C]. Proceedings of International Radar Symposium, Berlin, Germany, 2005: 43–47.
|
| [48] |
SAMCZYNSKI P and KULPA K. Concept of the coherent autofocus map-drift technique[C]. 2006 International Radar Symposium, Krakow, Poland, 2006: 1–4.
|
| [49] |
SAMCZYNSKI P and KULPA K. Non iterative map-drift technique[C]. 2008 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2008: 76–81.
|
| [50] |
JAKOWATZ JR C V and WAHL D E. Considerations for autofocus of spotlight-mode SAR imagery created using a beamforming algorithm[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVI, Orlando, FL, USA, 2009: 73370A.
|
| [51] |
ZHOU Song, YANG Lei, ZHAO Lifan, et al. Quasi-polar-based FFBP algorithm for miniature UAV SAR imaging without navigational data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7053–7065. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2739133 |
| [52] |
DING Zegang, LI Linghao, WANG Yan, et al. An autofocus approach for UAV-based ultrawideband ultrawidebeam SAR data with frequency-dependent and 2-D space-variant motion errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5203518. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3062183 |
| [53] |
RAN Lei, XIE Rong, LIU Zheng, et al. Simultaneous range and cross-range variant phase error estimation and compensation for highly squinted SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4448–4463. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2820102 |
| [54] |
ASH J N. An autofocus method for backprojection imagery in synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 104–108. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2161456 |
| [55] |
HU Kebin, ZHANG Xiaoling, HE Shufeng, et al. A less-memory and high-efficiency autofocus back projection algorithm for SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 890–894. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2365612 |
| [56] |
CHEN Leping, AN Daoxiang, and HUANG Xiaotao. Extended autofocus backprojection algorithm for low-frequency SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(8): 1323–1327. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2711005 |
| [57] |
LUO Yin, ZHAO Fengjun, LI Ning, et al. An autofocus cartesian factorized backprojection algorithm for spotlight synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(8): 1244–1248. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2829483 |
| [58] |
LOU Yishan, LIU Wenkang, XING Mengdao, et al. A novel motion compensation method applicable to ground cartesian back-projection algorithm for airborne circular SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5208917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3276051 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: