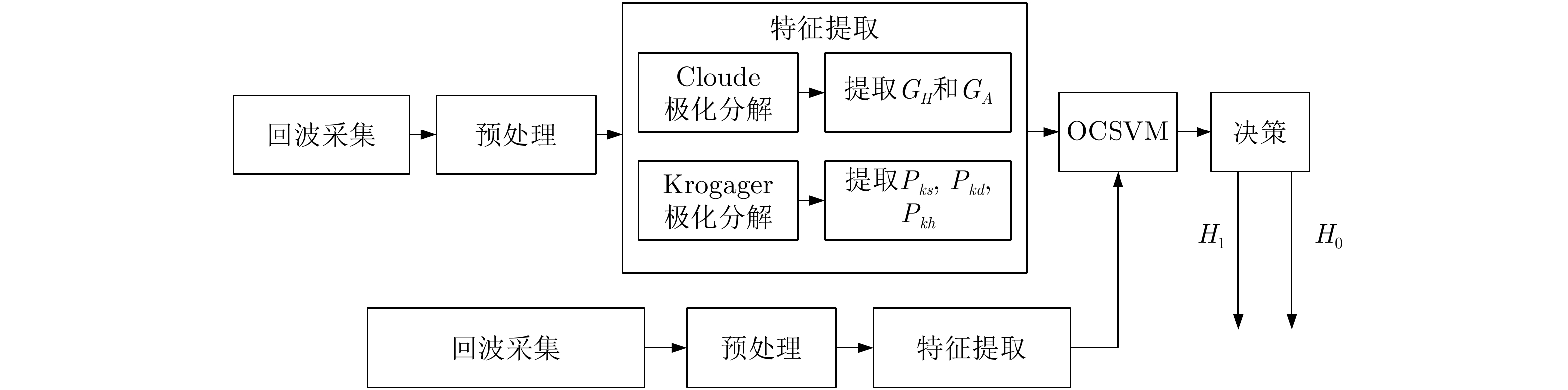
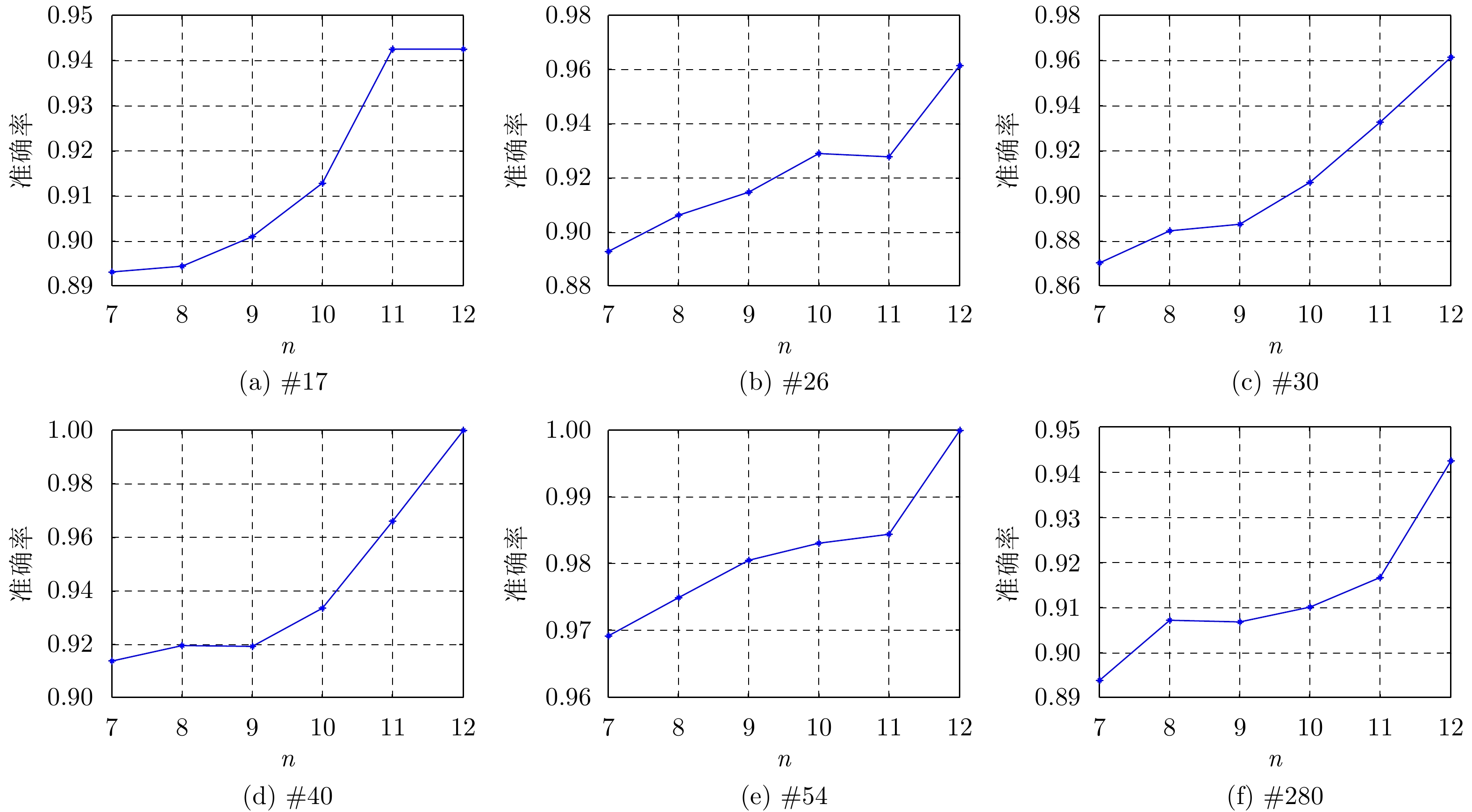
| [1] |
FARINA A and STUDER F A. A review of CFAR detection techniques in radar systems[J]. Microware Journal, 1986, 29(5): 115, 116, 118.
|
| [2] |
丁昊, 刘宁波, 董云龙, 等. 雷达海杂波测量试验回顾与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006DING Hao, LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, et al. Overview and prospects of radar sea clutter measurement experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006 |
| [3] |
刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089 |
| [4] |
丁昊, 王国庆, 刘宁波, 等. 逆Gamma纹理背景下两类子空间目标的自适应检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088DING Hao, WANG Guoqing, LIU Ningbo, et al. Adaptive detectors for two types of subspace targets in an inverse gamma textured background[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR16088 |
| [5] |
许述文, 石星宇, 水鹏朗. 复合高斯杂波下抑制失配信号的自适应检测器[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 326–334. doi: 10.12000/JR19030XU Shuwen, SHI Xingyu, and SHUI Penglang. An adaptive detector with mismatched signals rejection in compound Gaussian clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 326–334. doi: 10.12000/JR19030 |
| [6] |
SHI Yanling, XIE Xiaoyan, and LI Dongchen. Range distributed floating target detection in sea clutter via feature-based detector[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1847–1850. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2614750 |
| [7] |
左磊, 产秀秀, 禄晓飞, 等. 基于空域联合时频分解的海面微弱目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035ZUO Lei, CHAN Xiuxiu, LU Xiaofei, et al. A weak target detection method in sea clutter based on joint space-time-frequency decomposition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 335–343. doi: 10.12000/JR19035 |
| [8] |
LUO Feng, ZHANG Danting, and ZHANG Bo. The fractal properties of sea clutter and their applications in maritime target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1295–1299. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2237750 |
| [9] |
陈世超, 罗丰, 胡冲, 等. 基于多普勒谱非广延熵的海面目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 344–354. doi: 10.12000/JR19012CHEN Shichao, LUO Feng, HU Chong, et al. Small target detection in sea clutter background based on Tsallis entropy of Doppler spectrum[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 344–354. doi: 10.12000/JR19012 |
| [10] |
SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 |
| [11] |
XU Shuwen and PU Jia. Floating small targets detection in sea clutter based on four-polarization-channels fusion[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(3): 324–329. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.03.011 |
| [12] |
田玉芳, 尹志盈, 姬光荣, 等. 基于SVM的海面弱目标检测[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2013, 43(7): 104–109.
TIAN Yufang, YIN Zhiying, JI Guangrong, et al. Weak targets detection in sea clutter based on SVM[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(7): 104–109.
|
| [13] |
WU Peng, WANG Jun, and WANG Wenguang, et al. Small target detection in sea clutter based on polarization characteristics decomposition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(4): 816–822. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00678 |
| [14] |
XU Shuwen, ZHENG Jibin, PU Jia, et al. Sea-surface floating small target detection based on polarization features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(10): 1505–1509. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2852560 |
| [15] |
MORRIS J T and ANDERSON S J. Aspect dependence of the polarimetric characteristics of sea clutter: I. Variation with elevation angle[C]. 2008 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2008: 106–110.
|
| [16] |
ANDERSON S J and MORRIS J T. Aspect dependence of the polarimetric characteristics of sea clutter: II. Variation with azimuth angle[C]. 2008 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2008: 581–585.
|
| [17] |
张新勋, 周生华, 刘宏伟. 目标极化散射特性对极化分集雷达检测性能的影响[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 510–518. doi: 10.12000/JR18112ZHANG Xinxun, ZHOU Shenghua, and LIU Hongwei. Influence of target polarization scattering characteristics on the detection performance of polarization diversity radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 510–518. doi: 10.12000/JR18112 |
| [18] |
AN Wentao, CUI Yi, and YANG Jian. Three-component model-based decomposition for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(6): 2732–2739. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2041242 |
| [19] |
CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 |
| [20] |
AN Wentao, CUI Yi, ZHANG Weijie, et al. Data compression for multilook polarimetric SAR Data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 476–480. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2017498 |
| [21] |
KROGAGER E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J]. Electronics Letters, 1990, 26(18): 1525–1527. doi: 10.1049/el:19900979 |
| [22] |
KROGAGER E, BOERNER W M, and MADSEN S N. Feature-motivated Sinclair matrix (sphere/diplane/helix) decomposition and its application to target sorting for land feature classification[C]. The SPIE 3120, Wideband Interferometric Sensing and Imaging Polarimetry, San Diego, USA, 1997. doi: 10.1117/12.300620. |
| [23] |
CHAMUNDEESWARI V V, SINGH D, and SINGH K. An analysis of texture measures in PCA-based unsupervised classification of SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 214–218. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2009954 |
| [24] |
ZHANG Wei, DU Lan, LI Liling, et al. Infinite Bayesian one-class support vector machine based on Dirichlet process mixture clustering[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 78: 56–78. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.01.006 |
| [25] |
XU Huan and HUANG Deshuang. One class support vector machines for distinguishing photographs and graphics[C]. IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, Sanya, China, 2008. doi: 10.1109/ICNSC.2008.4525289. |
| [26] |
CHO H W. Data description and noise filtering based detection with its application and performance comparison[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36(1): 434–441. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2007.09.053 |
| [27] |
TIAN Jiang, GU Hong, GAO Chiyang, et al. Local density one-class support vector machines for anomaly detection[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2011, 64(1/2): 127–130. doi: 10.1007/s11071-010-9851-y |
| [28] |
BOUNSIAR A and MADDEN M G. Kernels for one-class support vector machines[C]. 2014 International Conference on Information Science & Applications (ICISA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2014. doi: 10.1109/ICISA.2014.6847419. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: