- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | Liu Junkai, Li Jianbing, Ma Liang, Chen Zhongkuan, Cai Yichao. Radar Target Detection Method of Aircraft Wake Vortices Based on Matrix Information Geometry[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 699-708. doi: 10.12000/JR17058 |
Radar Target Detection Method of Aircraft Wake Vortices Based on Matrix Information Geometry
DOI: 10.12000/JR17058 CSTR: 32380.14.JR17058
-
Abstract
The application of matrix information geometry to radar signal processing and target detection is a new and interesting subject. Wake vortices are Doppler-spread after Fourier transform. The traditional Moving Target Detection (MTD) method cannot adequately accumulate returns power of the whole spectrum. Based on matrix information geometry, a matrix Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) detection method is proposed to improve the detection performance of a weak wake target. In this method, covariance matrices of the observed data can be constructed into a matrix manifold; compared with CFAR detection, the geodesic distance between the covariance matrix in the detection cell and the mean of covariance matrices in the secondary cell is regarded as the detection statistics. Using simulated wake vortices, the return data in background noise and the iterative estimation performance of Riemannian mean are analyzed; the geodesic distance of covariance matrices of target return and noise with varying signal-noise rate is analyzed; and the detection performance of the matrix CFAR and the conventional MTD method is compared.
-

-
References
[1] 孙华飞, 张真宁, 彭林玉, 等. 信息几何导引[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.Sun Hua-fei, Zhang Zhen-ning, Peng Lin-yu, et al.. An Elementary Introduction to Information Geometry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016.[2] Rao C. Information and the accuracy attainable in the estimation of statistical parameters[J]. Bulletin of Calcutta Mathematical Society, 1945, 37: 81–91.[3] Chencov N N. Statistical Decision Rules and Optimal Inference[M]. Rhode Island, USA: American Mathematical Society, 1982.[4] Amari S I and Nagaoka H. Methods of Information Geometry[M]. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, 2000.[5] Lenglet C, Rousson M, Deriche R, et al. Statistics on the manifold of multivariate normal distributions: Theory and application to diffusion tensor MRI processing[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2006, 25(3): 423–444. DOI: 10.1007/s10851-006-6897-z[6] Moakher M. A differential geometric approach to the geometric mean of symmetric positive-definite matrices[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2005, 26(3): 735–747. DOI: 10.1137/S0895479803436937[7] Nielsen F and Bhatia R. Matrix Information Geometry[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2013.[8] Barbaresco F. Interactions between symmetric cone and information geometries: Bruhat-Tits and Siegel spaces models for high resolution autoregressive Doppler imagery[C]. Proceedings of ETVC 2008 Conference, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009: 124–163.[9] Barbaresco F. Innovative tools for radar signal processing based on Cartan’s geometry of SPD matrices & information geometry[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, 2008: 1–6.[10] Pennec X. Intrinsic statistics on Riemannian manifolds: Basic tools for geometric measurements[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2006, 25(1): 127–154. DOI: 10.1007/s10851-006-6228-4[11] Barbaresco F. Robust statistical radar processing in Fréchet metric space: OS-HDR-CFAR and OS-STAP processing in Siegel homogeneous bounded domains[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Radar Symposium, Leipzig, Germany, 2011: 639–644.[12] 黎湘, 程永强, 王宏强, 等. 雷达信号处理的信息几何方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.Li Xiang, Cheng Yong-qiang, Wang Hong-qiang, et al.. Methods of Information Geometry of Radar Signal Processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014.[13] Broderick A J, Bevilaqua P, Crouch J, et al.. Wake Turbulence: An Obstacle to Increased Air Traffic Capacity[M]. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2008: 1–59.[14] 刘俊凯, 李文臣, 王雪松, 等. 基于多普勒特性的飞机尾流回波提取方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2011, 23(7): 1323–1328. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2011.07.015Liu Jun-kai, Li Wen-chen, Wang Xue-song, et al. Extraction of aircraft wake vortices radar returns based on the Doppler characteristics[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2011, 23(7): 1323–1328. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2011.07.015[15] Gerz T, Holzäpfel F, and Darracq D. Commercial aircraft wake vortices[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2002, 38(3): 181–208. DOI: 10.1016/S0376-0421(02)00004-0[16] Shephard D J, Kyte A P, and Segura C A. Radar wake vortex measurements at F and I band[C]. Proceedings of IEE Colloquium on Radar and Microwave Imaging, London, 1994: 7/1–7/5.[17] 王首勇, 万洋, 刘俊凯, 等, 著. 现代雷达目标检测理论与方法[M]. 第2版, 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.Wang Shou-yong, Wan Yang, Liu Jun-kai, et al.. Modern Radar Target Detection Theory and Methods[M]. Second Edition, Beijing: Science Press, 2015.[18] Calvo M and Oller J M. An explicit solution of information geodesic equations for the multivariate normal model[J]. Statistics&Risk Modeling, 1991, 9(1/2): 119–138. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Simulation of the aircraft wake radar echo
- Figure 2. The Power Spectrum measured by the X-band radar in Marconi Research Center
- Figure 3. Block diagram of CA-CFAR detector based on information geometry
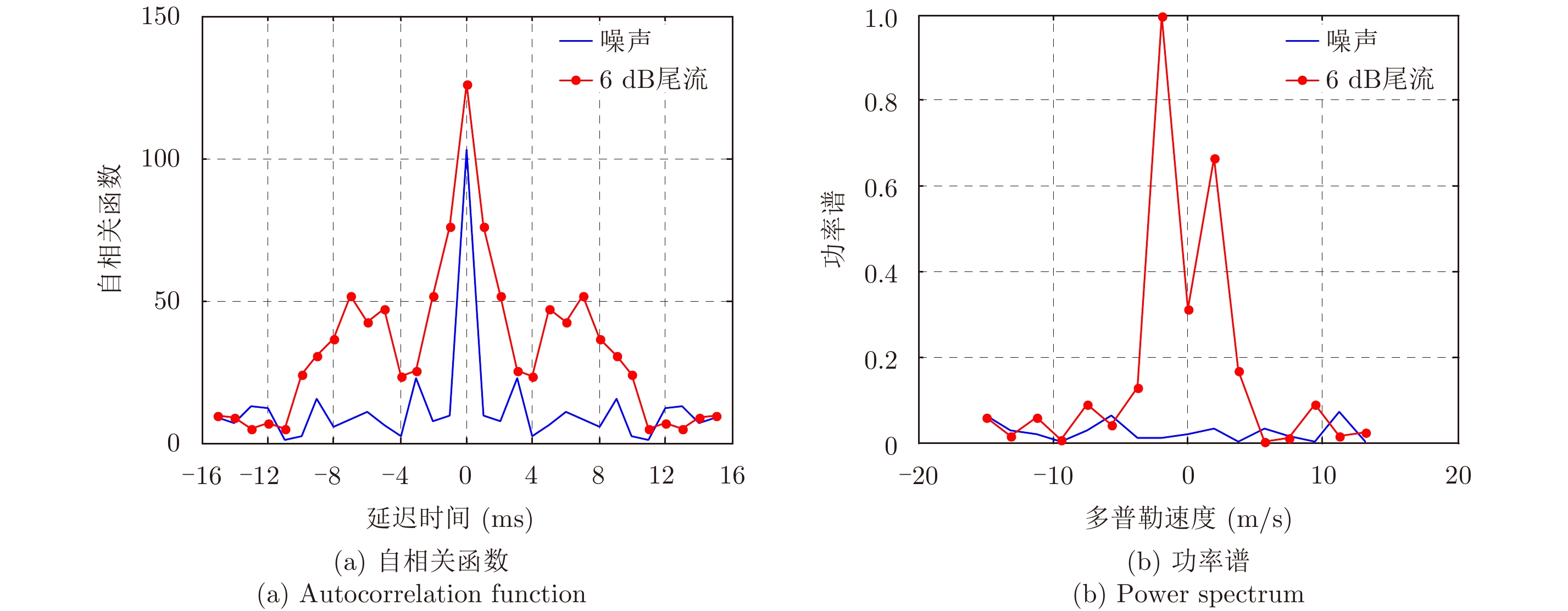
- Figure 4. Autocorrelation function and power spectrum when the pulse number is 16
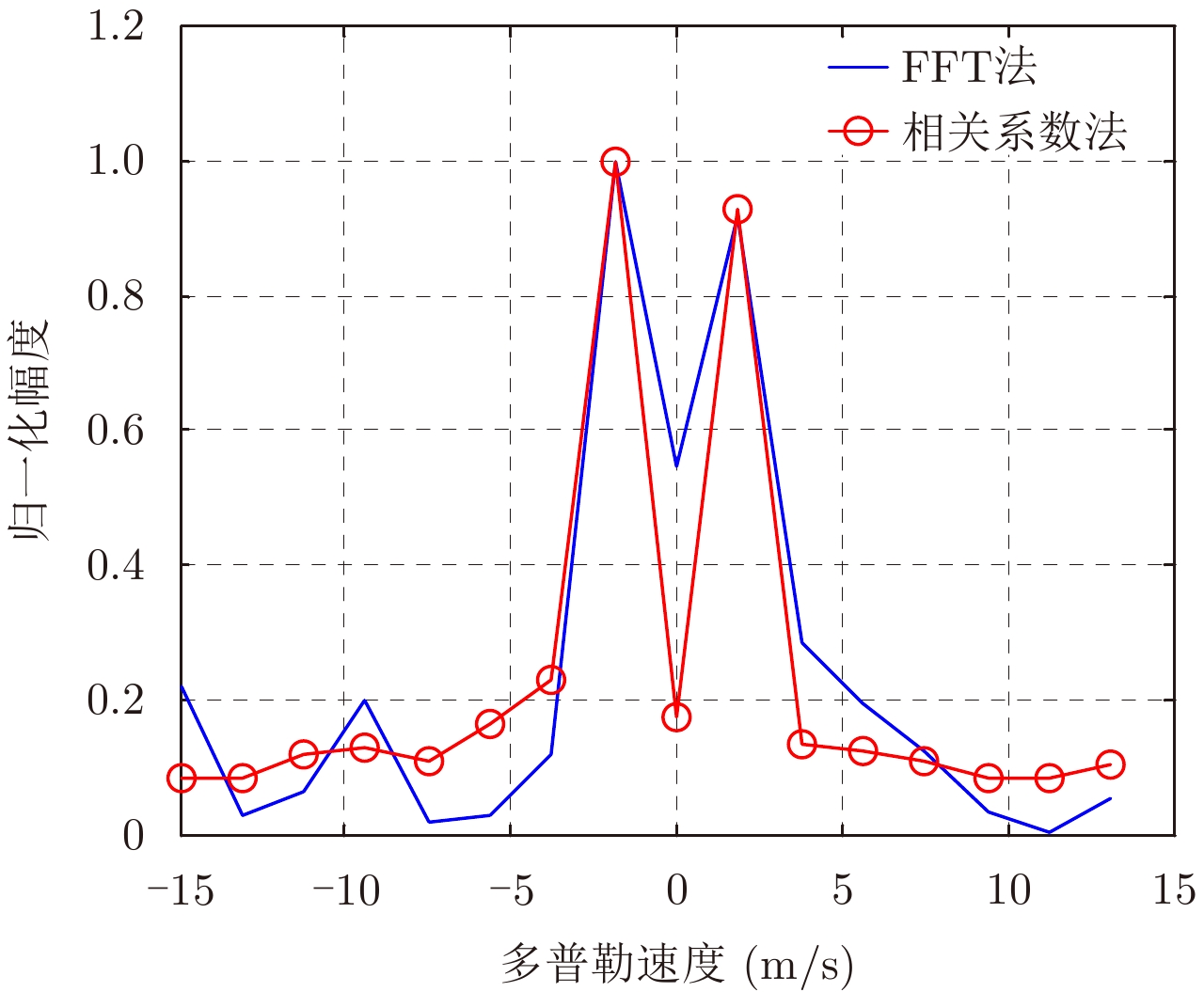
- Figure 5. The power spectrum before and after the covariance matrix reduces the dimension
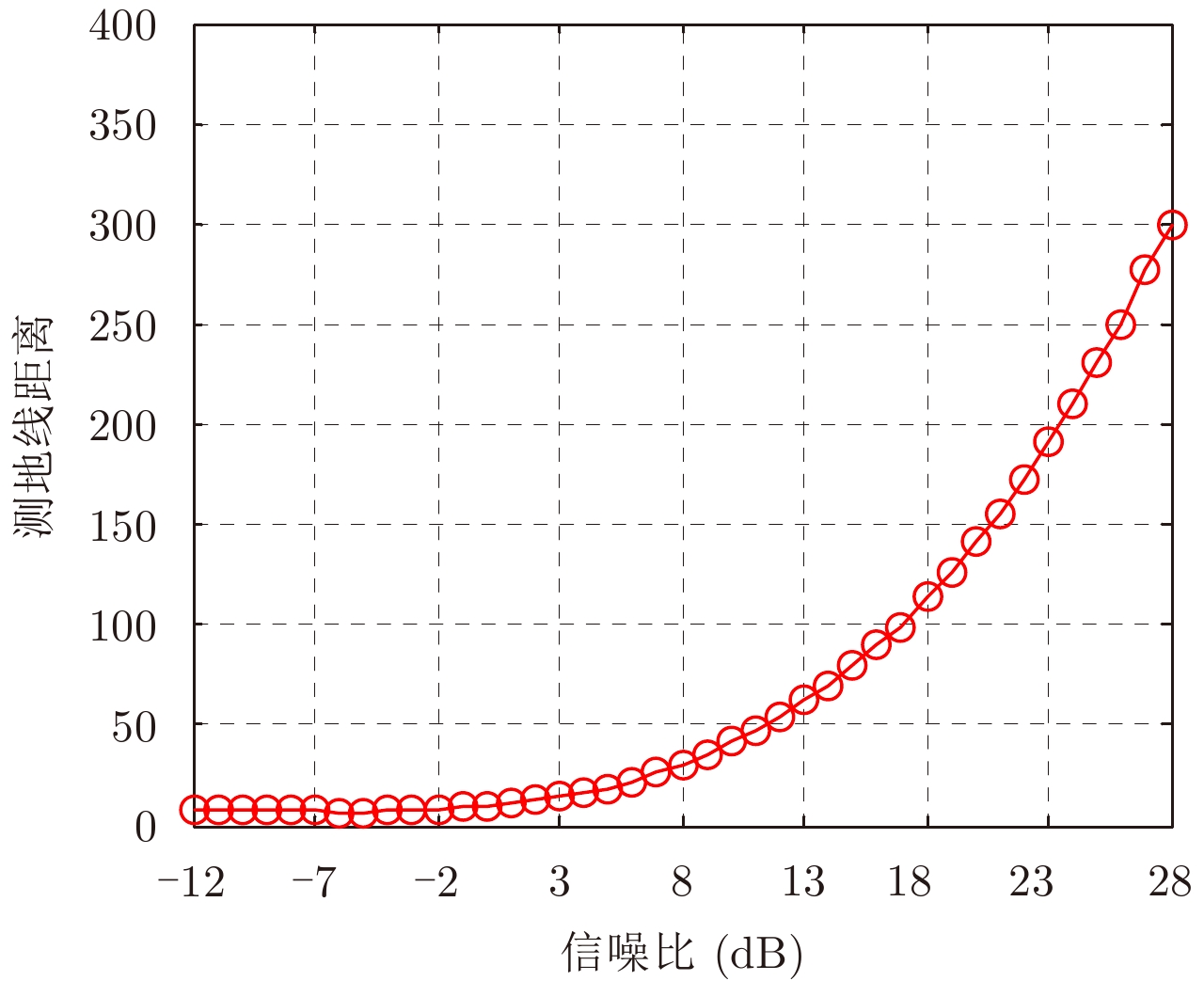
- Figure 6. The variation of geodesic distance with the variation of SNR
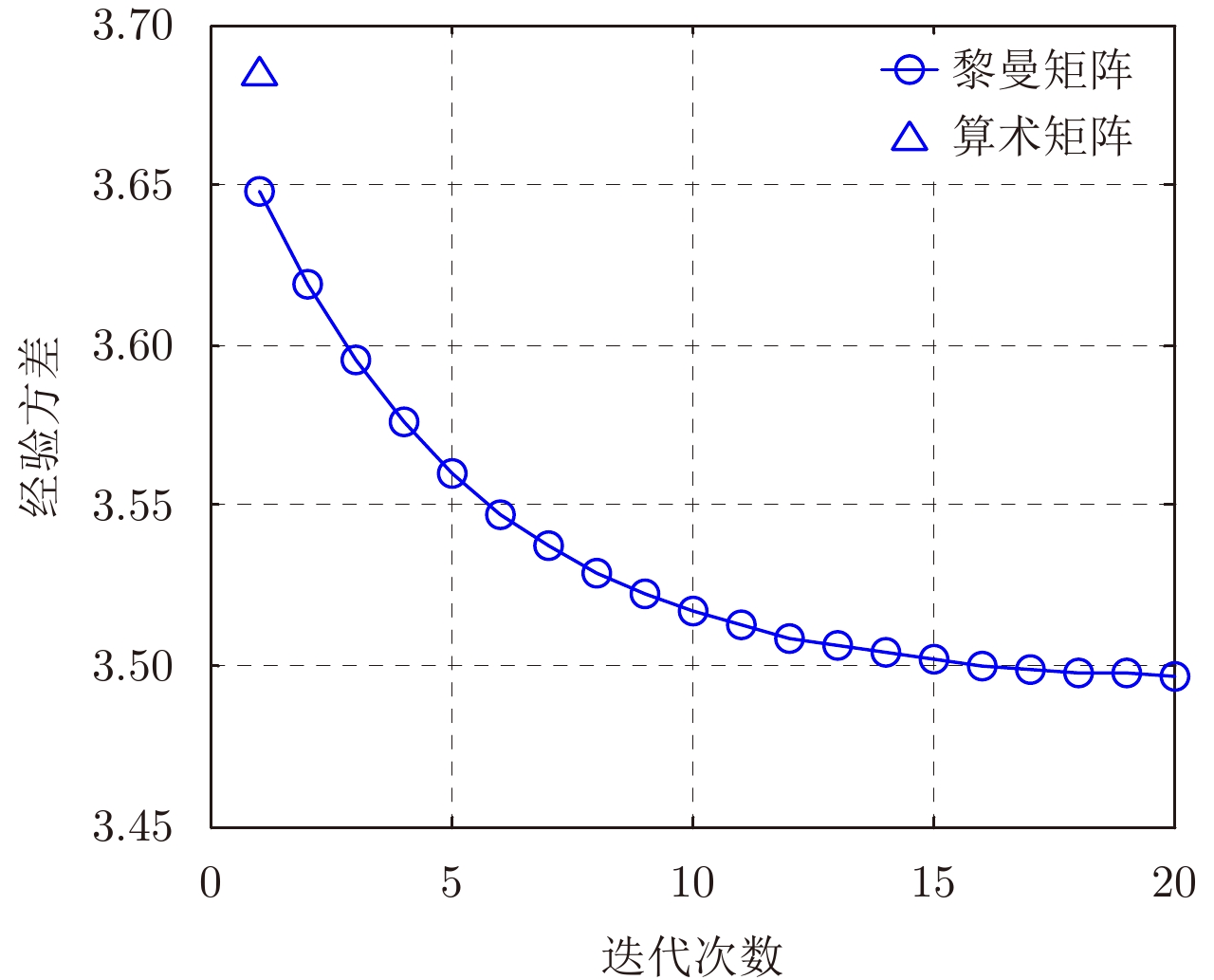
- Figure 7. Iterative estimation performance of matrix mean
- Figure 8. The statistical histogram of detection statistics with and without the vortex target
- Figure 9. Detection probability of the vortex target based on matrix CFAR


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: