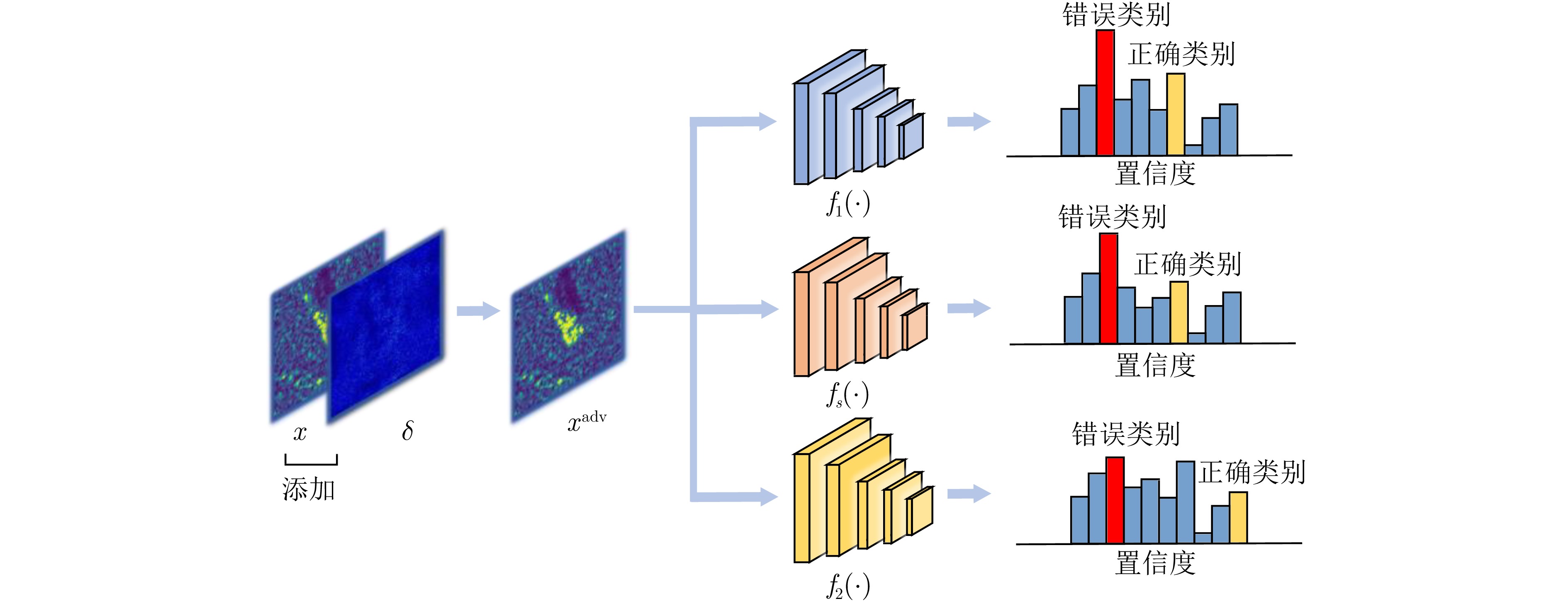
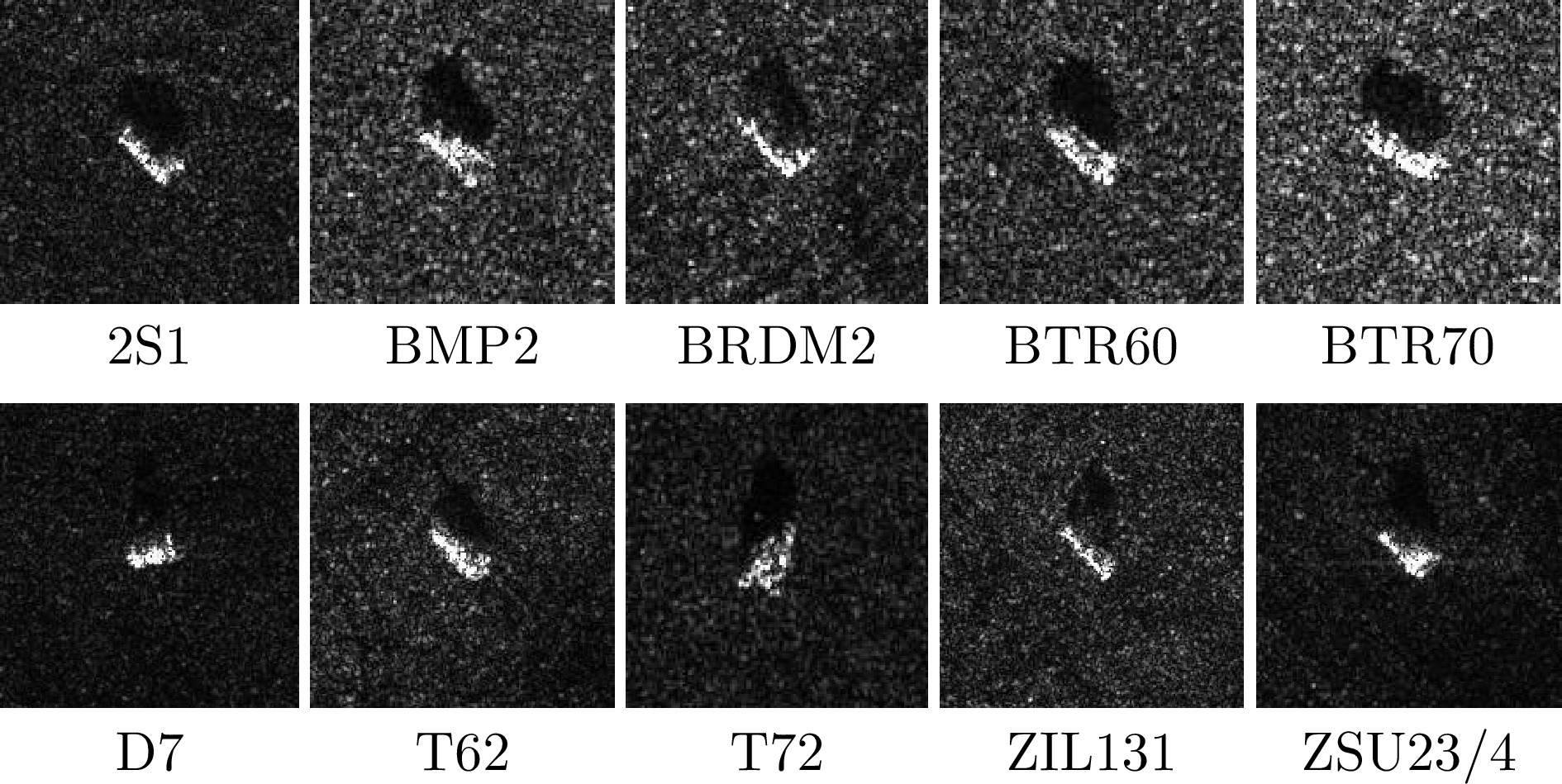
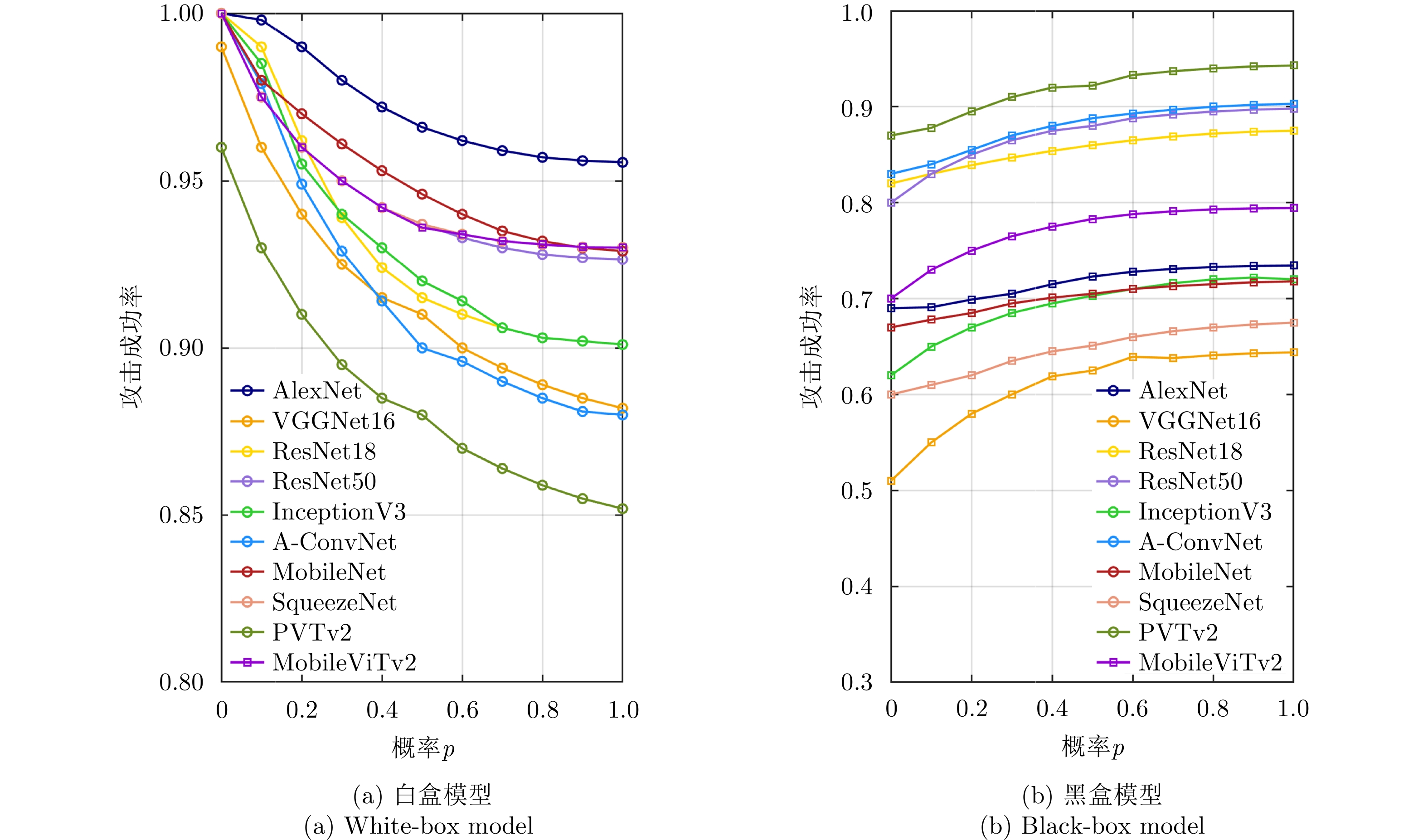
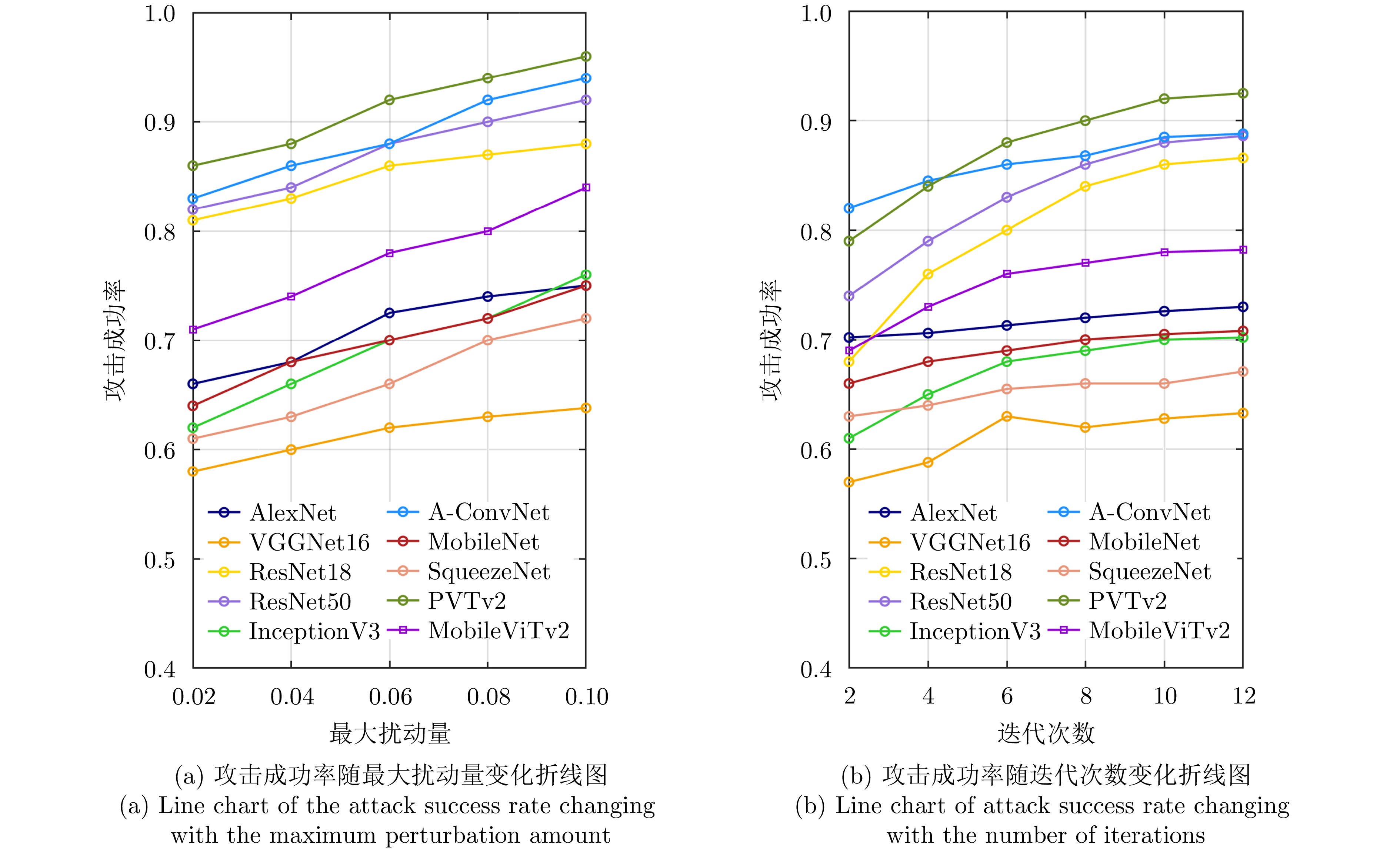
| [1] |
XU Yan and SCOOT K A. Sea ice and open water classification of SAR imagery using CNN-based transfer learning[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 2017: 3262–3265. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8127693. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Yue, SUN Xian, SUN Hao, et al. High resolution SAR image classification with deeper convolutional neural network[C]. International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 2374–2377. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8518829. |
| [3] |
SHAO Jiaqi, QU Changwen, and LI Jianwei. A performance analysis of convolutional neural network models in SAR target recognition[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications, Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124917. |
| [4] |
ZHANG Ming, AN Jubai, YU Dahua, et al. Convolutional neural network with attention mechanism for SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4004205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3031593. |
| [5] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720. |
| [6] |
徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130. |
| [7] |
吕艺璇, 王智睿, 王佩瑾, 等. 基于散射信息和元学习的SAR图像飞机目标识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 652–665. doi: 10.12000/JR22044. LYU Yixuan, WANG Zhirui, WANG Peijin, et al. Scattering information and meta-learning based SAR images interpretation for aircraft target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 652–665. doi: 10.12000/JR22044. |
| [8] |
HUANG Teng, ZHANG Qixiang, LIU Jiabao, et al. Adversarial attacks on deep-learning-based SAR image target recognition[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 162: 102632. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102632. |
| [9] |
孙浩, 陈进, 雷琳, 等. 深度卷积神经网络图像识别模型对抗鲁棒性技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 571–594. doi: 10.12000/JR21048. SUN Hao, CHEN Jin, LEI Lin, et al. Adversarial robustness of deep convolutional neural network-based image recognition models: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 571–594. doi: 10.12000/JR21048. |
| [10] |
高勋章, 张志伟, 刘梅, 等. 雷达像智能识别对抗研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098. GAO Xunzhang, ZHANG Zhiwei, LIU Mei, et al. Intelligent radar image recognition countermeasures: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098. |
| [11] |
SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014.
|
| [12] |
GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, and SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015: 1050.
|
| [13] |
KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW L J, and BENGIO S. Adversarial examples in the physical world[C]. The 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 99–112.
|
| [14] |
PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings[C]. 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, Saarbruecken, Germany, 2016: 372–387. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP.2016.36. |
| [15] |
BRENDEL W, RAUBER J, and BETHGE M. Decision-based adversarial attacks: Reliable attacks against black-box machine learning models[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018.
|
| [16] |
CARLINI N and WAGNER D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, CA, USA, 2017: 39–57. doi: 10.1109/SP.2017.49. |
| [17] |
SU Jiawei, VARGAS D V, and SAKURAI K. One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(5): 828–841. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2890858. |
| [18] |
CHEN Pinyu, ZHANG Huan, SHARMA Y, et al. ZOO: Zeroth order optimization based black-box attacks to deep neural networks without training substitute models[C]. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 15–26. doi: 10.1145/3128572.3140448. |
| [19] |
CHEN Jianbo, JORDAN M I, and WAINWRIGHT M J. HopSkipJumpAttack: A query-efficient decision-based attack[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020: 1277–1294. doi: 10.1109/SP40000.2020.00045. |
| [20] |
DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fengzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 9185–9193. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00957. |
| [21] |
ZHAO Haojun, LIN Yun, GAO Song, et al. Evaluating and improving adversarial attacks on DNN-based modulation recognition[C]. GLOBECOM 2020–2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, China, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM42002.2020.9322088. |
| [22] |
WANG Xiaosen and HE Kun. Enhancing the transferability of adversarial attacks through variance tuning[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 2021: 1924–1933. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00196. |
| [23] |
XIE Cihang, ZHANG Zhishuai, ZHOU Yuyin, et al. Improving transferability of adversarial examples with input diversity[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 2725–2734. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00284. |
| [24] |
CZAJA W, FENDLEY N, PEKALA M J, et al. Adversarial examples in remote sensing[C]. The 26th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Seattle, USA, 2018: 408–411. doi: 10.1145/3274895.3274904. |
| [25] |
CHEN Li, XU Zewei, LI Qi, et al. An empirical study of adversarial examples on remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7419–7433. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3051641. |
| [26] |
DU Chuan, HUO Chaoying, ZHANG Lei, et al. Fast C&W: A fast adversarial attack algorithm to fool SAR target recognition with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4010005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3058011. |
| [27] |
DU Chuan and ZHANG Lei. Adversarial attack for SAR target recognition based on UNet-generative adversarial network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(21): 4358. doi: 10.3390/rs13214358. |
| [28] |
ZHOU Junfan, SUN Hao, and KUANG Gangyao. Template-based universal adversarial perturbation for SAR target classification[C]. The 8th China High Resolution Earth Observation Conference, Singapore, Singapore, 2023: 351–360. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-8202-6_32. |
| [29] |
XIA Weijie, LIU Zhe, and LI Yi. SAR-PeGA: A generation method of adversarial examples for SAR image target recognition network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 1910–1920. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3206261. |
| [30] |
PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, ZHOU Jie, et al. Scattering model guided adversarial examples for SAR target recognition: Attack and defense[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5236217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213305. |
| [31] |
HANSEN L K and SALAMON P. Neural network ensembles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1990, 12(10): 993–1001. doi: 10.1109/34.58871. |
| [32] |
DING Jun, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2513754. |
| [33] |
LEE J S. Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1980, PAMI-2(2): 165–168. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1980.4766994. |
| [34] |
ZHUANG Juntang, TANG T, DING Yifan, et al. AdaBelief optimizer: Adapting stepsizes by the belief in observed gradients[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020: 795–806.
|
| [35] |
NESTEROV Y. A method for unconstrained convex minimization problem with the rate of convergence[J]. Mathematics, 1983, 269: 543–547.
|
| [36] |
MA J and YARATS D. Quasi-hyperbolic momentum and Adam for deep learning[C]. The 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2019: 1–38.
|
| [37] |
KEYDEL E R, LEE S W, and MOORE J T. MSTAR extended operating conditions: A tutorial[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 228–242. doi: 10.1117/12.242059. |
| [38] |
HOU Xiyue, AO Wei, SONG Qian, et al. FUSAR-Ship: Building a high-resolution SAR-AIS matchup dataset of Gaofen-3 for ship detection and recognition[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(4): 140303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2772-5. |
| [39] |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1106–1114.
|
| [40] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015.
|
| [41] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. |
| [42] |
SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.308. |
| [43] |
HOWARD A G, ZHU Menglong, CHEN Bo, et al. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861, 2017.
|
| [44] |
IANDOLA F N, HAN Song, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360, 2016.
|
| [45] |
WANG Wenhai, XIE Enze, LI Xiang, et al. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021: 548–558. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00061. |
| [46] |
MEHTA S and RASTEGARI M. MobileViT: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[C]. The Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022.
|
| [47] |
KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 2015: 1–15.
|
| [48] |
WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: